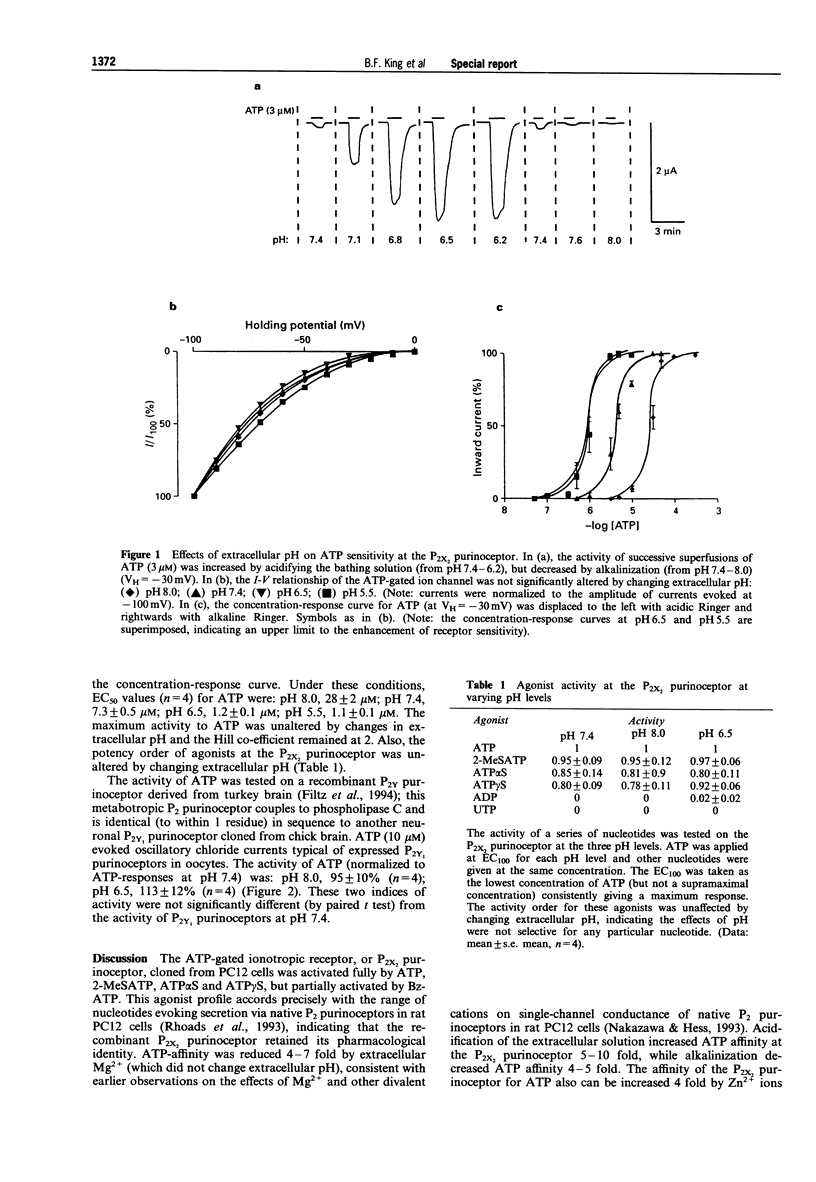
Abstract
A full pharmacological characterization was carried out on a recombinant ATP-gated ion channel (P2X2 purinoceptor) expressed in Xenopus oocytes. This slowly-desensitizing neuronal P2X2 purinoceptor, activated by ATP (EC50 = 4.6 +/- 1 microM at pH 7.4; n = 4), showed the agonist potency order: ATP > or = 2-MeSATP = ATP gamma S > or = ATP alpha S > > Bz-ATP. The receptor affinity for ATP was enhanced 5-10 fold by acidifying the bathing solution (to pH 6.5) but was diminished 4-5 fold in an alkaline solution (pH 8.0). The maximum activity of P2X2 purinoceptors and the activity order of a series of nucleotides were unaltered by changing extracellular pH. Interestingly, ATP sensitivity at a recombinant P2Y1 purinoceptor remained unaltered with changing extracellular pH. These results indicate that acidotic conditions in the synaptic cleft could strengthen purinergic transmission at neuronal P2X2 purinoceptors.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bo X., Burnstock G. Distribution of [3H]alpha,beta-methylene ATP binding sites in rat brain and spinal cord. Neuroreport. 1994 Aug 15;5(13):1601–1604. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199408150-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo X., Zhang Y., Nassar M., Burnstock G., Schoepfer R. A P2X purinoceptor cDNA conferring a novel pharmacological profile. FEBS Lett. 1995 Nov 13;375(1-2):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01203-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake A. J., Wagenbach M. J., Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):519–523. doi: 10.1038/371519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Gibb A. J., Colquhoun D. ATP receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):144–147. doi: 10.1038/359144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filtz T. M., Li Q., Boyer J. L., Nicholas R. A., Harden T. K. Expression of a cloned P2Y purinergic receptor that couples to phospholipase C. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;46(1):8–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Scarpa A. Internal pH of isolated chromaffin vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2189–2191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Osipchuk Y. V., Shelest T. N., Smirnoff S. V. Rapid extracellular pH transients related to synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 15;436(2):352–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91678-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Fujimori K., Takanaka A., Inoue K. Comparison of adenosine triphosphate- and nicotine-activated inward currents in rat phaeochromocytoma cells. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:647–660. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Hess P. Block by calcium of ATP-activated channels in pheochromocytoma cells. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Mar;101(3):377–392. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads A. R., Parui R., Vu N. D., Cadogan R., Wagner P. D. ATP-induced secretion in PC12 cells and photoaffinity labeling of receptors. J Neurochem. 1993 Nov;61(5):1657–1666. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb09800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanovsky Y., Reymann K., Haas H. L. pH-dependent facilitation of synaptic transmission by histamine in the CA1 region of mouse hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Oct 1;7(10):2017–2020. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb00624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




