Abstract
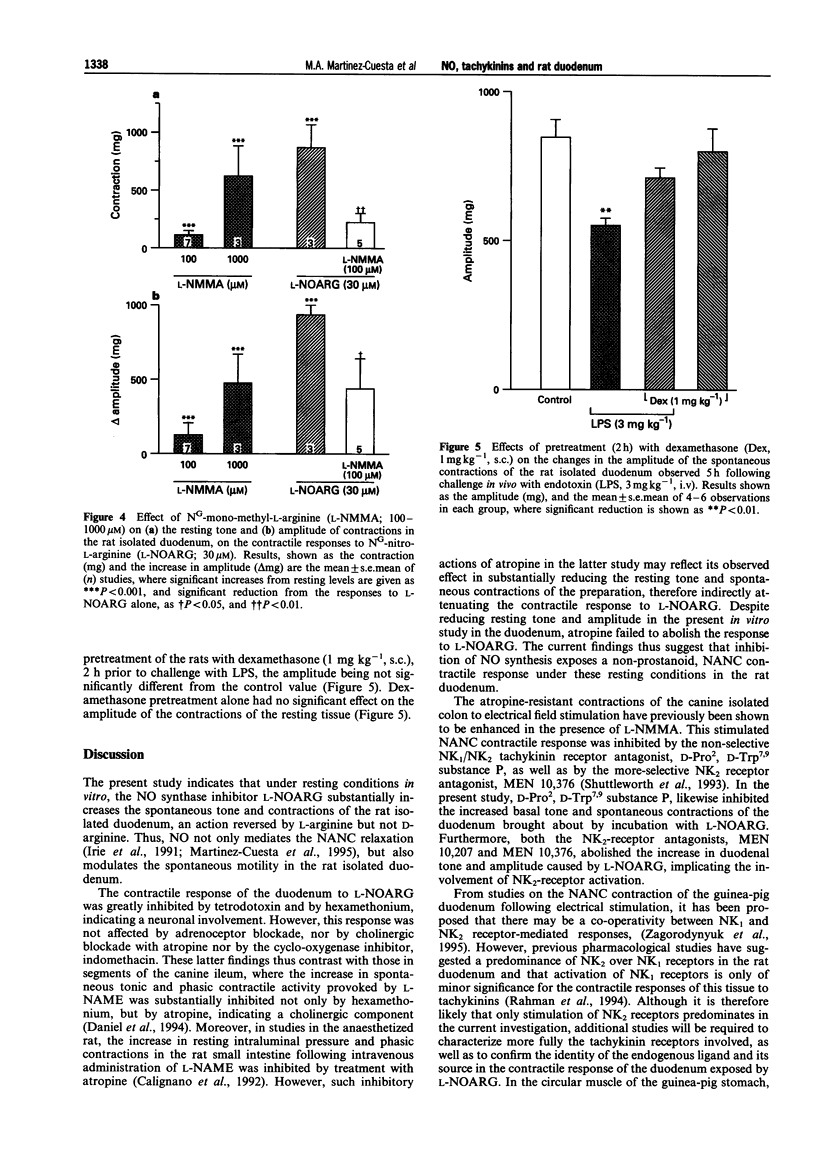
1. Incubation of proximal segments of the rat isolated duodenum with NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOARG; 3-100 microM) produced a concentration-dependent increase in both resting tone and the amplitude of the spontaneous contractions. These effects were attenuated by concurrent incubation with L-arginine (1 mM) but not D-arginine (1 mM). 2. These changes in resting tone and motility induced by L-NOARG (30 microM) were substantially reduced by concurrent incubation with tetrodotoxin (1 microM) or hexamethonium (10 microM), implicating the involvement of a local neuronal response. 3. The L-NOARG-induced increase in duodenal motility was not, however, inhibited by atropine (1 microM), guanethidine (6.4 microM) phentolamine (1 microM), or indomethacin (10 microM), indicating a non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic and non-prostanoid-mediated contractile response. 4. The NK1/NK2 tachykinin receptor antagonist, (D-Pro2, D-Trp7.9 substance P, 1-10 microM), and the NK2-receptor antagonists, MEN 10,207 and MEN 10,376 (1-5 microM), concentration-dependently reduced the effect of L-NOARG (30 microM) on spontaneous duodenal motility. 5. The resting tone and amplitude of the spontaneous contractions was likewise increased by incubation with NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA; 100-1000 microM). However, incubation with L-NMMA (100 microM) attenuated the actions of more potent L-NOARG (30 microM) on resting motility. 6. Administration of E.coli endotoxin (3 mg kg-1, i.v.) to the rat 5 h prior to tissue removal, at a time of known induction of NO synthase, reduced the amplitude of spontaneous contractions of the isolated duodenum, an effect inhibited by pretreatment of the rats with dexamethasone (1 mg kg-1) 2 h prior to endotoxin challenge. 7. These findings indicate a role of endogenous NO in the modulation of spontaneous tone and motility in the rat duodenum. Induction of NO synthase may result in a reduction in spontaneous motility of the tissue. By contrast, inhibition of constitutive NO biosynthesis unmasks a contractile response that is neuronally mediated and involves tachykinin NK2 receptors.
Full text
PDF

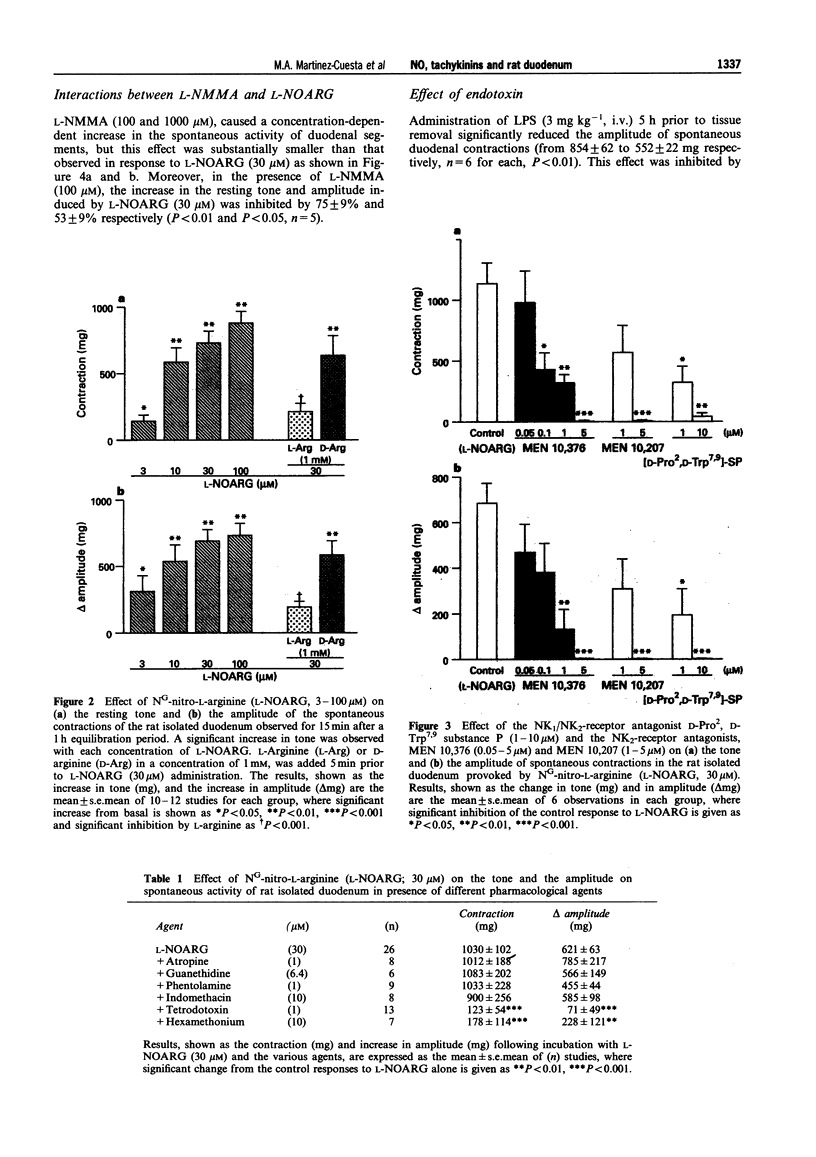


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bogers J. J., Bult H., De Man J. G., Oosterbosch L., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Release of nitric oxide upon stimulation of nonadrenergic noncholinergic nerves in the rat gastric fundus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):441–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bult H., De Man J. G., Herman A. G., van Maercke Y. M. Evidence for nitric oxide as mediator of non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxations induced by ATP and GABA in the canine gut. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):434–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12191.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Involvement of nitric oxide in the inhibitory innervation of the human isolated colon. Gastroenterology. 1993 Mar;104(3):690–697. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91003-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bult H., Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Jordaens F. H., Van Maercke Y. M., Herman A. G. Nitric oxide as an inhibitory non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmitter. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):346–347. doi: 10.1038/345346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burleigh D. E. Ng-nitro-L-arginine reduces nonadrenergic, noncholinergic relaxations of human gut. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):679–683. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90120-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calignano A., Whittle B. J., Di Rosa M., Moncada S. Involvement of endogenous nitric oxide in the regulation of rat intestinal motility in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 15;229(2-3):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90567-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel E. E., Haugh C., Woskowska Z., Cipris S., Jury J., Fox-Threlkeld J. E. Role of nitric oxide-related inhibition in intestinal function: relation to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 1):G31–G39. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.266.1.G31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai K. M., Sessa W. C., Vane J. R. Involvement of nitric oxide in the reflex relaxation of the stomach to accommodate food or fluid. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):477–479. doi: 10.1038/351477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie K., Muraki T., Furukawa K., Nomoto T. L-NG-nitro-arginine inhibits nicotine-induced relaxation of isolated rat duodenum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 17;202(2):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin J. G., Misra S., Grider J. R., Makhlouf G. M. Functional difference between SP and NKA: relaxation of gastric muscle by SP is mediated by VIP and NO. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):G678–G685. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.4.G678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanada A., Hata F., Suthamnatpong N., Maehara T., Ishii T., Takeuchi T., Yagasaki O. Key roles of nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in nonadrenergic and noncholinergic inhibition in rat ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 5;216(2):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90372-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre R. A., Hasrat J., Gobert A. Influence of NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester on vagally induced gastric relaxation in the anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):315–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. G., Rand M. J. Nitric oxide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mediate non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory transmission to smooth muscle of the rat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 4;191(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94162-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Barbanti G., Turini D., Giuliani S. Effect of NG-monomethyl L-arginine (L-NMMA) and NG-nitro L-arginine (L-NOARG) on non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation in the circular muscle of the human ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1970–1972. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Gillespie J. S., Gibson I. F. Actions and interactions of NG-substituted analogues of L-arginine on NANC neurotransmission in the bovine retractor penis and rat anococcygeus muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):242–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Cuesta M. A., Massuda H., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. Impairment of nitrergic-mediated relaxation of rat isolated duodenum by experimental diabetes. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;114(5):919–924. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton S. J., Cuthbert A. W., Shorthouse M., Hunter J. O. Nitric oxide affects mammalian distal colonic smooth muscle by tonic neural inhibition. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;108(4):974–979. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niklasson L. G., Fasth S., Hultén L., Delbro D. S. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase causes excitation of the circular muscle in rat distal colon. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Apr;144(4):489–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman M., Lördal M., al-Saffar A., Hellström P. M. Intestinal motility responses to neuropeptide gamma in vitro and in vivo in the rat: comparison with neurokinin 1 and neurokinin 2 receptor agonists. Acta Physiol Scand. 1994 Aug;151(4):497–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1994.tb09772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M., Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Widespread tissue distribution, species distribution and changes in activity of Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent nitric oxide synthases. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 7;291(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81123-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth C. W., Sanders K. M., Keef K. D. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis reveals non-cholinergic excitatory neurotransmission in the canine proximal colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepperman B. L., Brown J. F., Whittle B. J. Nitric oxide synthase induction and intestinal epithelial cell viability in rats. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):G214–G218. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.2.G214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N., Baba H., Okamura T. Role of nitric oxide in non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic nerve-mediated relaxation in dog duodenal longitudinal muscle strips. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;53(2):281–284. doi: 10.1254/jjp.53.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. M., Dalziel H. H., Bradley M. E., Buxton I. L., Keef K., Westfall D. P., Sanders K. M. Involvement of cyclic GMP in non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory neurotransmission in dog proximal colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):1075–1082. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund C. U., Olgart C., Wiklund N. P., Gustafsson L. E. Modulation of cholinergic and substance P-like neurotransmission by nitric oxide in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):833–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorodnyuk V., Santicioli P., Maggi C. A., Giachetti A. Evidence that tachykinin NK1 and NK2 receptors mediate non-adrenergic non-cholinergic excitation and contraction in the circular muscle of guinea-pig duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(2):237–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15869.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



