Abstract
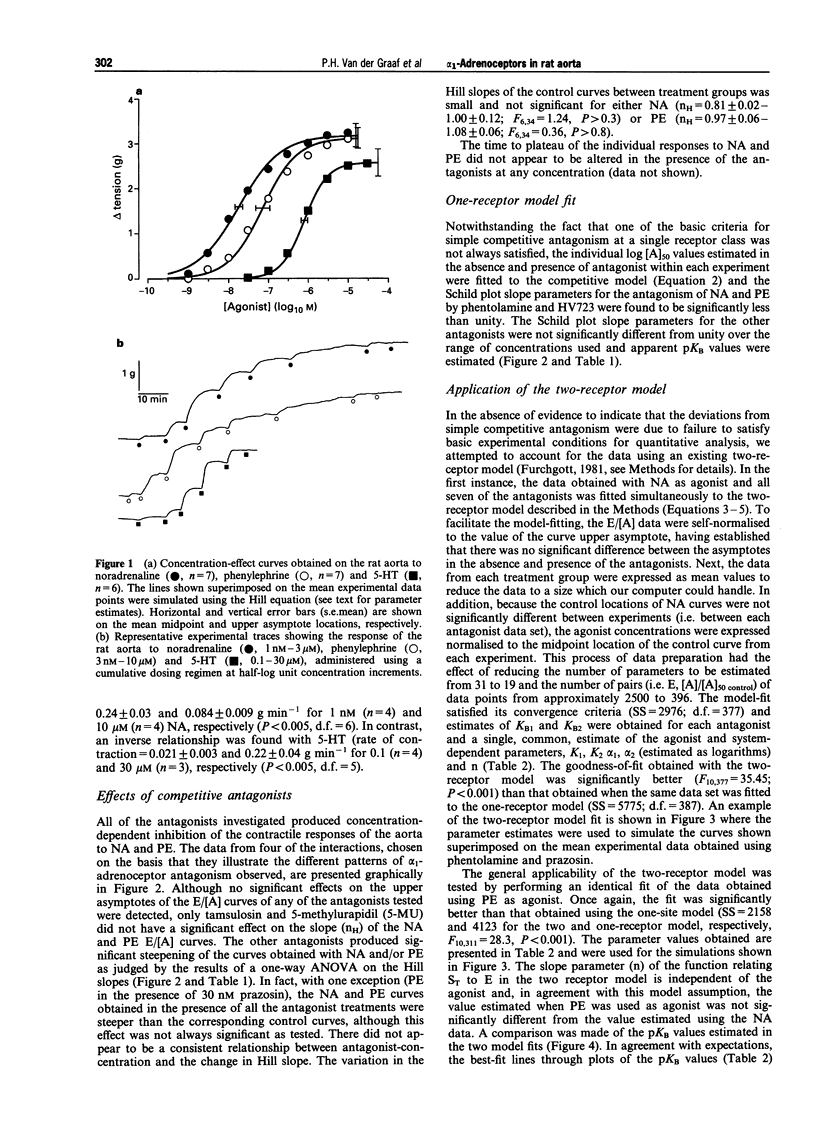
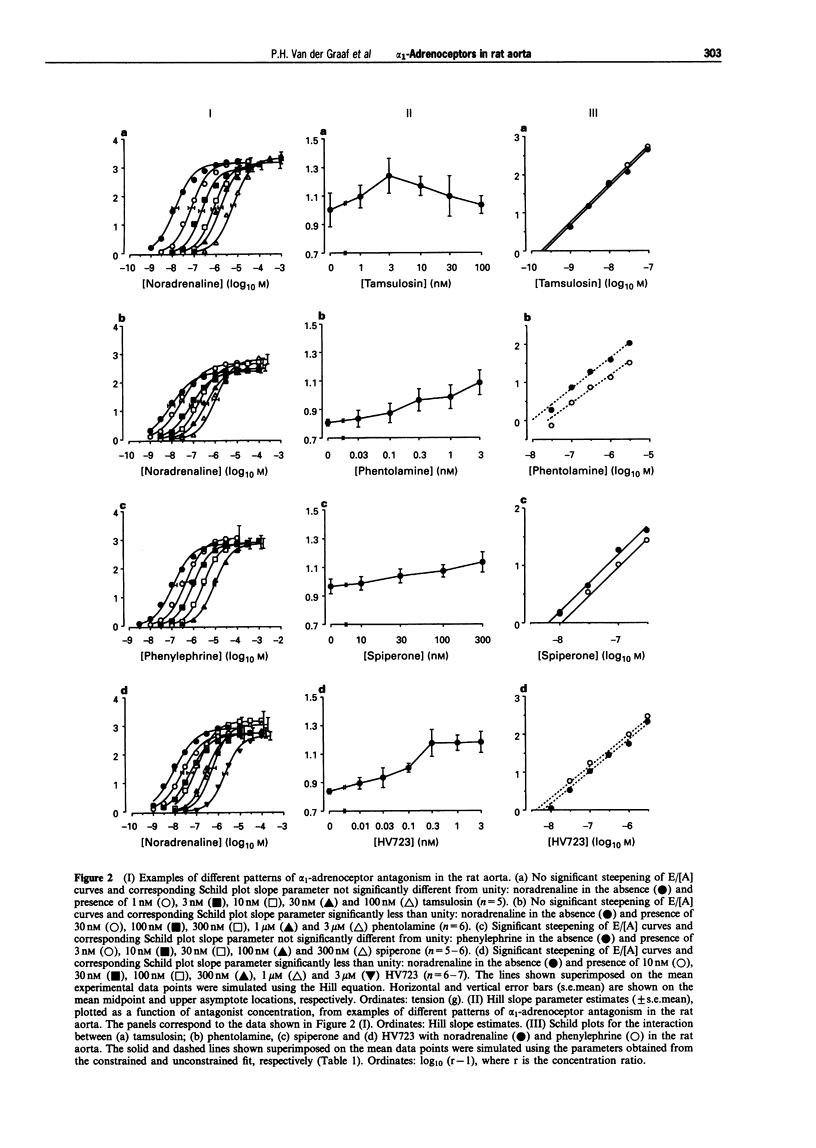
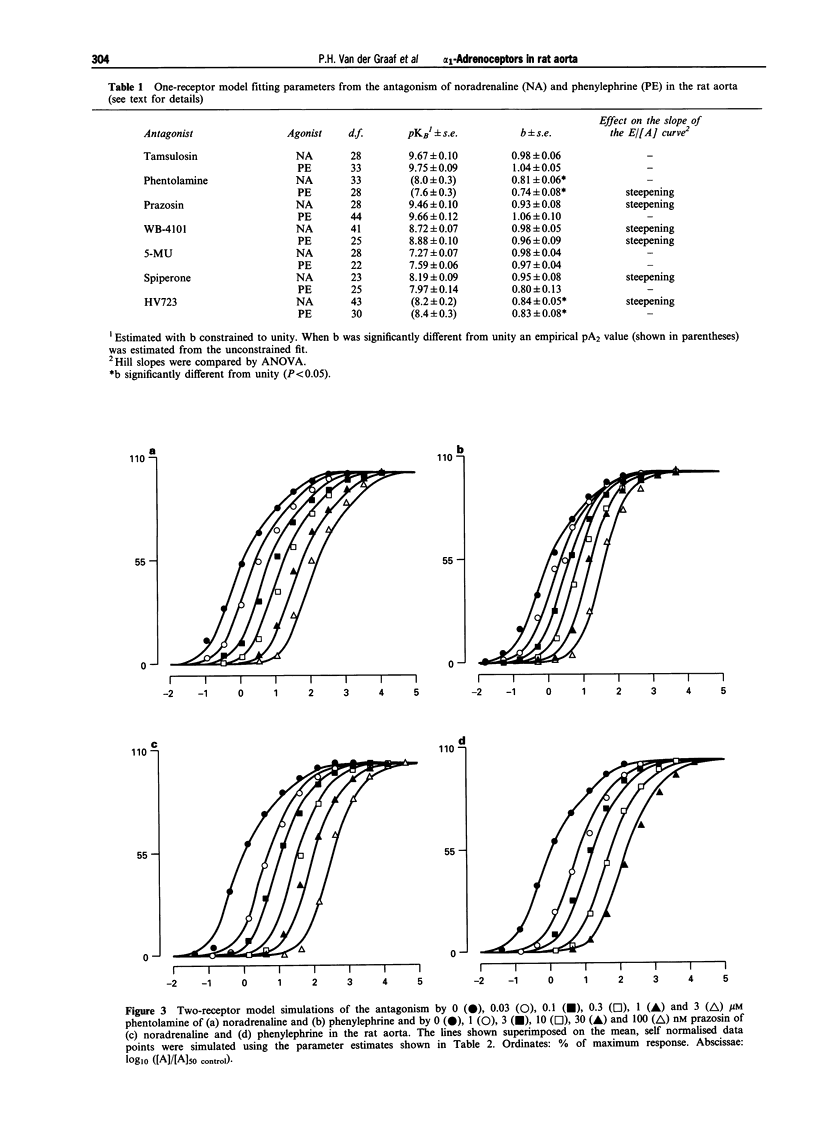
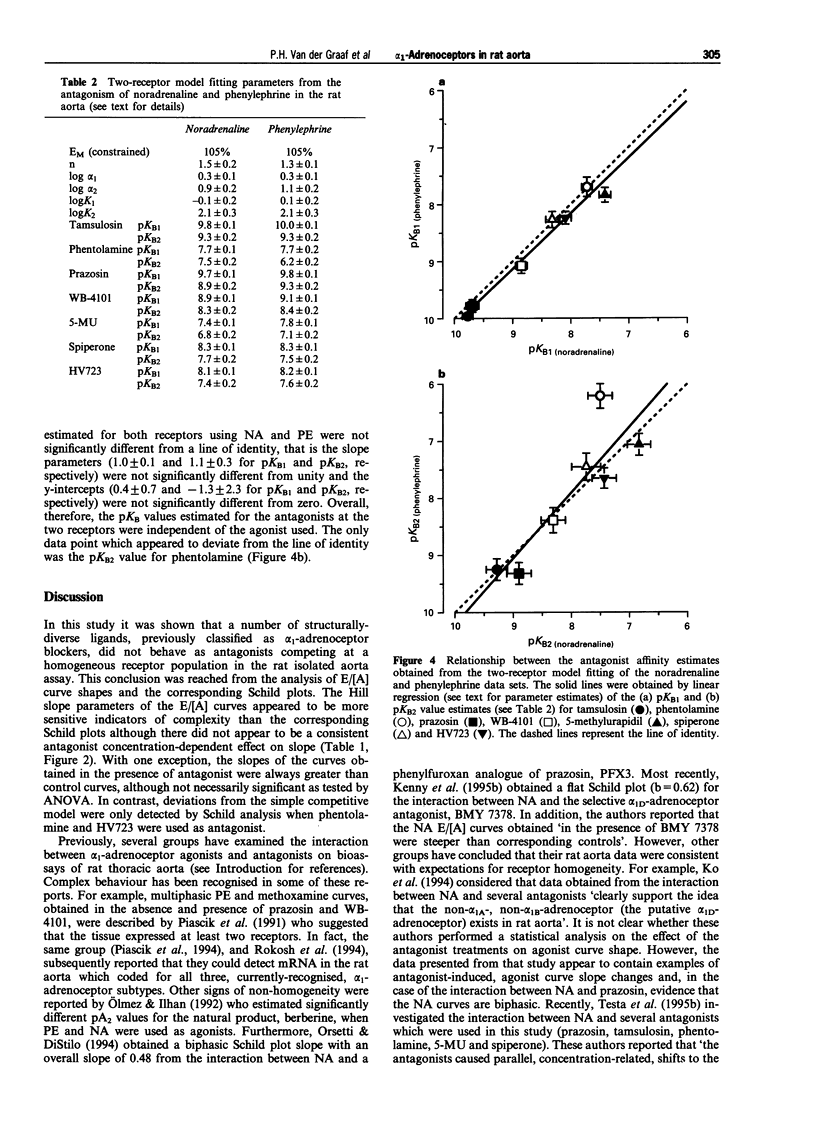
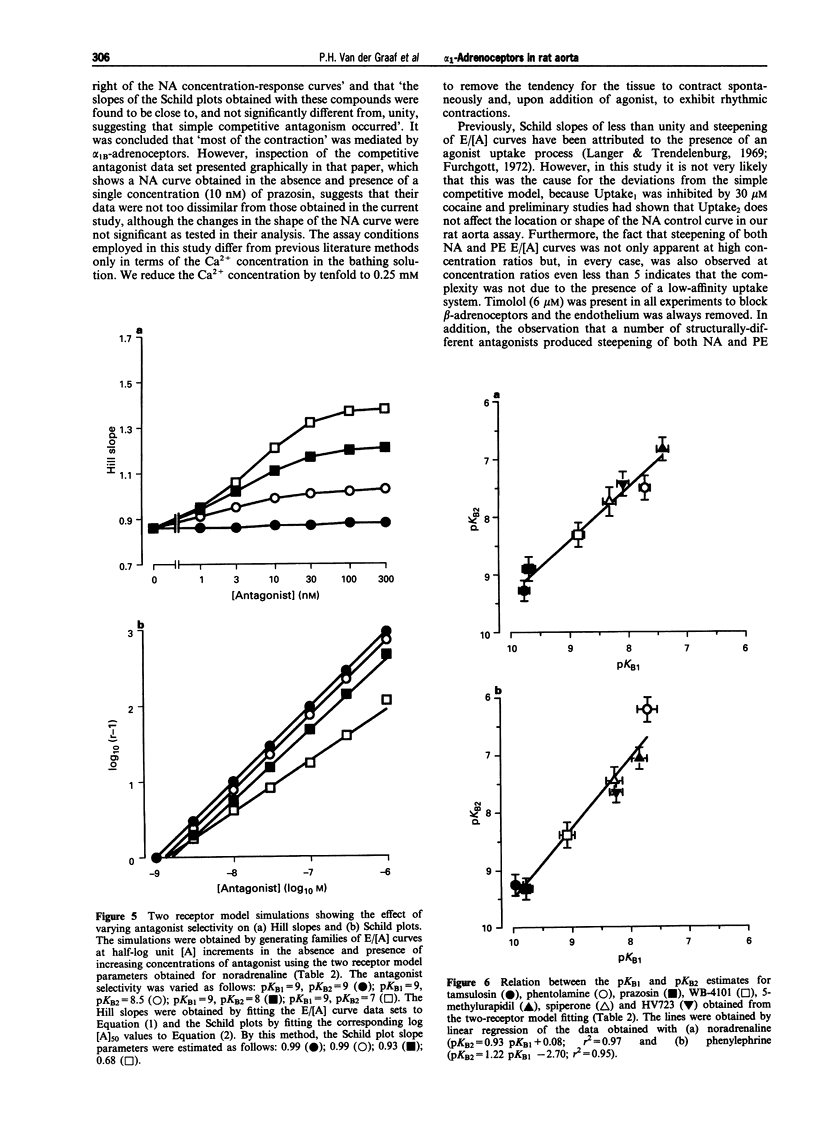
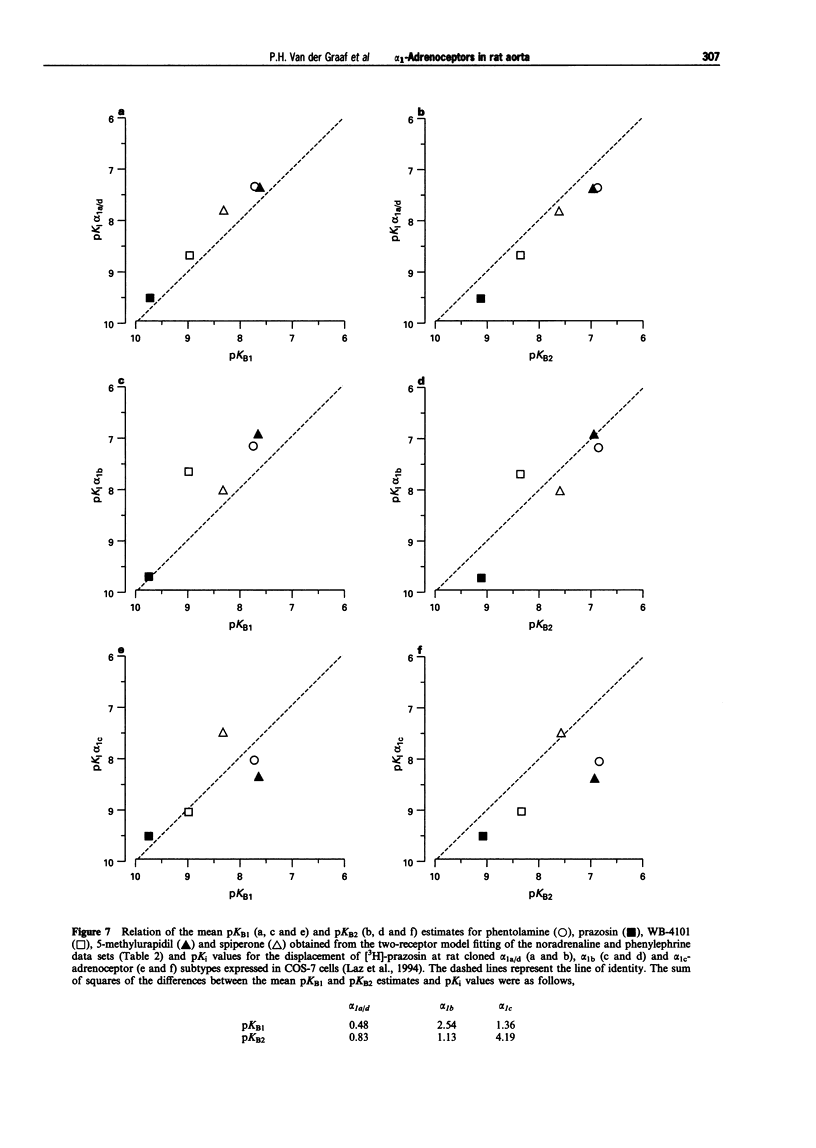
1. In this study, the effect of seven alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonists (tamsulosin, phentolamine, prazosin, WB-4101, 5-methylurapidil, spiperone and HV723) have been examined on the contractile response to noradrenaline (NA) and phenylephrine (PE) in rat isolated aorta. 2. NA and PE, when administered using a cumulative dosing schedule, both produced concentration-dependent contraction of aortic rings. It was possible to fit the individual concentration-effect (E/[A]) curve data to the Hill equation to provide estimates of the curve midpoint location (p[A]50 = 7.74 +/- 0.10 and 7.14 +/- 0.18), midpoint slope (nH = 0.82 +/- 0.03 and 0.99 +/- 0.10) and upper asymptote (alpha = 3.2 +/- 0.3 and 3.1 +/- 0.2 g) parameters for NA and PE, respectively. However, the Hill equation provided a better fit to the E/[A] curve data obtained with another contractile agent, 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) (p[A50] = 6.09 +/- 0.08, nH = 1.49 +/- 0.09, alpha = 2.6 +/- 0.3 g), as judged by calculation of the mean sum of squares of the differences between the observed and predicted values. 3. All of the antagonists investigated produced concentration-dependent inhibition of the contractile responses of the aorta to NA and PE. Although no significant effects on the upper asymptotes of the E/[A] curves of any of the antagonists tested were detected, only tamsulosin and 5-methylurapidil did not have a significant effect on the slope (nH) of the NA and PE E/[A] curves. The other antagonists produced significant steepening of the curves obtained with NA and/or PE. 4. Notwithstanding the fact that one of the basic criteria for simple competitive antagonism at a single receptor class was not always satisfied, the individual log [A]50 values estimated in the absence and presence of antagonist within each experiment were fitted to the competitive model. The Schild plot slope parameters for the antagonism of NA and PE by phentolamine and HV723 were found to be significantly less than unity. The Schild plot slope parameters for the other antagonists were not significantly different from unity. 5. In the absence of evidence to suggest that the deviations from simple competitive antagonism were due to failure to satisfy basic experimental conditions for quantitative analysis, an attempt was made to see whether the data could be accounted for by an existing two-receptor model (Furchgott, 1981). The goodness-of-fit obtained with the two-receptor model was significantly better than that obtained with the one-receptor model. Furthermore, with the exception of the data obtained with phentolamine, the pKB estimates for the two receptors were independent of whether NA or PE was used as agonist. 6. To determine which alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes may be associated with those defined by the two receptor model, the mean pKB estimates obtained from the two-receptor model fit were compared with affinities measured by Laz et al. (1994) for rat cloned alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes expressed in COS-7 cells. The sum of squared differences of the data points from the line of identity was smallest for both pKB1 and pKB2 in the case of the alpha 1a/d-adrenoceptor (now referred to as alpha 1d-adrenoceptor; Hieble et al., 1995). Therefore, the complexity exposed in this study may be due to the expression of closely-related forms of the alpha 1d-adrenoceptor. However, relatively good matches were also found between pKB1 and alpha 1c and between pKB2 and alpha 1b. Therefore, on the basis of these data, it is not possible to rule out the involvement of all three alpha 1-adrenoceptors. The conflicting reports concerning the characteristics of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor population mediating contraction of the rat aorta may, at least in part, be due to the lack of highly selective ligands and to between-assay variation in the expression of multiple alpha 1-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboud R., Shafii M., Docherty J. R. Investigation of the subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediating contractions of rat aorta, vas deferens and spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):80–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia G., Shannon M., Borgundvaag B., Titeler M. Properties of [3H]prazosin-labeled alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in rat brain and porcine neurointermediate lobe tissue. J Neurochem. 1983 Aug;41(2):538–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Leff P., Shankley N. P. Further analysis of anomalous pKB values for histamine H2-receptor antagonists on the mouse isolated stomach assay. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):581–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Leff P., Shankley N. P., Wood J. An operational model of pharmacological agonism: the effect of E/[A] curve shape on agonist dissociation constant estimation. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):561–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12941.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue D. R., Jr, Bonhaus D. W., Ford A. P., Pfister J. R., Sharif N. A., Shieh I. A., Vimont R. L., Williams T. J., Clarke D. E. Functional evidence equating the pharmacologically-defined alpha 1A- and cloned alpha 1C-adrenoceptor: studies in the isolated perfused kidney of rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(2):283–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer R., Grassegger A., Schudt C., Glossmann H. (+)-Niguldipine binds with very high affinity to Ca2+ channels and to a subtype of alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 11;172(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Fuller R. W., Wiley K. S. Evidence for 5-HT2 receptors mediating contraction in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Aug;218(2):421–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltze M., Boer R. The adrenoceptor agonist, SDZ NVI 085, discriminates between alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptor subtypes in vas deferens, kidney and aorta of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 2;224(2-3):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90796-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esbenshade T. A., Hirasawa A., Tsujimoto G., Tanaka T., Yano J., Minneman K. P., Murphy T. J. Cloning of the human alpha 1d-adrenergic receptor and inducible expression of three human subtypes in SK-N-MC cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 May;47(5):977–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure C., Pimoule C., Arbilla S., Langer S. Z., Graham D. Expression of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat tissues: implications for alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 15;268(2):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Williams T. J., Blue D. R., Clarke D. E. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification: sharpening Occam's razor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jun;15(6):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forray C., Bard J. A., Wetzel J. M., Chiu G., Shapiro E., Tang R., Lepor H., Hartig P. R., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. A. The alpha 1-adrenergic receptor that mediates smooth muscle contraction in human prostate has the pharmacological properties of the cloned human alpha 1c subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):703–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T., Kaba A. The role of calcium in the action of drugs on vascular smooth muscle. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1972 Apr;196(Suppl):–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T., Miller R. C., Lima J. S. Selective alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist-induced contractions and 45Ca fluxes in the rat isolated aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;77(4):597–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09337.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Hanft G., Rugevics C. 5-Methyl-urapidil discriminates between subtypes of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 7;151(2):333–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90819-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Heterogeneity of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors revealed by chlorethylclonidine. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;32(4):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Li J., Minneman K. P. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat blood vessels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94116-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., Bylund D. B., Clarke D. E., Eikenburg D. C., Langer S. Z., Lefkowitz R. J., Minneman K. P., Ruffolo R. R., Jr International Union of Pharmacology. X. Recommendation for nomenclature of alpha 1-adrenoceptors: consensus update. Pharmacol Rev. 1995 Jun;47(2):267–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B. A., Chalmers D. H., Philpott P. C., Naylor A. M. Characterization of an alpha 1D-adrenoceptor mediating the contractile response of rat aorta to noradrenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;115(6):981–986. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B. A., Naylor A. M., Greengrass P. M., Russell M. J., Friend S. J., Read A. M., Wyllie M. G. Pharmacological properties of the cloned alpha 1A/D-adrenoceptor subtype are consistent with the alpha 1A-adrenoceptor characterized in rat cerebral cortex and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):1003–1008. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killam A. L., Nikam S. S., Lambert G. M., Martin A. R., Nelson D. L. Comparison of two different arterial tissues suggests possible 5-hydroxytryptamine2 receptor heterogeneity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko F. N., Guh J. H., Yu S. M., Hou Y. S., Wu Y. C., Teng C. M. (-)-Discretamine, a selective alpha 1D-adrenoceptor antagonist, isolated from Fissistigma glaucescens. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;112(4):1174–1180. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong J. Q., Taylor D. A., Fleming W. W. Functional distribution and role of alpha-1 adrenoceptor subtypes in the mesenteric vasculature of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Mar;268(3):1153–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z., Trendelenburg U. The effect of a saturable uptake mechanism on the slopes of dose-response curves for sympathomimetic amines and on the shifts of dose-response curves produced by a competitive antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 May;167(1):117–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laz T. M., Forray C., Smith K. E., Bard J. A., Vaysse P. J., Branchek T. A., Weinshank R. L. The rat homologue of the bovine alpha 1c-adrenergic receptor shows the pharmacological properties of the classical alpha 1A subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):414–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P., Prentice D. J., Giles H., Martin G. R., Wood J. Estimation of agonist affinity and efficacy by direct, operational model-fitting. J Pharmacol Methods. 1990 May;23(3):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(90)90066-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinotti E., Breschi M. C., Omini C., Pani M., Ciucci M. A., Nieri P. Comparative study of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors in aorta obtained from human and other mammalian species. Pharmacol Res. 1991 Jan;23(1):57–69. doi: 10.1016/s1043-6618(05)80107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Loury D. N., Whiting R. L. Identification of a single alpha 1-adrenoceptor corresponding to the alpha 1A-subtype in rat submaxillary gland. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):883–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Comparison of cloned and pharmacologically defined rat tissue alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;350(2):136–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00241087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Creese I. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: a reevaluation of [3H]WB4104 and [3H]prazosin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Ransnas L. A. Fitting curves to data using nonlinear regression: a practical and nonmathematical review. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):365–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Kigoshi S., Ohmura T. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors involved in noradrenaline-induced contractions of rat thoracic aorta and dog carotid artery. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;57(4):535–544. doi: 10.1254/jjp.57.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Ohmura T., Kigoshi S., Hashimoto S., Oshita M. Pharmacological subclassification of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in vascular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):197–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols A. J., Ruffolo R. R., Jr The relationship of alpha-adrenoceptor reserve and agonist intrinsic efficacy to calcium utilization in the vasculature. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jul;9(7):236–241. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmez E., Ilhan M. Evaluation of the alpha-adrenoceptor antagonistic action of berberine in isolated organs. Arzneimittelforschung. 1992 Sep;42(9):1095–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriowo M. A., Nichols A. J., Ruffolo R. R., Jr Receptor protection studies with phenoxybenzamine indicate that a single alpha 1-adrenoceptor may be coupled to two signal transduction processes in vascular smooth muscle. Pharmacology. 1992;45(1):17–26. doi: 10.1159/000138968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriowo M. A., Ruffolo R. R., Jr Activation of a single alpha-1-adrenoceptor subtype in rat aorta mobilizes intracellular and extracellular pools of calcium. Pharmacology. 1992;44(3):139–149. doi: 10.1159/000138906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriowo M. A., Ruffolo R. R., Jr Heterogeneity of postjunctional alpha 1-adrenoceptors in mammalian aortae: subclassification based on chlorethylclonidine, WB 4101 and nifedipine. J Vasc Res. 1992 Jan-Feb;29(1):33–40. doi: 10.1159/000158929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshita M., Kigoshi S., Muramatsu I. Three distinct binding sites for [3H]-prazosin in the rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;104(4):961–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Graham R. M. Solution-phase library screening for the identification of rare clones: isolation of an alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Malik N., Gaivin R., Graham R. M. Cloning, expression, and tissue distribution of the rat homolog of the bovine alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor provide evidence for its classification as the alpha 1A subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;46(5):823–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piascik M. T., Smith M. S., Soltis E. E., Perez D. M. Identification of the mRNA for the novel alpha 1D-adrenoceptor and two other alpha 1-adrenoceptors in vascular smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;46(1):30–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piascik M. T., Sparks M. S., Pruitt T. A., Soltis E. E. Evidence for a complex interaction between the subtypes of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90491-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimoule C., Langer S. Z., Graham D. Further evidence that the classical alpha 1A- and cloned alpha 1c-adrenoceptors are the same subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Jun 23;290(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. T., Chari R. S., Berkowitz D. E., Meyers W. C., Schwinn D. A. Expression of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype mRNA in rat tissues and human SK-N-MC neuronal cells: implications for alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype classification. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;46(2):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokosh D. G., Bailey B. A., Stewart A. F., Karns L. R., Long C. S., Simpson P. C. Distribution of alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor mRNA in adult rat tissues by RNase protection assay and comparison with alpha 1B and alpha 1D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1177–1184. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENSON R. P. A modification of receptor theory. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Dec;11(4):379–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Johnston G. I., Page S. O., Mosley M. J., Wilson K. H., Worman N. P., Campbell S., Fidock M. D., Furness L. M., Parry-Smith D. J. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of human alpha-1 adrenergic receptors: sequence corrections and direct comparison with other species homologues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jan;272(1):134–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Szklut P. J., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W. Pharmacologic characterization of cloned alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes: selective antagonists suggest the existence of a fourth subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 1;227(4):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90162-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Page S. O., Middleton J. P., Lorenz W., Liggett S. B., Yamamoto K., Lapetina E. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. The alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor: characterization of signal transduction pathways and mammalian tissue heterogeneity. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):619–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight A. J., Koek W., Bigg D. C. Binding of antipsychotic drugs at alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptors: risperidone is selective for the alpha 1B-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul 20;238(2-3):407–410. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90876-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa R., Destefani C., Guarneri L., Poggesi E., Simonazzi I., Taddei C., Leonardi A. The alpha 1d-adrenoceptor subtype is involved in the noradrenaline-induced contractions of rat aorta. Life Sci. 1995;57(13):PL159–PL163. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(95)02079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa R., Guarneri L., Poggesi E., Simonazzi I., Taddei C., Leonardi A. Mediation of noradrenaline-induced contractions of rat aorta by the alpha 1B-adrenoceptor subtype. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Feb;114(4):745–750. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas H. M., Cunningham D., Zhou L., Hartman H. B., Gorman A. J. Cardiovascular effects of chloroethylclonidine, an irreversible alpha 1B-adrenoceptor antagonist, in the unanesthetized rat: a pharmacological analysis in vivo and in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Aug;266(2):864–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa H., Honda K. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype in the rat prostate is preferentially the alpha 1A type. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;62(3):297–304. doi: 10.1254/jjp.62.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


