Abstract
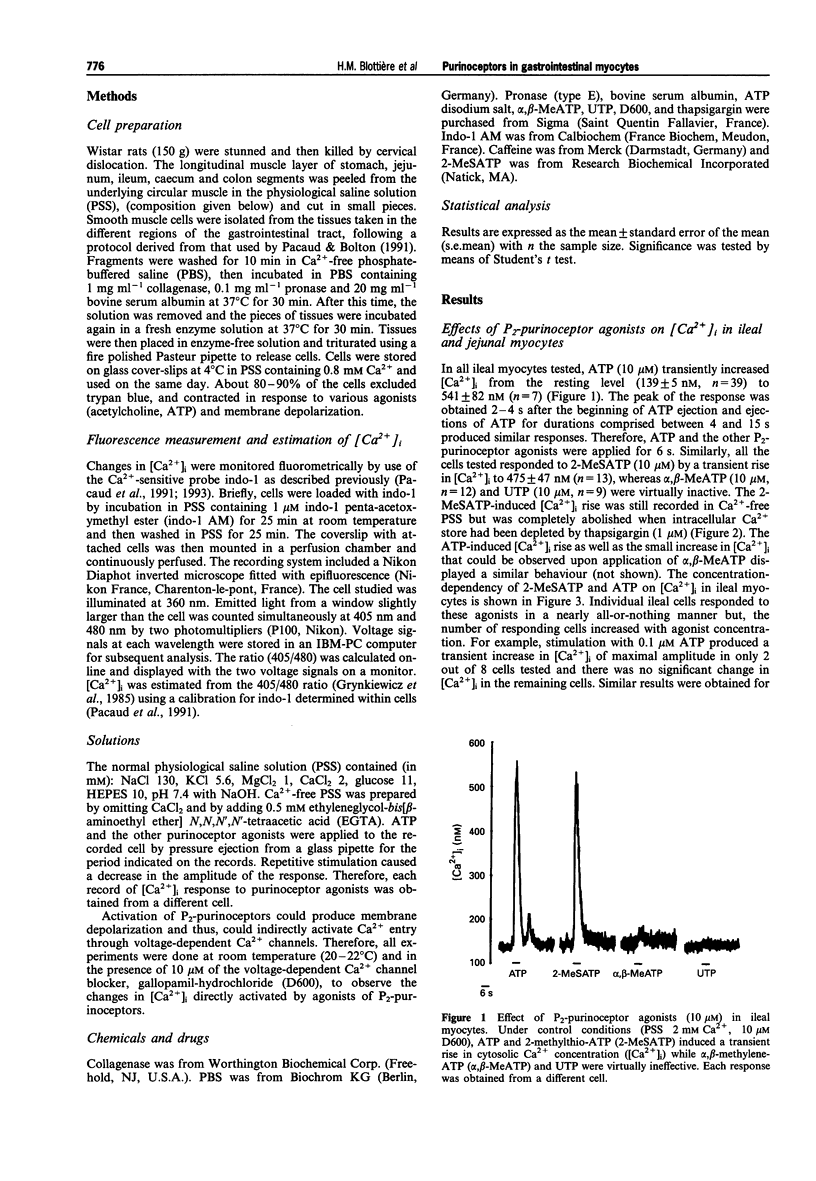
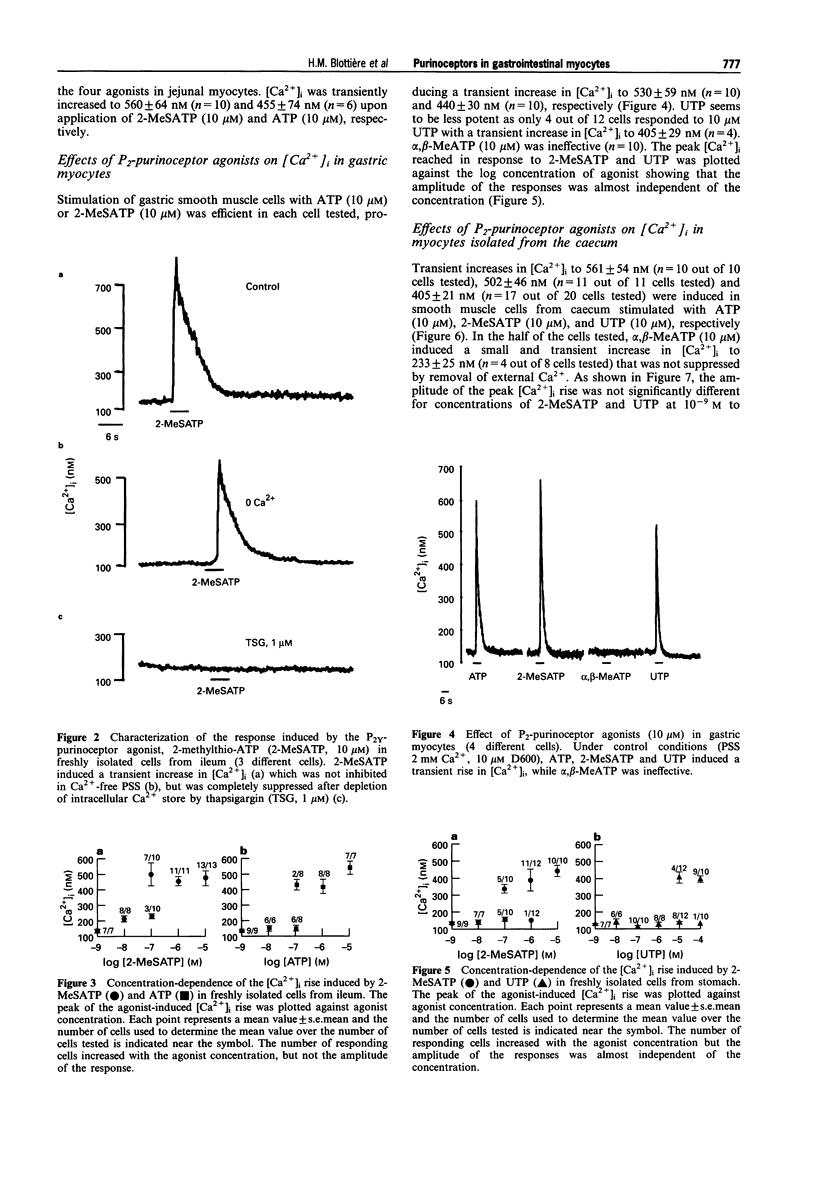
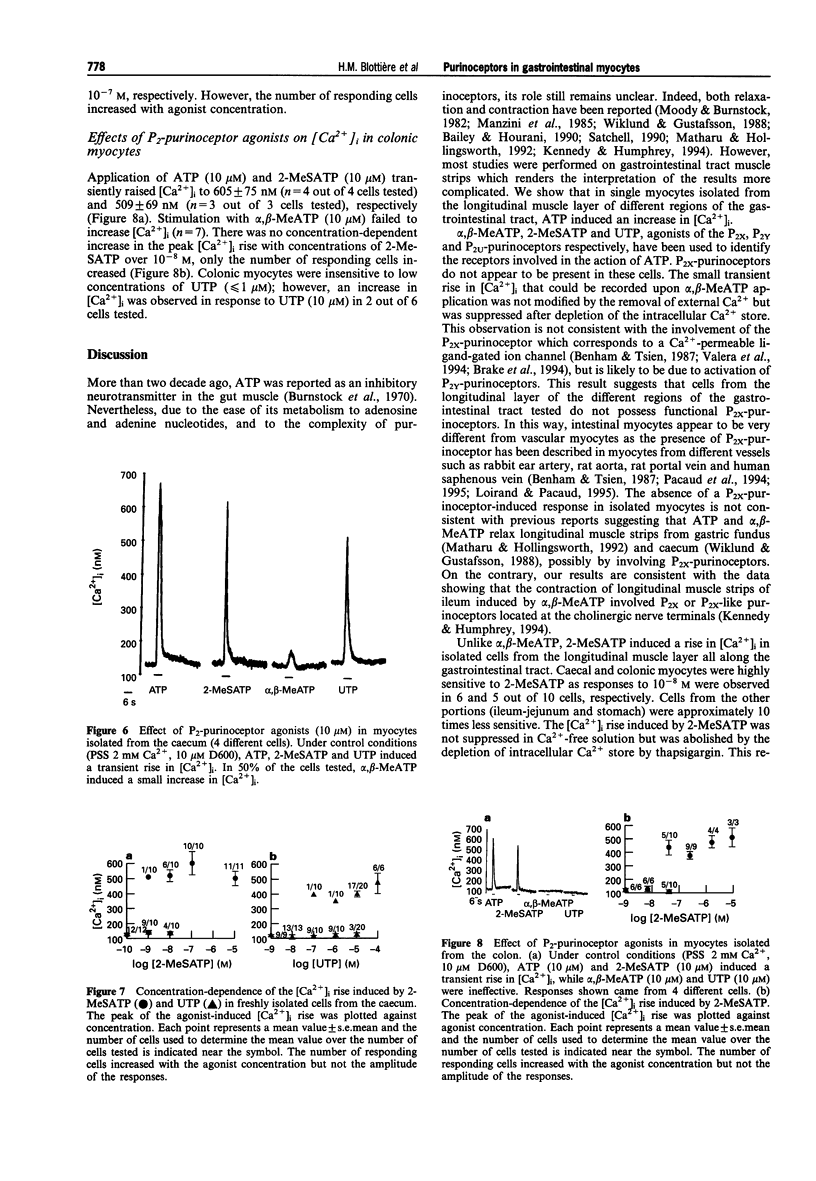
1. The changes in the free cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in response to agonists of P2-purinoceptors were studied in myocytes isolated from the longitudinal muscle layer of different regions of the rat gastrointestinal tract (stomach, jejunum, ileum, caecum and colon). [Ca2+]i was estimated by emission from the fluorescent dye, indo-1. 2. ATP and the P2Y-purinoceptor agonist, 2-methylthio-ATP (2-MeSATP), transiently increased [Ca2+]i in single myocytes from all segments of the gastrointestinal tract, whereas alpha,beta-methylene-ATP, a P2x-purinoceptor agonist, had no effect. 3. The rise in [Ca2+]i induced by ATP and 2-MeSATP was maintained in Ca(2+)-free solution but was abolished by depletion of the intracellular store with thapsigargin (1 microM). 4. Single myocytes from stomach, caecum and colon also responded to UTP by a transient increase in [Ca2+]i. 5. Individual myocytes responded to ATP, 2-McSATP and UTP in a nearly all-or-nothing manner. The increasing of agonist concentration enhanced the number of responding cells but did not increase the amplitude of the [Ca2+]i rise. 6. These results suggest that myocytes from the longitudinal layer of gastrointestinal muscle do not possess functional P2x-purinoceptors and that agonists of P2Y and P2U-purinoceptors induced a rise in [Ca2+]i, probably via an all-or-nothing mobilization of Ca2+ from intracellular stores.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey S. J., Hourani S. M. A study of the purinoceptors mediating contraction in the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):753–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake A. J., Wagenbach M. J., Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):519–523. doi: 10.1038/371519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Campbell G., Satchell D., Smythe A. Evidence that adenosine triphosphate or a related nucleotide is the transmitter substance released by non-adrenergic inhibitory nerves in the gut. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;40(4):668–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., el-Moatassim C. Signal transduction via P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):C577–C606. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.3.C577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G., Daly J. W., Harden T. K., Jacobson K. A., Leff P., Williams M. Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):143–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Nomoto T. Postnatal changes in response to adenosine and adenine nucleotides in rat duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1111–1118. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Yamazawa T., Miyashita Y., Endo M., Kasai H. Critical intracellular Ca2+ concentration for all-or-none Ca2+ spiking in single smooth muscle cells. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5287–5291. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. R., Hourani S. M. Contractile effects of uridine 5'-triphosphate in the rat duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1191–1196. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17123.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Leff P. How should P2X purinoceptors be classified pharmacologically? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 May;16(5):168–174. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)89010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I., Humphrey P. P. Evidence for the presence of two types of P2 purinoceptor in the guinea-pig ileal longitudinal smooth muscle preparation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug 22;261(3):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loirand G., Pacaud P. Mechanism of the ATP-induced rise in cytosolic Ca2+ in freshly isolated smooth muscle cells from human saphenous vein. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Jul;430(3):429–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00373919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzini S., Maggi C. A., Meli A. Further evidence for involvement of adenosine-5'-triphosphate in non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation of the isolated rat duodenum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 31;113(3):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matharu M. S., Hollingsworth M. Purinoceptors mediating relaxation and spasm in the rat gastric fundus. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;106(2):395–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14346.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody C. J., Burnstock G. Evidence for the presence of P1-purinoceptors on cholinergic nerve terminals in the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan 8;77(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90527-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J., Hourani S. M., Kitchen I. The ontogeny of purinoceptors in rat urinary bladder and duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):874–878. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Ito S., Nakazato Y. All-or-nothing responses to carbachol in single intestinal smooth muscle cells of rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;112(3):972–976. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Bolton T. B. Relation between muscarinic receptor cationic current and internal calcium in guinea-pig jejunal smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:477–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Grégoire G., Loirand G. Release of Ca2+ from intracellular store in smooth muscle cells of rat portal vein by ATP-induced Ca2+ entry. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Oct;113(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Loirand G., Baron A., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Ca2+ channel activation and membrane depolarization mediated by Cl- channels in response to noradrenaline in vascular myocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;104(4):1000–1006. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Loirand G., Grégoire G., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Noradrenaline-activated heparin-sensitive Ca2+ entry after depletion of intracellular Ca2+ store in portal vein smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3866–3872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Malam-Souley R., Loirand G., Desgranges C. ATP raises [Ca2+]i via different P2-receptor subtypes in freshly isolated and cultured aortic myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jul;269(1 Pt 2):H30–H36. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1995.269.1.H30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchell D. The effects of ATP and related nucleotides on visceral smooth muscle. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:53–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera S., Hussy N., Evans R. J., Adami N., North R. A., Surprenant A., Buell G. A new class of ligand-gated ion channel defined by P2x receptor for extracellular ATP. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):516–519. doi: 10.1038/371516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall D. P., Sedaa K. O., Shinozuka K., Bjur R. A., Buxton I. L. ATP as a cotransmitter. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:300–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund N. P., Gustafsson L. E. Indications for P2-purinoceptor subtypes in guinea pig smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 13;148(3):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



