Abstract
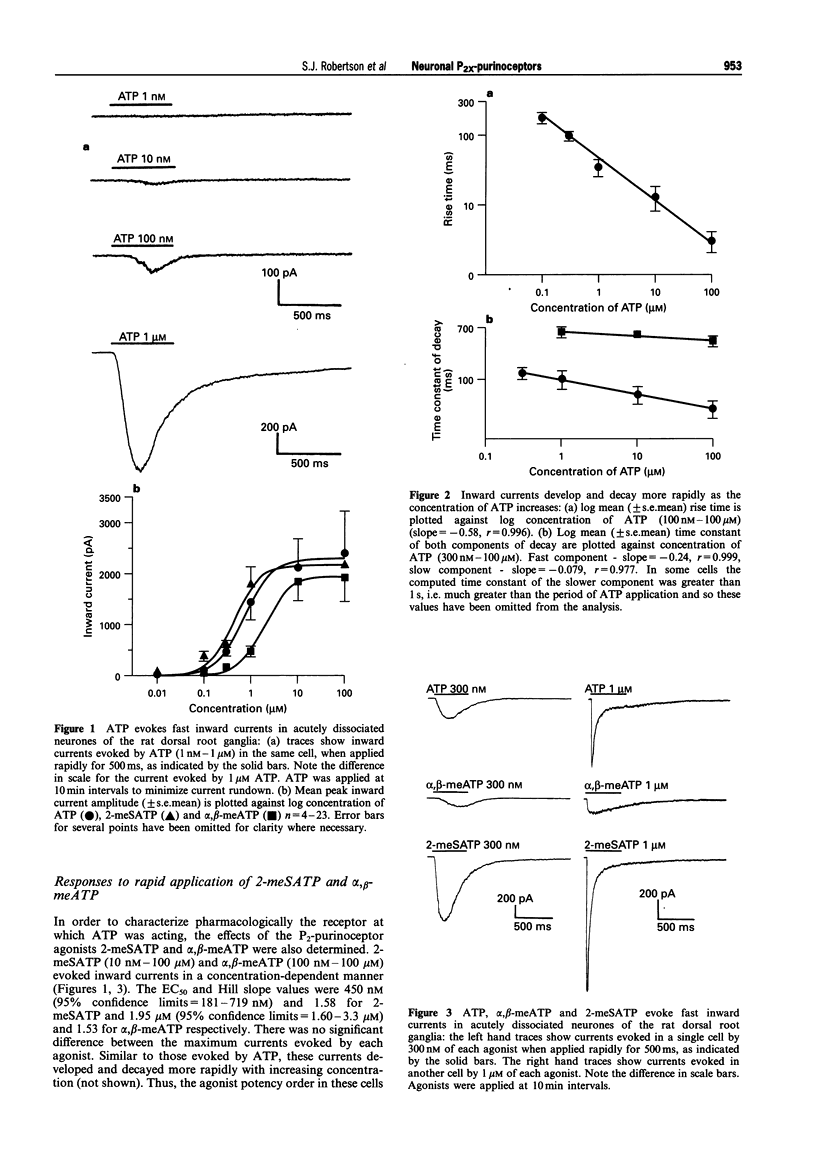
1. The electrophysiological actions of the P2-purinoceptor agonists, adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP), 2-methylthio ATP (2-meSATP) and alpha, beta-methyleneATP (alpha, beta-meATP) and of uridine 5'-triphosphate (UTP) were studied under concentration and voltage-clamp conditions in dissociated neurones of 1-6 day old rat dorsal root ganglia. 2. ATP (10 nM-100 microM) applied rapidly via a U-tube perfusion system (equilibration time < 10 ms) activated concentration-dependent inward currents with a latency to onset of a few ms, an EC50 of 719 nM and a Hill slope of 1.47. 3. 2-meSATP (10 nM- 100 microM) and alpha, beta-meATP (100 nM - 100 microM) also evoked transient inward currents. The EC50 and Hill slopes were 450 nM and 1.58 for 2-meSATP and 1.95 microM and 1.53 for alpha, beta-meATP respectively. There was no significant difference between the maximum currents evoked by the three agonists. 4. As the concentration of ATP increased so the rate of rise and decay of the currents also increased. At 100 and 300 nM ATP the decay of the current was best fitted by a single exponential, but at 1 microM and above two exponentials were required. Log-log plots of the rise time or time constants of decay versus concentration were linear. Currents evoked by 2-meSATP and alpha, beta-meATP showed a similar concentration-dependence in their kinetics. 5. Inward currents evoked by ATP, 2-meSATP and alpha, beta-meATP (300 nM) were abolished by the P2-purinoceptor antagonist, suramin (100 microM). 6. UTP (10 microM) evoked similar transient inward currents, which were sensitive to suramin (100 microM). ATP (10 microM), applied 2 min beforehand, reduced the response to UTP (10 microM) by 80 +/- 10%. 7. This study shows that ATP, 2-meSATP and alpha, beta-meATP act via a suramin-sensitive P2x-purinoceptor to evoke rapid, transient inward currents in dissociated neurones of rat dorsal root ganglia. The pyrimidine nucleotide, UTP, was also active. It is likely that the agonists were acting at the P2x3-subtype to produce these effects.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. ATP-activated channels in rat and bullfrog sensory neurons: concentration dependence and kinetics. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleehen T., Keele C. A. Observations on the algogenic actions of adenosine compounds on the human blister base preparation. Pain. 1977 Aug;3(4):367–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(77)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo X., Zhang Y., Nassar M., Burnstock G., Schoepfer R. A P2X purinoceptor cDNA conferring a novel pharmacological profile. FEBS Lett. 1995 Nov 13;375(1-2):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01203-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M. M., Evans M. L., Benham C. D. Calcium Influx Induced by Stimulation of ATP Receptors on Neurons Cultured from Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia. Eur J Neurosci. 1991;3(3):285–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1991.tb00090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake A. J., Wagenbach M. J., Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):519–523. doi: 10.1038/371519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Overview. Purinergic mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Akopian A. N., Sivilotti L., Colquhoun D., Burnstock G., Wood J. N. A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):428–431. doi: 10.1038/377428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen B., Reimann W., Selve N., Friderichs E., Bültmann R. Antinociceptive effect of intrathecally administered P2-purinoceptor antagonists in rats. Brain Res. 1994 Dec 15;666(2):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90770-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Gibb A. J., Colquhoun D. ATP receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):144–147. doi: 10.1038/359144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Derkach V., Surprenant A. ATP mediates fast synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):503–505. doi: 10.1038/357503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Kennedy C. Characterization of P2-purinoceptors in the smooth muscle of the rat tail artery: a comparison between contractile and electrophysiological responses. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;113(3):853–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17071.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Lewis C., Buell G., Valera S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Pharmacological characterization of heterologously expressed ATP-gated cation channels (P2x purinoceptors). Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;48(2):178–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D. An ATP-sensitive conductance in single smooth muscle cells from the rat vas deferens. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:361–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho B. T., Huo Y. Y., Lu J. G., Newman R. A., Levin V. A. Analgesic activity of anticancer agent suramin. Anticancer Drugs. 1992 Apr;3(2):91–94. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199204000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Leff P. How should P2X purinoceptors be classified pharmacologically? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 May;16(5):168–174. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)89010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Leff P. Painful connection for ATP. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):385–386. doi: 10.1038/377385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C. P1- and P2-purinoceptor subtypes--an update. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Jan-Feb;303:30–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakh B. S., Humphrey P. P., Surprenant A. Electrophysiological properties of P2X-purinoceptors in rat superior cervical, nodose and guinea-pig coeliac neurones. J Physiol. 1995 Apr 15;484(Pt 2):385–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakh B. S., Surprenant A., Humphrey P. P. A study on P2X purinoceptors mediating the electrophysiological and contractile effects of purine nucleotides in rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(1):177–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Marchenko S. M., Pidoplichko V. I. Receptor for ATP in the membrane of mammalian sensory neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jan 31;35(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90524-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyrozis A., Goldstein P. A., Heath M. J., MacDermott A. B. Calcium entry through a subpopulation of AMPA receptors desensitized neighbouring NMDA receptors in rat dorsal horn neurons. J Physiol. 1995 Jun 1;485(Pt 2):373–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C., Neidhart S., Holy C., North R. A., Buell G., Surprenant A. Coexpression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):432–435. doi: 10.1038/377432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Peoples R. W., Li Z., Weight F. F. Zn2+ potentiates excitatory action of ATP on mammalian neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8264–8267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulkey R. M., Endo S., Shenolikar S., Malenka R. C. Involvement of a calcineurin/inhibitor-1 phosphatase cascade in hippocampal long-term depression. Nature. 1994 Jun 9;369(6480):486–488. doi: 10.1038/369486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelleg A., Hurt C. M. Mechanism of action of ATP on canine pulmonary vagal C fibre nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1996 Jan 1;490(Pt 1):265–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera S., Hussy N., Evans R. J., Adami N., North R. A., Surprenant A., Buell G. A new class of ligand-gated ion channel defined by P2x receptor for extracellular ATP. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):516–519. doi: 10.1038/371516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



