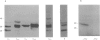Abstract
1. We sought to reconstitute and characterize G-protein linked phosphatidyl-D-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2)-directed phospholipase C (PLC) isoform activity in pig aortic vascular smooth muscle. 2. Six soluble PLC isoforms, namely gamma 1, delta 1 and beta 1 to beta 4 were partially separated by heparin affinity chromatography and were identified by Western blotting using specific antibodies. 3. In separate experiments, PLC activity was measured in the eluted fractions. Four of the partially resolved PLC isoforms gamma 1, beta 4, beta 2 and beta 1, showed corresponding activity using exogenous [3H]-PIP2 as substrate. 4. The isolated soluble PLC isoforms were reconstituted with receptors and guanyl nucleotide regulatory proteins (G-proteins) by addition of plasma membranes, the phospholipids which had been prelabelled with [3H]-myo-inositol. When so reconstituted PLC beta 2, beta 3 and beta 4 were inhibited (40 +/- 9, 47 +/- 12 and 40 +/- 5% respectively n = 12, +/-s.e.mean and each P < 0.05) by the addition of 1 mM guanosine 5'[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate (p[NH]ppG). 5. By contrast, when plasma membranes were preincubated with pertussis toxin to inhibit the activity of G-protein subunits G alpha i/alpha o the activities of PLC beta 2, beta 3 and beta 4 were stimulated (46 +/- 11, 31 +/- 9 and 37 +/- 8% respectively, n = 12, +/- s.e.mean and each P < 0.05) by the addition of p[NH]ppG. 6. Using well resolved fractions containing only PLC beta 3, time-dependent activity in the presence of p[NH]ppG was measurable only with membranes pretreated with pertussis toxin. 7. PLC beta 3 activity, measured with pertussis pretreated membranes, showed a dose-dependent increase in the presence of p[NH]ppG or guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]). This increase with 10 microM p[NH]ppG or GTP[S] 10% +/- 4 and 12% +/- 5 respectively (both P < 0.05 vs control without GTP analogue +/- s.e.mean, n = 10) was abolished by 50 microM guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate (GDP[S]) which also reduced constitutive PLC beta 3 activity by 9% +/- 4. 8. G-protein antibodies were used to neutralize PLC activity. Antibody to G alpha q/alpha 11, added to membrane fractions pretreated with pertussis toxin and assayed with GTP[S], reduced PLC beta 3 activity by 21% +/- 6 P < 0.02, n = 6, but was without effect on non-pertussis pretreated membranes. Antibodies to G alpha i1/alpha i2 had no effect. Antibodies to G-protein beta subunits had no effect on PLC beta 3 activity with pertussis pretreated preparations but activity without pertussis pretreatment was increased by 30% +/- 10, P < 0.03, n = 6. All results were expressed as % change from controls containing rabbit IgG. 9. In conclusion, pig aortic vascular smooth muscle contains six PLC isoforms. Activation of pertussis sensitive G-protein by GTP analogues results in inhibition of PLC beta 3 activity from liberated G-protein beta gamma subunits. Stimulation of PLC beta 3 activity is associated with a G-protein of the G alpha q family acting through the alpha subunit. The results suggest that the G-protein linked PLC beta isoforms in vascular smooth muscle demonstrate dual regulation by an inhibitory pertussis-sensitive pathway and a stimulatory G-protein of the G alpha q family, which is the case for PLC beta 3. This dual regulation is analogous to that of adenyl cyclase.
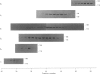
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
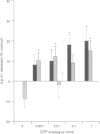
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Latif A. A. Calcium-mobilizing receptors, polyphosphoinositides, and the generation of second messengers. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Sep;38(3):227–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassare J. J., Tarver A. P., Henderson P. A., Mackin W. M., Sahagan B., Fisher G. J. Reconstitution of thromboxane A2 receptor-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in isolated platelet membranes: involvement of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-beta and GTP-binding protein Gq. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):235–240. doi: 10.1042/bj2910235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Abramowitz J., Brown A. M. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):163–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizzarri C., Di Girolamo M., D'Orazio M. C., Corda D. Evidence that a guanine nucleotide-binding protein linked to a muscarinic receptor inhibits directly phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blayney L. M., Newby A. C. Histamine and a guanine nucleotide increase calcium permeability in pig aortic microsomal fractions. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):105–109. doi: 10.1042/bj2670105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Waldo G. L., Harden T. K. Beta gamma-subunit activation of G-protein-regulated phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25451–25456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Woolkalis M. J., Manning D. R. Interactions in platelets between G proteins and the agonists that stimulate phospholipase C and inhibit adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5348–5355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Carozzi A., Schnabel P., Scheer A., Parker P. J., Gierschik P. Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):684–686. doi: 10.1038/360684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherifi Y., Pigeon C., Le Romancer M., Bado A., Reyl-Desmars F., Lewin M. J. Purification of a histamine H3 receptor negatively coupled to phosphoinositide turnover in the human gastric cell line HGT1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25315–25320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson J. M., Camps M., Gierschik P., Hill S. J. Activation of phospholipase C by G-protein beta gamma subunits in DDT1MF-2 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Feb 15;288(3):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson J. M., Hill S. J. Intracellular cross-talk between receptors coupled to phospholipase C via pertussis toxin-sensitive and insensitive G-proteins in DDT1MF-2 cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):719–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N. Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 12;1053(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90029-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwins P., Fredholm B. B. ATP and its metabolite adenosine act synergistically to mobilize intracellular calcium via the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in a smooth muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16081–16087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwins P., Fredholm B. B. Stimulation of adenosine A1 receptors and bradykinin receptors, which act via different G proteins, synergistically raises inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and intracellular free calcium in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7330–7334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Stephens L., Hawkins P. T., Downes C. P. Turkey erythrocyte membranes as a model for regulation of phospholipase C by guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9057–9061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhon D. Y., Lee H. H., Park D., Lee C. W., Lee K. H., Yoo O. J., Rhee S. G. Cloning, sequencing, purification, and Gq-dependent activation of phospholipase C-beta 3. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6654–6661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Parker P. J. Purification of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from a particulate fraction of bovine brain. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. W., Lee K. H., Lee S. B., Park D., Rhee S. G. Regulation of phospholipase C-beta 4 by ribonucleotides and the alpha subunit of Gq. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25335–25338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. W., Park D. J., Lee K. H., Kim C. G., Rhee S. G. Purification, molecular cloning, and sequencing of phospholipase C-beta 4. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21318–21327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. Y., Ryu S. H., Suh P. G., Choi W. C., Rhee S. G. Phospholipase C associated with particulate fractions of bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5540–5544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. B., Rhee S. G. Significance of PIP2 hydrolysis and regulation of phospholipase C isozymes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao F., Shin H. S., Rhee S. G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 induced by cross-linking of the high-affinity or low-affinity Fc receptor for IgG in U937 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I. Guanine nucleotides mediate stimulatory and inhibitory effects on cerebral-cortical membrane phospholipase C activity. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):245–251. doi: 10.1042/bj2610245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Sulkholutskaya I., Weng C. G protein-mediated inhibition of phospholipase C activity in a solubilized membrane preparation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8692–8697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martelli A. M., Gilmour R. S., Bertagnolo V., Neri L. M., Manzoli L., Cocco L. Nuclear localization and signalling activity of phosphoinositidase C beta in Swiss 3T3 cells. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):242–245. doi: 10.1038/358242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhee F., Downes C. P., Lowe G. Studies of inositol analogues as inhibitors of the phosphoinositide pathway, and incorporation of 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-myo-inositol to give analogues of phosphatidylinositol intermediates. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):407–412. doi: 10.1042/bj2770407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhee F., Lowe G., Vaziri C., Downes C. P. Phosphatidylinositol synthase and phosphatidylinositol/inositol exchange reactions in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 1;275(Pt 1):187–192. doi: 10.1042/bj2750187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Waldo G. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. A receptor and G-protein-regulated polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from turkey erythrocytes. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13501–13507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D., Jhon D. Y., Kriz R., Knopf J., Rhee S. G. Cloning, sequencing, expression, and Gq-independent activation of phospholipase C-beta 2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16048–16055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Hemmings B. A., Gierschik P. PH domains and phospholipases--a meaningful relationship? Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):54–55. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Jackson T. R., Hawkins P. T. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate supply by agonists and non-hydrolysable GTP analogues. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 1;296(Pt 2):481–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2960481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C. The active role of beta gamma in signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;6(2):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Choi W. C., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Monoclonal antibodies to three phospholipase C isozymes from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14497–14504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. M., Geny B., Cockcroft S. Identification of a novel cytosolic poly-phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PLC-86) as the major G-protein-regulated enzyme. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2507–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Geet C., Deckmyn H., Kienast J., Wittevrongel C., Vermylen J. Guanine nucleotide-dependent inhibition of phospholipase C in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7920–7926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaziri C., Downes C. P., Macfarlane S. C. Direct labelling of hormone-sensitive phosphoinositides by a plasma-membrane-associated PtdIns synthase in turkey erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 15;294(Pt 3):793–799. doi: 10.1042/bj2940793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D. C., Moxham C. M., Morris A. J., Malbon C. C. Suppression of Gi alpha 2 enhances phospholipase C signalling. Biochem J. 1994 May 1;299(Pt 3):593–596. doi: 10.1042/bj2990593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zini N., Martelli A. M., Cocco L., Manzoli F. A., Maraldi N. M. Phosphoinositidase C isoforms are specifically localized in the nuclear matrix and cytoskeleton of Swiss 3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Sep;208(1):257–269. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]