Abstract
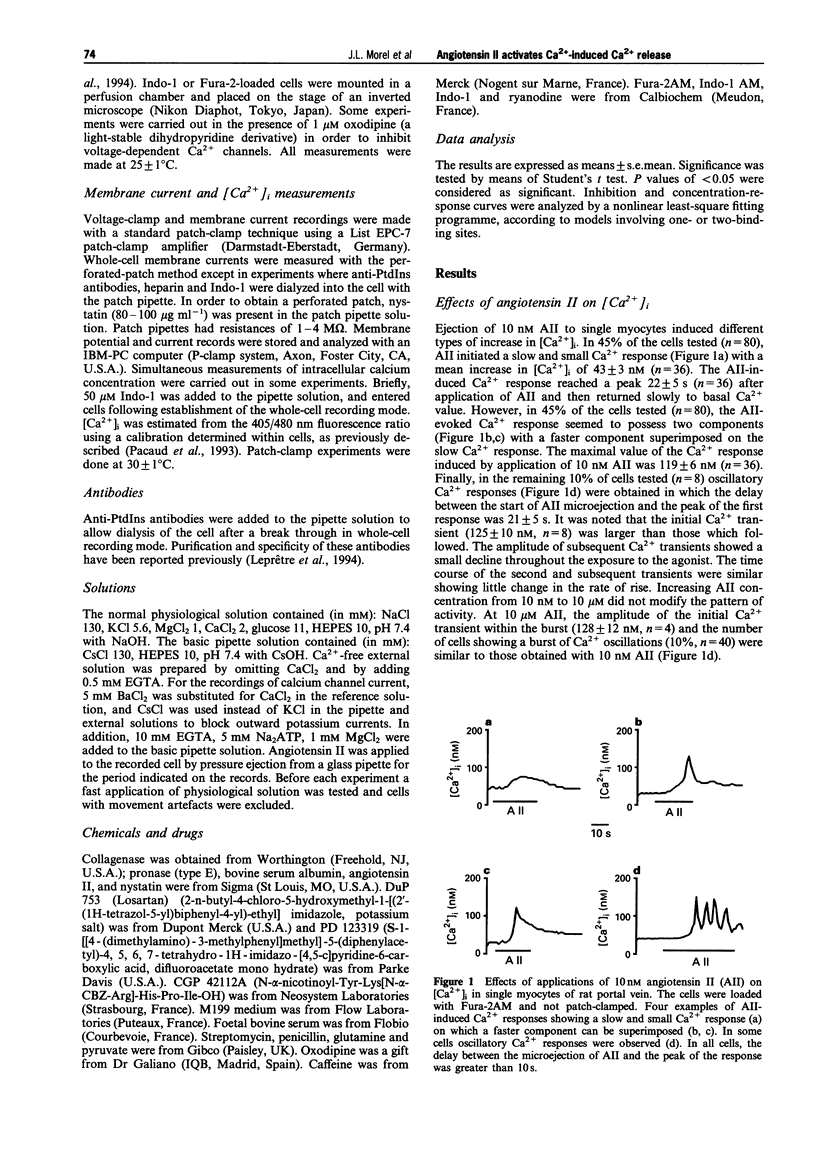
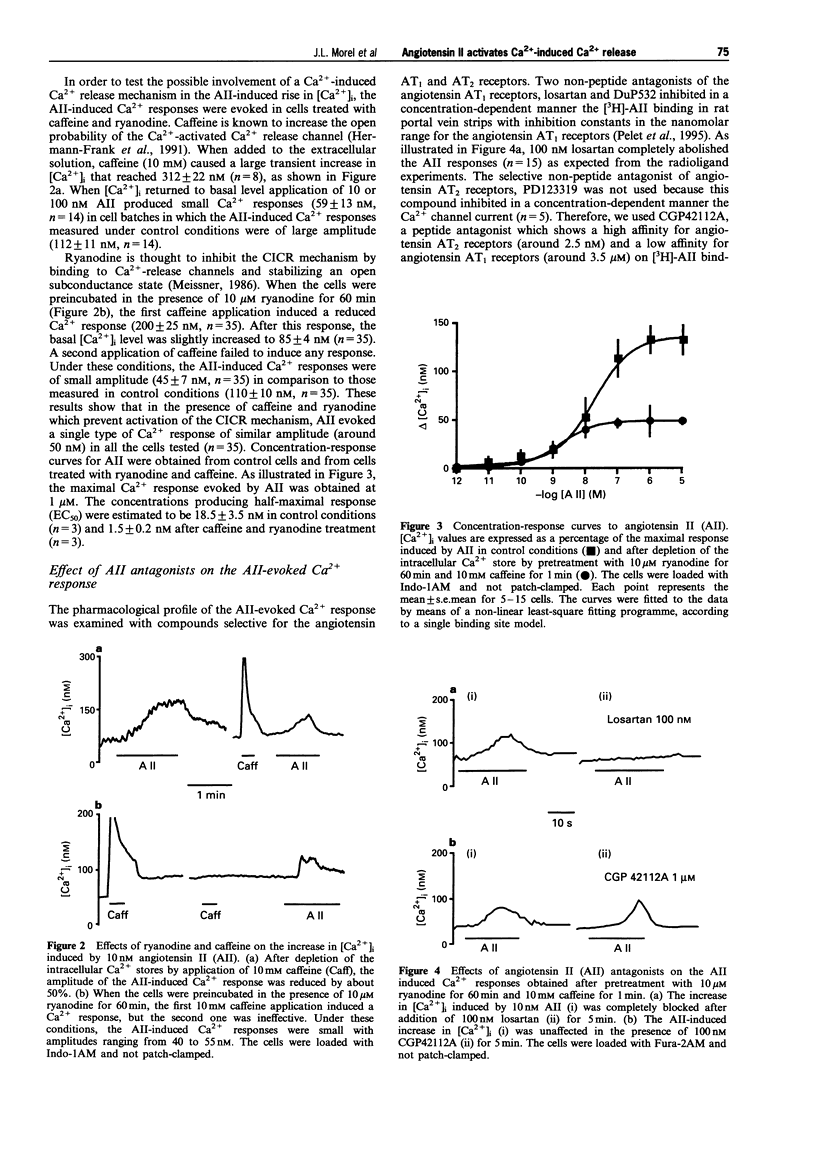
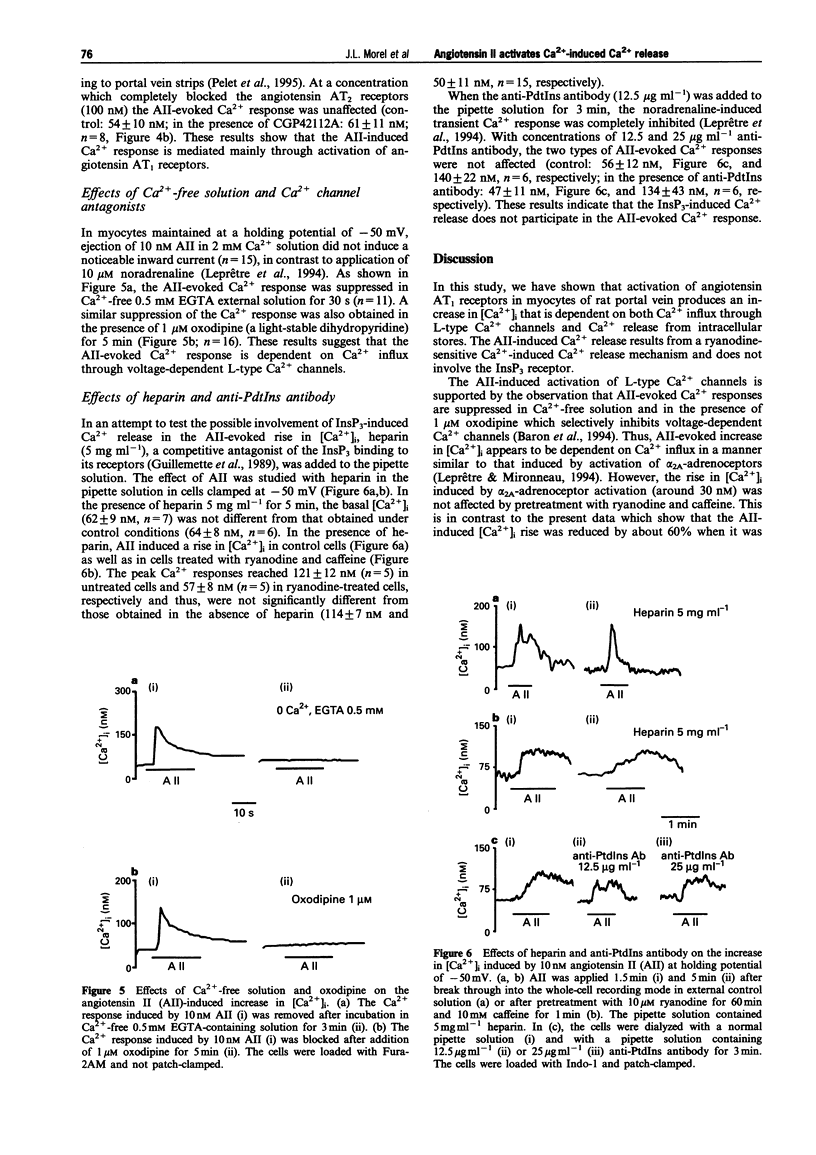
1. The action of angiotensin II (AII) was studied in single myocytes from rat portal vein in which the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration was estimated by emission from dyes Fura-2 or Indo-1 and the Ca2+ channel current was measured with the whole-cell mode of the patch-clamp technique. 2. Most of the AII-evoked increases in [Ca2+]i were reduced by about 60% after pretreatment with ryanodine and caffeine to deplete intracellular Ca2+ stores. However, in some cells the AII-induced Ca2+ responses were of small amplitude and resembled those obtained in the presence of ryanodine and caffeine. Both types of Ca2+ responses induced by AII were selectively inhibited by losartan, suggesting that the AII effects resulted from activation of the angiotensin AT1 receptors. 3. The concentration-response curve to AII had an EC50 value close to 1 nM for the increase in [Ca2+]i obtained after depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores. This value was increased to around 18 nM in experiments where the intracellular Ca2+ stores were not depleted. 4. AII-evoked Ca2+ responses were abolished in the absence of external Ca2+ and in the presence of 1 microM oxodipine to block L-type Ca2+ channels. 5. Intracellular applications of the InsP3 receptor antagonist, heparin or an anti-PdtIns antibody did not modify AII-induced Ca2+ responses. 6. Our results show that AII releases Ca2+ from intracellular stores without involving InsP3 but through a Ca2+ release mechanism activated by Ca2+ influx through L-type Ca2+ channels.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand-Srivastava M. B. Angiotensin II receptors negatively coupled to adenylate cyclase in rat aorta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):420–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A., Rakotoarisoa L., Leprêtre N., Mironneau J. Inhibition of L-type Ca2+ channels in portal vein myocytes by the enantiomers of oxodipine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Sep 15;269(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bkaily G., Peyrow M., Sculptoreanu A., Jacques D., Chahine M., Regoli D., Sperelakis N. Angiotensin II increases Isi and blocks IK in single aortic cell of rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Sep;412(4):448–450. doi: 10.1007/BF01907567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont G., Goldbeter A. Properties of intracellular Ca2+ waves generated by a model based on Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2191–2204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80705-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grégoire G., Loirand G., Pacaud P. Ca2+ and Sr2+ entry induced Ca2+ release from the intracellular Ca2+ store in smooth muscle cells of rat portal vein. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:483–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Lamontagne S., Boulay G., Mouillac B. Differential effects of heparin on inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate binding, metabolism, and calcium release activity in the bovine adrenal cortex. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez L. M., Zhao X. L., Hosey M. M. Protein kinase C-mediated regulation of L-type Ca channels from skeletal muscle requires phosphorylation of the alpha 1 subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jul 29;202(2):857–865. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann-Frank A., Darling E., Meissner G. Functional characterization of the Ca(2+)-gated Ca2+ release channel of vascular smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Pflugers Arch. 1991 May;418(4):353–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00550873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Yamazawa T., Miyashita Y., Endo M., Kasai H. Critical intracellular Ca2+ concentration for all-or-none Ca2+ spiking in single smooth muscle cells. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5287–5291. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Theler J. M., Capponi A. M., Vallotton M. B. Characterization of oscillations in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration and measurement of cytosolic Na+ concentration changes evoked by angiotensin II and vasopressin in individual rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Use of microfluorometry and digital imaging. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12618–12626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubalak S. W., Webb J. G. Angiotensin II enhancement of hormone-stimulated cAMP formation in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 2):H86–H96. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.264.1.H86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepretre N., Mironneau J., Arnaudeau S., Tanfin Z., Harbon S., Guillon G., Ibarrondo J. Activation of alpha-1A adrenoceptors mobilizes calcium from the intracellular stores in myocytes from rat portal vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Jan;268(1):167–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprêtre N., Mironneau J. Alpha 2-adrenoceptors activate dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels via Gi-proteins and protein kinase C in rat portal vein myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Dec;429(2):253–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00374320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Ryanodine activation and inhibition of the Ca2+ release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6300–6306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mironneau J., Mironneau C., Grosset A., Hamon G., Savineau J. P. Action of angiotensin II on the electrical and mechanical activity of rat uterine smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Dec 5;68(3):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90525-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Sperelakis N. Involvement of a GTP-binding protein in stimulating action of angiotensin II on calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1991 Mar;68(3):763–771. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.3.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Loirand G., Grégoire G., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Noradrenaline-activated heparin-sensitive Ca2+ entry after depletion of intracellular Ca2+ store in portal vein smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3866–3872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelet C., Mironneau C., Rakotoarisoa L., Neuilly G. Angiotensin II receptor subtypes and contractile responses in portal vein smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Jun 6;279(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Wakui M. Oscillating intracellular Ca2+ signals evoked by activation of receptors linked to inositol lipid hydrolysis: mechanism of generation. J Membr Biol. 1990 Nov;118(2):93–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01868467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Ochsner M., Whitebread S., De Gasparo M. Down-regulation of protein kinase C potentiates angiotensin II-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in vascular smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):285–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2620285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachinidis A., Ko Y., Weisser P., Meyer zu Brickwedde M. K., Düsing R., Christian R., Wieczorek A. J., Vetter H. EXP3174, a metabolite of losartan (MK 954, DuP 753) is more potent than losartan in blocking the angiotensin II-induced responses in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Hypertens. 1993 Feb;11(2):155–162. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199302000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varol F. G., Hadjiconstantinou M., Zuspan F. P., Neff N. H. Angiotensin II stimulates phosphoinositide turnover in the rat myometrium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 14;162(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


