Abstract
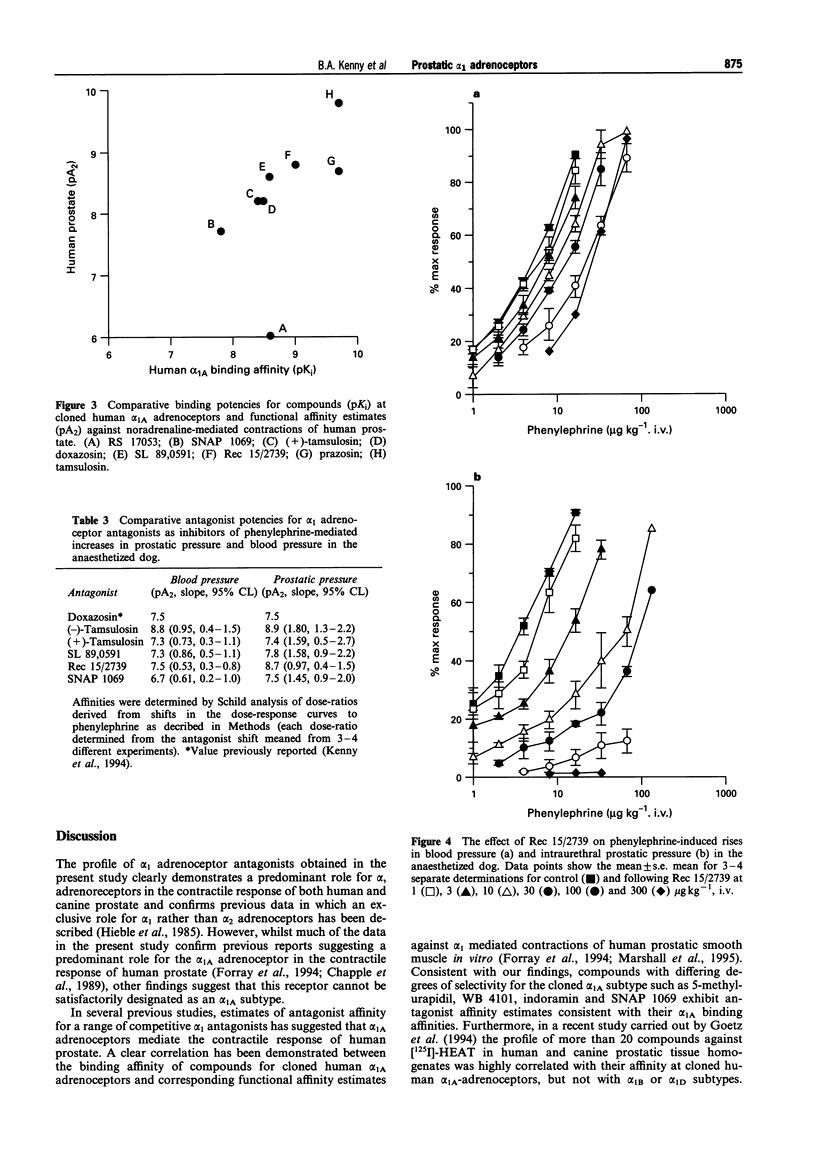
1. The profile of a range of alpha 1 adrenoceptor antagonists was determined in vitro against cloned human alpha 1A, alpha 1B and alpha 1D adrenoceptors and against noradrenaline-mediated contractions of rat aorta and human prostate. The in vivo profile of compounds was determined in an anaesthetized dog model which allowed the simultaneous assessment of antagonist potency against phenylephrine-mediated increases in blood pressure and prostatic pressure. 2. The quinazoline antagonists, prazosin, doxazosin and alfuzosin displayed high affinity but were non selective for the three cloned human alpha 1 adrenoceptors. Indoramin and SNAP 1069 showed selectivity for alpha 1A and alpha 1B adrenoceptors relative to the alpha 1D subtype. Rec 15/2739, WB 4101, SL 89,0591, (+)- and (-)- tamsulosin showed selectivity for alpha 1A and alpha 1D adrenoceptors relative to the alpha 1B subtype. RS 17053 showed high affinity and selectivity for alpha 1A adrenoceptors (pKi 8.6) relative to alpha 1B (pKi = 7.3) and alpha 1D (pKi = 7.1) subtypes. 3. (+)-Tamsulosin, (-)-tamsulosin, SL 89,0591, Rec 15/2739, SNAP 1069 and RS 17053 appeared to act as competitive antagonists of noradrenaline-mediated contractions of rat aorta yielding pA2 affinity estimates which were similar to binding affinities at cloned human alpha 1D adrenoceptors. The following rank order was obtained: prazosin = (-)-tamsulosin > doxazosin > SL 89,0591 = (+)-tamsulosin > Rec 15/2739 > RS 17053 = SNAP 1069. 4. (-)-Tamsulosin was a very potent, insurmountable antagonist of noradrenaline-mediated contractions of human prostate, yielding an approximate pA2 estimate of 9.8 at 1 nM. The corresponding (+)-enantiomer was 30 fold weaker. SL 89,0591, SNAP 1069 and Rec 15/2739 yielded pA2 estimates which compared well with their alpha 1A binding affinities. The affinity estimate for prazosin on human prostate was lower than the corresponding binding affinity determined at alpha 1A adrenoceptors and RS 17053 was a very weak antagonist on human prostate (pA2 = 6.0) relative to the high affinity (pKi = 8.6) determined at cloned human alpha 1A adrenoceptors. 5. In the anaesthetized dog, in vivo pseudo "pA2' values showed that doxazosin, (+)- and (-)-tamsulosin inhibited phenylephrine-induced increases in prostatic and blood pressure with similar affinity, implying that these agents show little or no selectivity for prostatic responses in this model. SL 89,0591 and SNAP 1069 were moderately selective (3 and 6 fold respectively) for prostatic pressure relative to blood pressure. Rec 15/2739 was a more potent antagonist of phenylephrine-mediated increases in prostatic pressure ("pA2' = 8.74) compared to blood pressure ("pA2' = 7.51). 6. Data in this study suggest that the alpha 1 adrenoceptor mediating noradrenaline-induced contractions of human prostate, whilst having some of the characteristics of an alpha 1A adrenoceptor, cannot be satisfactorily aligned with cloned alpha 1A, alpha 1B or alpha 1D adrenoceptors. In addition, studies in the anaesthetized dog have shown that agents having high affinity and selectivity for prostatic alpha 1 adrenoceptors, particularly over the alpha 1D subtype, appear to inhibit phenylephrine-induced increases in prostatic pressure selectively compared to blood pressure.
Full text
PDF


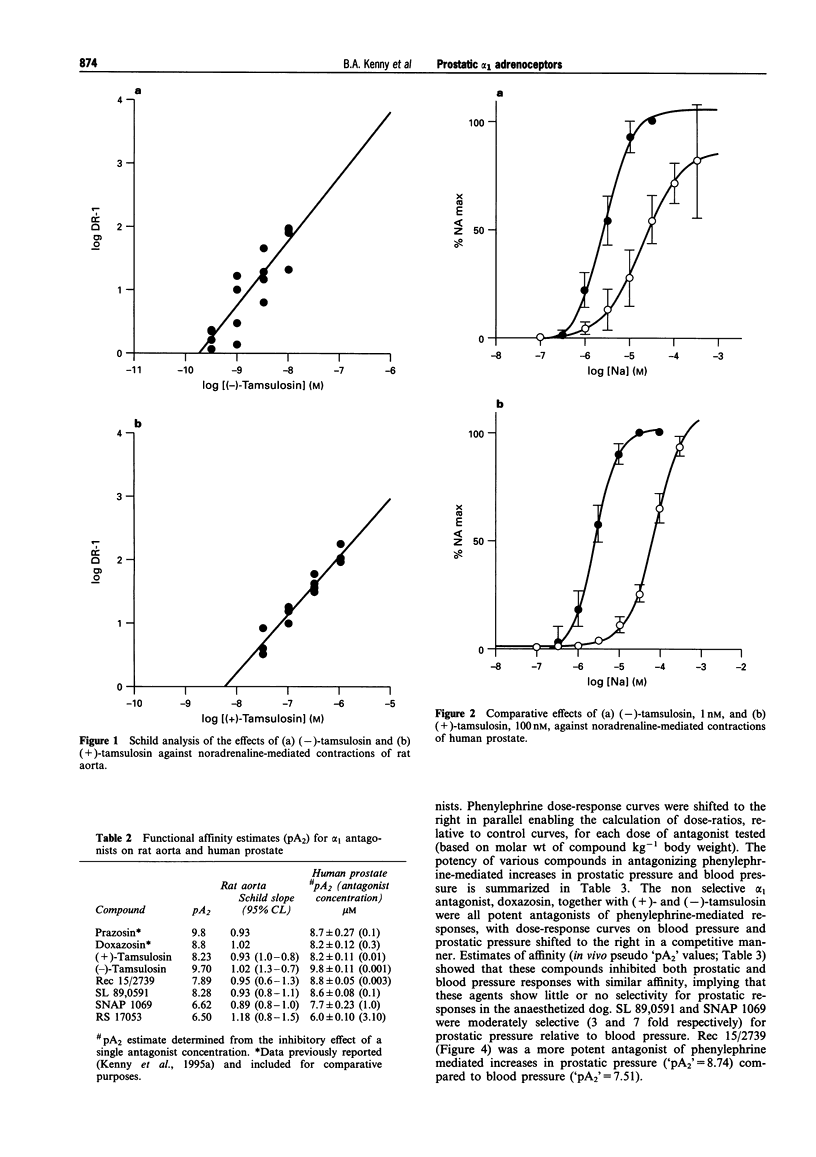



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslin D., Fields D. W., Chou T. C., Marion D. N., Kane M., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Felsen D. Medical management of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a canine model comparing the in vivo efficacy of alpha-1 adrenergic antagonists in the prostate. J Urol. 1993 Feb;149(2):395–399. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapple C. R., Aubry M. L., James S., Greengrass P. M., Burnstock G., Turner-Warwick R. T., Milroy E. J., Davey M. J. Characterisation of human prostatic adrenoceptors using pharmacology receptor binding and localisation. Br J Urol. 1989 May;63(5):487–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1989.tb05942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure C., Pimoule C., Vallancien G., Langer S. Z., Graham D. Identification of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes present in the human prostate. Life Sci. 1994;54(21):1595–1605. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Williams T. J., Blue D. R., Clarke D. E. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification: sharpening Occam's razor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jun;15(6):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forray C., Bard J. A., Wetzel J. M., Chiu G., Shapiro E., Tang R., Lepor H., Hartig P. R., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. A. The alpha 1-adrenergic receptor that mediates smooth muscle contraction in human prostate has the pharmacological properties of the cloned human alpha 1c subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):703–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz A. S., Lutz M. W., Rimele T. J., Saussy D. L., Jr Characterization of alpha-1 adrenoceptor subtypes in human and canine prostate membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Dec;271(3):1228–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., Bylund D. B., Clarke D. E., Eikenburg D. C., Langer S. Z., Lefkowitz R. J., Minneman K. P., Ruffolo R. R., Jr International Union of Pharmacology. X. Recommendation for nomenclature of alpha 1-adrenoceptors: consensus update. Pharmacol Rev. 1995 Jun;47(2):267–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., Caine M., Zalaznik E. In vitro characterization of the alpha-adrenoceptors in human prostate. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 2;107(2):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa A., Shibata K., Horie K., Takei Y., Obika K., Tanaka T., Muramoto N., Takagaki K., Yano J., Tsujimoto G. Cloning, functional expression and tissue distribution of human alpha 1c-adrenoceptor splice variants. FEBS Lett. 1995 Apr 24;363(3):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00330-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B. A., Chalmers D. H., Philpott P. C., Naylor A. M. Characterization of an alpha 1D-adrenoceptor mediating the contractile response of rat aorta to noradrenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;115(6):981–986. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B. A., Naylor A. M., Carter A. J., Read A. M., Greengrass P. M., Wyllie M. G. Effect of alpha 1 adrenoceptor antagonists on prostatic pressure and blood pressure in the anesthetized dog. Urology. 1994 Jul;44(1):52–57. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(94)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Tang R., Shapiro E., Lepor H. Characterization and localization of prostatic alpha 1 adrenoceptors using radioligand receptor binding on slide-mounted tissue section. J Urol. 1993 Dec;150(6):2002–2006. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35954-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefèvre-Borg F., O'Connor S. E., Schoemaker H., Hicks P. E., Lechaire J., Gautier E., Pierre F., Pimoule C., Manoury P., Langer S. Z. Alfuzosin, a selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist in the lower urinary tract. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1282–1289. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13762.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepor H., Tang R., Shapiro E. The alpha-adrenoceptor subtype mediating the tension of human prostatic smooth muscle. Prostate. 1993;22(4):301–307. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990220404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall I., Burt R. P., Chapple C. R. Noradrenaline contractions of human prostate mediated by alpha 1A-(alpha 1c-) adrenoceptor subtype. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;115(5):781–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeal J. Pathology of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Insight into etiology. Urol Clin North Am. 1990 Aug;17(3):477–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Comparison of cloned and pharmacologically defined rat tissue alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;350(2):136–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00241087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Kenny B., Schwinn D. A. Classification of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;352(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00169183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Ohmura T., Kigoshi S., Hashimoto S., Oshita M. Pharmacological subclassification of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in vascular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):197–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Oshita M., Ohmura T., Kigoshi S., Akino H., Gobara M., Okada K. Pharmacological characterization of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in the human prostate: functional and binding studies. Br J Urol. 1994 Nov;74(5):572–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1994.tb09186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. T., Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Allen L. F., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification, quantification, and localization of mRNA for three distinct alpha 1 adrenergic receptor subtypes in human prostate. J Urol. 1993 Aug;150(2 Pt 1):546–551. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35544-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Nichols A. J., Stadel J. M., Hieble J. P. Structure and function of alpha-adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Dec;43(4):475–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Johnston G. I., Page S. O., Mosley M. J., Wilson K. H., Worman N. P., Campbell S., Fidock M. D., Furness L. M., Parry-Smith D. J. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of human alpha-1 adrenergic receptors: sequence corrections and direct comparison with other species homologues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jan;272(1):134–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibasaki M., Sudoh K., Inagaki O., Uchida W., Honda K. Effect of the optical isomers of YM-12617 on increased intra-urethral pressure induced by phenylephrine in anaesthetized dogs. J Auton Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;12(4):263–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1992.tb00340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde M. I., Fitton A., McTavish D. Alfuzosin. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Drugs. 1993 Mar;45(3):410–429. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199345030-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


