Abstract
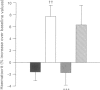
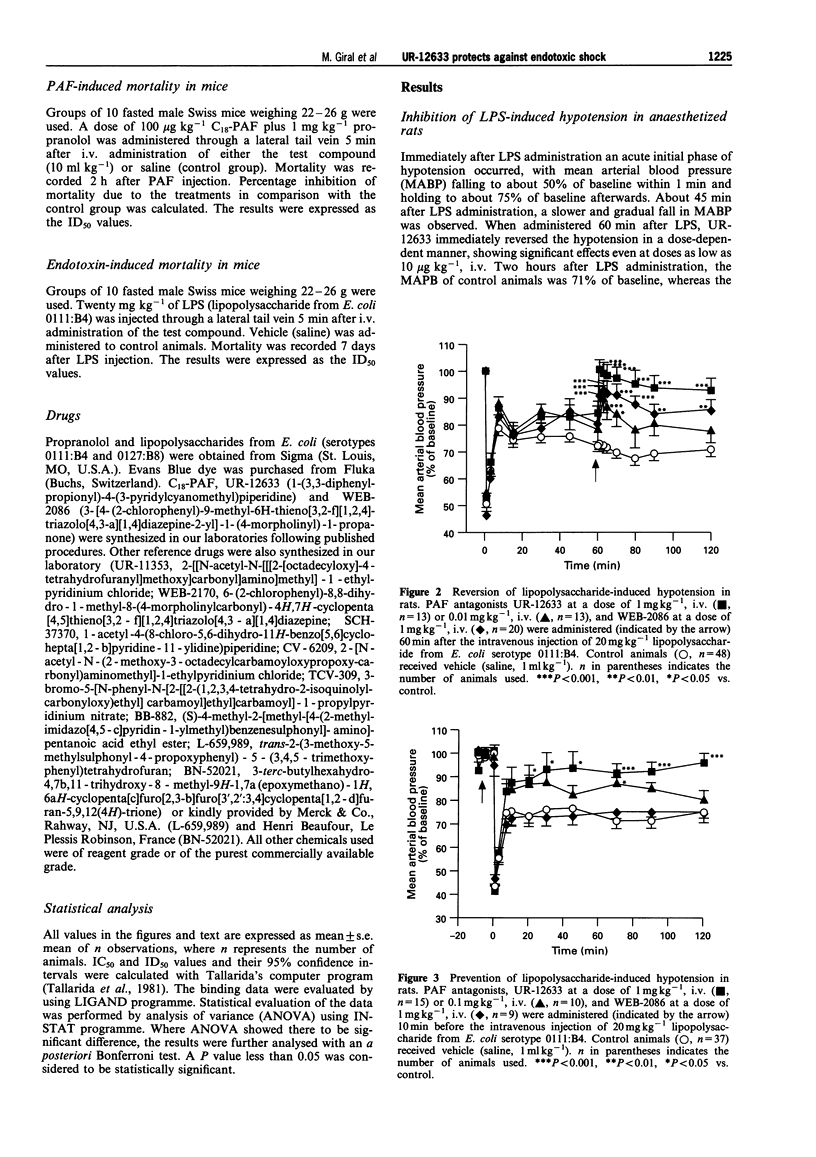
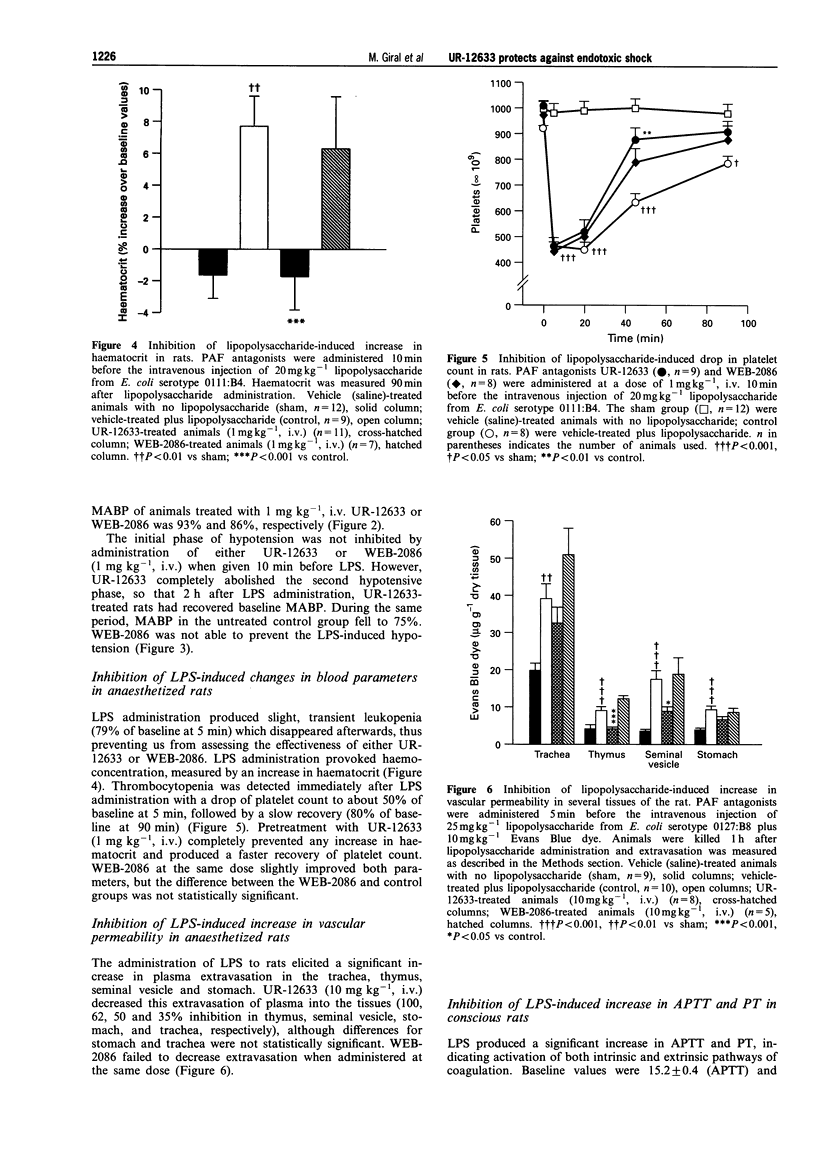
1. The effects of the selective and potent novel platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonist, UR-12633 (1-(3,3-diphenylpropionyl)-4-(3-pyridylcyanomethyl)piperidin e) on several markers of endotoxic shock syndrome were evaluated in rats and mice. 2. UR-12633, administered 60 min after E. coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS), reversed the LPS-induced sustained hypotension in rats at doses of 0.01 to 1 mg kg-1, i.v. The reference compound WEB-2086 (1 mg kg-1) also reversed the LPS-induced hypotension. UR-12633 (1 mg kg-1), administered 10 min before LPS, almost fully inhibited sustained hypotension. The immediate hypotension (within 1 min) caused by LPS was not prevented by either UR-12633 or WEB-2086. 3. Pretreatment with 10 mg kg-1, i.v. of either UR-12633 or WEB-2086 inhibited the increase in disseminated intravascular coagulation markers, such as activated partial thromboplastin time (55 and 74% inhibition, respectively), and prothrombin time (22 and 72% inhibition) and prevented the decrease in plasma fibrinogen content (100 and 29% inhibition). 4. Increases in acid phosphatase (ACP) plasma activity, a marker of lysosomal activation, and in lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a marker of tissue damage, were inhibited by pretreatment with 10 mg kg-1, i.v. of either UR-12633 or WEB-2086 (100% and 69% inhibition, ACP; 62 and 48% inhibition, LDH). Hyperglycaemia (71 and 46%) and hyperlactacidaemia (92 and 56%) were also inhibited. 5. UR-12633, but not WEB-2086, inhibited the LPS-induced increase in vascular permeability in rats, as shown by prevention of haemoconcentration and, to a lesser degree, the increase in Evans blue dye extravasation. 6. In a series of nine reference compounds and UR-12633, we found a high correlation (P < 0.001) between PAF antagonist activity, measured as the inhibition of PAF-induced rabbit platelet aggregation or PAF-induced mortality in mice and the inhibition of LPS-induced mortality. 7. In spite of the multifactorial nature of endotoxic shock, in which many mediators may be involved, the new potent PAF antagonist, UR-12633, proved effective in protecting against changes in most shock markers. These data strongly suggest a key role for PAF in the pathogenesis of endotoxic shock in rodents.
Full text
PDF
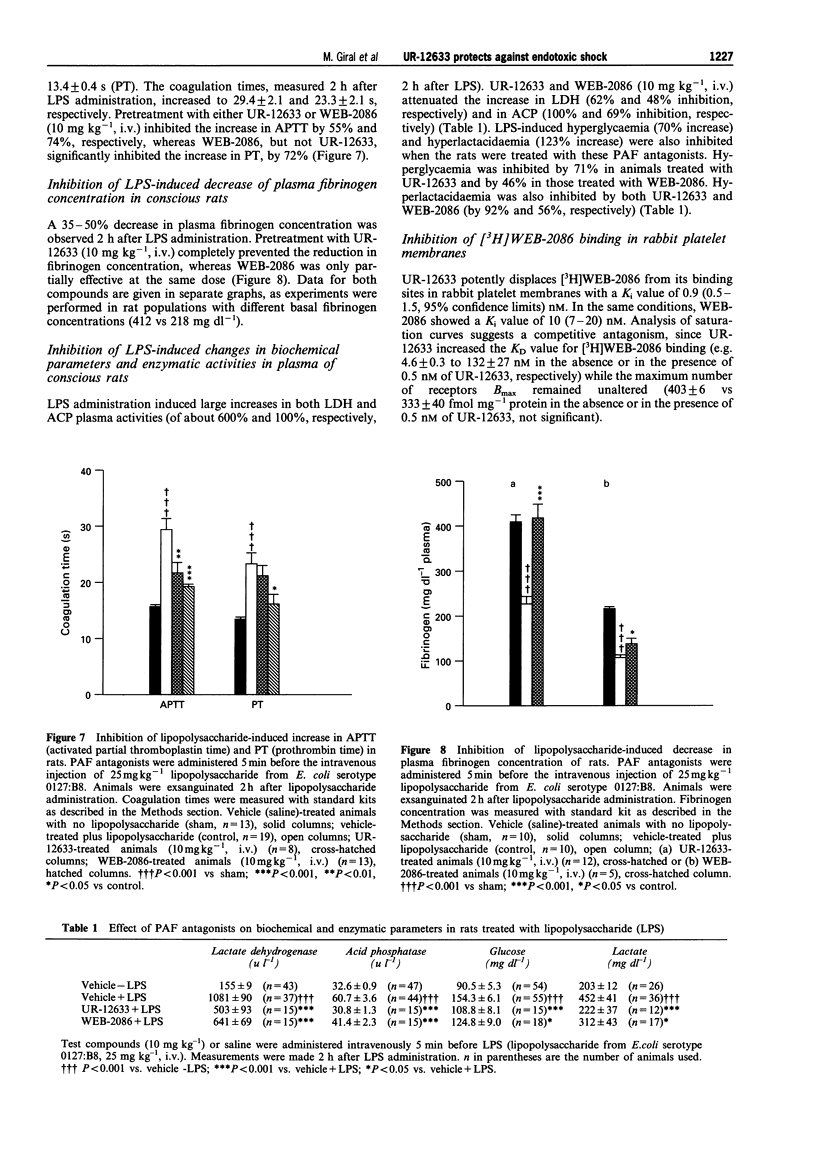



Images in this article
Selected References
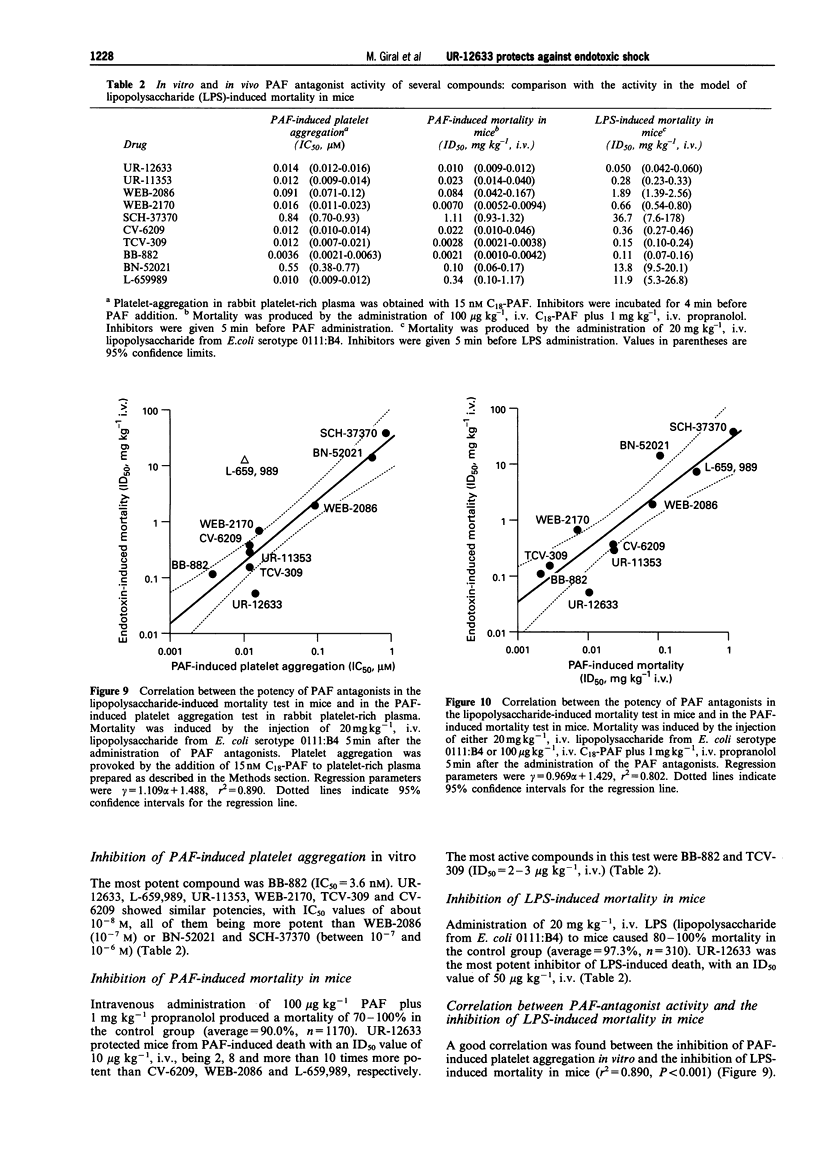
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecht H. M., Adamus W. S., Heuer H. O., Birke F. W., Kempe E. R. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and safety profile of the new platelet-activating factor antagonist apafant in man. Arzneimittelforschung. 1991 Jan;41(1):51–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. W., Feddersen C. O., Henson P. M., Voelkel N. F. Platelet-activating factor mediates hemodynamic changes and lung injury in endotoxin-treated rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1498–1509. doi: 10.1172/JCI112980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner R. L., Elin R. J., Hosseini J. M., Wesley R. A., Reilly J. M., Parillo J. E. Endotoxemia in human septic shock. Chest. 1991 Jan;99(1):169–175. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.1.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doebber T. W., Wu M. S., Robbins J. C., Choy B. M., Chang M. N., Shen T. Y. Platelet activating factor (PAF) involvement in endotoxin-induced hypotension in rats. Studies with PAF-receptor antagonist kadsurenone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 29;127(3):799–808. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., Kluft C. PAF-acether-induced release of tissue-type plasminogen activator from vessel walls. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):86–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T. W., Dent G., Rogers D. F., Aursudkij B., Chung K. F., Barnes P. J. Effect of a Paf antagonist, WEB 2086, on airway microvascular leakage in the guinea-pig and platelet aggregation in man. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 May;94(1):164–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming I., Dambacher T., Busse R. Endothelium-derived kinins account for the immediate response of endothelial cells to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992;20 (Suppl 12):S135–S138. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199204002-00038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Reidy M. A., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., Striker G. E. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated bovine endothelial cell injury in vitro. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosford D. J., Domingo M. T., Chabrier P. E., Braquet P. Ginkgolides and platelet-activating factor binding sites. Methods Enzymol. 1990;187:433–446. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)87050-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. C. Reappraisal of the role of endotoxin in the sepsis syndrome. Lancet. 1993 May 1;341(8853):1133–1135. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)93139-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami K., Meade C. J., Heuer H. O., Birke F. Hetrazepine PAF antagonists. J Lipid Mediat. 1992 Jun-Jul;5(2):177–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imura Y., Terashita Z., Nishikawa K. Possible role of platelet activating factor (PAF) in disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), evidenced by use of a PAF antagonist, CV-3988. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 14;39(2):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñarrea P., Gomez-Cambronero J., Nieto M., Crespo M. S. Characteristics of the binding of platelet-activating factor to platelets of different animal species. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 15;105(3-4):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90623-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katori M., Majima M., Odoi-Adome R., Sunahara N., Uchida Y. Evidence for the involvement of a plasma kallikrein-kinin system in the immediate hypotension produced by endotoxin in anaesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1383–1391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12688.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura M., Terashita Z., Imura Y., Shino A., Nishikawa K. Inhibitory effect of TCV-309, a novel platelet activating factor (PAF) antagonist, on endotoxin-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation in rats: possible role of PAF in tissue factor generation. Thromb Res. 1993 May 15;70(4):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(93)90101-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltai M., Hosford D., Guinot P., Esanu A., Braquet P. PAF. A review of its effects, antagonists and possible future clinical implications (Part II). Drugs. 1991 Aug;42(2):174–204. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199142020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltai M., Hosford D., Guinot P., Esanu A., Braquet P. Platelet activating factor (PAF). A review of its effects, antagonists and possible future clinical implications (Part I). Drugs. 1991 Jul;42(1):9–29. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199142010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang C. H., Dobrescu C., Hargrove D. M., Bagby G. J., Spitzer J. J. Platelet-activating factor-induced increases in glucose kinetics. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):E193–E200. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.2.E193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B. O., Ryan U. S., Brigham K. L. Direct effects of E coli endotoxin on structure and permeability of pulmonary endothelial monolayers and the endothelial layer of intimal explants. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jan;122(1):140–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E. Pathogenetic mechanisms of septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 20;328(20):1471–1477. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305203282008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi M., Jones S. B. Contribution of platelet activating factor to hemodynamic and sympathetic responses to bacterial endotoxin in conscious rats. Circ Shock. 1990 Oct;32(2):153–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovici R., Esser K. M., Lysko P. G., Yue T. L., Griswold D. E., Hillegass L. M., Bugelski P. J., Hallenbeck J. M., Feuerstein G. Priming by platelet-activating factor of endotoxin-induced lung injury and cardiovascular shock. Circ Res. 1991 Jul;69(1):12–25. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring P. C., Seldon P. M., Barnes P. J., Giembycz M. A. Pharmacological characterization of a receptor for platelet-activating factor on guinea pig peritoneal macrophages using [3H]apafant, a selective and competitive platelet-activating factor antagonist: evidence that the noncompetitive behavior of apafant in functional studies relates to slow kinetics of dissociation. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;43(2):302–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Beijer L. Inhalation of endotoxin stimulates alveolar macrophage production of platelet-activating factor. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):83–86. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Mitchell J. A., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Nitric oxide-mediated hyporeactivity to noradrenaline precedes the induction of nitric oxide synthase in endotoxin shock. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):786–792. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Wu C. C., Mitchell J. A., Gross S. S., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Platelet-activating factor contributes to the induction of nitric oxide synthase by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Circ Res. 1993 Dec;73(6):991–999. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.6.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taveira da Silva A. M., Kaulbach H. C., Chuidian F. S., Lambert D. R., Suffredini A. F., Danner R. L. Brief report: shock and multiple-organ dysfunction after self-administration of Salmonella endotoxin. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 20;328(20):1457–1460. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305203282005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. A., Coyle S., Van Zee K., Oldenburg H., Trousdale R., Rogy M., Felsen D., Moldawer L., Lowry S. F. The metabolic effects of platelet-activating factor antagonism in endotoxemic man. Arch Surg. 1994 Jan;129(1):72–79. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420250084011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Boughton-Smith N. K., Hutcheson I. R., Esplugues J. V., Wallace J. L. Increased intestinal formation of Paf in endotoxin-induced damage in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):3–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer S. J., Büller H. R., ten Cate J. W., Aarden L. A., Hack C. E., Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic, and complement pathways. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2520–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]