Abstract
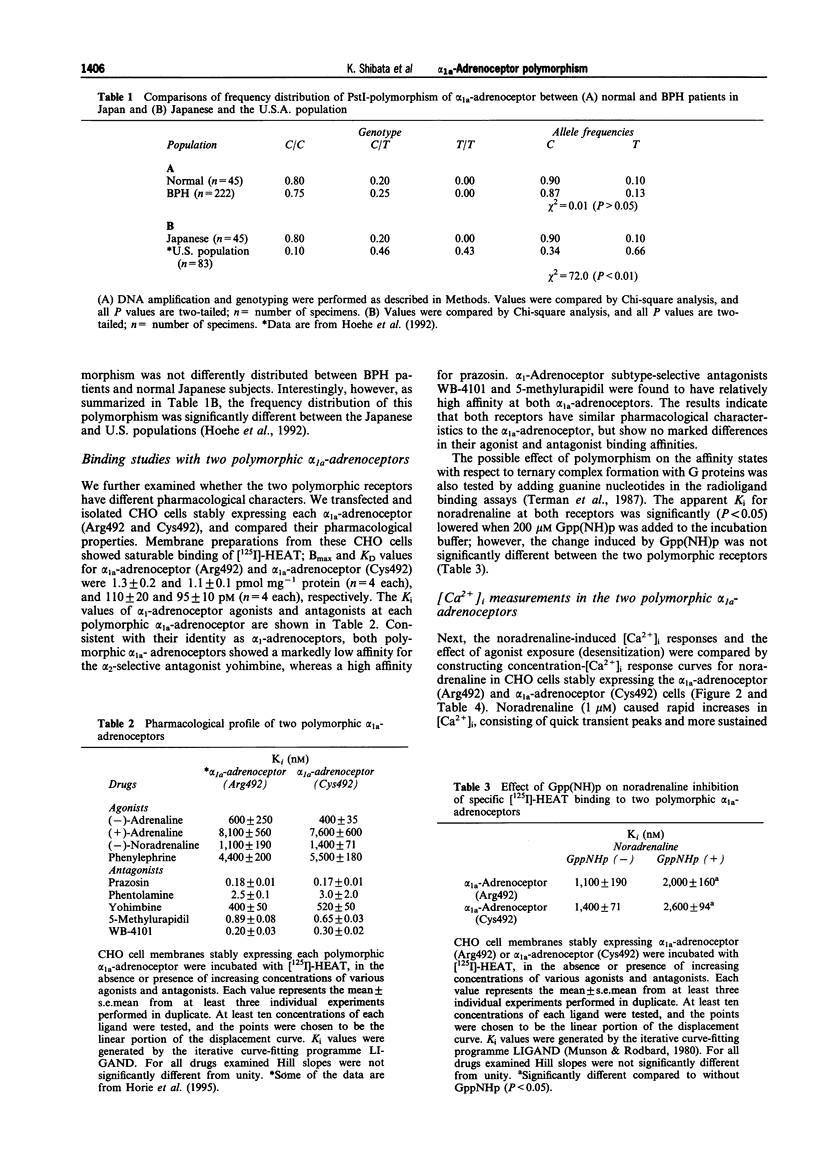
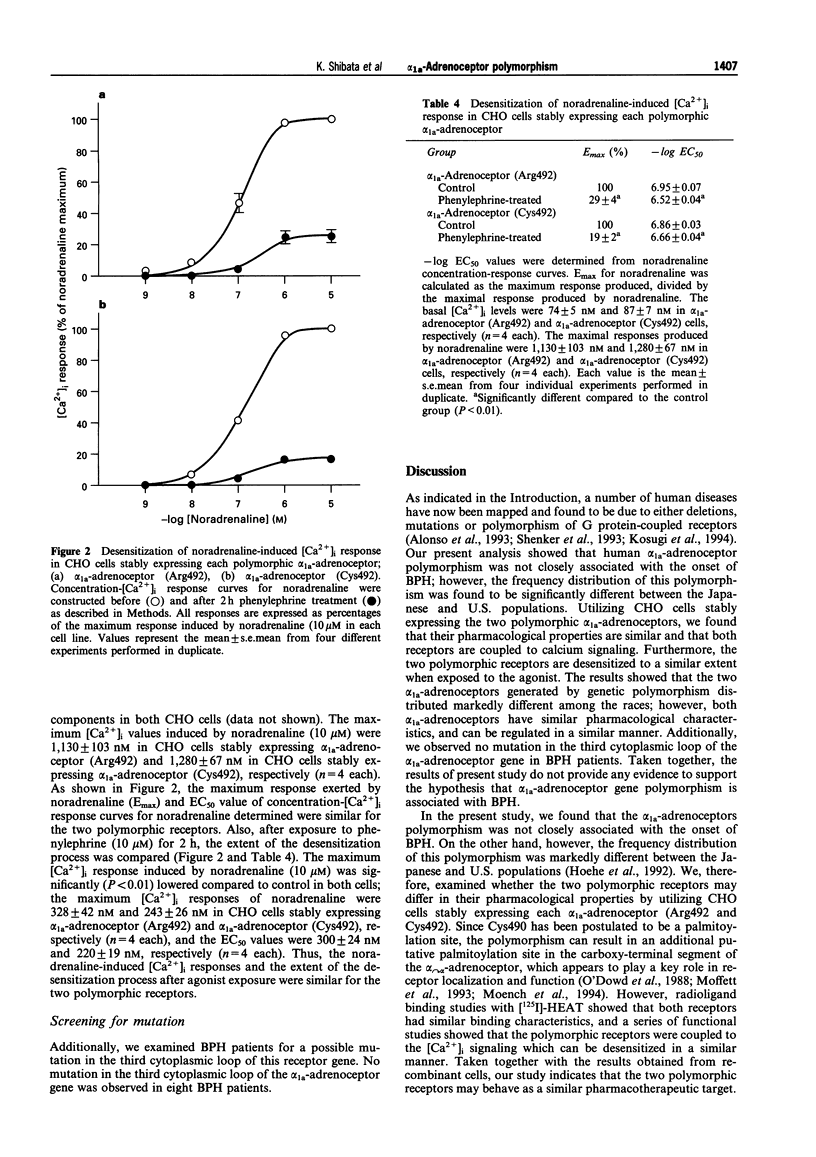
1. Two restriction fragment length polymorphisms of the human alpha 1a-adrenoceptor gene digested with PstI restriction enzyme exist; the nucleotide change causes the substitution of C residue for T at nucleotide 1441, thereby Arg492 to Cys492 transition, which might confer an additional putative palmitoylation site in the carboxy-terminal segment of the alpha 1a-adrenoceptor. In the present study, we compared their pharmacological properties and examined whether this alpha 1a-adrenoceptor polymorphism is associated with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). 2. The frequency of alpha 1a-adrenoceptor polymorphism was not differently distributed between patients with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) and normal subjects in Japan; thus, the relative frequencies of the C and T alleles were 0.90 : 0.10 in normal male subjects (n = 45) and 0.87 : 0.13 in BPH patients (n = 222), respectively. However, the frequency distribution of this polymorphism was significantly different between the Japanese and U.S. populations; thus, C and T alleles were 0.34 and 0.66 in U.S. populations. 3. Utilizing Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells stably expressing the two polymorphic alpha 1a-adrenoceptors (Arg492 and Cys492), we compared their binding affinity and signal transduction. Radioligand binding studies with 2-[beta-(4-hydroxy-3[125I]-iodophenyl) ethylamino-methyl]tetralone ([125I]-HEAT) showed no marked difference in the antagonist or agonist binding affinities between the two receptors. Also, both receptors were found to be coupled to the calcium signaling, and the concentration-cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations ([Ca2+]i) response relationships for noradrenaline were similar for the two polymorphic receptors. Furthermore, the receptor-mediated [Ca2+]i response was markedly desensitized after a 2 h exposure of phenylephrine (10 microM), and the extent of the desensitization was not significantly different between the two receptors. 4. In summary, the results showed that the two alpha 1a-adrenoceptors generated by genetic polymorphism have similar pharmacological characteristics, and the receptor-mediated [Ca2+]i response can be desensitized in a similar manner. The study did not provide any evidence to support the hypothesis that alpha 1a-adrenoceptor gene polymorphism is associated with BPH.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen L. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Cotecchia S. G-protein-coupled receptor genes as protooncogenes: constitutively activating mutation of the alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor enhances mitogenesis and tumorigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11354–11358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Llamazares A., Zamanillo D., Fernández A., Chinchetru M. A., Calvo P. Differential expression of the alpha 1c adrenergic receptor subtype in rat tissues. Neuroreport. 1993 Sep 10;4(11):1266–1268. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199309000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caine M., Raz S., Zeigler M. Adrenergic and cholinergic receptors in the human prostate, prostatic capsule and bladder neck. Br J Urol. 1975 Apr;47(2):193–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1975.tb03947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Exum S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regions of the alpha 1-adrenergic receptor involved in coupling to phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and enhanced sensitivity of biological function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2896–2900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forray C., Bard J. A., Wetzel J. M., Chiu G., Shapiro E., Tang R., Lepor H., Hartig P. R., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. A. The alpha 1-adrenergic receptor that mediates smooth muscle contraction in human prostate has the pharmacological properties of the cloned human alpha 1c subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):703–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., Bylund D. B., Clarke D. E., Eikenburg D. C., Langer S. Z., Lefkowitz R. J., Minneman K. P., Ruffolo R. R., Jr International Union of Pharmacology. X. Recommendation for nomenclature of alpha 1-adrenoceptors: consensus update. Pharmacol Rev. 1995 Jun;47(2):267–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa A., Horie K., Tanaka T., Takagaki K., Murai M., Yano J., Tsujimoto G. Cloning, functional expression and tissue distribution of human cDNA for the alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Sep 15;195(2):902–909. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie K., Hirasawa A., Tsujimoto G. The pharmacological profile of cloned and stably expressed alpha 1b-adrenoceptor in CHO cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug 16;268(3):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie K., Obika K., Foglar R., Tsujimoto G. Selectivity of the imidazoline alpha-adrenoceptor agonists (oxymetazoline and cirazoline) for human cloned alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Sep;116(1):1611–1618. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelsberg M. A., Cotecchia S., Ostrowski J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Constitutive activation of the alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor by all amino acid substitutions at a single site. Evidence for a region which constrains receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1430–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosugi S., Shenker A., Mori T. Constitutive activation of cyclic AMP but not phosphatidylinositol signaling caused by four mutations in the 6th transmembrane helix of the human thyrotropin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 19;356(2-3):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepor H., Tang R., Meretyk S., Shapiro E. Alpha 1 adrenoceptor subtypes in the human prostate. J Urol. 1993 Mar;149(3):640–642. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moench S. J., Moreland J., Stewart D. H., Dewey T. G. Fluorescence studies of the location and membrane accessibility of the palmitoylation sites of rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1994 May 17;33(19):5791–5796. doi: 10.1021/bi00185a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett S., Mouillac B., Bonin H., Bouvier M. Altered phosphorylation and desensitization patterns of a human beta 2-adrenergic receptor lacking the palmitoylated Cys341. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):349–356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Regan J. W., Leader W. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cytoplasmic domains of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Localization of regions involved in G protein-receptor coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15985–15992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. T., Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Allen L. F., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification, quantification, and localization of mRNA for three distinct alpha 1 adrenergic receptor subtypes in human prostate. J Urol. 1993 Aug;150(2 Pt 1):546–551. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35544-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober J. M., Trainor G. L., Dam R. J., Hobbs F. W., Robertson C. W., Zagursky R. J., Cocuzza A. J., Jensen M. A., Baumeister K. A system for rapid DNA sequencing with fluorescent chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):336–341. doi: 10.1126/science.2443975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramarao C. S., Denker J. M., Perez D. M., Gaivin R. J., Riek R. P., Graham R. M. Genomic organization and expression of the human alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21936–21945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanda M. G., Beaty T. H., Stutzman R. E., Childs B., Walsh P. C. Genetic susceptibility of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 1994 Jul;152(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)32831-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker A., Laue L., Kosugi S., Merendino J. J., Jr, Minegishi T., Cutler G. B., Jr A constitutively activating mutation of the luteinizing hormone receptor in familial male precocious puberty. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):652–654. doi: 10.1038/365652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata K., Foglar R., Horie K., Obika K., Sakamoto A., Ogawa S., Tsujimoto G. KMD-3213, a novel, potent, alpha 1a-adrenoceptor-selective antagonist: characterization using recombinant human alpha 1-adrenoceptors and native tissues. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;48(2):250–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terman B. I., Slivka S. R., Hughes R. J., Insel P. A. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-linked guanine nucleotide-binding protein in muscle and kidney epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;31(1):12–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




