Abstract
1. The abilities of the four diastereoisomers of 1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (ACPD) to stimulate, and the metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) antagonist (+/-)-alpha-methylcarboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) to inhibit, phosphoinositide turnover in neonatal rat cerebral cortex have been studied. Two indices of phosphoinositide cycle activity were assessed; inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) mass accumulation, and total inositol phosphate [3H]-InsPx accumulation (in the presence of Li+) in myo-[3H]-inositol prelabelled slices. 2. The diastereoisomers of ACPD stimulated each response with a rank order of potency of 1S, 3R > 1R, 3R > 1S, 3S >> 1R, 3S. The response to 1R, 3R-ACPD was largely prevented by pre-addition of the NMDA-receptor antagonist, MK-801, or omission of extracellular Ca2+, suggesting that this isomer acts indirectly on phosphoinositide responses through activation of NMDA-type ionotropic glutamate receptors. In contrast, the responses to 1S, 3R- and 1S, 3S-ACPD were unaffected by prior addition of MK-801, but were blocked by MCPG. 3. The concentration of 1S, 3R-ACPD required to half-maximally stimulate the Ins(1,4,5)P3 response (-log EC50 (M), -4.09 +/- 0.10) was significantly higher than that required to exert a similar effect on [3H]-InsPx accumulation (-log EC50 (M), -4.87 +/- 0.07; P < 0.01; n = 4). A similar marked 8-9 fold discrepancy between these two values was observed for the 1S, 3S isomer, which elicited similar maximal responses to those caused by 1S, 3R-ACPD. 4. Significant differences were also observed with respect to the ability of (+/-)-MCPG (1 mM) to cause a rightward shift in the concentration-response relationships for 1S, 3R-ACPD-stimulated Ins(1,4,5)P3 (5.59 +/- 0.24 fold shift) and [3H]-InsPx (3.04 +/- 0.34 fold shift; P < 0.01; n = 4) responses, giving rise to Kd values of 218 and 490 microM for (+/-)-MCPG antagonism of the respective responses. 5. The potency difference between the 1S, 3R-ACPD-stimulated Ins(1,4,5)P3 and [3H]-InsPx responses was reduced when experiments were performed in nominally calcium-free medium ([Ca2+]e = 2 - 5 microM) and EC50 values were almost identical when extracellular calcium was reduced further by EGTA addition ([Ca2+]e < or = 100 nM). Similarly, the Kd value for (+/-)-MCPG antagonism of the 1S, 3R-ACPD-stimulated [3H]-InsPx response decreased under [Ca2+]e-free conditions, approaching those obtained for the 1S, 3R-ACPD-stimulated Ins(1,4,5)P3 response in the presence of normal [Ca2+]e. 6. These data suggest that estimates of the activities of mGluR agonists and antagonists, derived by measuring phosphoinositide turnover, can differ significantly depending on whether Ins(1,4,5)P3 mass or [3H]-InsPx responses are measured. In particular, the possibility that the mGluR-mediated [3H]-InsPx response may not simply reflect direct receptor/G protein/phosphoinositidase C (PIC) activation, but may also be the consequence of stimulation of a facilitatory Ca2+-influx pathway is discussed.
Full text
PDF

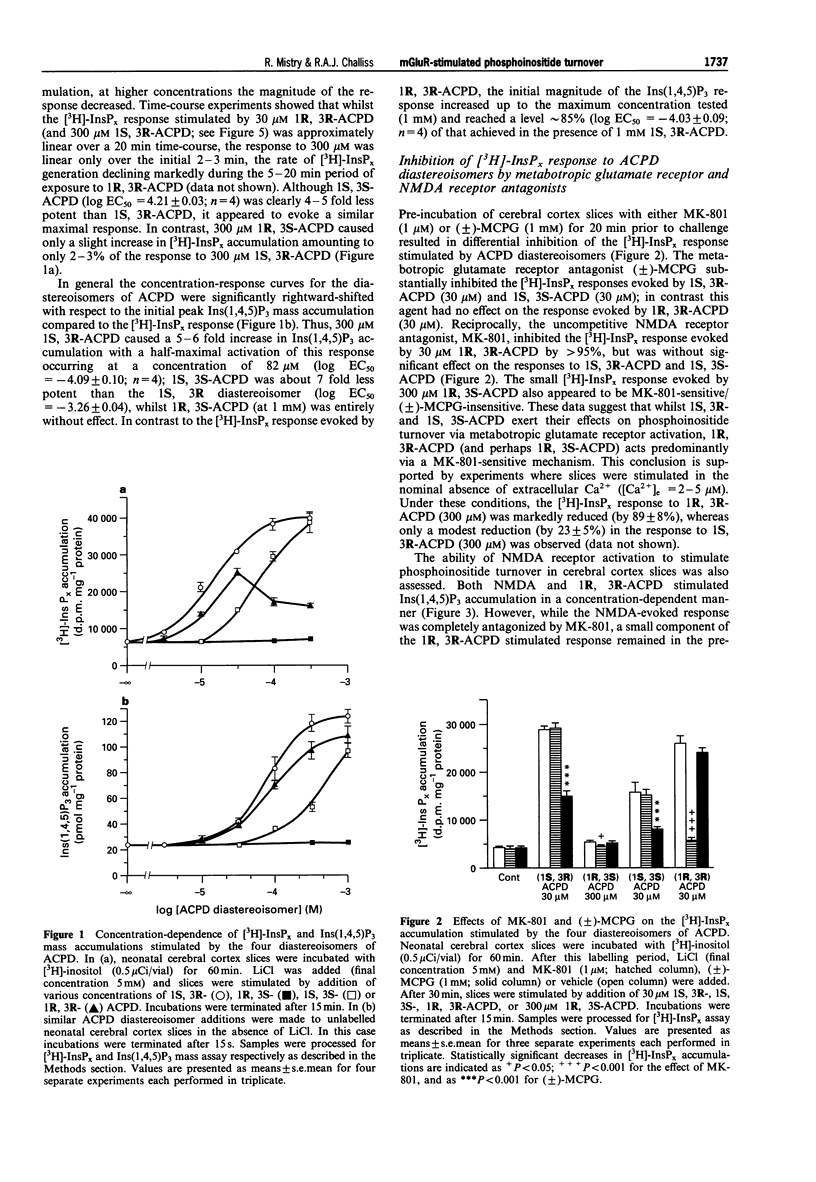
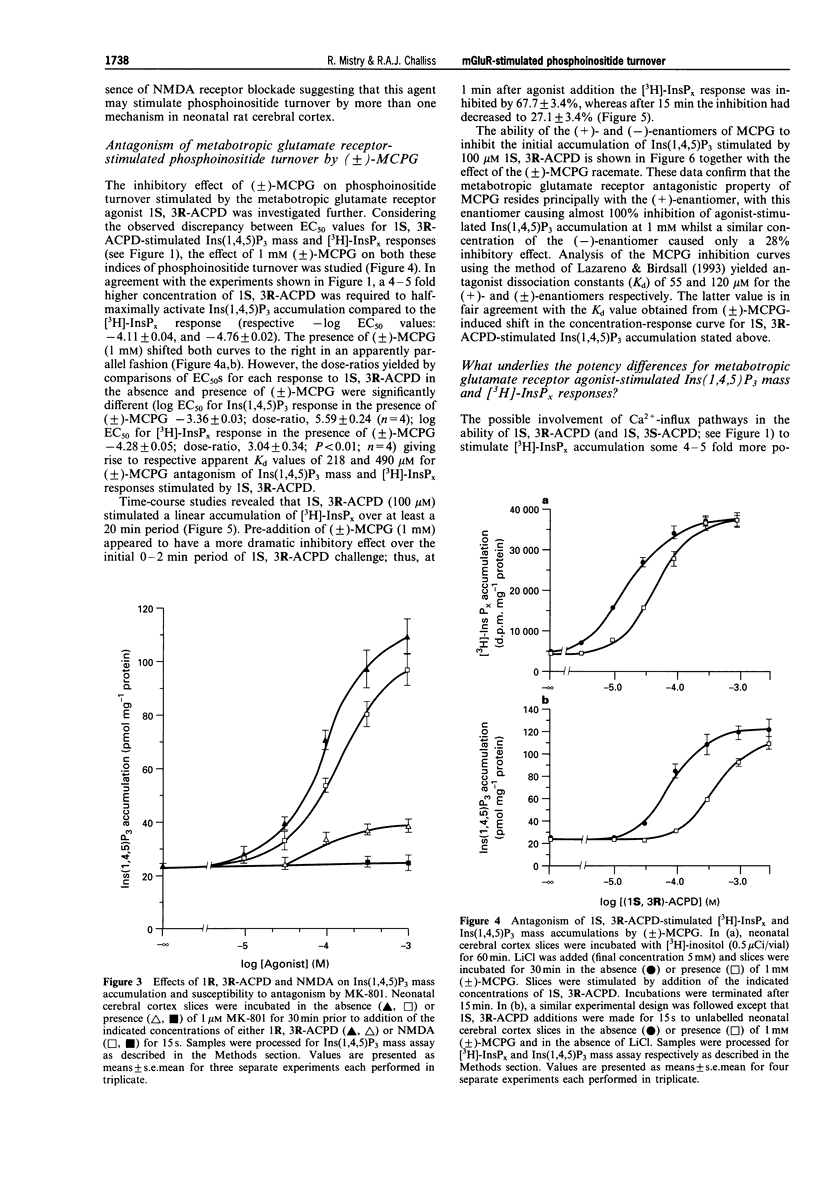
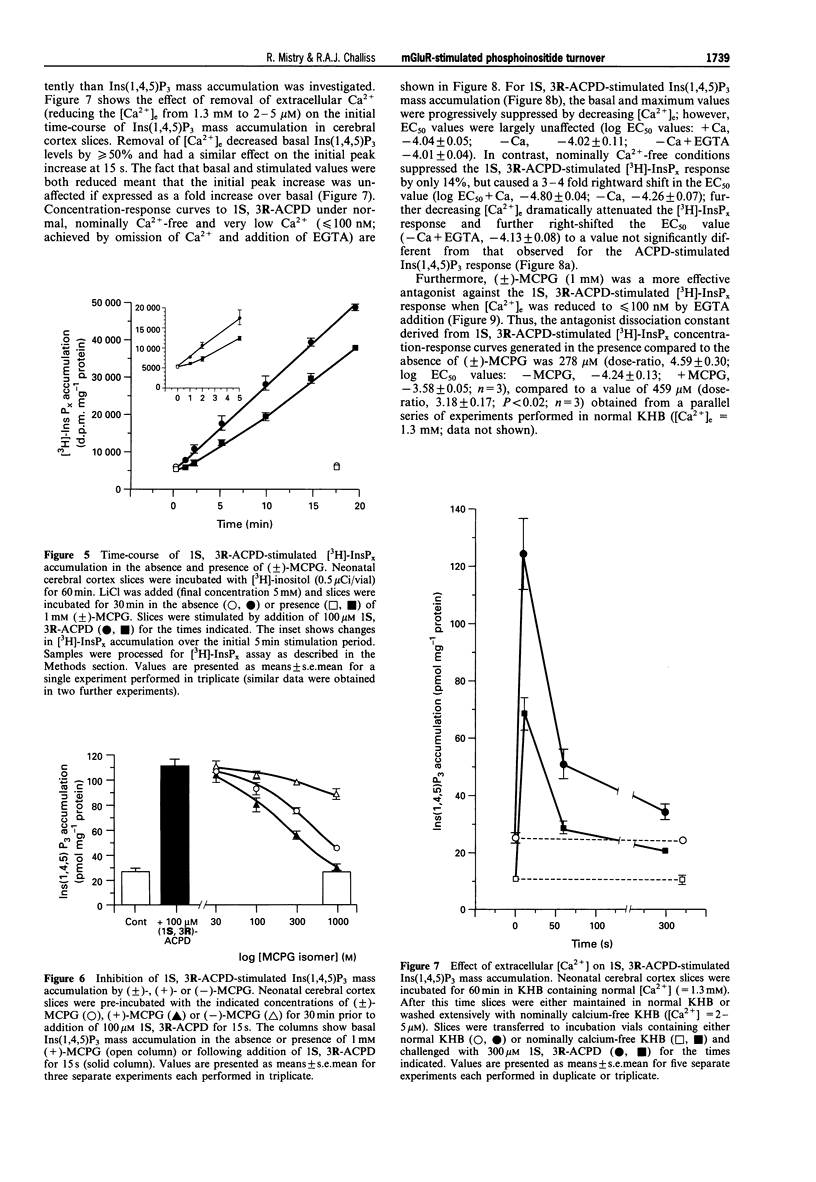
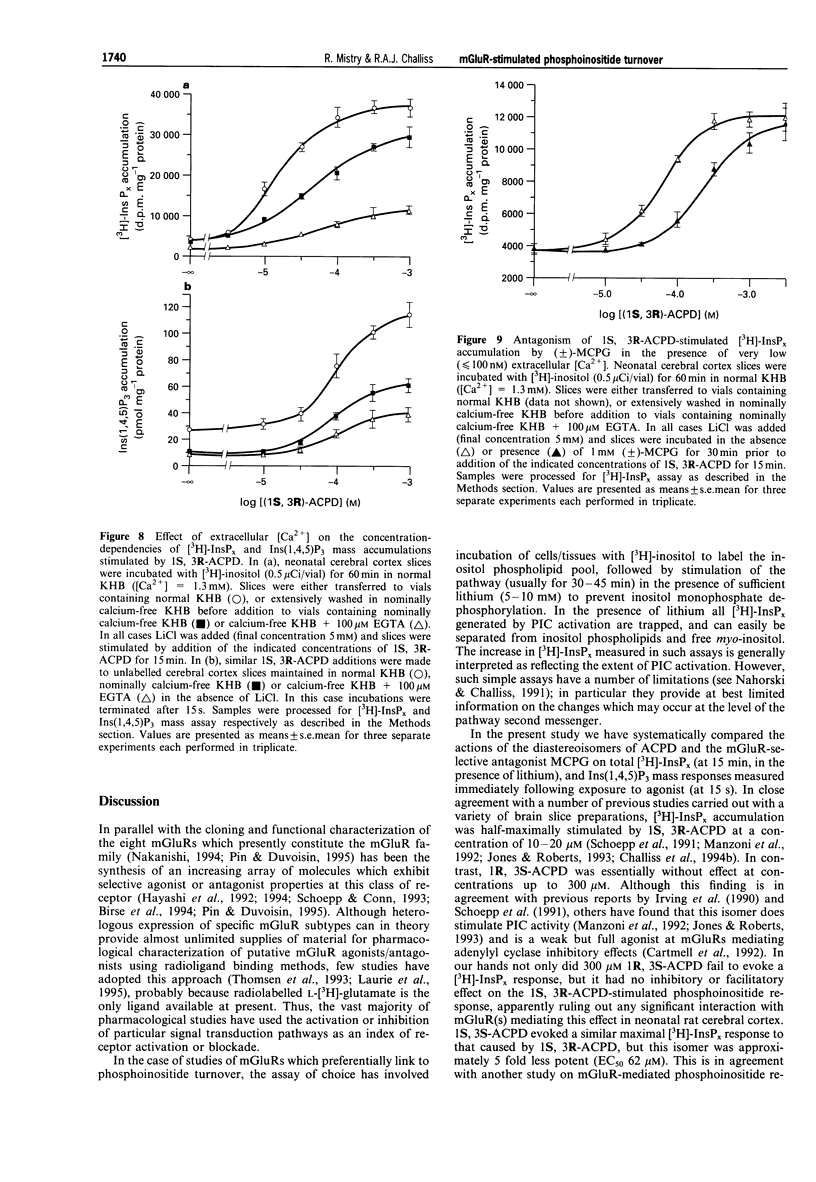



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Sugihara H., Nawa H., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13361–13368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramori I., Nakanishi S. Signal transduction and pharmacological characteristics of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR1, in transfected CHO cells. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90096-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birse E. F., Eaton S. A., Jane D. E., Jones P. L., Porter R. H., Pook P. C., Sunter D. C., Udvarhelyi P. M., Wharton B., Roberts P. J. Phenylglycine derivatives as new pharmacological tools for investigating the role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1993 Feb;52(3):481–488. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90400-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartmell J., Kemp J. A., Alexander S. P., Hill S. J., Kendall D. A. Inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP formation by 1-aminocyclopentane-trans-1,3-dicarboxylate in guinea-pig cerebral cortical slices. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1964–1966. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challis R. A., Mistry R., Gray D. W., Nahorski S. R. Modulation of muscarinic cholinoceptor-stimulated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate accumulation by N-methyl-D-aspartate in neonatal rat cerebral cortex. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Jan;33(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Mistry R., Gray D. W., Nahorski S. R. Modulatory effects of NMDA on phosphoinositide responses evoked by the metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist 1S,3R-ACPD in neonatal rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):231–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Nahorski S. R. Depolarization and agonist-stimulated changes in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate mass accumulation in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):1042–1051. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavis P., Nooney J. M., Bockaert J., Fagni L., Feltz A., Bossu J. L. Facilitatory coupling between a glutamate metabotropic receptor and dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in cultured cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci. 1995 Jan;15(1 Pt 1):135–143. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00135.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Murawsky M. M., Stauderman K. A. Histamine-induced Ca2+ entry precedes Ca2+ mobilization in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1994 Dec 1;304(Pt 2):469–476. doi: 10.1042/bj3040469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry K., Peet M. J., Magnuson D. S., McLennan H. Synthesis, resolution, and absolute configuration of the isomers of the neuronal excitant 1-amino-1,3-cyclopentanedicarboxylic acid. J Med Chem. 1988 Apr;31(4):864–867. doi: 10.1021/jm00399a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D. A., Holz R. W. Intracellular Ca2+ activates phospholipase C. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Dec;11(12):517–520. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene C. C., Schwindt P. C., Crill W. E. Properties and ionic mechanisms of a metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated slow afterdepolarization in neocortical neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Aug;72(2):693–704. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.2.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guérineau N. C., Gähwiler B. H., Gerber U. Reduction of resting K+ current by metabotropic glutamate and muscarinic receptors in rat CA3 cells: mediation by G-proteins. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 1;474(1):27–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp019999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Sekiyama N., Nakanishi S., Jane D. E., Sunter D. C., Birse E. F., Udvarhelyi P. M., Watkins J. C. Analysis of agonist and antagonist activities of phenylglycine derivatives for different cloned metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 2):3370–3377. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-03370.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Tanabe Y., Aramori I., Masu M., Shimamoto K., Ohfune Y., Nakanishi S. Agonist analysis of 2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine isomers for cloned metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R., Lovinger D. M., McCool B. A., Lewis D. L. Heterologous expression of metabotropic glutamate receptors in adult rat sympathetic neurons: subtype-specific coupling to ion channels. Neuron. 1995 May;14(5):1029–1038. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving A. J., Schofield J. G., Watkins J. C., Sunter D. C., Collingridge G. L. 1S,3R-ACPD stimulates and L-AP3 blocks Ca2+ mobilization in rat cerebellar neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 21;186(2-3):363–365. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90462-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly C., Gomeza J., Brabet I., Curry K., Bockaert J., Pin J. P. Molecular, functional, and pharmacological characterization of the metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 splice variants: comparison with mGluR1. J Neurosci. 1995 May;15(5 Pt 2):3970–3981. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-05-03970.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp M., Roberts P., Pook P., Jane D., Jones A., Jones P., Sunter D., Udvarhelyi P., Watkins J. Antagonism of presynaptically mediated depressant responses and cyclic AMP-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 15;266(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. J., Danzeisen M., Boddeke H. W., Sommer B. Ligand binding profile of the rat metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR3 expressed in a transfected cell line. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995 May;351(5):565–568. doi: 10.1007/BF00171050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazareno S., Birdsall N. J. Estimation of competitive antagonist affinity from functional inhibition curves using the Gaddum, Schild and Cheng-Prusoff equations. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1110–1119. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman L., Glatt B. S., Robinson M. B. Multiple subtypes of excitatory amino acid receptors coupled to the hydrolysis of phosphoinositides in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1993 Aug;61(2):586–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb02162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni O., Prezeau L., Rassendren F. A., Sladeczek F., Curry K., Bockaert J. Both enantiomers of 1-aminocyclopentyl-1,3-dicarboxylate are full agonists of metabotropic glutamate receptors coupled to phospholipase C. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;42(2):322–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: synaptic transmission, modulation, and plasticity. Neuron. 1994 Nov;13(5):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Meek J. L., Iadarola M. J., Chuang D. M., Roth B. L., Costa E. Coupling of inositol phospholipid metabolism with excitatory amino acid recognition sites in rat hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):40–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering D. S., Thomsen C., Suzdak P. D., Fletcher E. J., Robitaille R., Salter M. W., MacDonald J. F., Huang X. P., Hampson D. R. A comparison of two alternatively spliced forms of a metabotropic glutamate receptor coupled to phosphoinositide turnover. J Neurochem. 1993 Jul;61(1):85–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pin J. P., Duvoisin R. The metabotropic glutamate receptors: structure and functions. Neuropharmacology. 1995 Jan;34(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)00129-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prézeau L., Carrette J., Helpap B., Curry K., Pin J. P., Bockaert J. Pharmacological characterization of metabotropic glutamate receptors in several types of brain cells in primary cultures. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):570–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi M. R., Ikonomovic S., Wroblewski J. T., Grayson D. R. Temporal and depolarization-induced changes in the absolute amounts of mRNAs encoding metabotropic glutamate receptors in cerebellar granule neurons in vitro. J Neurochem. 1994 Oct;63(4):1207–1217. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63041207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saugstad J. A., Segerson T. P., Westbrook G. L. L-2-amino-3-phosphonopropionic acid competitively antagonizes metabotropic glutamate receptors 1 alpha and 5 in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Apr 28;289(2):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D., Conn P. J. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in brain function and pathology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jan;14(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90107-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D., Johnson B. G., True R. A., Monn J. A. Comparison of (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (1S,3R-ACPD)- and 1R,3S-ACPD-stimulated brain phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 14;207(4):351–353. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90010-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. B., Challiss R. A., Nahorski S. R. Neuronal Ca2+ stores: activation and function. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Jul;18(7):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)93919-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Pin J. P., Récasens M., Bockaert J., Weiss S. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):717–719. doi: 10.1038/317717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa C. M., Standaert D. G., Young A. B., Penney J. B., Jr Metabotropic glutamate receptor mRNA expression in the basal ganglia of the rat. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 2):3005–3018. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-03005.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen C., Mulvihill E. R., Haldeman B., Pickering D. S., Hampson D. R., Suzdak P. D. A pharmacological characterization of the mGluR1 alpha subtype of the metabotropic glutamate receptor expressed in a cloned baby hamster kidney cell line. Brain Res. 1993 Aug 13;619(1-2):22–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91592-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willars G. B., Nahorski S. R. Quantitative comparisons of muscarinic and bradykinin receptor-mediated Ins (1,4,5)P3 accumulation and Ca2+ signalling in human neuroblastoma cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;114(6):1133–1142. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcikiewicz R. J., Tobin A. B., Nahorski S. R. Muscarinic receptor-mediated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells is regulated acutely by cytosolic Ca2+ and by rapid desensitization. J Neurochem. 1994 Jul;63(1):177–185. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63010177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng F., Gallagher J. P. Burst firing of rat septal neurons induced by 1S,3R-ACPD requires influx of extracellular calcium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 11;211(2):281–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90542-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Río E., Nicholls D. G., Downes C. P. Involvement of calcium influx in muscarinic cholinergic regulation of phospholipase C in cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 1994 Aug;63(2):535–543. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63020535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



