Abstract
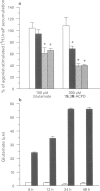
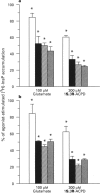
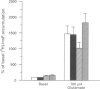
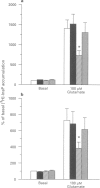
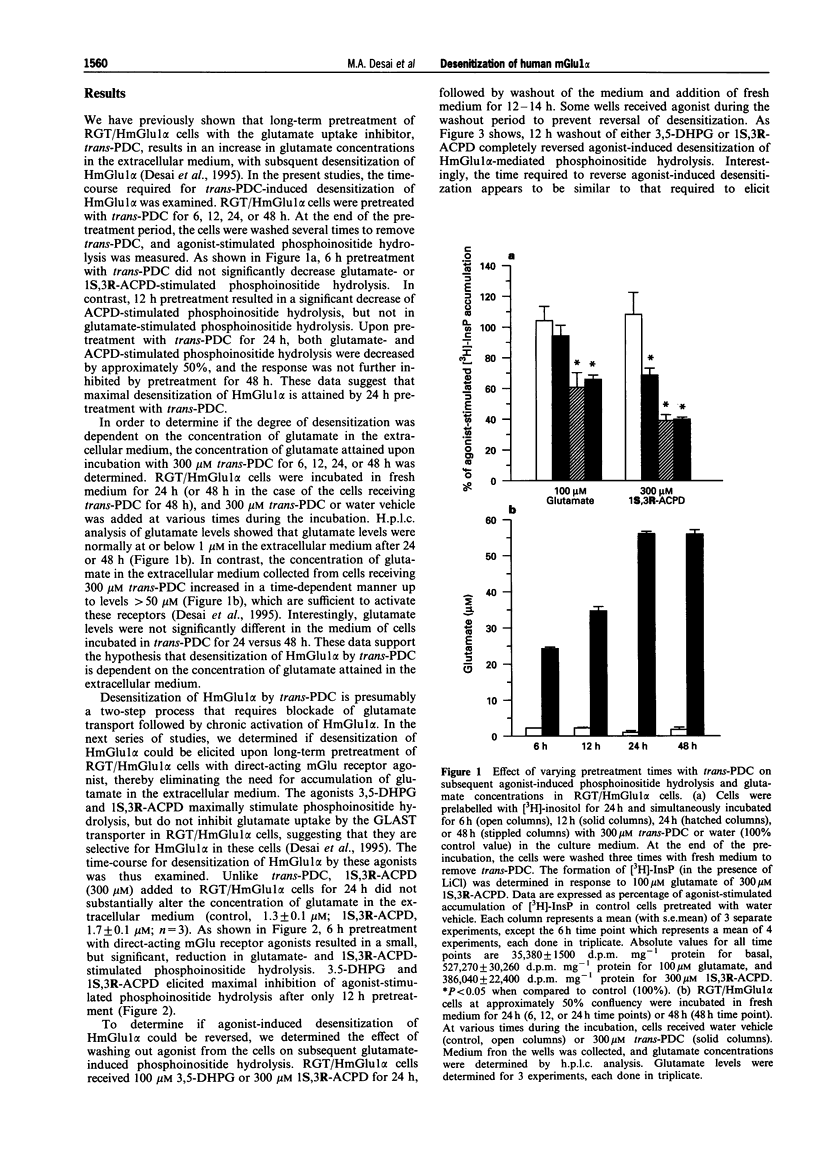
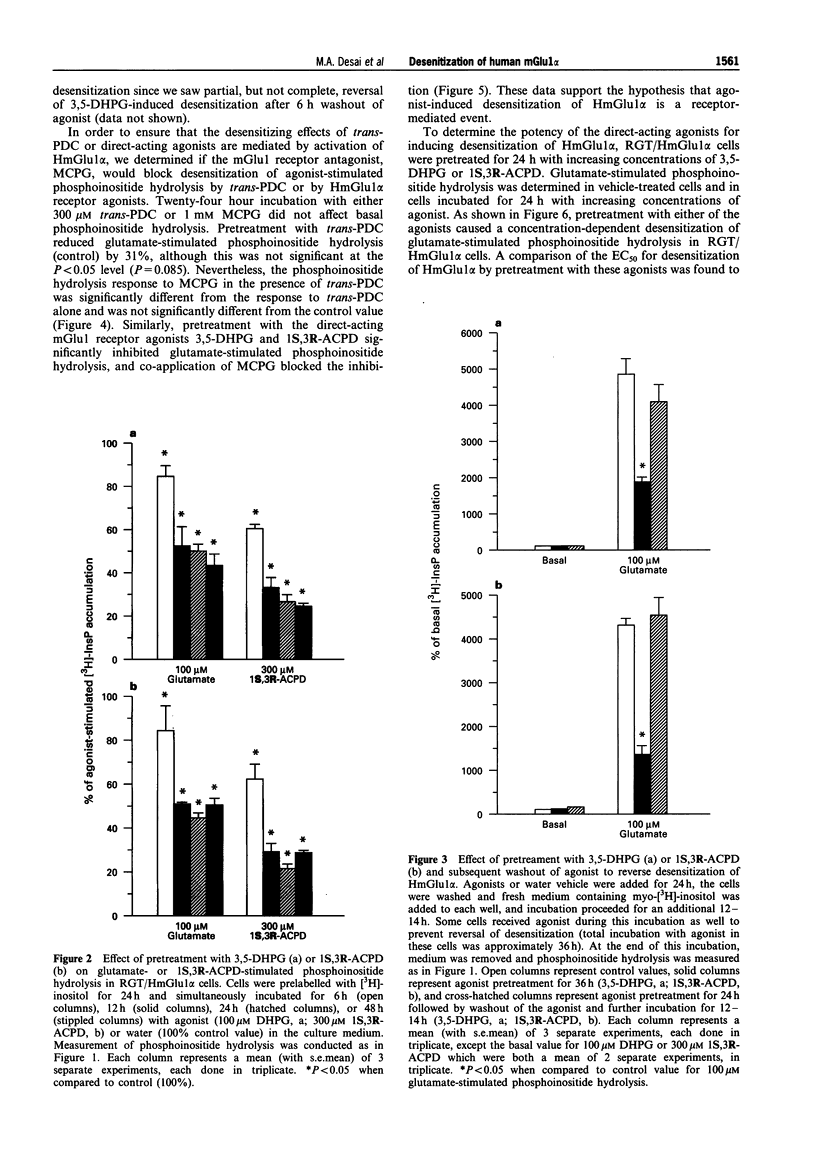
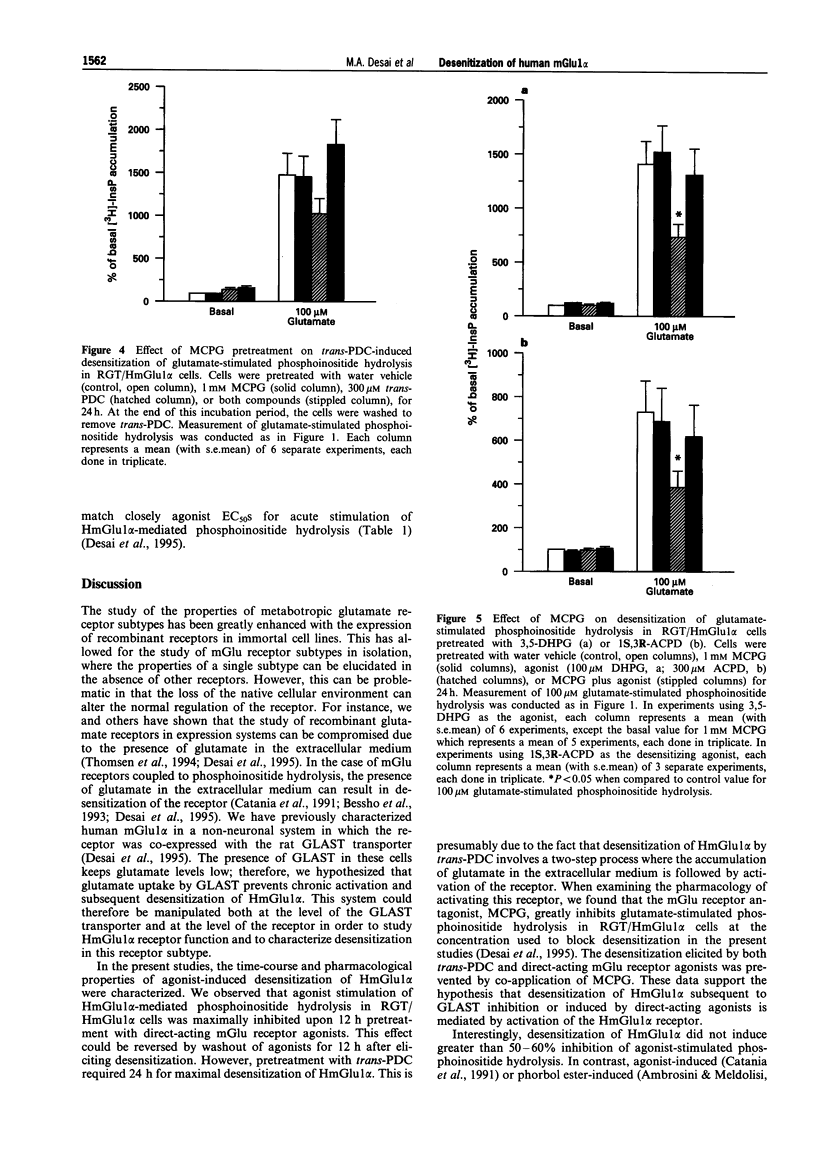
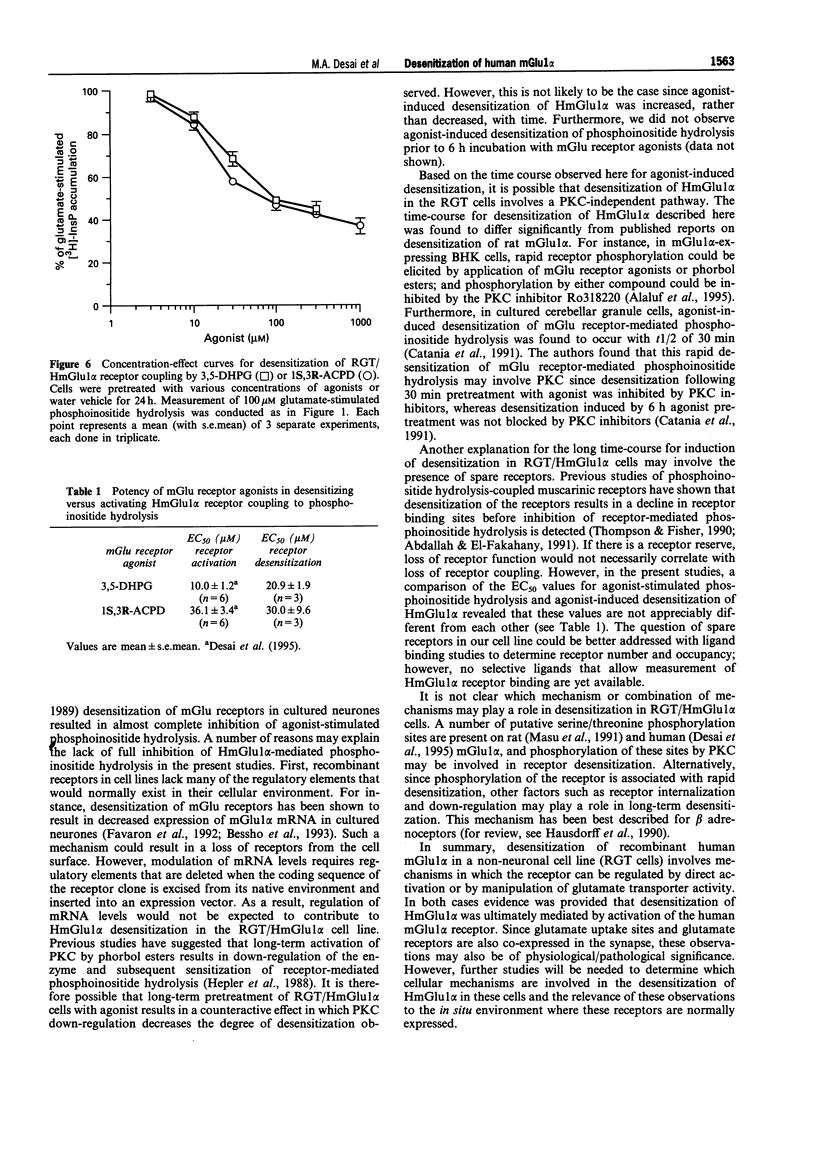
1. Stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis by human mGlu1 alpha (HmGlu1 alpha) was examined in a non-neuronal cell line (AV12-664) co-expressing both HmGlu1 alpha and a rat glutamate/aspartate transporter (GLAST). 2. Desensitization of HmGlu1 alpha could be elicited by inhibition of the GLAST transporter with the glutamate uptake inhibitor, L-trans-pyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid (trans-PDC). Maximal inhibition of HmGlu1 alpha-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis was induced upon 24 h pretreatment with trans-PDC. The concentration of glutamate in the extracellular medium also rose significantly in cells pretreated with trans-PDC. Glutamate levels increased upon incubation with trans-PDC in a time-dependent manner, with maximal glutamate levels attained after 24 h incubation with trans-PDC. 3. The time required for desensitization of HmGlu1 alpha by trans-PDC was compared to the time course for desensitization elicited by the direct-acting mGlu receptor agonists, 1-aminocyclopentane-1S,3R-dicarboxylic acid (1S,3R-ACPD) and (R,S)-3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine (3,5-DHPG). Both direct-acting mGlu receptor agonists elicited desensitization of HmGlu1 alpha more rapidly than did trans-PDC, with maximal inhibition of agonist-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis upon 12 h pretreatment. Agonist-induced desensitization could be fully reversed upon washout of agonist for 12 h. 4. Both mGlu receptor agonist- and trans-PDC-induced desensitization of HmGlu1 alpha could be blocked by inclusion of (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG), an mGlu receptor antagonist, in the pretreatment medium. 5. Agonist-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis by HmGlu1 alpha was found to parallel closely agonist-induced desensitization of HmGlu1 alpha. Thus, the EC50 values for 1S,3R-ACPD- and 3,5-DHPG-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis were similar to the EC50 values for eliciting desensitization of HmGlu1 alpha. 6. These studies demonstrate desensitization of recombinant human mGlu1 alpha receptor in a non-neuronal cell line in which the receptor can be regulated by direct activation or by manipulation of glutamate transporter activity. Desensitization of HmGlu1 alpha was found to be mediated by activation of the receptor since the mGlu receptor antagonist, MCPG, blocked both mGlu receptor agonist- and trans-PDC-induced desensitization of HmGlu1 alpha. Furthermore, agonist-induced desensitization of HmGlu1 alpha was found to parallel receptor-mediated stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdallah E. A., el-Fakahany E. E. Lack of desensitization of muscarinic receptor-mediated second messenger signals in rat brain upon acute and chronic inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. J Biochem Toxicol. 1991 Winter;6(4):261–268. doi: 10.1002/jbt.2570060405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe T., Sugihara H., Nawa H., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13361–13368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alaluf S., Mulvihill E. R., McIlhinney R. A. Rapid agonist mediated phosphorylation of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 alpha by protein kinase C in permanently transfected BHK cells. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jul 3;367(3):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00575-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosini A., Meldolesi J. Muscarinic and quisqualate receptor-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis in primary cultures of striatal and hippocampal neurons. Evidence for differential mechanisms of activation. J Neurochem. 1989 Sep;53(3):825–833. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb11779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronica E., Dell'Albani P., Condorelli D. F., Nicoletti F., Hack N., Balázs R. Mechanisms underlying developmental changes in the expression of metabotropic glutamate receptors in cultured cerebellar granule cells: homologous desensitization and interactive effects involving N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;44(5):981–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. T., McClure D. B., Grinnell B. W. High-level expression of secreted proteins from cells adapted to serum-free suspension culture. Biotechniques. 1993 Jun;14(6):972–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessho Y., Nawa H., Nakanishi S. Glutamate and quisqualate regulate expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor mRNA in cultured cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 1993 Jan;60(1):253–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb05845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. L., Favit A., Catania M. V., Nicoletti F. Phorbol esters attenuate glutamate-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in neuronal cultures. J Neurochem. 1988 Oct;51(4):1049–1053. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania M. V., Aronica E., Sortino M. A., Canonico P. L., Nicoletti F. Desensitization of metabotropic glutamate receptors in neuronal cultures. J Neurochem. 1991 Apr;56(4):1329–1335. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb11429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai M. A., Burnett J. P., Mayne N. G., Schoepp D. D. Cloning and expression of a human metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 alpha: enhanced coupling on co-transfection with a glutamate transporter. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Oct;48(4):648–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaron M., Rimland J. M., Manev H. Depolarization- and agonist-regulated expression of neuronal metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1). Life Sci. 1992;50(22):PL189–PL194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90431-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Turning off the signal: desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2881–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Earp H. S., Harden T. K. Long-term phorbol ester treatment down-regulates protein kinase C and sensitizes the phosphoinositide signaling pathway to hormone and growth factor stimulation. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C in agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7610–7619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houamed K. M., Kuijper J. L., Gilbert T. L., Haldeman B. A., O'Hara P. J., Mulvihill E. R., Almers W., Hagen F. S. Cloning, expression, and gene structure of a G protein-coupled glutamate receptor from rat brain. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1318–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.1656524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley S. C., Parker P. J., Fabbro D., Jaken S. Differential regulation of protein kinase C isozymes by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in GH4C1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23761–23768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lameh J., Philip M., Sharma Y. K., Moro O., Ramachandran J., Sadée W. Hm1 muscarinic cholinergic receptor internalization requires a domain in the third cytoplasmic loop. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13406–13412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu M., Tanabe Y., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. Sequence and expression of a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):760–765. doi: 10.1038/349760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Agonist regulation of cellular G protein levels and distribution: mechanisms and functional implications. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Nov;14(11):413–418. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90064-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minakami R., Katsuki F., Sugiyama H. A variant of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5: an evolutionally conserved insertion with no termination codon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jul 30;194(2):622–627. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pin J. P., Waeber C., Prezeau L., Bockaert J., Heinemann S. F. Alternative splicing generates metabotropic glutamate receptors inducing different patterns of calcium release in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10331–10335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D., Johnson B. G. Selective inhibition of excitatory amino acid-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in the rat hippocampus by activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 15;37(22):4299–4305. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. B., Challiss R. A., Nahorski S. R. Chronic activation of muscarinic and metabotropic glutamate receptors down-regulates type I inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor expression in cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 1994 Dec;63(6):2369–2372. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63062369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storck T., Schulte S., Hofmann K., Stoffel W. Structure, expression, and functional analysis of a Na(+)-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10955–10959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. A family of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90118-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. K., Fisher S. K. Relationship between agonist-induced muscarinic receptor loss and desensitization of stimulated phosphoinositide turnover in two neuroblastomas: methodological considerations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):744–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen C., Hansen L., Suzdak P. D. L-glutamate uptake inhibitors may stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis in baby hamster kidney cells expressing mGluR1a via heteroexchange with L-glutamate without direct activation of mGluR1a. J Neurochem. 1994 Dec;63(6):2038–2047. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63062038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen C., Mulvihill E. R., Haldeman B., Pickering D. S., Hampson D. R., Suzdak P. D. A pharmacological characterization of the mGluR1 alpha subtype of the metabotropic glutamate receptor expressed in a cloned baby hamster kidney cell line. Brain Res. 1993 Aug 13;619(1-2):22–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91592-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcikiewicz R. J., Nakade S., Mikoshiba K., Nahorski S. R. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor immunoreactivity in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells is reduced by chronic muscarinic receptor activation. J Neurochem. 1992 Jul;59(1):383–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcikiewicz R. J., Tobin A. B., Nahorski S. R. Desensitization of cell signalling mediated by phosphoinositidase C. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jul;14(7):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]