Abstract
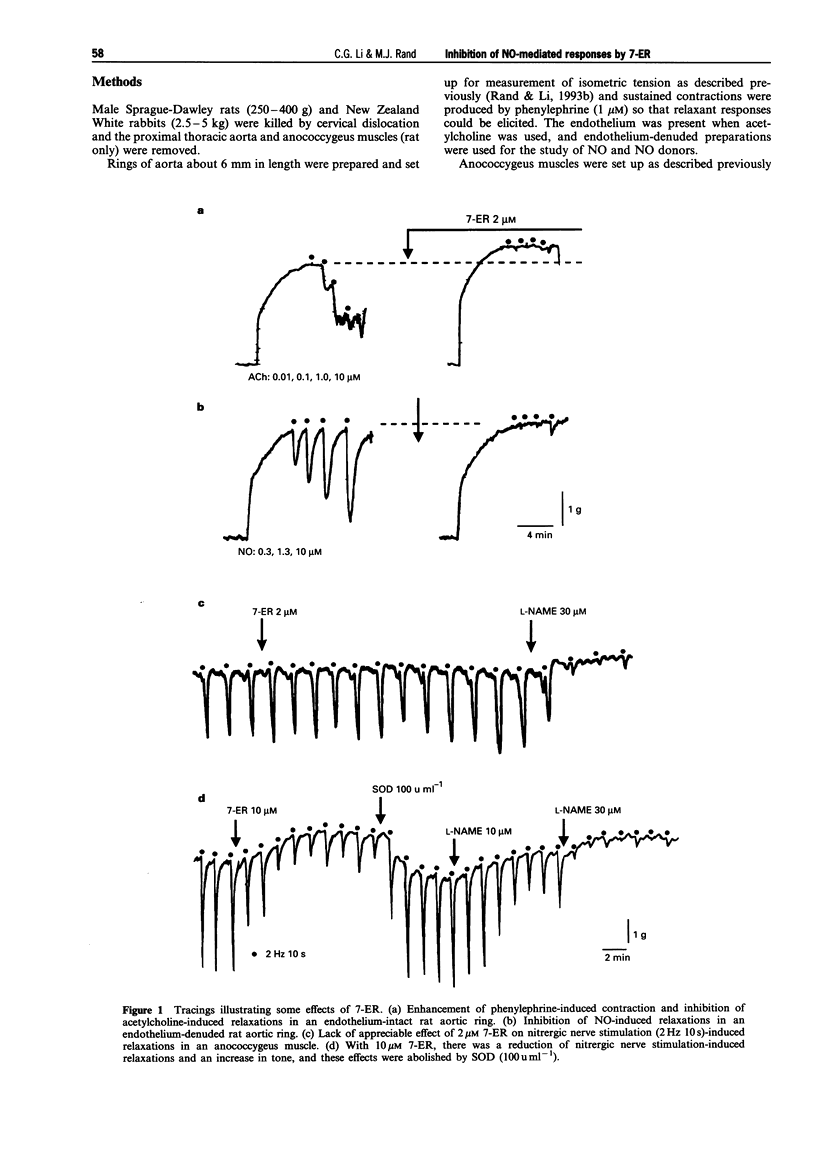
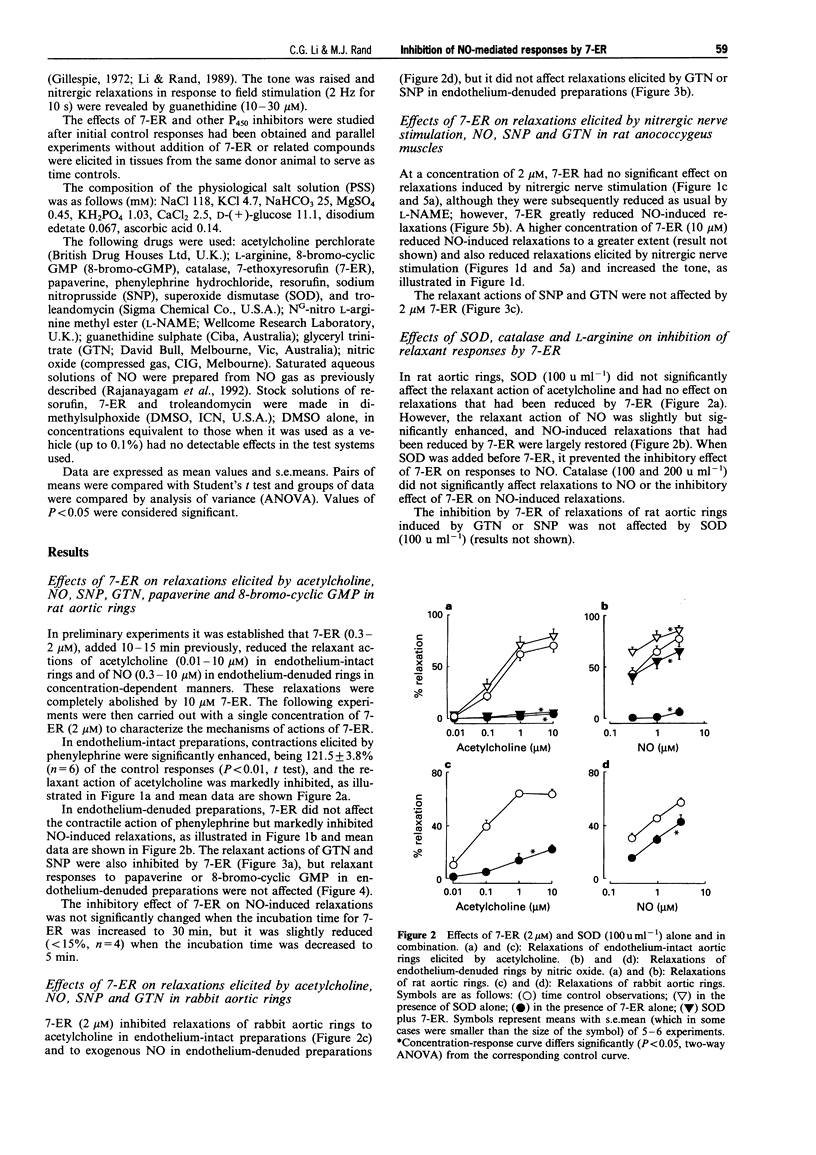
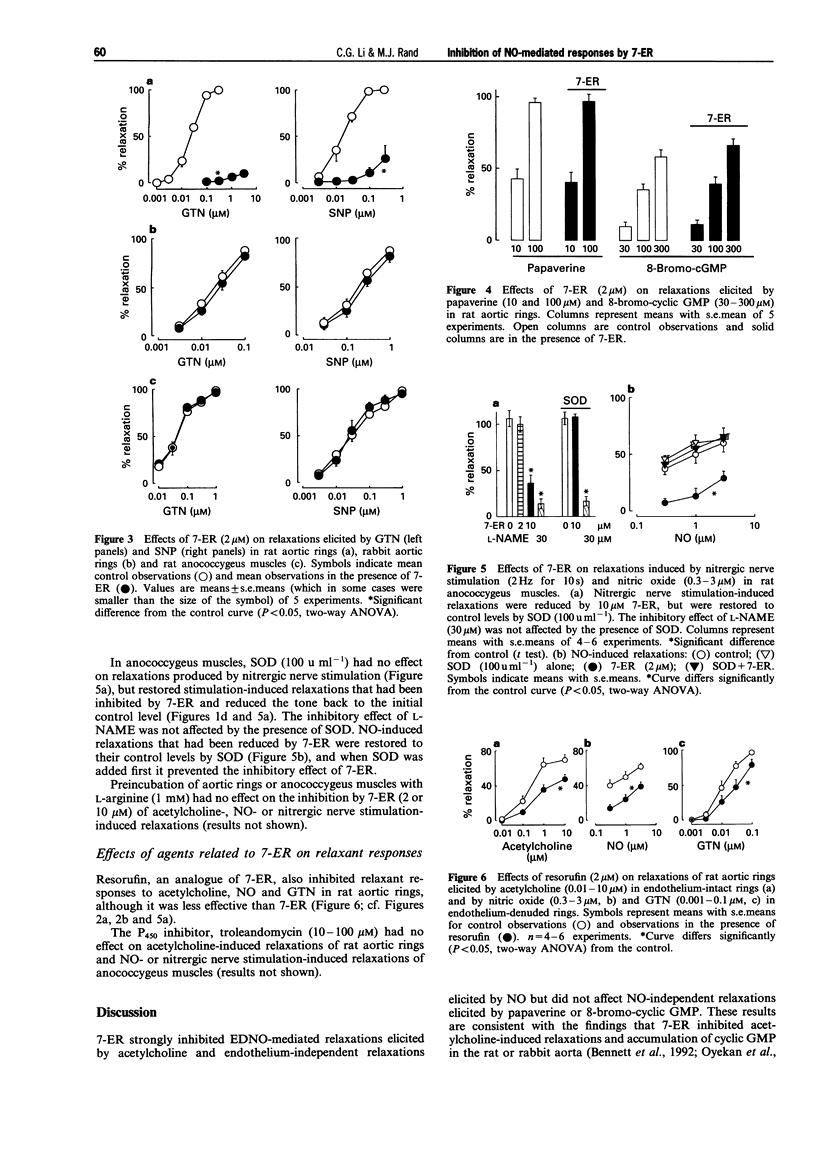
1. The effects of 7-ethoxyresorufin (7-ER), which is a substrate for and competitive inhibitor of cytochrome P450, were studied on responses to nitric oxide (NO), the NO donors sodium nitroprusside (SNP) and glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), acetylcholine-induced endothelium-dependent relaxations of rat and rabbit aortic rings and nitrergic nerve stimulation-induced relaxations of rat anococcygeus muscles. 2. In rat and rabbit aortic rings, 7-ER (2 microM) inhibited the relaxations to acetylcholine in endothelium-intact preparations and the relaxant action of NO in endothelium-denuded preparations. Relaxant responses to SNP and GTN were inhibited by 7-ER in the rat but not rabbit aortic rings. However, the relaxant actions of papaverine and 8-bromo-cyclic GMP were not affected by 7-ER. 3. In rat anococcygeus muscles, 7ER (2 microM) inhibited the relaxant action of NO, but relaxations elicited by nitrergic nerve stimulation were only partly inhibited by a higher concentration of 7-ER (10 microM). 4. After inhibition by 7-ER, superoxide dismutase (100 u ml-1) restored NO-induced relaxations of the rat aortic rings, but not acetylcholine-, SNP or GTN-induced relaxations, and restored NO- and nitrergic nerve stimulation-induced relaxations of anococcygeus muscles. 5. Another cytochrome P450 inhibitor, troleandomycin (10-30 microM), had no effect on NO- or acetylcholine-induced relaxations of rat aortic rings and NO- or nitrergic nerve stimulation-induced relaxations of anococcygeus muscles. However, resorufin, an analogue of 7-ER, inhibited responses to acetylcholine, NO and GTN in rat aortic rings. 6. The results suggest that 7-ER inhibited responses to NO and nitrergic nerve stimulation through generation of superoxide radicals. However, an additional mechanism may be involved in the reduction in acetylcholine-induced response in aortic rings. 7. A 7-ER sensitive P450 system may be involved in the bioactivation of GTN and SNP in rat aortic rings, but not in rabbit aorta or rat anococcygeus muscles.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbier A. J., Lefebvre R. A. Effect of LY 83583 on relaxation induced by non-adrenergic non-cholinergic nerve stimulation and exogenous nitric oxide in the rat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug 25;219(2):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90315-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates J. N., Baker M. T., Guerra R., Jr, Harrison D. G. Nitric oxide generation from nitroprusside by vascular tissue. Evidence that reduction of the nitroprusside anion and cyanide loss are required. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Dec 11;42 (Suppl):S157–S165. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90406-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B. M., McDonald B. J., Nigam R., Long P. G., Simon W. C. Inhibition of nitrovasodilator- and acetylcholine-induced relaxation and cyclic GMP accumulation by the cytochrome P-450 substrate, 7-ethoxyresorufin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;70(9):1297–1303. doi: 10.1139/y92-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., De Man J. G., De Winter B. Y., Herman A. G., Pelckmans P. A. Pharmacological similarity between nitric oxide and the nitrergic neurotransmitter in the canine ileocolonic junction. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Oct 13;264(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90640-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher J. L., Genet A., Vadon S., Delaforge M., Henry Y., Mansuy D. Cytochrome P450 catalyzes the oxidation of N omega-hydroxy-L-arginine by NADPH and O2 to nitric oxide and citrulline. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):880–886. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91279-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton D. R., Reed G. A., Parkinson A. Redox cycling of resorufin catalyzed by rat liver microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Feb 1;268(2):605–616. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton D., McGiff J. C., Quilley J. Contribution of NO and cytochrome P450 to the vasodilator effect of bradykinin in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):722–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey E. P., Tuttle J. V., Covington K., Merrill B. M., Wood E. R., Baylis S. A., Charles I. G. Purification and characterization of the constitutive nitric oxide synthase from human placenta. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994 Jun;311(2):235–241. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S. The rat anococcygeus muscle and its response to nerve stimulation and to some drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;45(3):404–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. J., Tucker J. F., Gibson A. Differentiation by hydroquinone of relaxations induced by exogenous and endogenous nitrates in non-vascular smooth muscle: role of superoxide anions. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):645–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imig J. D., Zou A. P., Ortiz de Montellano P. R., Sui Z., Roman R. J. Cytochrome P-450 inhibitors alter afferent arteriolar responses to elevations in pressure. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 2):H1879–H1885. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.5.H1879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenkare S. R., Benet L. Z. Effect of ethacrynic acid, a glutathione-S-transferase inhibitor, on nitroglycerin-mediated cGMP elevation and vasorelaxation of rabbit aortic strips. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jul 20;46(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90415-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatt P., Schmidt K., Mayer B. Brain nitric oxide synthase is a haemoprotein. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):15–17. doi: 10.1042/bj2880015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowaluk E. A., Seth P., Fung H. L. Metabolic activation of sodium nitroprusside to nitric oxide in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Sep;262(3):916–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. G., Rand M. J. Evidence for a role of nitric oxide in the neurotransmitter system mediating relaxation of the rat anococcygeus muscle. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1989 Dec;16(12):933–938. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1989.tb02404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Brien J. F., Marks G. S., McLaughlin B. E., Nakatsu K. Carbon monoxide does not inhibit glyceryl trinitrate biotransformation by or relaxation of aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 28;211(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., McAllister K. H., Paisley K. NANC neurotransmission in the bovine retractor penis muscle is blocked by superoxide anion following inhibition of superoxide dismutase with diethyldithiocarbamate. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Nov;33(11):1293–1301. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald B. J., Bennett B. M. Biotransformation of glyceryl trinitrate by rat aortic cytochrome P450. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 7;45(1):268–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90403-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Kamataki T., Waxman D. J., Guengerich F. P., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Gonzalez F. J., Coon M. J., Gunsalus I. C., Gotoh O. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers, early trivial names of enzymes, and nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Jan-Feb;12(1):1–51. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa Y., Davila J. C. Phencyclidine, a psychotomimetic agent and drug of abuse, is a suicide inhibitor of brain nitric oxide synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Aug 16;194(3):1435–1439. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyekan A. O., McGiff J. C., Quilley J. Cytochrome P-450-dependent vasodilator responses to arachidonic acid in the isolated, perfused kidney of the rat. Circ Res. 1991 Apr;68(4):958–965. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.4.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyekan A. O., McGiff J. C., Rosencrantz-Weiss P., Quilley J. Relaxant responses of rabbit aorta: influence of cytochrome P450 inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Jan;268(1):262–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajanayagam M. A., Li C. G., Rand M. J. Differential effects of hydroxocobalamin on NO-mediated relaxations in rat aorta and anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand M. J., Li C. G. Nitric oxide as a neurotransmitter in peripheral nerves: nature of transmitter and mechanism of transmission. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:659–682. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.003303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand M. J., Li C. G. The inhibition of nitric oxide-mediated relaxations in rat aorta and anococcygeus muscle by diphenylene iodonium. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1993 Mar;20(3):141–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1993.tb01661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud J. P., Boucher J. L., Vadon S., Delaforge M., Mansuy D. Particular ability of liver P450s3A to catalyze the oxidation of N omega-hydroxyarginine to citrulline and nitrogen oxides and occurrence in no synthases of a sequence very similar to the heme-binding sequence in P450s. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 15;192(1):53–60. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. Cytochrome P-450 mediates bioactivation of organic nitrates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):298–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Trockfeld J., Schmalix W. A., Brill T., Siewert J. R., Greim H., Doehmer J. Inhibition of cytochromes P4501A by nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3559–3563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassaneeyakul W., Birkett D. J., Veronese M. E., McManus M. E., Tukey R. H., Quattrochi L. C., Gelboin H. V., Miners J. O. Specificity of substrate and inhibitor probes for human cytochromes P450 1A1 and 1A2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Apr;265(1):401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K. A., Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide synthase is a cytochrome P-450 type hemoprotein. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6627–6631. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wink D. A., Osawa Y., Darbyshire J. F., Jones C. R., Eshenaur S. C., Nims R. W. Inhibition of cytochromes P450 by nitric oxide and a nitric oxide-releasing agent. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Jan;300(1):115–123. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D. J., Datto G. A., Samatovicz R. A. The dual mode of inhibition of calmodulin-dependent nitric-oxide synthase by antifungal imidazole agents. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9430–9436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeates R. A., Schmid M., Leitold M. Antagonism of glycerol trinitrate activity by an inhibitor of glutathione S-transferase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 1;38(11):1749–1753. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90408-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zembowicz A., Hatchett R. J., Radziszewski W., Gryglewski R. J. Inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by ebselen. Prevention by thiols suggests the inactivation by ebselen of a critical thiol essential for the catalytic activity of nitric oxide synthase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Dec;267(3):1112–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


