Abstract
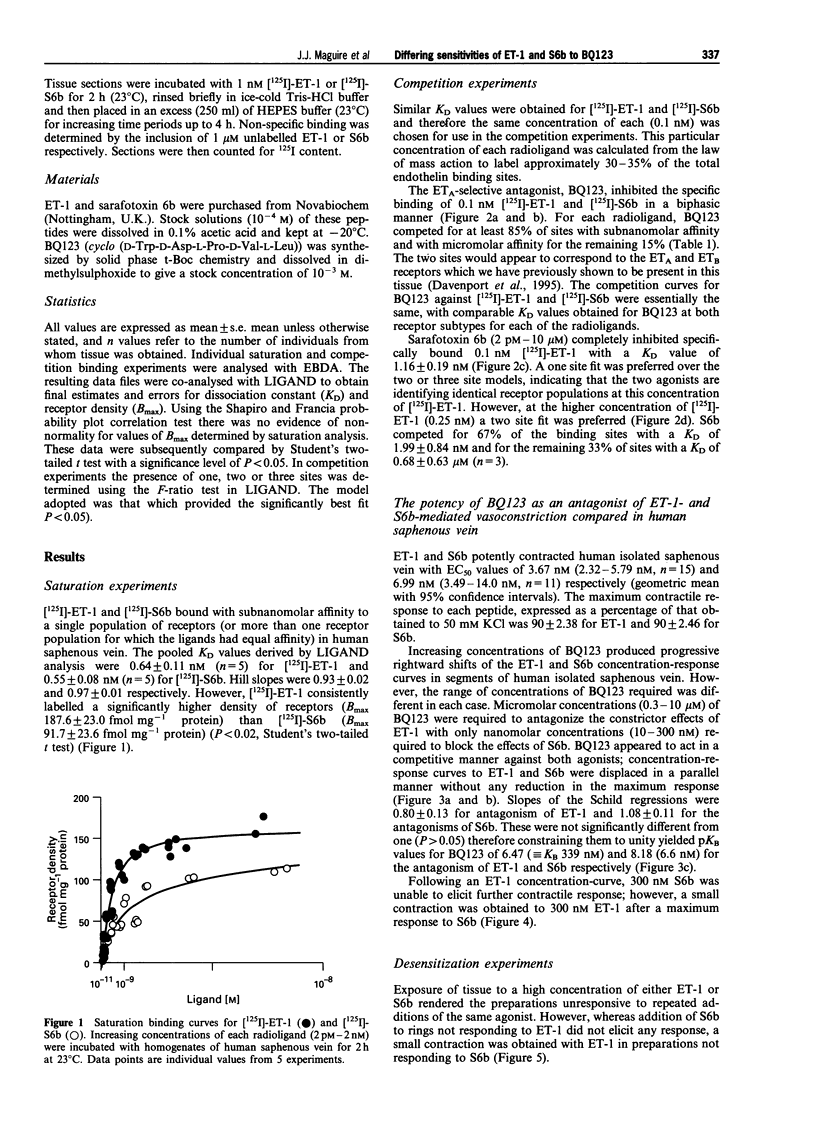
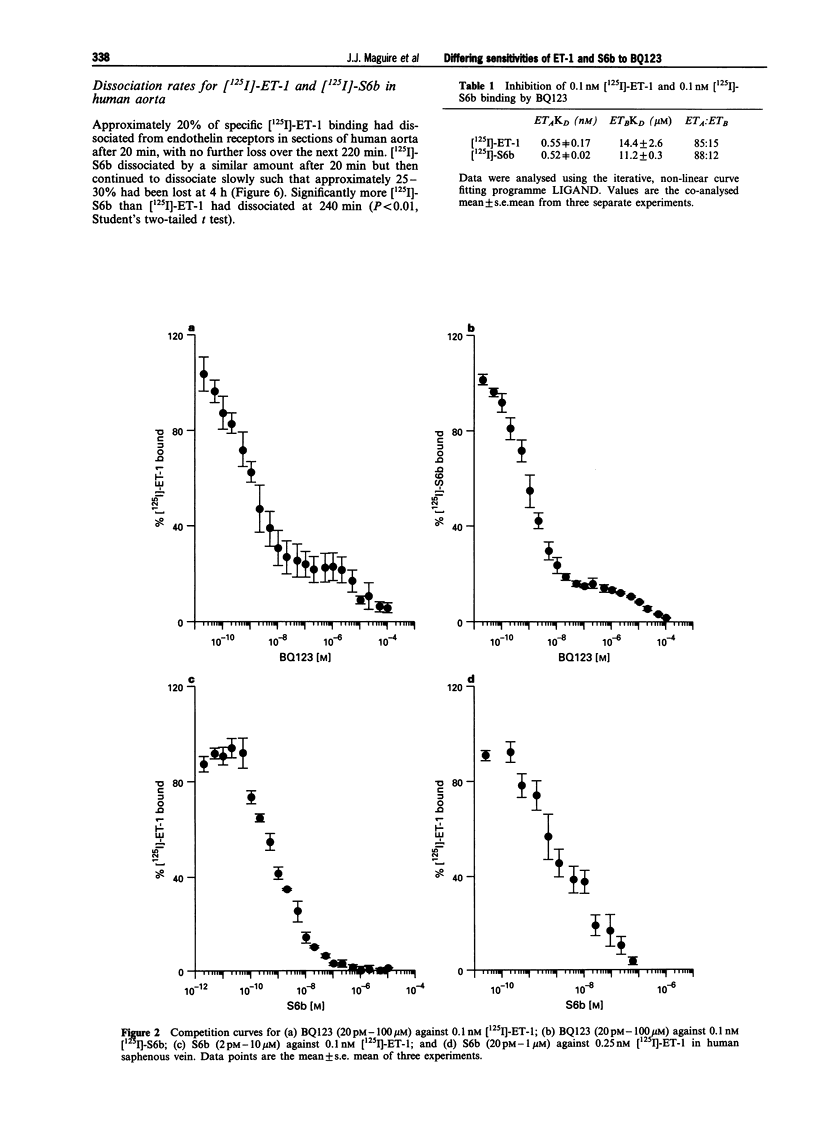
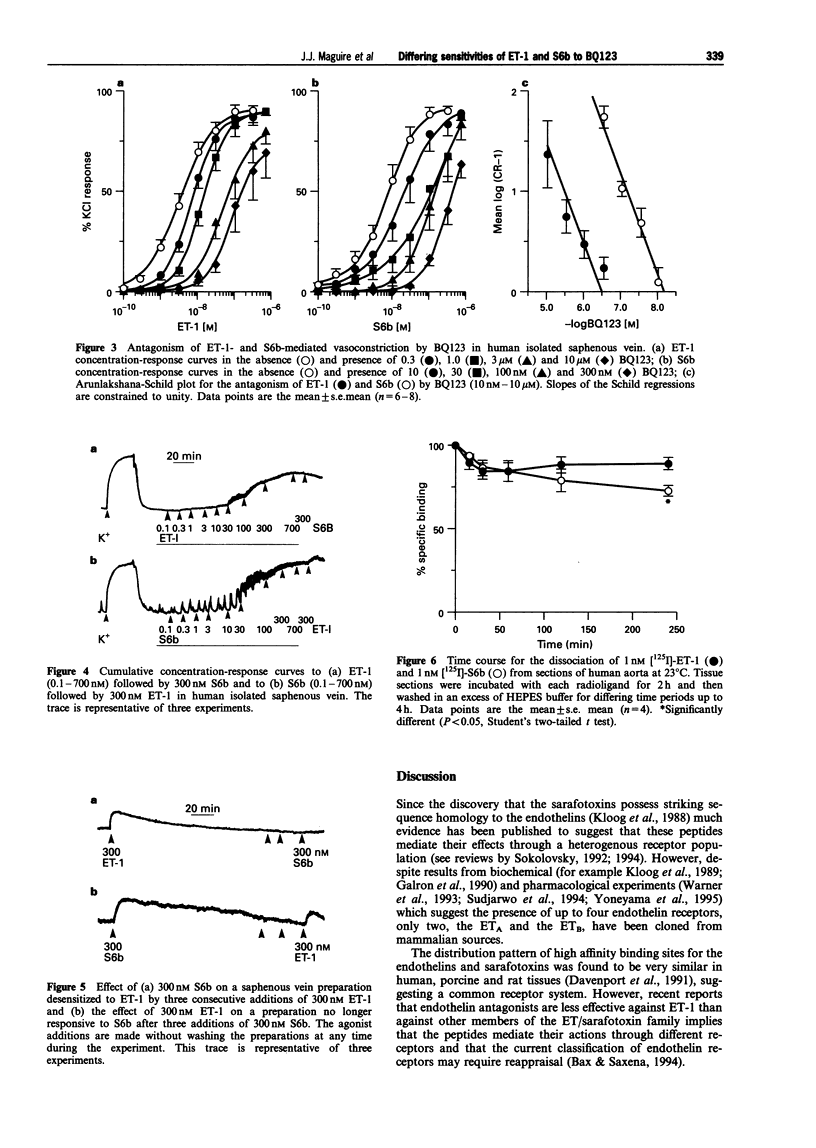
1. In homogenates of human saphenous vein, [125I]-ET-1 and [125I]-S6b each labelled a single population of high affinity binding sites with K(D) values of 0.64 +/- 0.11 nM and 0.55 +/- 0.08 nM respectively. Hill slopes were close to one. However, the density of receptors labelled by [125I]-ET-1 was significantly greater than that by [125I]-S6b (187.6 +/- 23.0 compared to 91.7 +/- 23.6 fmol mg-1 protein, P < 0.02). 2. BQ123, an ET(A-)selective antagonist, inhibited specific [125I]-ET-1 and [125I]-S6b binding with equal affinity. BQ123 competed in a biphasic manner for both [125I]-ET-1 (0.1 nM) and [125I]-S6b (0.1 nM) with ET(A) K(D) values of 0.55 +/- 0.17 nM and 0.52 +/- 0.02 nM and ET(B) K(D) values of 14.4 +/- 2.60 microM and 11.2 +/- 0.31 microM respectively. S6b monophasically inhibited 0.1 nM [125I]-ET-1 (K(D) 1.16 +/- 0.9 nM) but competed for 0.25 nM [125I]-ET-1 in a biphasic manner (K(D) high affinity site 1.99 +/- 0.84 nM, K(D) low affinity site 0.68 +/- 0.63 microM, ratio 67% : 33%). 3. BQ123 antagonized the vasoconstrictor responses of ET-1 with a pK(B) value of 6.47 whereas BQ123 exhibited 50 fold higher affinity against S6b-mediated vasoconstriction with a pK(B) value of 8.18. Regression slopes were 0.80 +/- 0.13 and 1.08 +/- 0.11 respectively. 4. In desensitization experiments, S6b (300 nM) did not contract preparations which were no longer responsive to ET-1 whereas a small contraction to ET-1 (300 nM) was obtained in preparations rendered unresponsive to S6b. 5. Medial sections of non-diseased human aorta, which express only ET(A) receptors, were used to compare dissociation rates of the two agonists. The time course for the dissociation of [125I]-ET-1 and [125I]-S6b was similar with 20-30% of each ligand dissociating at 4 h. 6. These data suggest that whilst BQ123, in common with other endothelin antagonists, is a much more potent blocker of S6b contractile responses than of ET-1 contractile responses, this is not reflected by the equal affinity of BQ123 determined in competition binding experiments against both [125I]-ET-1 and [125I]-S6b. This discrepancy in antagonist potency is probably not due to a marked difference in the rate of dissociation of [125I]-ET-1 and [125I]-S6b from endothelin receptors. One possible explanation is that ET-1 is activating an additional population of receptors which may have lower affinity for BQ123. This is suggested by the discrepancy in receptor density identified by [125I]-ET-1 and [125I]-S6b.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambar I., Kloog Y., Schvartz I., Hazum E., Sokolovsky M. Competitive interaction between endothelin and sarafotoxin: Binding and phosphoinositides hydrolysis in rat atria and brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Hori S., Aramori I., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):730–732. doi: 10.1038/348730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon C. R., Davenport A. P. Endothelin receptors in human coronary artery and aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Mar;117(5):986–992. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bax W. A., Aghai Z., van Tricht C. L., Wassenaar C., Saxena P. R. Different endothelin receptors involved in endothelin-1- and sarafotoxin S6B-induced contractions of the human isolated coronary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1471–1479. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bax W. A., Bos E., Saxena P. R. Heterogeneity of endothelin/sarafotoxin receptors mediating contraction of the human isolated saphenous vein. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 3;239(1-3):267–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)91010-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bax W. A., Bruinvels A. T., van Suylen R. J., Saxena P. R., Hoyer D. Endothelin receptors in the human coronary artery, ventricle and atrium. A quantitative autoradiographic analysis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;348(4):403–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00171340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bax W. A., Saxena P. R. The current endothelin receptor classification: time for reconsideration? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Oct;15(10):379–386. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodelsson G., Stjernquist M. Characterization of endothelin receptors and localization of 125I-endothelin-1 binding sites in human umbilical artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 16;249(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90526-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousso-Mittler D., Kloog Y., Wollberg Z., Bdolah A., Kochva E., Sokolovsky M. Functional endothelin/sarafotoxin receptors in the rat uterus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):952–957. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90765-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport A. P., Maguire J. J. Is endothelin-induced vasoconstriction mediated only by ETA receptors in humans? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jan;15(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport A. P., Morton A. J., Brown M. J. Localization of endothelin-1 (ET-1), ET-2, and ET-3, mouse VIC, and sarafotoxin S6b binding sites in mammalian heart and kidney. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991;17 (Suppl 7):S152–S155. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199100177-00042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport A. P., O'Reilly G., Kuc R. E. Endothelin ETA and ETB mRNA and receptors expressed by smooth muscle in the human vasculature: majority of the ETA sub-type. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;114(6):1110–1116. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13322.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport A. P., O'Reilly G., Molenaar P., Maguire J. J., Kuc R. E., Sharkey A., Bacon C. R., Ferro A. Human endothelin receptors characterized using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, in situ hybridization, and subtype-selective ligands BQ123 and BQ3020: evidence for expression of ETB receptors in human vascular smooth muscle. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;22 (Suppl 8):S22–S25. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199322008-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglezos A., Cucchi P., Patacchini R., Quartara L., Maggi C. A., Mizrahi J. Differential effects of BQ-123 against endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 on the rat vas deferens: evidence for an atypical endothelin receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):736–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galron R., Bdolah A., Kloog Y., Sokolovsky M. Endothelin/sarafotoxin receptor induced phosphoinositide turnover: effects of pertussis and cholera toxins and of phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):949–954. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90776-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T. Evidence for heterogeneity of endothelin receptor distribution in human coronary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):1201–1205. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13942.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu X. H., Casley D. J., Nayler W. G. Sarafotoxin S6b displaces specifically bound 125I-endothelin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 29;162(3):509–510. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati A., Rebello S. Characteristics of endothelin receptors in the central nervous system of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neuropharmacology. 1992 Mar;31(3):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(92)90174-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. W., Luttmann M. A., Hubbard W. C., Undem B. J. Endothelin receptor subtypes in human and guinea-pig pulmonary tissues. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):1175–1183. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Yoshimi H., Takaichi S., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Binding and receptor down-regulation of a novel vasoconstrictor endothelin in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 24;239(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Noguchi K., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Tsuchida S., Kimura S., Fukami T., Ishikawa K., Nishikibe M., Yano M. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ETA receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90331-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karet F. E., Kuc R. E., Davenport A. P. Novel ligands BQ123 and BQ3020 characterize endothelin receptor subtypes ETA and ETB in human kidney. Kidney Int. 1993 Jul;44(1):36–42. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloog Y., Ambar I., Sokolovsky M., Kochva E., Wollberg Z., Bdolah A. Sarafotoxin, a novel vasoconstrictor peptide: phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat heart and brain. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):268–270. doi: 10.1126/science.2845579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloog Y., Bousso-Mittler D., Bdolah A., Sokolovsky M. Three apparent receptor subtypes for the endothelin/sarafotoxin family. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 14;253(1-2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80958-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire J. J., Davenport A. P. ETA receptor-mediated constrictor responses to endothelin peptides in human blood vessels in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(1):191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire J. J., Kuc R. E., O'Reilly G., Davenport A. P. Vasoconstrictor endothelin receptors characterized in human renal artery and vein in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;113(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb16172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. R., Marsden P. A., Brenner B. M., Ballermann B. J. Identification and characterization of endothelin binding sites in rat renal papillary and glomerular membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91972-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland S., McMullen D. M., Delaney C. L., Lee V. G., Hunt J. T. Venous smooth muscle contains vasoconstrictor ETB-like receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91163-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riezebos J., Watts I. S., Vallance P. J. Endothelin receptors mediating functional responses in human small arteries and veins. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;111(2):609–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Miyazaki H., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):732–735. doi: 10.1038/348732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salom J. B., Torregrosa G., Barberá M. D., Jover T., Alborch E. Endothelin receptors mediating contraction in goat cerebral arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):826–830. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M. Endothelins and sarafotoxins: physiological regulation, receptor subtypes and transmembrane signaling. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;54(2):129–149. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M. Endothelins and sarafotoxins: receptor heterogeneity. Int J Biochem. 1994 Mar;26(3):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(94)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudjarwo S. A., Hori M., Tanaka T., Matsuda Y., Okada T., Karaki H. Subtypes of endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediating venous smooth muscle contraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 15;200(1):627–633. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner M. J., Cannon T. R., Mundin J. W., White D. G., Watts I. S. Endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediate vascular smooth muscle contraction. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):858–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Allcock G. H., Corder R., Vane J. R. Use of the endothelin antagonists BQ-123 and PD 142893 to reveal three endothelin receptors mediating smooth muscle contraction and the release of EDRF. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):777–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. G., Garratt H., Mundin J. W., Sumner M. J., Vallance P. J., Watts I. S. Human saphenous vein contains both endothelin ETA and ETB contractile receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 May 23;257(3):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Jr, Jones K. L., Pettibone D. J., Lis E. V., Clineschmidt B. V. Sarafotoxin S6c: an agonist which distinguishes between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama T., Hori M., Makatani M., Yamamura T., Tanaka T., Matsuda Y., Karaki H. Subtypes of endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediating tracheal smooth muscle contraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Feb 15;207(2):668–674. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


