Abstract
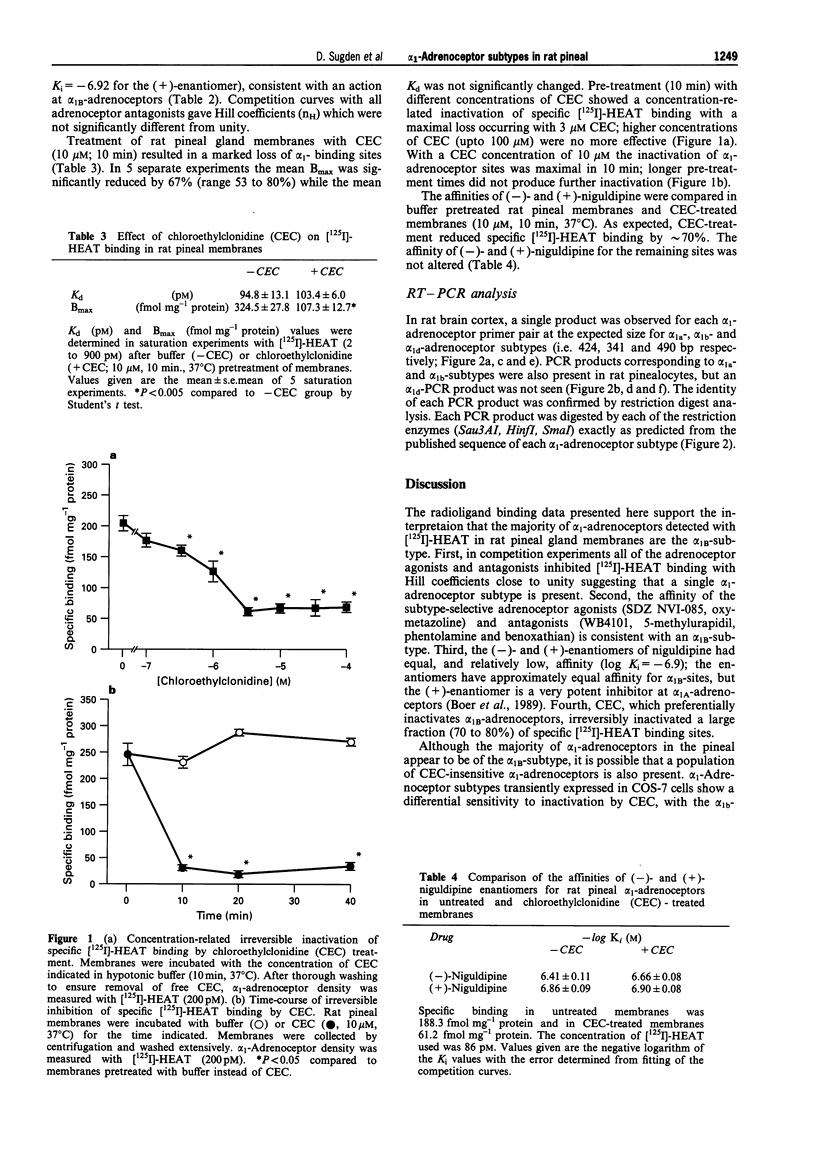
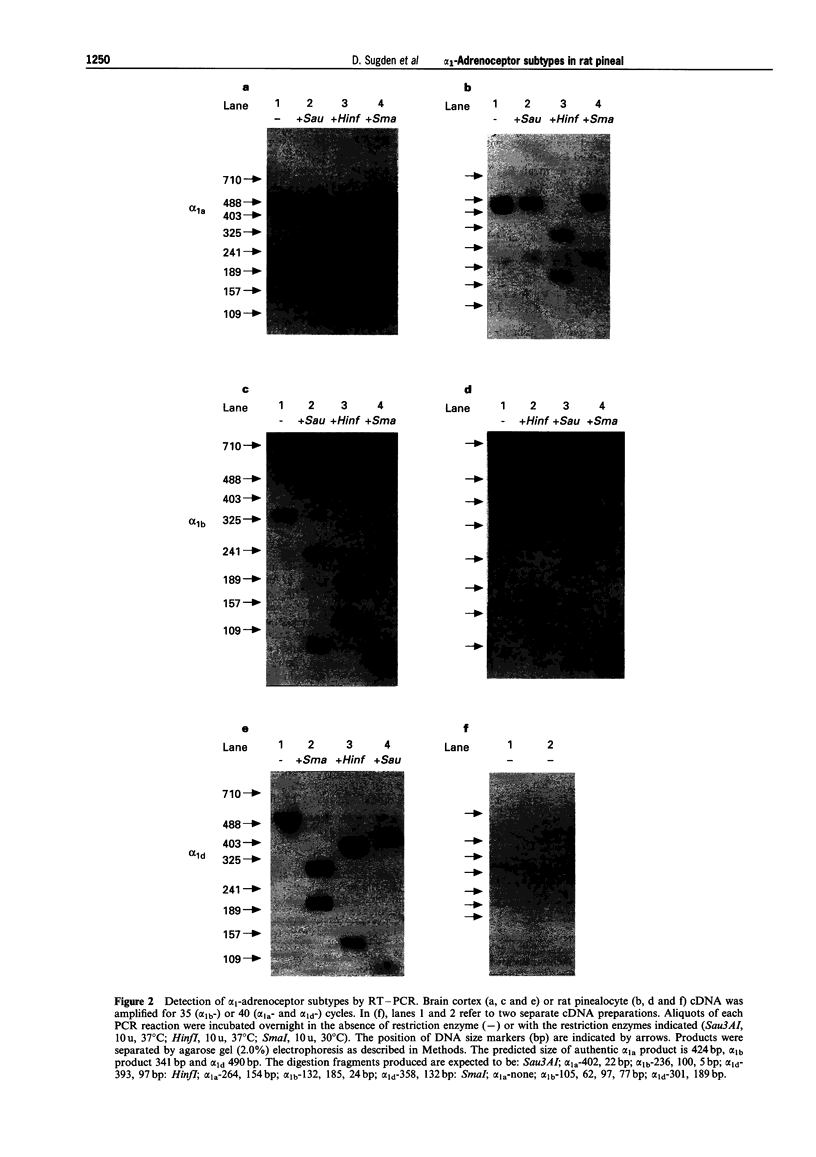
1. The pharmacological characteristics of alpha 1-adrenoceptor binding sites in rat pineal gland membranes, detected by use of a selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist ([125I]-iodo-2-[beta-(4-hydroxyphenyl) ethylaminomethyl]tetralone, [125I]-HEAT), were investigated with the alkylating agent, chloroethylclonidine (CEC), and in competition experiments with a number of adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists. 2. Chloroethylclonidine (CEC) treatment (10 microM, 10 min) of rat pineal membranes inactivated approximately 70% of specific [125I]-HEAT binding sites. Higher concentrations of CEC (up to 100 microM) or longer treatment periods (up to 40 min) were no more effective. 3. Adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists competitively inhibited [125I]-HEAT binding with Hill coefficients close to unity indicating a single alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype is present. The affinity (Ki) of subtype selective agonists (oxymetazoline, SDZ NVI-085) and antagonists (5-methylurapidil, WB4101, benoxathian, phentolamine) was consistent with binding to an alpha 1B-adrenoceptor subtype. 4. The (-)- and (+)-enantiomers of niguldipine had an equal and low affinity for alpha 1-adrenoceptor binding sites both in untreated (log Ki-6.66 and -6.90 respectively) and CEC-treated membranes in which approximately 70% of sites had been inactivated (log Ki-6.41 and -6.86 respectively). This indicates that the small proportion of alpha 1-adrenoceptors insensitive to CEC are not alpha 1A-adrenoceptors. 5. mRNA was isolated from rat pinealocytes, cDNA was synthesized and then amplified by the polymerase chain reaction with alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype specific primers. These experiments identified both alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptor mRNA, but not alpha 1D-mRNA in rat pinealocytes, although all three adrenoceptor subtypes were readily identified in rat brain cortex. 6. These data indicate that although both alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptor mRNAs are present in the pineal the major subtype of alpha 1-adrenoceptor expressed is the alpha 1B.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boer R., Grassegger A., Schudt C., Glossmann H. (+)-Niguldipine binds with very high affinity to Ca2+ channels and to a subtype of alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 11;172(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buda M., Klein D. C. A suspension culture of pinealocytes: regulation of N-acetyltransferase activity. Endocrinology. 1978 Oct;103(4):1483–1493. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-4-1483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Eikenberg D. C., Hieble J. P., Langer S. Z., Lefkowitz R. J., Minneman K. P., Molinoff P. B., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Trendelenburg U. International Union of Pharmacology nomenclature of adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):121–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Williams T. J., Blue D. R., Clarke D. E. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification: sharpening Occam's razor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jun;15(6):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A. Alpha 1-adrenergic action: receptor subtypes, signal transduction and regulation. Cell Signal. 1993 Sep;5(5):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(93)90049-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Heterogeneity of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors revealed by chlorethylclonidine. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;32(4):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. K., Chik C. L., Klein D. C. Permissive role of calcium in alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of pineal phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase (phospholipase C) activity. J Pineal Res. 1988;5(6):553–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079x.1988.tb00798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein D. C., Sugden D., Weller J. L. Postsynaptic alpha-adrenergic receptors potentiate the beta-adrenergic stimulation of pineal serotonin N-acetyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klijn K., Slivka S. R., Bell K., Insel P. A. Renal alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes: MDCK-D1 cells, but not rat cortical membranes possess a single population of receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;39(3):407–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano R., Iwanaga T., Nakajima T., Masuda T., Takahashi Y. Immunocytochemical demonstration of hydroxyindole O-methyltransferase (HIOMT), neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and S-100 protein in the bovine pineal gland. Brain Res. 1983 Sep 5;274(1):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90535-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laz T. M., Forray C., Smith K. E., Bard J. A., Vaysse P. J., Branchek T. A., Weinshank R. L. The rat homologue of the bovine alpha 1c-adrenergic receptor shows the pharmacological properties of the classical alpha 1A subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):414–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes, inositol phosphates, and sources of cell Ca2+. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Jun;40(2):87–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Esbenshade T. A. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1994;34:117–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.34.040194.001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Han C., Abel P. W. Comparison of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes distinguished by chlorethylclonidine and WB 4101. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Theroux T. L., Hollinger S., Han C., Esbenshade T. A. Selectivity of agonists for cloned alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;46(5):929–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Malik N., Gaivin R., Graham R. M. Cloning, expression, and tissue distribution of the rat homolog of the bovine alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor provide evidence for its classification as the alpha 1A subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;46(5):823–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud A., Nishino S., Dement W. C., Guilleminault C., Mignot E. Effects of SDZ NVI-085, a putative subtype-selective alpha 1-agonist, on canine cataplexy, a disorder of rapid eye movement sleep. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov 19;205(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90763-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. P., Kendall D. A. Niguldipine discriminates between alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated second messenger responses in rat cerebral cortex slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 May;100(1):3–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Nichols A. J., Stadel J. M., Hieble J. P. Structure and function of alpha-adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Dec;43(4):475–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad N. C., Parfitt A., Russell J. T., Schaffner A. E., Korf H. W., Klein D. C. Single-cell [Ca2+]i analysis and biochemical characterization of pinealocytes immobilized with novel attachment peptide preparation. Brain Res. 1993 Jun 18;614(1-2):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91042-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Szklut P. J., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W. Pharmacologic characterization of cloned alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes: selective antagonists suggest the existence of a fourth subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 1;227(4):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90162-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. L., Eichberg J., Hauser G. Postsynaptic localization of the alpha receptor-mediated stimulation of phosphatidylinositol turnover in pineal gland. Life Sci. 1979 Jun 4;24(23):2179–2184. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. F., Rokosh D. G., Bailey B. A., Karns L. R., Chang K. C., Long C. S., Kariya K., Simpson P. C. Cloning of the rat alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor from cardiac myocytes. alpha 1C, alpha 1B, and alpha 1D mRNAs are present in cardiac myocytes but not in cardiac fibroblasts. Circ Res. 1994 Oct;75(4):796–802. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.4.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden A. L., Sugden D., Klein D. C. Essential role of calcium influx in the adrenergic regulation of cAMP and cGMP in rat pinealocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11608–11612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden D., Klein D. C. Development of the rat pineal alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Brain Res. 1985 Jan 28;325(1-2):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden D., Klein D. C. Rat pineal alpha 1-adrenoceptors: identification and characterization using [125I]iodo-2-[beta-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-ethylaminomethyl]tetralone. Endocrinology. 1984 Feb;114(2):435–440. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-2-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden D., Klein D. C. Regulation of rat pineal alpha 1-adrenoceptors. J Neurochem. 1985 Jan;44(1):63–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden D. Melatonin biosynthesis in the mammalian pineal gland. Experientia. 1989 Oct 15;45(10):922–932. doi: 10.1007/BF01953049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden D., Vanecek J., Klein D. C., Thomas T. P., Anderson W. B. Activation of protein kinase C potentiates isoprenaline-induced cyclic AMP accumulation in rat pinealocytes. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):359–361. doi: 10.1038/314359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden L. A., Sugden D., Klein D. C. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor activation elevates cytosolic calcium in rat pinealocytes by increasing net influx. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):741–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanecek J., Sugden D., Weller J., Klein D. C. Atypical synergistic alpha 1- and beta-adrenergic regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in rat pinealocytes. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2167–2173. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt M. M., Kispert J., Chin H. M. Sequence of a rat brain cDNA encoding an alpha-1B adrenergic receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1053–1053. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicht H., Korf H. W., Schaad N. C. Morphological and immunocytochemical heterogeneity of cultured pinealocytes from one-week- and two-month-old rats: planimetric and densitometric investigations. J Pineal Res. 1993 Apr;14(3):128–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079x.1993.tb00495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. M., Minneman K. P. Different pathways of [3H]inositol phosphate formation mediated by alpha 1a- and alpha 1b-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17601–17606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]