Abstract
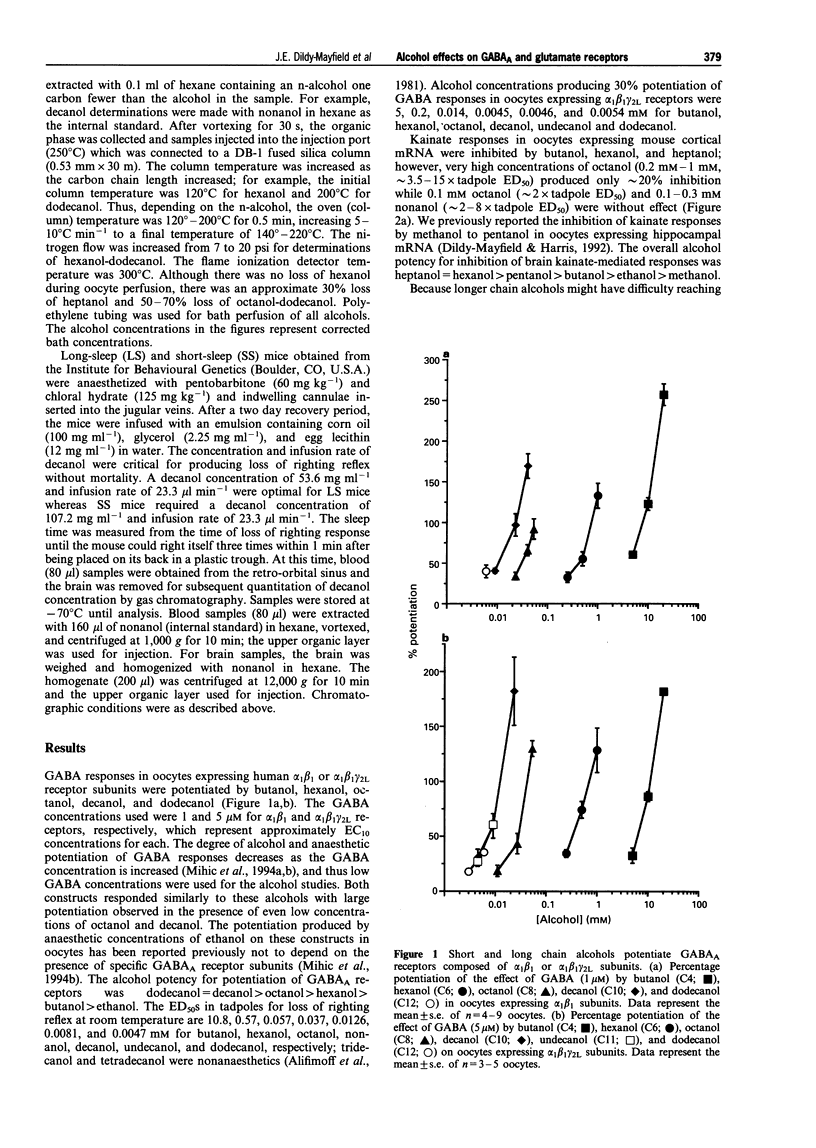
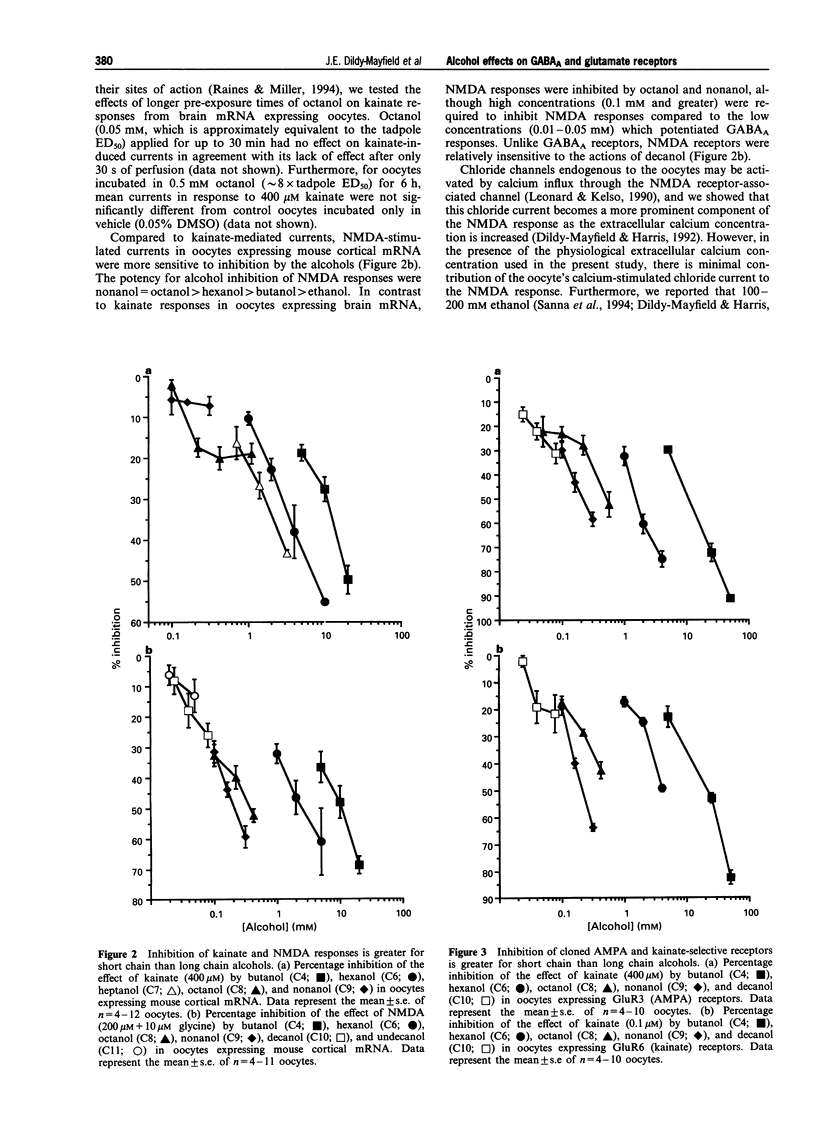
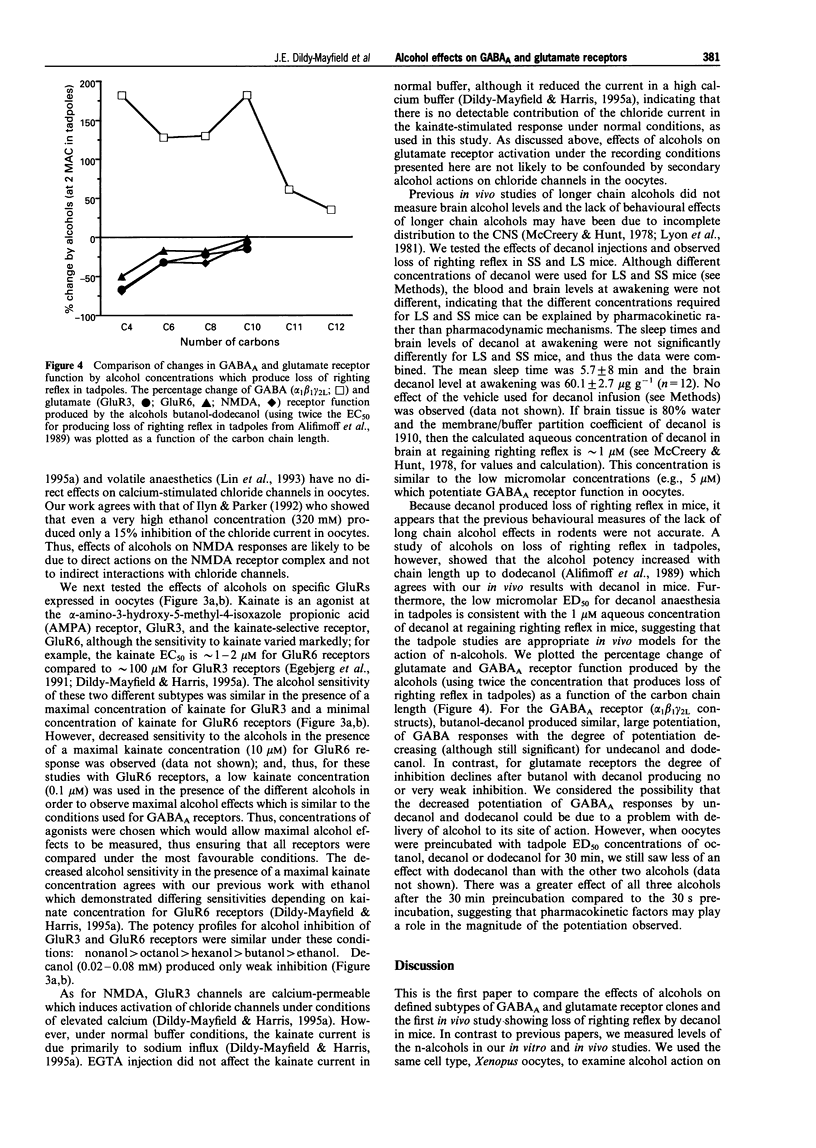
1. The effects of n-alcohols on GABAA and glutamate receptor systems were examined, and in vitro effectiveness was compared with in vivo effects in mice and tadpoles. We expressed GABAA, NMDA, AMPA, or kainate receptors in Xenopus oocytes and examined the actions of n-alcohols on receptor function using two-electrode voltage clamp recording. 2. The function of GABAA receptors composed of alpha 1 beta 1 or alpha 1 beta 1 gamma 2L subunits was potentiated by all of the n-alcohols studied (butanol-dodecanol). 3. In contrast to GABAA receptors, glutamate receptors expressed from mouse cortical mRNA or from cRNAs encoding AMPA (GluR3)- or kainate (GluR6)-selective subunits were much less sensitive to longer chain alcohols. In general, octanol and decanol were either without effect or high concentrations were required to produce inhibition. 4. In contrast to the lack of behavioural effects by long chain alcohols reported previously, decanol produced loss of righting reflex in short- and long-sleep mice, indicating that the in vivo effects of decanol may be due in part to actions at GABAA receptors. Furthermore, butanol, hexanol, octanol, and decanol produce similar potentiation of GABAA receptor function at concentrations required to cause loss of righting reflex in tadpoles, an in vivo model where alcohol distribution is not a compromising factor. 5. Thus, the in vivo effects of long chain alcohols are not likely to be due to their actions on NMDA, AMPA, or kainate receptors, but may be due instead to potentiation of GABAA receptor function.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alifimoff J. K., Firestone L. L., Miller K. W. Anaesthetic potencies of primary alkanols: implications for the molecular dimensions of the anaesthetic site. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;96(1):9–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildy-Mayfield J. E., Harris R. A. Comparison of ethanol sensitivity of rat brain kainate, DL-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxalone proprionic acid and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Aug;262(2):487–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildy-Mayfield J. E., Harris R. A. Ethanol inhibits kainate responses of glutamate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes: role of calcium and protein kinase C. J Neurosci. 1995 Apr;15(4):3162–3171. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-04-03162.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Bettler B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Heinemann S. Cloning of a cDNA for a glutamate receptor subunit activated by kainate but not AMPA. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):745–748. doi: 10.1038/351745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Göthert M. Inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced noradrenaline release by alcohols is related to their hydrophobicity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 27;191(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94152-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Mapping of general anaesthetic target sites provides a molecular basis for cutoff effects. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):349–351. doi: 10.1038/316349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R. A., Westbrook S. L., Bridges L. T. Alcohol-induced inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate-evoked release of [3H]norepinephrine from brain is related to lipophilicity. Neuropharmacology. 1991 May;30(5):441–446. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(91)90004-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A., Proctor W. R., McQuilkin S. J., Klein R. L., Mascia M. P., Whatley V., Whiting P. J., Dunwiddie T. V. Ethanol increases GABAA responses in cells stably transfected with receptor subunits. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1995 Feb;19(1):226–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1995.tb01496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huidobro-Toro J. P., Bleck V., Allan A. M., Harris R. A. Neurochemical actions of anesthetic drugs on the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-chloride channel complex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Sep;242(3):963–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilyin V., Parker I. Effects of alcohols on responses evoked by inositol trisphosphate in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:339–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koblin D. D., Chortkoff B. S., Laster M. J., Eger E. I., 2nd, Halsey M. J., Ionescu P. Polyhalogenated and perfluorinated compounds that disobey the Meyer-Overton hypothesis. Anesth Analg. 1994 Dec;79(6):1043–1048. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199412000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata Y., Marszalec W., Hamilton B. J., Carter D. B., Narahashi T. Alcohol modulation of cloned GABAA receptor-channel complex expressed in human kidney cell lines. Brain Res. 1993 Dec 17;631(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91200-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. P., Kelso S. R. Apparent desensitization of NMDA responses in Xenopus oocytes involves calcium-dependent chloride current. Neuron. 1990 Jan;4(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90443-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Peoples R. W., Weight F. F. Alcohol action on a neuronal membrane receptor: evidence for a direct interaction with the receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8200–8204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. H., Leonard S., Harris R. A. Enflurane inhibits the function of mouse and human brain phosphatidylinositol-linked acetylcholine and serotonin receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;43(6):941–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M., White G., Weight F. F. Ethanol inhibits NMDA-activated ion current in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1721–1724. doi: 10.1126/science.2467382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M., White G., Weight F. F. NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic excitation selectively inhibited by ethanol in hippocampal slice from adult rat. J Neurosci. 1990 Apr;10(4):1372–1379. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-04-01372.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon R. C., McComb J. A., Schreurs J., Goldstein D. B. A relationship between alcohol intoxication and the disordering of brain membranes by a series of short-chain alcohols. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):669–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCreery M. J., Hunt W. A. Physico-chemical correlates of alcohol intoxication. Neuropharmacology. 1978 Jul;17(7):451–461. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(78)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie D., Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Actions of general anaesthetics on a neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in isolated identified neurones of Lymnaea stagnalis. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(2):275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLarnon J. G., Wong J. H., Sawyer D., Baimbridge K. G. The actions of intermediate and long-chain n-alkanols on unitary NMDA currents in hippocampal neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;69(10):1422–1427. doi: 10.1139/y91-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihic S. J., McQuilkin S. J., Eger E. I., 2nd, Ionescu P., Harris R. A. Potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor-mediated chloride currents by novel halogenated compounds correlates with their abilities to induce general anesthesia. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;46(5):851–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihic S. J., Whiting P. J., Harris R. A. Anaesthetic concentrations of alcohols potentiate GABAA receptor-mediated currents: lack of subunit specificity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 15;268(2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrell R. D., Braun M. S., Haydon D. A. Actions of n-alcohols on nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels in cultured rat myotubes. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:431–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahiro M., Arakawa O., Narahashi T. Modulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-channel complex by alcohols. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peoples R. W., Weight F. F. Cutoff in potency implicates alcohol inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in alcohol intoxication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2825–2829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines D. E., Miller K. W. On the importance of volatile agents devoid of anesthetic action. Anesth Analg. 1994 Dec;79(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199412000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanna E., Dildy-Mayfield J. E., Harris R. A. Ethanol inhibits the function of 5-hydroxytryptamine type 1c and muscarinic M1 G protein-linked receptors in Xenopus oocytes expressing brain mRNA: role of protein kinase C. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 May;45(5):1004–1012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Tal N., Goldberg O., Luini A. Barbiturates, alcohols and the CNS excitatory neurotransmission: specific effects on the kainate and quisqualate receptors. Brain Res. 1984 Jan 23;291(2):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford K. A., Burnett D. M., Leidenheimer N. J., Burt D. R., Wang J. B., Kofuji P., Dunwiddie T. V., Harris R. A., Sikela J. M. Ethanol sensitivity of the GABAA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes requires 8 amino acids contained in the gamma 2L subunit. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. C., Forman S. A., Miller K. W. Short chain and long chain alkanols have different sites of action on nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels from Torpedo. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;39(3):332–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


