Abstract
1. Morphine produces a plethora of pharmacological effects and its chronic administration induces several side-effects. The cellular mechanisms by which opiates induce these side-effects are not fully understood. Several studies suggest that regulation of adenylyl cyclase activity by opioids and other transmitters plays an important role in the control of neural function. 2. The aim of this study was to evaluate desensitization of mu- and delta- opioid receptors, defined as a reduced ability of opioid agonists to inhibit adenylyl cyclase activity, in four different brain structures known to be involved in opiate drug actions: caudate putamen, nucleus accumbens, thalamus and periaqueductal gray (PAG). Opiate regulation of adenylyl cyclase in these regions has been studied in control and morphine-dependent rats. 3. The chronic morphine treatment used in the present study (subcutaneous administration of 15.4 mg morphine/rat/day for 6 days via osmotic pump) induced significant physical dependence as indicated by naloxone-precipitated withdrawal symptoms. 4. Basal adenylyl cyclase in the four brain regions was not modified by this chronic morphine treatment. In the PAG and the thalamus, a desensitization of mu- and delta-opioid receptors was observed, characterized by a reduced ability of Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-(NMe)Phe-Gly-ol (DAMGO; mu), Tyr-D-Pen-Gly-Phe-D-Pen (DPDPE; delta) and [D-Ala2]-deltorphin-II (DT-II; delta) to inhibit adenylyl cyclase, activity following chronic morphine treatment. 5. The opioid receptor desensitization in PAG and thalamus appeared to be heterologous since the metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists, L-AP4 and glutamate, and the 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)1A receptor agonist, R(+)-8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin hydrobromide (8-OH-DPAT), also showed reduced inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity following chronic morphine treatment. 6. In the nucleus accumbens and the caudate putamen, desensitization of delta-opioid receptor-mediated inhibition without modification of mu-opioid receptor-mediated inhibition was observed. An indirect mechanism probably involving dopaminergic systems is proposed to explain the desensitization of delta-mediated responses and the lack of mu-opioid receptor desensitization after chronic morphine treatment in caudate putamen and nucleus accumbens. 7. These results suggest that adaptive responses occurring during chronic morphine administration are not identical in all opiate-sensitive neural populations.
Full text
PDF

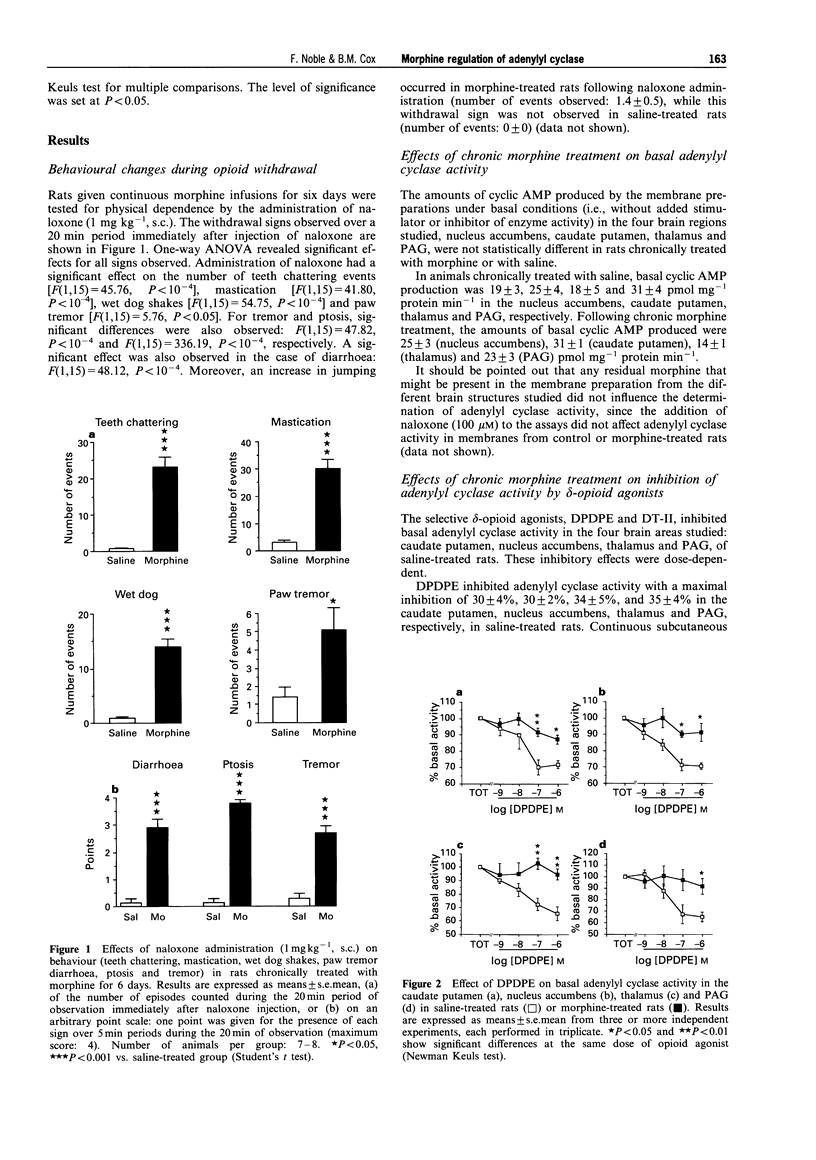

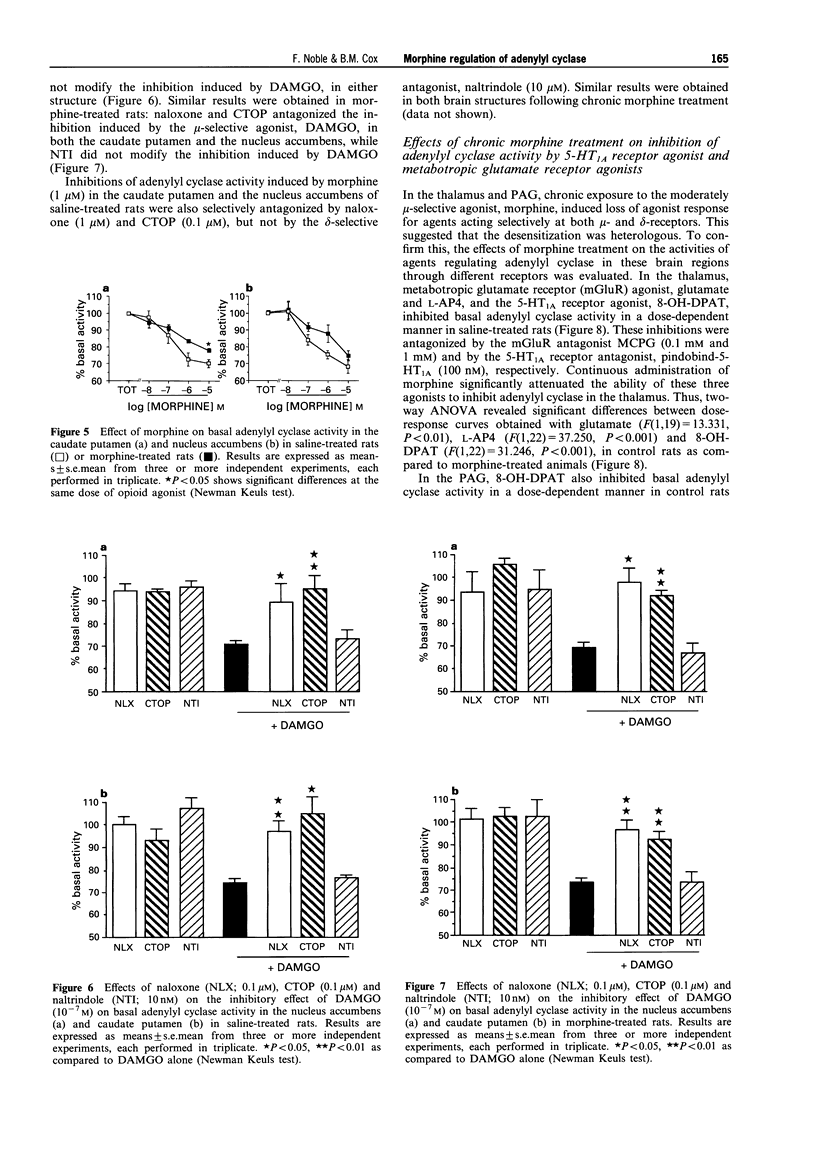
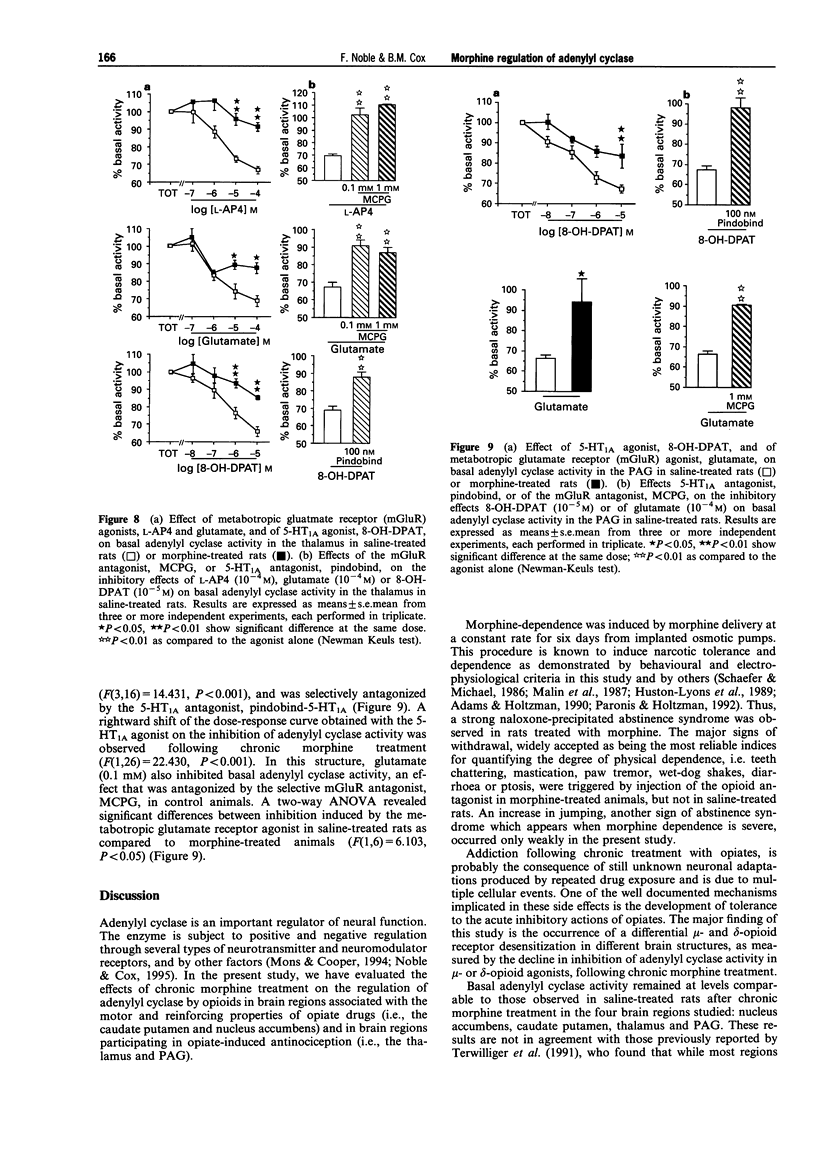



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acquas E., Di Chiara G. Depression of mesolimbic dopamine transmission and sensitization to morphine during opiate abstinence. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1620–1625. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. U., Holtzman S. G. Tolerance and dependence after continuous morphine infusion from osmotic pumps measured by operant responding in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1990;100(4):451–458. doi: 10.1007/BF02243995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aghajanian G. K. Tolerance of locus coeruleus neurones to morphine and suppression of withdrawal response by clonidine. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):186–188. doi: 10.1038/276186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attali B., Saya D., Vogel Z. Kappa-opiate agonists inhibit adenylate cyclase and produce heterologous desensitization in rat spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1989 Feb;52(2):360–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandler R., Shipley M. T. Columnar organization in the midbrain periaqueductal gray: modules for emotional expression? Trends Neurosci. 1994 Sep;17(9):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basbaum A. I., Fields H. L. Endogenous pain control systems: brainstem spinal pathways and endorphin circuitry. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:309–338. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.07.030184.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitner-Johnson D., Guitart X., Nestler E. J. Neurofilament proteins and the mesolimbic dopamine system: common regulation by chronic morphine and chronic cocaine in the rat ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci. 1992 Jun;12(6):2165–2176. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-06-02165.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitner-Johnson D., Nestler E. J. Morphine and cocaine exert common chronic actions on tyrosine hydroxylase in dopaminergic brain reward regions. J Neurochem. 1991 Jul;57(1):344–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boess F. G., Martin I. L. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):275–317. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozarth M. A. Neural basis of psychomotor stimulant and opiate reward: evidence suggesting the involvement of a common dopaminergic system. Behav Brain Res. 1986 Nov;22(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(86)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozarth M. A. Physical dependence produced by central morphine infusions: an anatomical mapping study. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1994 Fall;18(3):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(94)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. L., Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Sgherzi A. M. A simple and sensitive saturation assay method for the measurement of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):561–562. doi: 10.1042/bj1210561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cador M., Taylor J. R., Robbins T. W. Potentiation of the effects of reward-related stimuli by dopaminergic-dependent mechanisms in the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1991;104(3):377–385. doi: 10.1007/BF02246039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain S. M., Crain B., Peterson E. R. Development of cross-tolerance to 5-hydroxytryptamine in organotypic cultures of mouse spinal cord-ganglia during chronic exposure to morphine. Life Sci. 1982 Jul 19;31(3):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90584-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vries T. J., Tjon Tien Ril G. H., Van der Laan J. W., Mulder A. H., Schoffelmeer A. N. Chronic exposure to morphine and naltrexone induces changes in catecholaminergic neurotransmission in rat brain without altering mu-opioid receptor sensitivity. Life Sci. 1993;52(21):1685–1693. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90476-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duman R. S., Tallman J. F., Nestler E. J. Acute and chronic opiate-regulation of adenylate cyclase in brain: specific effects in locus coeruleus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):1033–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erspamer V., Melchiorri P., Falconieri-Erspamer G., Negri L., Corsi R., Severini C., Barra D., Simmaco M., Kreil G. Deltorphins: a family of naturally occurring peptides with high affinity and selectivity for delta opioid binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5188–5192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa B. K., Land A. C., Lord J. A., Morgan B. A., Rance M. J., Smith C. F. Analogues of beta-LPH61-64 possessing selective agonist activity at mu-opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 9;70(4):531–540. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston-Lyons D., Bain G. T., Kornetsky C. Opiate dependence alters central reward of nalbuphine or pentazocine plus tripelennamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 4;169(1):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90827-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet Y. F., Lajtha A. The periaqueductal gray: site of morphine analgesia and tolerance as shown by 2-way cross tolerance between systemic and intracerebral injections. Brain Res. 1976 Feb 27;103(3):501–513. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90448-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser V., Benoist J. M., Gautron M., Guilbaud G. Effects of ES52, an enkephalinase inhibitor, on responses of ventrobasal thalamic neurons in rat. Peptides. 1984 Nov-Dec;5(6):1159–1165. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keay K. A., Clement C. I., Owler B., Depaulis A., Bandler R. Convergence of deep somatic and visceral nociceptive information onto a discrete ventrolateral midbrain periaqueductal gray region. Neuroscience. 1994 Aug;61(4):727–732. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp M., Roberts P., Pook P., Jane D., Jones A., Jones P., Sunter D., Udvarhelyi P., Watkins J. Antagonism of presynaptically mediated depressant responses and cyclic AMP-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 15;266(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob G. F., Wall T. L., Bloom F. E. Nucleus accumbens as a substrate for the aversive stimulus effects of opiate withdrawal. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1989;98(4):530–534. doi: 10.1007/BF00441954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laschka E., Teschemacher H., Mehraein P., Herz A. Sites of action of morphine involved in the development of physical dependence in rats. II. Morphine withdrawal precipitated by application of morphine antagonists into restricted parts of the ventricular system and by microinjection into various brain areas. Psychopharmacologia. 1976 Mar 16;46(2):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00421383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau L. M., Sleight A. J., Pitha J., Peroutka S. J. Characterization of a novel and potent 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor antagonist. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991 Mar;38(3):555–559. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(91)90013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado R., Stinus L., Gold L. H., Koob G. F. Role of different brain structures in the expression of the physical morphine withdrawal syndrome. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):669–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malin D. H., Harter L., Jenkins P. D., Monfort R. D., Bruce P. D., Farley P. A., Ferebee R., Thrasher K. L., Marullo D. S. Cerebrospinal fluid from morphine-dependent rats precipitates opiate abstinence syndrome. Life Sci. 1987 Jul 20;41(3):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Humphrey P. P. Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine: current perspectives on classification and nomenclature. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):261–273. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka I., Maldonado R., Defer N., Noël F., Hanoune J., Roques B. P. Chronic morphine administration causes region-specific increase of brain type VIII adenylyl cyclase mRNA. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 15;268(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogil J. S., Marek P., O'Toole L. A., Helms M. L., Sadowski B., Liebeskind J. C., Belknap J. K. Mu-opiate receptor binding is up-regulated in mice selectively bred for high stress-induced analgesia. Brain Res. 1994 Aug 8;653(1-2):16–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90366-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mons N., Cooper D. M. Selective expression of one Ca(2+)-inhibitable adenylyl cyclase in dopaminergically innervated rat brain regions. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Mar;22(1-4):236–244. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Gee K., Yamamura H. I., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F. Bis-penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5871–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Erdos J. J., Terwilliger R., Duman R. S., Tallman J. F. Regulation of G proteins by chronic morphine in the rat locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 9;476(2):230–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Hope B. T., Widnell K. L. Drug addiction: a model for the molecular basis of neural plasticity. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):995–1006. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90213-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Tallman J. F. Chronic morphine treatment increases cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity in the rat locus coeruleus. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;33(2):127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble F., Cox B. M. Differential regulation of D1 dopamine receptor- and of A2a adenosine receptor-stimulated adenylyl cyclase by mu-, delta 1-, and delta 2-opioid agonists in rat caudate putamen. J Neurochem. 1995 Jul;65(1):125–133. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65010125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto N., Hori S., Akazawa C., Hayashi Y., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a new metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR7 coupled to inhibitory cyclic AMP signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1231–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paronis C. A., Holtzman S. G. Development of tolerance to the analgesic activity of mu agonists after continuous infusion of morphine, meperidine or fentanyl in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. G., LePiane F. G. Reward produced by microinjection of (D-Ala2),Met5-enkephalinamide into the ventral tegmental area. Behav Brain Res. 1982 Jun;5(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(82)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puttfarcken P. S., Cox B. M. Morphine-induced desensitization and down-regulation at mu-receptors in 7315C pituitary tumor cells. Life Sci. 1989;45(20):1937–1942. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90548-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puttfarcken P. S., Werling L. L., Cox B. M. Effects of chronic morphine exposure on opioid inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in 7315c cell membranes: a useful model for the study of tolerance at mu opioid receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):520–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen K., Beitner-Johnson D. B., Krystal J. H., Aghajanian G. K., Nestler E. J. Opiate withdrawal and the rat locus coeruleus: behavioral, electrophysiological, and biochemical correlates. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2308–2317. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02308.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts V. J., Dong W. K. The effect of thalamic nucleus submedius lesions on nociceptive responding in rats. Pain. 1994 Jun;57(3):341–349. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(94)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer G. J., Michael R. P. Changes in response rates and reinforcement thresholds for intracranial self-stimulation during morphine withdrawal. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1986 Dec;25(6):1263–1269. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(86)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. Dual regulation of adenylate cyclase accounts for narcotic dependence and tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe L. G., Garnett J. E., Cicero T. J. Analgesia and hyperreactivity produced by intracranial microinjections of morphine into the periaqueductal gray matter of the rat. Behav Biol. 1974 Jul;11(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6773(74)90548-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinus L., Le Moal M., Koob G. F. Nucleus accumbens and amygdala are possible substrates for the aversive stimulus effects of opiate withdrawal. Neuroscience. 1990;37(3):767–773. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90106-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Nomura A., Masu M., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Signal transduction, pharmacological properties, and expression patterns of two rat metabotropic glutamate receptors, mGluR3 and mGluR4. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1372–1378. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01372.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger R. Z., Beitner-Johnson D., Sevarino K. A., Crain S. M., Nestler E. J. A general role for adaptations in G-proteins and the cyclic AMP system in mediating the chronic actions of morphine and cocaine on neuronal function. Brain Res. 1991 May 10;548(1-2):100–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91111-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unterwald E. M., Cox B. M., Kreek M. J., Cote T. E., Izenwasser S. Chronic repeated cocaine administration alters basal and opioid-regulated adenylyl cyclase activity. Synapse. 1993 Sep;15(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/syn.890150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. O., Smith D. J. Nuclei within the rostral ventromedial medulla mediating morphine antinociception from the periaqueductal gray. Brain Res. 1994 Jul 25;652(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90311-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


