Abstract
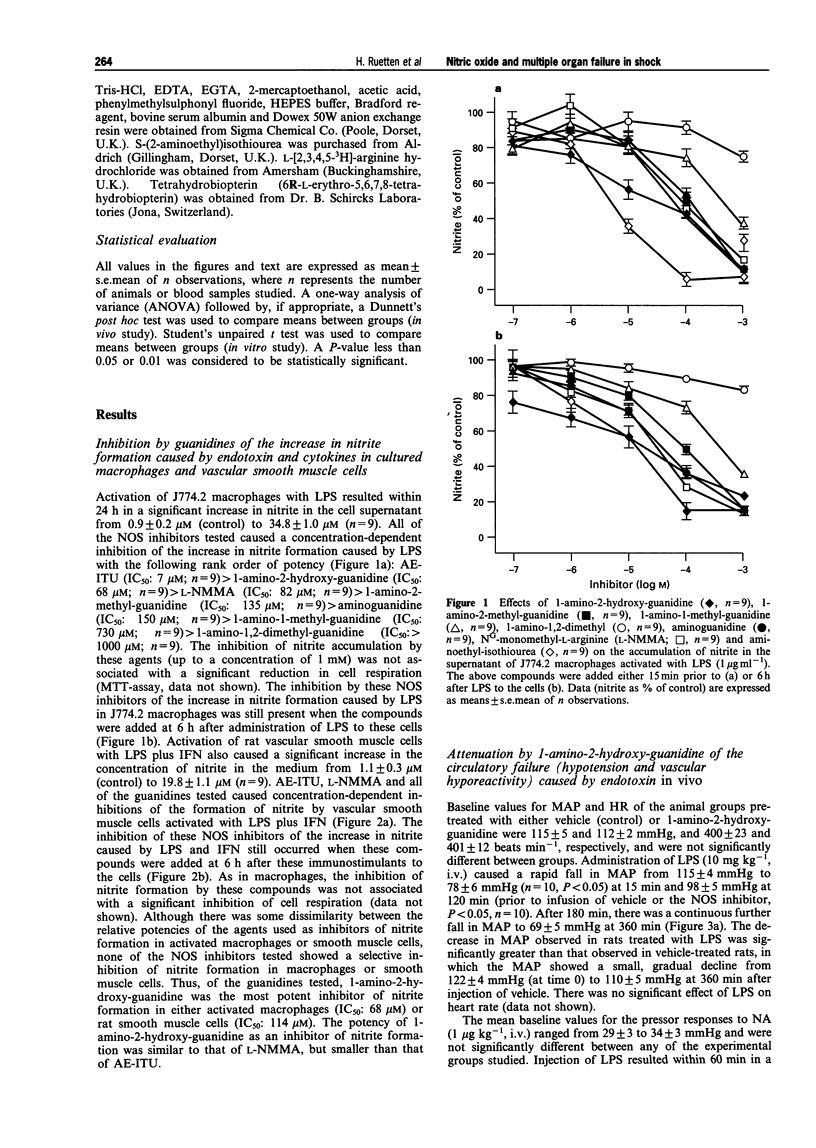
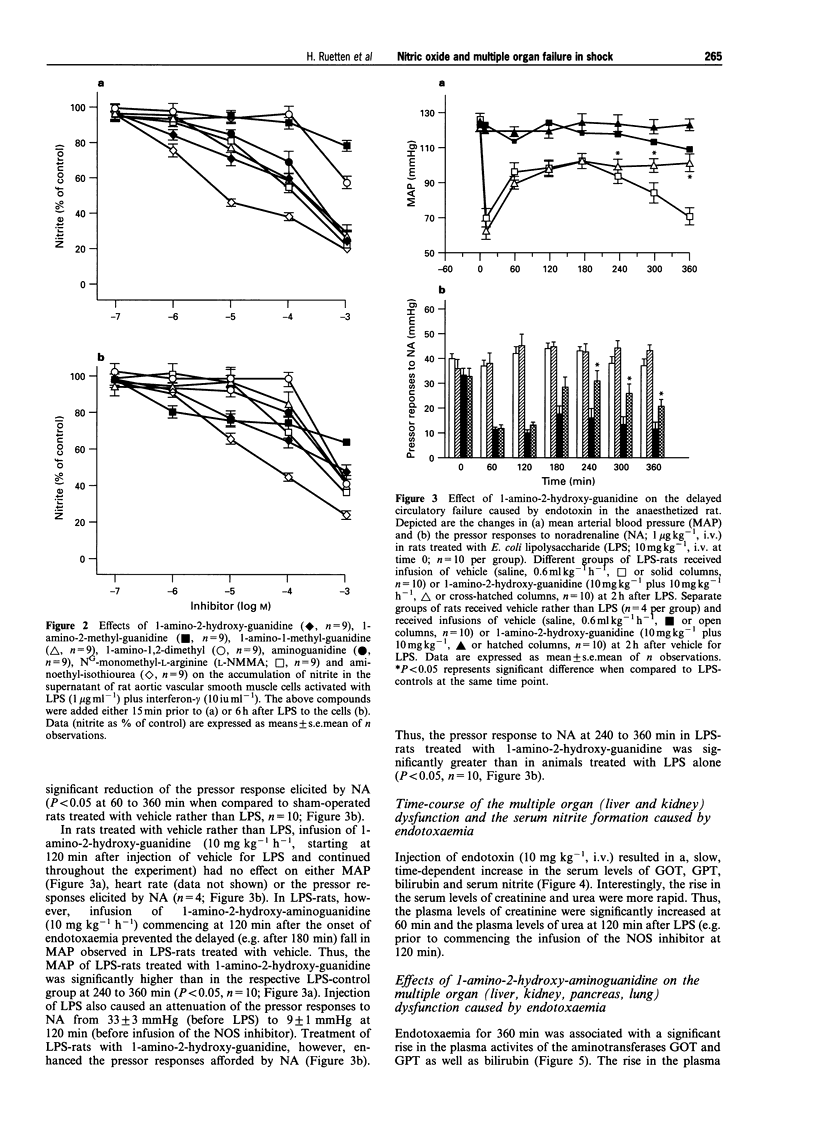
1. We have investigated the effects of (i) several guanidines on the activity of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide (NO) synthase (iNOS) in murine cultured macrophages and rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (RASM); and (ii) 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine, the most potent inhibitor of iNOS activity discovered, on haemodynamics, multiple organ (liver, renal, and pancreas) dysfunction and iNOS activity in rats with endotoxic shock. 2. The synthesized guanidine analogues caused concentration-dependent inhibitions of the increase in nitrite formation caused by lipopolysaccaride (LPS, 1 microgram ml-1) in J774.2 macrophages and RASM cells with the following rank order of potency: 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine > 1-amino-2-methyl-guanidine > 1-amino-1-methyl-guanidine > 1-amino-1,2-dimethyl-guanidine. Interestingly, 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine (IC50: J774.2, 68 microM; RASM, 114 microM) was more potent in inhibiting nitrite formation caused by LPS than NG-methyl-L-arginine, but less potent than aminoethyl-isothiourea. 3. In the anaesthetized rat, LPS caused a fall in mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) from 115 +/- 4 mmHg (time 0) to 98 +/- 5 mmHg at 2 h (P < 0.05, n = 10) and 69 +/- 5 mmHg at 6 h (P < 0.05, n = 10). The pressor effect of noradrenaline (NA, 1 mg kg-1, i.v.) was also significantly reduced at 1 to 6 h after LPS (vascular hyporeactivity). Treatment of LPS-rats with 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine (10 mg kg-1, i.v. plus 10 mg kg-1 h-1 starting at 2 h after LPS) prevented the delayed hypotension and vascular hyporeactivity seen in LPS-rats. However, 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine had no effect on either MAP or the pressor effect elicited by NA in rats infused with saline rather than LPS. 4. Endotoxaemia for 6 h caused a significant rise in the serum levels of aspartate or alanine aminotransferase (i.e. GOT or GPT) and bilirubin, and hence, liver dysfunction. Treatment of LPS-rats with 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine significantly attenuated the liver dysfunction caused by LPS (P < 0.05, n = 10). Injection of LPS also caused a rapid (almost maximal at 2 h) increase in the serum levels of urea and creatinine, and hence, renal dysfunction. This renal dysfunction was not affected by 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine (P > 0.05; n = 10). Endotoxaemia also caused a dysfunction of pancreas (rise in serum levels of lipase) as well as a metabolic acidosis (falls in PCO2, HCO3 and base excess). Both pancreatic dysfunction and metabolic acidosis were largely attenuated by treatment of LPS-rats with 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine. In rats infused with saline rather than LPS, 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine had no effect on liver, renal or pancreatic function (n = 4). 5. Endotoxaemia for 6 h resulted in a rise in the serum levels of nitrite (11.0 +/- 0.8 microM, P < 0.01, n = 10), which was significantly reduced by 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine (6.5 +/- 0.7 microM, P < 0.05, n = 10). Endotoxaemia for 6 h was also associated with a significant increase in iNOS activity in lung and liver, which was significantly reduced in lung or liver homogenates obtained from LPS-rats treated with 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine. In addition, endotoxaemia for 6 h resulted in a significant increase in myeloperoxidase activity (MPO), an indicator of neutrophil infiltration, in the liver. Treatment of LPS-rats with 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine did not affect the rise in MPO-activity in the liver caused by endotoxin. 6. Thus, 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine is a potent inhibitor of iNOS activity in macrophages or RASM in culture as well as in rats with endotoxic shock. Inhibition of iNOS activity with 1-amino-2-hydroxy-guanidine prevents the delayed circulatory failure and attenuates the dysfunction of liver, and pancreas, as well as the metabolic acidosis caused by endotoxaemia.
Full text
PDF


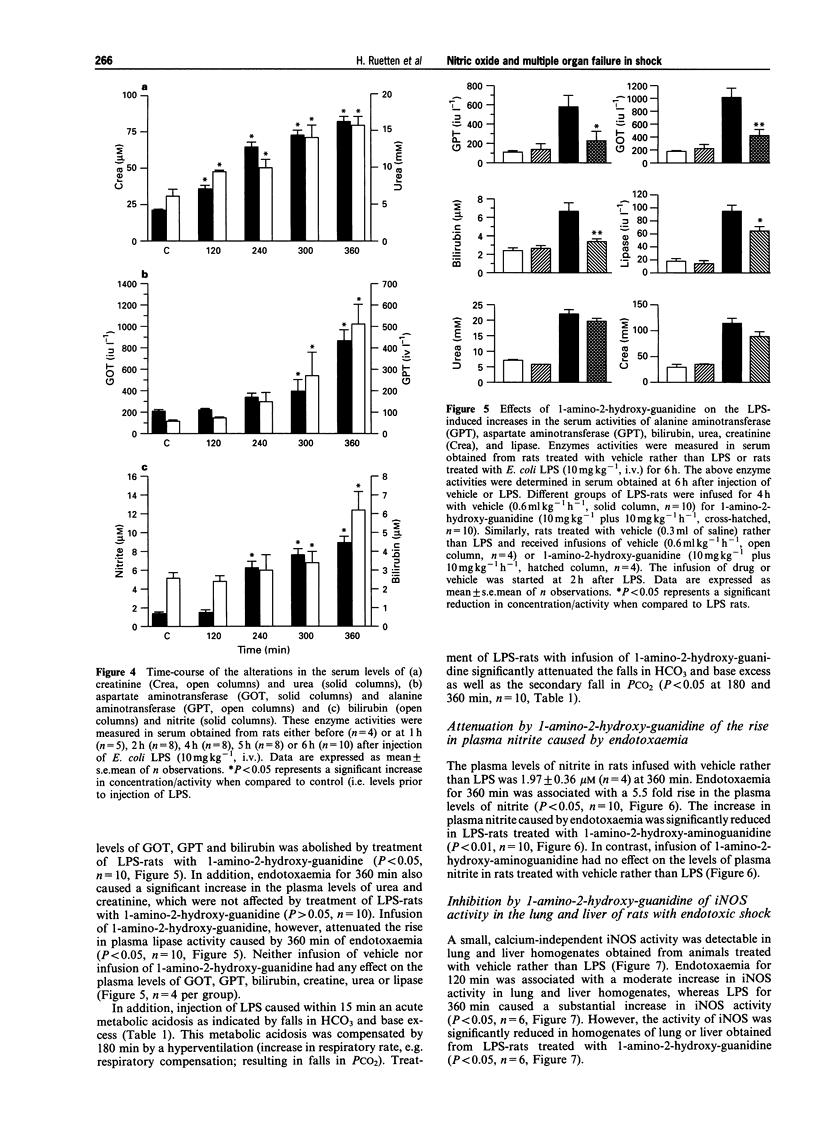
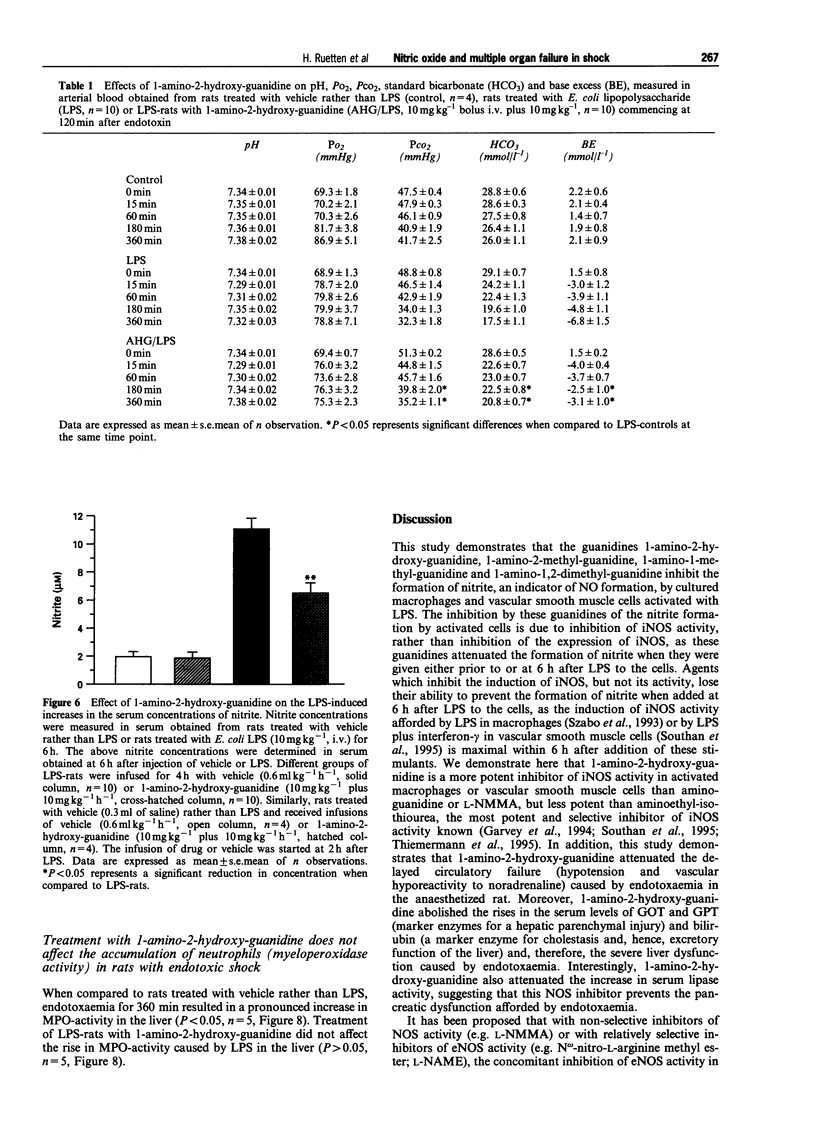


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., Stuehr D. J., West M. A., Bentz B. G., Simmons R. L. An L-arginine-dependent mechanism mediates Kupffer cell inhibition of hepatocyte protein synthesis in vitro. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1467–1472. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. Gram-positive organisms and sepsis. Arch Intern Med. 1994 Jan 10;154(1):26–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrain N. A., Geller D. A., Koty P. P., Sitrin N. F., Nussler A. K., Hoffman E. P., Billiar T. R., Hutchinson N. I., Mudgett J. S. Molecular cloning, structure, and chromosomal localization of the human inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6765–6772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Tilton R. G., Chang K., Hasan K. S., Ido Y., Wang J. L., Sweetland M. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Williamson J. R., McDaniel M. L. Aminoguanidine, a novel inhibitor of nitric oxide formation, prevents diabetic vascular dysfunction. Diabetes. 1992 Apr;41(4):552–556. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A. Multiple organ failure. Pathophysiology and potential future therapy. Ann Surg. 1992 Aug;216(2):117–134. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199208000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey E. P., Oplinger J. A., Tanoury G. J., Sherman P. A., Fowler M., Marshall S., Harmon M. F., Paith J. E., Furfine E. S. Potent and selective inhibition of human nitric oxide synthases. Inhibition by non-amino acid isothioureas. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26669–26676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller D. A., Lowenstein C. J., Shapiro R. A., Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Wang S. C., Nakayama D. K., Simmons R. L., Snyder S. H., Billiar T. R. Molecular cloning and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase from human hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3491–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller D. A., Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Lowenstein C. J., Shapiro R. A., Wang S. C., Simmons R. L., Billiar T. R. Cytokines, endotoxin, and glucocorticoids regulate the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):522–526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Ruiz de Luzuriaga K., Wagner D. A., Rand W., Istfan N., Young V. R., Tannenbaum S. R. Nitrate biosynthesis in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7764–7768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths M. J., Messent M., MacAllister R. J., Evans T. W. Aminoguanidine selectively inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):963–968. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbrecht B. G., Billiar T. R., Stadler J., Demetris A. J., Ochoa J., Curran R. D., Simmons R. L. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis during endotoxemia promotes intrahepatic thrombosis and an oxygen radical-mediated hepatic injury. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Oct;52(4):390–394. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.4.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan K., Heesen B. J., Corbett J. A., McDaniel M. L., Chang K., Allison W., Wolffenbuttel B. H., Williamson J. R., Tilton R. G. Inhibition of nitric oxide formation by guanidines. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 2;249(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90667-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett J. A., Roth R. A. The coagulation system, but not circulating fibrinogen, contributes to liver injury in rats exposed to lipopolysaccharide from gram-negative bacteria. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jan;272(1):53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutcheson I. R., Whittle B. J., Boughton-Smith N. K. Role of nitric oxide in maintaining vascular integrity in endotoxin-induced acute intestinal damage in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;101(4):815–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly G. A., Ayres M., Chelly F., Kilbourn R. G. Effects of NG-methyl-L-arginine, NG-nitro-L-arginine, and aminoguanidine on constitutive and inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat aorta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 28;199(1):147–154. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke K. D., Brenner H. H., Rodriguez M. L., Etzkorn K., Noack E. A., Kolb H., Kolb-Bachofen V. Pancreatic islet cells are highly susceptible towards the cytotoxic effects of chemically generated nitric oxide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 8;1182(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(93)90144-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laight D. W., Lad N., Woodward B., Waterfall J. F. Assessment of myeloperoxidase activity in renal tissue after ischemia/reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Nov 1;292(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0926-6917(94)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misko T. P., Moore W. M., Kasten T. P., Nickols G. A., Corbett J. A., Tilton R. G., McDaniel M. L., Williamson J. R., Currie M. G. Selective inhibition of the inducible nitric oxide synthase by aminoguanidine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 16;233(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90357-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs A. The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):2002–2012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. M., Jr, Billiar T. R. New insights into the regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):E829–E839. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.266.6.E829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M., Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Widespread tissue distribution, species distribution and changes in activity of Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent nitric oxide synthases. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 7;291(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81123-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz P. J., Raij L. Endogenously synthesized nitric oxide prevents endotoxin-induced glomerular thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1718–1725. doi: 10.1172/JCI116045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southan G. J., Szabó C., Thiemermann C. Isothioureas: potent inhibitors of nitric oxide synthases with variable isoform selectivity. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;114(2):510–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Harbrecht B. G., Di Silvio M., Curran R. D., Jordan M. L., Simmons R. L., Billiar T. R. Endogenous nitric oxide inhibits the synthesis of cyclooxygenase products and interleukin-6 by rat Kupffer cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Feb;53(2):165–172. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J. S., Singel D. J., Loscalzo J. Biochemistry of nitric oxide and its redox-activated forms. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1898–1902. doi: 10.1126/science.1281928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Mitchell J. A., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Nitric oxide-mediated hyporeactivity to noradrenaline precedes the induction of nitric oxide synthase in endotoxin shock. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):786–792. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Salzman A. L. Endogenous peroxynitrite is involved in the inhibition of mitochondrial respiration in immuno-stimulated J774.2 macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Apr 17;209(2):739–743. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Southan G. J., Thiemermann C. Beneficial effects and improved survival in rodent models of septic shock with S-methylisothiourea sulfate, a potent and selective inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12472–12476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Thiemermann C. Regulation of the expression of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase. Adv Pharmacol. 1995;34:113–153. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C., Ruetten H., Wu C. C., Vane J. R. The multiple organ dysfunction syndrome caused by endotoxin in the rat: attenuation of liver dysfunction by inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Dec;116(7):2845–2851. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15935.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C. The role of the L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway in circulatory shock. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;28:45–79. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60493-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C., Wu C. C., Szabó C., Perretti M., Vane J. R. Role of tumour necrosis factor in the induction of nitric oxide synthase in a rat model of endotoxin shock. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):177–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Rees D. D., Moncada S. Protective and pathological roles of nitric oxide in endotoxin shock. Cardiovasc Res. 1992 Jan;26(1):48–57. doi: 10.1093/cvr/26.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


