Abstract
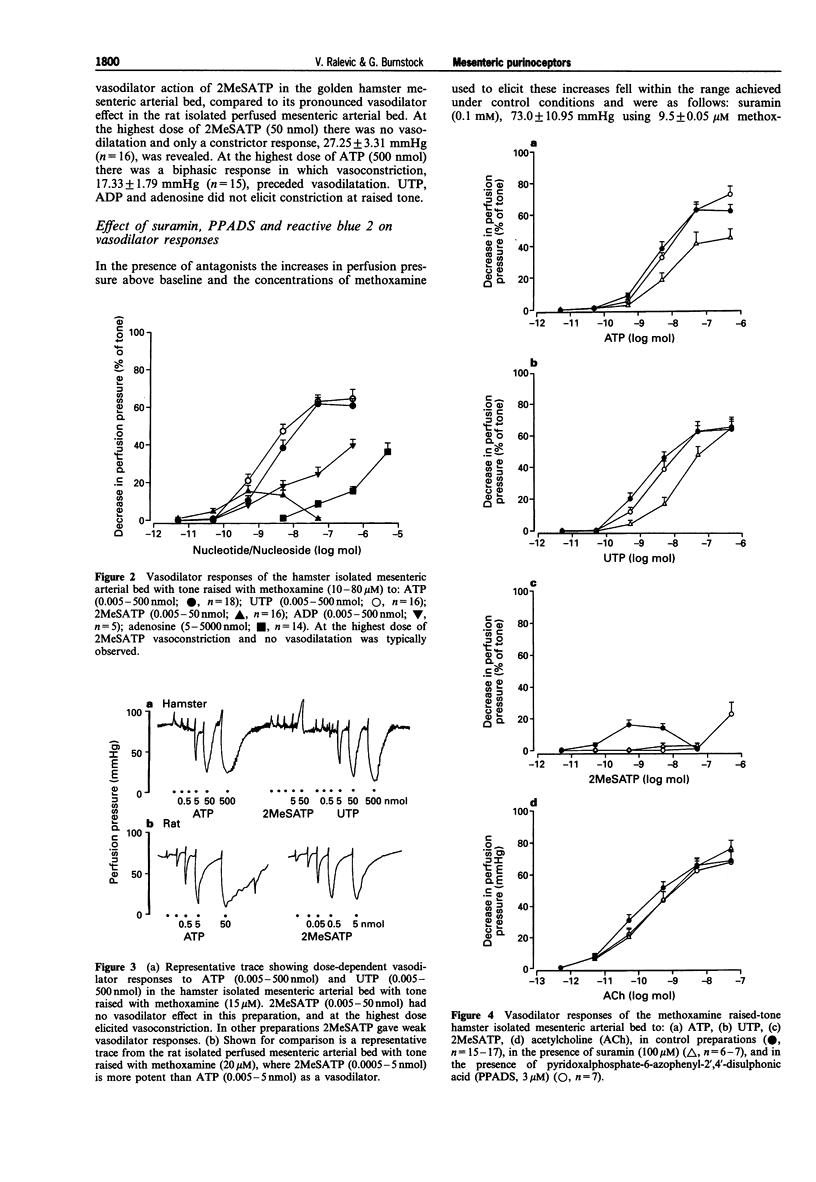
1. P2-purinoceptors were characterized pharmacologically in the constantly perfused isolated mesenteric arterial vascular bed of the golden hamster. Vasoconstrictor and vasodilator responses to the nucleotides ATP, ADP, 2 methylthio ATP (2MeSATP), alpha,beta-methylene ATP (alpha,beta-meATP) and uridine 5'-triphosphate (UTP) and a role for ATP in sympathetic constriction were examined. 2. At basal tone nucleotides elicited dose-dependent vasoconstriction with an observed rank order of potency of alpha,beta-meATP >> 2MeSATP > ATP = ADP > UTP (based on the doses required to elicit constrictor responses of 25 mmHg). Adenosine had no vasoconstrictor action at doses up to 5 mumol. After application of a single dose (0.5 mumol) of alpha,beta-meATP preparations were desensitized to constriction by subsequent application of nucleotides. 3. Electrical field stimulation (4-64 Hz, 90 V, 1 ms, 30 s) elicited frequency-dependent constrictions which were abolished by guanethidine (5 microM) and by prazosin (1 microM). 4. The non-selective P2-purinoceptor antagonist suramin (100 microM) did not significantly affect vasoconstrictor responses to ATP. The P2X-selective purinoceptor antagonist pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulphonic acid (PPADS, 3 microM), virtually abolished responses to ATP. When the endothelium was removed vasoconstrictor responses to ATP and noradrenaline were augmented. 5. In preparations with tone raised with methoxamine (10-80 microM) nucleotides elicited vasodilatation with an observed potency order of ATP = UTP > ADP >> adenosine. 2MeSATP had relatively minor vasodilator effects and at the highest dose tested (50 nmol) elicited only vasoconstriction. alpha,beta-meATP did not elicit vasodilatation but produced further constriction of the raised tone preparation. At the highest doses of ATP and ADP (0.5 microM) responses were biphasic with vasoconstriction preceding vasodilatation. After removal of the endothelium, with the exception of adenosine, vasodilator responses to purines and to UTP were abolished; vasoconstriction to ATP, ADP, UTP and 2MeSATP was evident at the highest doses. 6. Suramin (100 microM) inhibited vasodilatation to both ATP and UTP and abolished responses to 2MeSATP. PPADS (3 microM) inhibited relaxation to 2MeSATP but did not affect relaxation to ATP, UTP, adenosine and acetylcholine and ADP. 7. Reactive blue 2 (30 microM) blocked vasodilator responses to ATP, UTP, 2MeSATP and acetylcholine; it was without effect when used at 3 microM. 8. The results of this study show that ATP elicits vasoconstriction of mesenteric arteries of the golden hamster via P2X-purinoceptors located on the smooth muscle, and vasodilatation via P2U-receptors which are located on the endothelium. 2MeSATP has marginal vasodilator activity, suggesting that P2Y-purinoceptors contribute minimally to relaxation to ATP in hamster mesenteric arteries.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G. Purinoceptors: are there families of P2X and P2Y purinoceptors? Pharmacol Ther. 1994;64(3):445–475. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(94)00048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Zohn I. E., Jacobson K. A., Harden T. K. Differential effects of P2-purinoceptor antagonists on phospholipase C- and adenylyl cyclase-coupled P2Y-purinoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Oct;113(2):614–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C., Tanna B., Boarder M. R. PPADS: an antagonist at endothelial P2Y-purinoceptors but not P2U-purinoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Nov;116(5):2413–2416. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Warland J. J. P2-purinoceptors of two subtypes in the rabbit mesenteric artery: reactive blue 2 selectively inhibits responses mediated via the P2y-but not the P2x-purinoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;90(2):383–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crack B. E., Beukers M. W., McKechnie K. C., Ijzerman A. P., Leff P. Pharmacological analysis of ecto-ATPase inhibition: evidence for combined enzyme inhibition and receptor antagonism in P2X-purinoceptor ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1432–1438. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Kennedy C. Characterization of P2-purinoceptors in the smooth muscle of the rat tail artery: a comparison between contractile and electrophysiological responses. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;113(3):853–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17071.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Hogaboom G. K., O'Donnell J. P., Colby J., Westfall D. P. Contribution by purines to the neurogenic response of the vas deferens of the guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 5;69(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90600-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Boyer J. L., Nicholas R. A. P2-purinergic receptors: subtype-associated signaling responses and structure. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1995;35:541–579. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.35.040195.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogaboom G. K., O'Donnell J. P., Fedan J. S. Purinergic receptors: photoaffinity analog of adenosine triphosphate is a specific adenosine triphosphate antagonist. Science. 1980 Jun 13;208(4449):1273–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.6103581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood A. M., Burnstock G. ATP mediates coronary vasoconstriction via P2x-purinoceptors and coronary vasodilatation via P2y-purinoceptors in the isolated perfused rat heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 7;136(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90777-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston D. A., Burnstock G., Vanhoutte P. M. Different P2-purinergic receptor subtypes of endothelium and smooth muscle in canine blood vessels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Knight G. E., Burnstock G. Suramin antagonizes responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists and purinergic nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig urinary bladder and taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):617–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C. P1- and P2-purinoceptor subtypes--an update. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Jan-Feb;303:30–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakh B. S., Surprenant A., Humphrey P. P. A study on P2X purinoceptors mediating the electrophysiological and contractile effects of purine nucleotides in rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(1):177–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht G., Friebe T., Grimm U., Windscheif U., Bungardt E., Hildebrandt C., Bäumert H. G., Spatz-Kümbel G., Mutschler E. PPADS, a novel functionally selective antagonist of P2 purinoceptor-mediated responses. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;217(2-3):217–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90877-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P., Wood B. E., O'Connor S. E. Suramin is a slowly-equilibrating but competitive antagonist at P2x-receptors in the rabbit isolated ear artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):645–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Cusack N. J., Carleton J. S., Gordon J. L. Specificity of P2-purinoceptor that mediates endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 5;108(3):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathieson J. J., Burnstock G. Purine-mediated relaxation and constriction of isolated rabbit mesenteric artery are not endothelium-dependent. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 3;118(3):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motte S., Pirotton S., Boeynaems J. M. Heterogeneity of ATP receptors in aortic endothelial cells. Involvement of P2y and P2u receptors in inositol phosphate response. Circ Res. 1993 Mar;72(3):504–510. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.3.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E., Dainty I. A., Leff P. Further subclassification of ATP receptors based on agonist studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Burnstock G. Actions mediated by P2-purinoceptor subtypes in the isolated perfused mesenteric bed of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):637–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Burnstock G. Effects of purines and pyrimidines on the rat mesenteric arterial bed. Circ Res. 1991 Dec;69(6):1583–1590. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.6.1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Burnstock G. Roles of P2-purinoceptors in the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 1991 Jul;84(1):1–14. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Hoyle C. H., Burnstock G. Pivotal role of phosphate chain length in vasoconstrictor versus vasodilator actions of adenine dinucleotides in rat mesenteric arteries. J Physiol. 1995 Mar 15;483(Pt 3):703–713. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V. Modulation by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide of sympathetic and sensory-motor neurotransmission via P1-purinoceptors in the rat mesenteric arterial bed. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Apr;114(8):1541–1548. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb14937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubino A., Ralevic V., Burnstock G. Contribution of P1-(A2b subtype) and P2-purinoceptors to the control of vascular tone in the rat isolated mesenteric arterial bed. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;115(4):648–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb14981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. F., McKechnie K., Dainty I. A., Boarder M. R. P2Y purinoceptor and nucleotide receptor-induced relaxation of precontracted bovine aortic collateral artery rings: differential sensitivity to suramin and indomethacin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Feb;268(2):881–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windscheif U., Ralevic V., Bäumert H. G., Mutschler E., Lambrecht G., Burnstock G. Vasoconstrictor and vasodilator responses to various agonists in the rat perfused mesenteric arterial bed: selective inhibition by PPADS of contractions mediated via P2x-purinoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;113(3):1015–1021. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziganshin A. U., Hoyle C. H., Lambrecht G., Mutschler E., Bümert H. G., Burnstock G. Selective antagonism by PPADS at P2X-purinoceptors in rabbit isolated blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;111(3):923–929. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14827.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


