Abstract
1. The effect of the biguanide metformin on hexose transport activity was studied in bovine cultured aortic endothelial (BEC) and smooth muscle cells (BSMC). 2. Metformin elevated the rate of hexose transport determined with 2-deoxyglucose (2DG) in a dose- and time-dependent manner in both cell types. Similar ED50 values (0.8-1.0 mM) were determined for the effect of metformin on 2DG uptake in both BEC and BSMC following 24 h exposure to increasing concentrations of metformin, with maximal stimulation at 2 mM. 3. In BEC, metformin increased the hexose transport rate 2-3 fold at all glucose concentrations tested (3.3-22.2 mM). In BSMC incubated with 22.2 mM glucose, metformin elevated the hexose transport approximately 2 fold. The drug was also effective at lower glucose levels, but did not exceed the maximal transport rate observed in glucose-deprived cells. 4. Similar results were obtained when the effect of metformin on hexose transport activity was assessed with the non-metabolizable hexose analogue, 3-O-methylglucose, suggesting that the drug affects primarily the rate of hexose transport rather than its subsequent phosphorylation. 5. The metformin-induced increase in hexose transport in BSMC treated for 24 h with the drug correlated with increased abundance of GLUT1 protein in the plasma membrane, as determined by Western blot analysis. 6. These data indicate that in addition to its known effects on hexose metabolism in insulin responsive tissues, metformin also affects the hexose transport system in vascular cells. This may contribute to its blood glucose lowering capacity in patients with Type 2, non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Full text
PDF

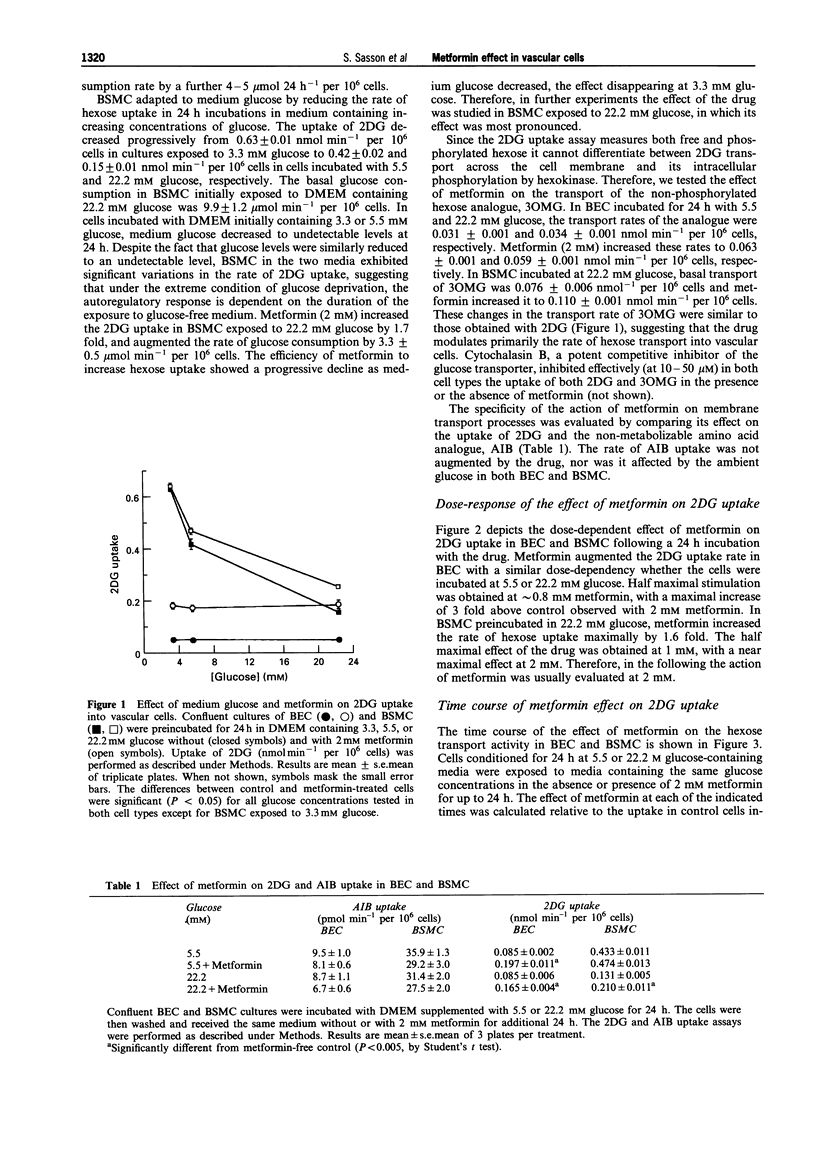
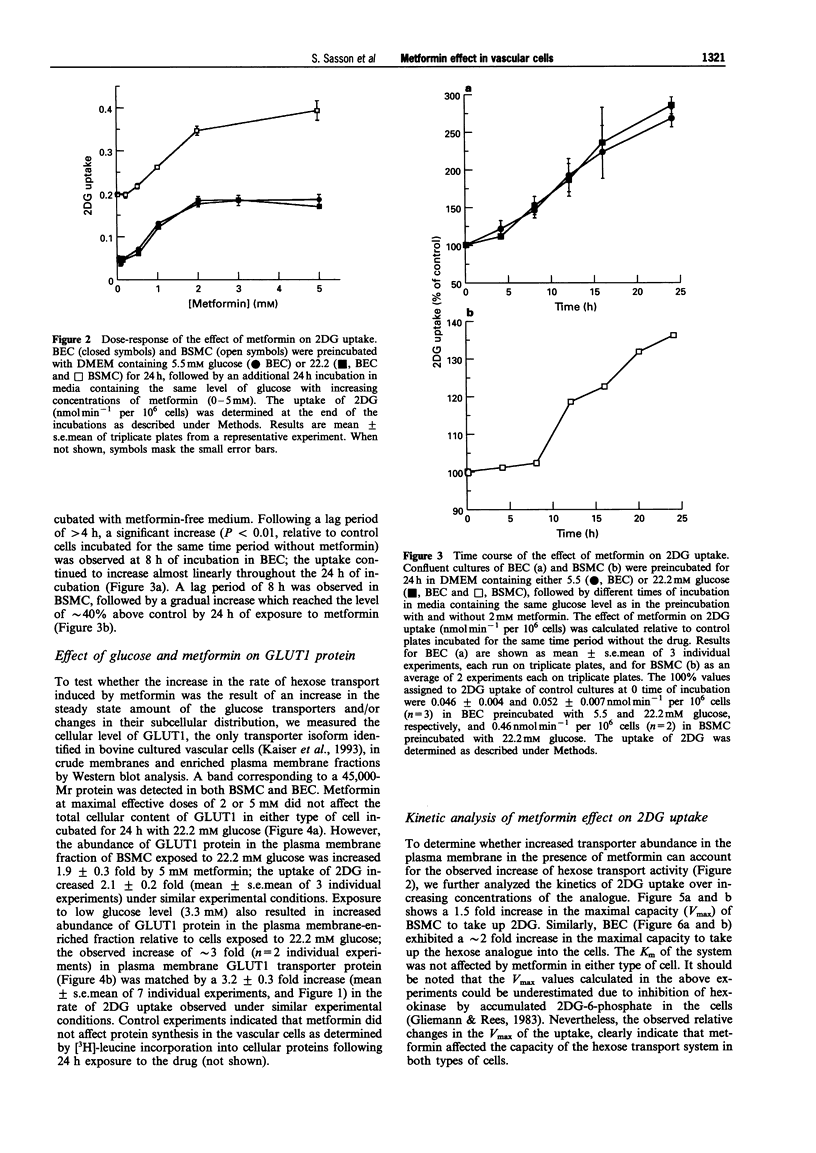
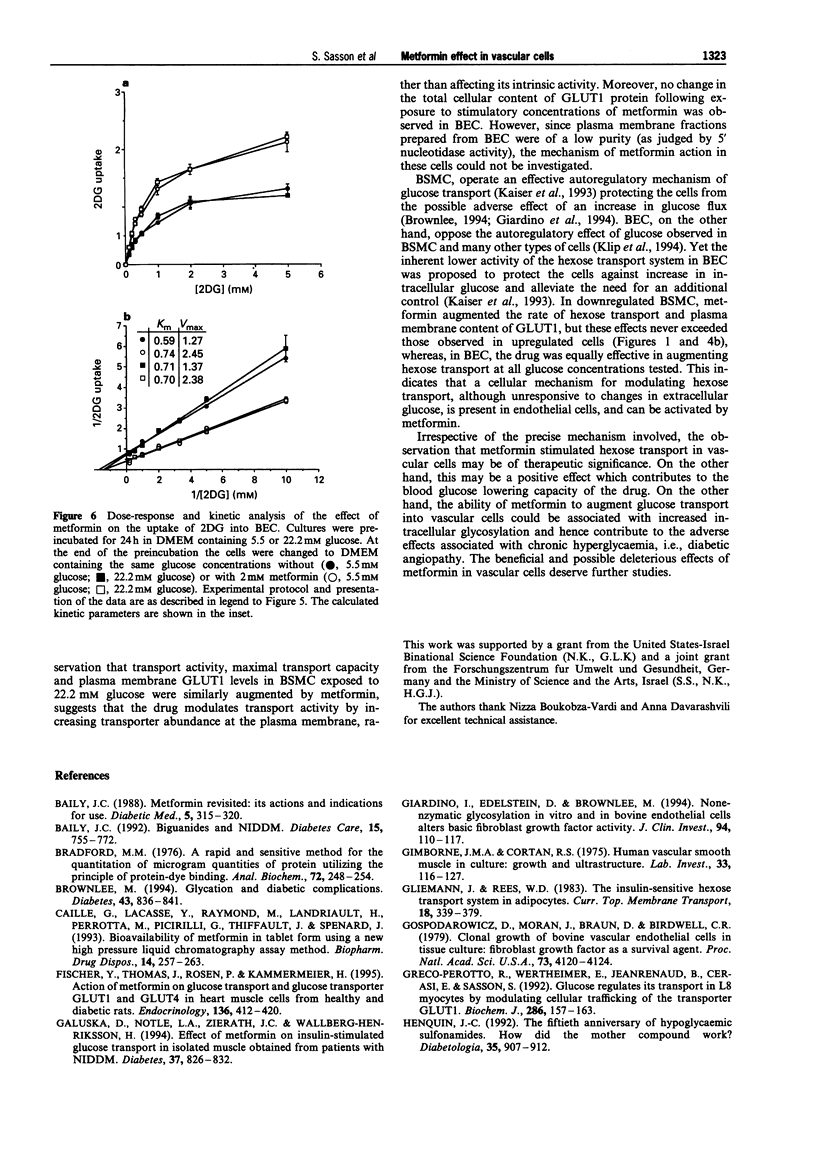

Images in this article
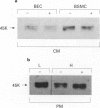
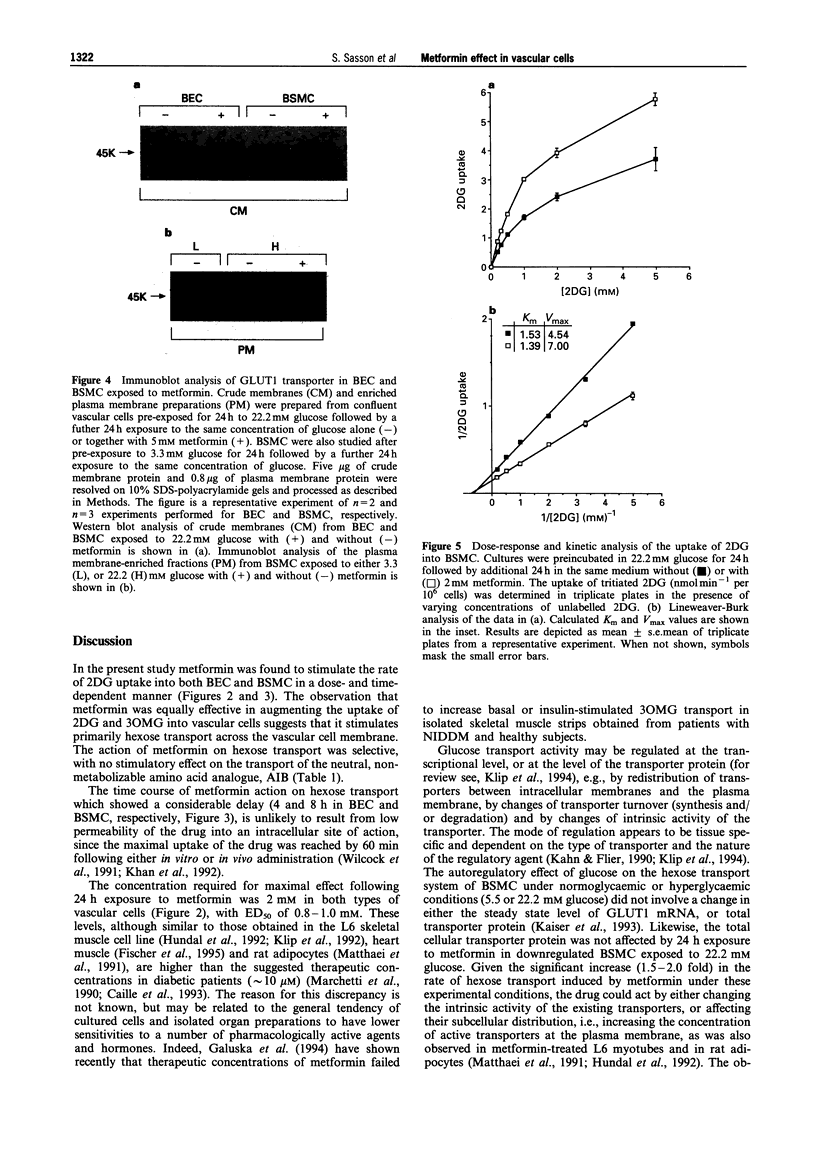
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey C. J. Biguanides and NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1992 Jun;15(6):755–772. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.6.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey C. J. Metformin revisited: its actions and indications for use. Diabet Med. 1988 May-Jun;5(4):315–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1988.tb00996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M. Lilly Lecture 1993. Glycation and diabetic complications. Diabetes. 1994 Jun;43(6):836–841. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.6.836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillé G., Lacasse Y., Raymond M., Landriault H., Perrotta M., Picirilli G., Thiffault J., Spénard J. Bioavailability of metformin in tablet form using a new high pressure liquid chromatography assay method. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1993 Apr;14(3):257–263. doi: 10.1002/bdd.2510140308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer Y., Thomas J., Rösen P., Kammermeier H. Action of metformin on glucose transport and glucose transporter GLUT1 and GLUT4 in heart muscle cells from healthy and diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 1995 Feb;136(2):412–420. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.2.7835271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardino I., Edelstein D., Brownlee M. Nonenzymatic glycosylation in vitro and in bovine endothelial cells alters basic fibroblast growth factor activity. A model for intracellular glycosylation in diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jul;94(1):110–117. doi: 10.1172/JCI117296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J., Braun D., Birdwell C. Clonal growth of bovine vascular endothelial cells: fibroblast growth factor as a survival agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco-Perotto R., Wertheimer E., Jeanrenaud B., Cerasi E., Sasson S. Glucose regulates its transport in L8 myocytes by modulating cellular trafficking of the transporter GLUT-1. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 15;286(Pt 1):157–163. doi: 10.1042/bj2860157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. The fiftieth anniversary of hypoglycaemic sulphonamides. How did the mother compound work? Diabetologia. 1992 Oct;35(10):907–912. doi: 10.1007/BF00401417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundal H. S., Ramlal T., Reyes R., Leiter L. A., Klip A. Cellular mechanism of metformin action involves glucose transporter translocation from an intracellular pool to the plasma membrane in L6 muscle cells. Endocrinology. 1992 Sep;131(3):1165–1173. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.3.1505458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Hawa M. I., Jaspan J. B., Sim B. M., Disilvio L., Featherbe D., Kurtz A. B. Mechanism of metformin action in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1987 May;36(5):632–640. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.5.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Flier J. S. Regulation of glucose-transporter gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jun;13(6):548–564. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.6.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser N., Sasson S., Feener E. P., Boukobza-Vardi N., Higashi S., Moller D. E., Davidheiser S., Przybylski R. J., King G. L. Differential regulation of glucose transport and transporters by glucose in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):80–89. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan N. A., Wiernsperger N., Quemener V., Havouis R., Moulinoux J. P. Characterization of metformin transport system in NIH 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Aug;152(2):310–316. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Gumà A., Ramlal T., Bilan P. J., Lam L., Leiter L. A. Stimulation of hexose transport by metformin in L6 muscle cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1992 May;130(5):2535–2544. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.5.1572281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Tsakiridis T., Marette A., Ortiz P. A. Regulation of expression of glucose transporters by glucose: a review of studies in vivo and in cell cultures. FASEB J. 1994 Jan;8(1):43–53. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.1.8299889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti P., Gregorio F., Benzi L., Giannarelli R., Cecchetti P., Villani G., Di Cianni G., Di Carlo A., Brunetti P., Navalesi R. Diurnal pattern of plasma metformin concentrations and its relation to metabolic effects in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabete Metab. 1990 Dec;16(6):473–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthaei S., Hamann A., Klein H. H., Benecke H., Kreymann G., Flier J. S., Greten H. Association of Metformin's effect to increase insulin-stimulated glucose transport with potentiation of insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters from intracellular pool to plasma membrane in rat adipocytes. Diabetes. 1991 Jul;40(7):850–857. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.7.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Ipaktchi M., Clauser H. Specific inhibition of gluconeogenesis by biguanides. Nature. 1967 Jan 14;213(5072):203–204. doi: 10.1038/213203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Nielsen O., Bak J., Richelsen B., Beck-Nielsen H., Sørensen N. The effects of metformin on adipocyte insulin action and metabolic control in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 1989 Apr;6(3):249–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1989.tb01156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. G., Pearson J. D. The influence of hypoglycaemic agents on the growth and metabolism of human endothelial cells. Diabet Med. 1992 Jan-Feb;9(1):30–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1992.tb01710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarabia V., Lam L., Burdett E., Leiter L. A., Klip A. Glucose transport in human skeletal muscle cells in culture. Stimulation by insulin and metformin. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1386–1395. doi: 10.1172/JCI116005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasson S., Cerasi E. Substrate regulation of the glucose transport system in rat skeletal muscle. Characterization and kinetic analysis in isolated soleus muscle and skeletal muscle cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16827–16833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland M., Schürmann A., Schmidt W. E., Joost H. G. Development of the hormone-sensitive glucose transport activity in differentiating 3T3-L1 murine fibroblasts. Role of the two transporter species and their subcellular localization. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):331–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2700331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock C., Wyre N. D., Bailey C. J. Subcellular distribution of metformin in rat liver. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;43(6):442–444. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1991.tb03507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollen N., Bailey C. J. Inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis by metformin. Synergism with insulin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 15;37(22):4353–4358. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90617-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M. S., Johnston P., Sheu W. H., Hollenbeck C. B., Jeng C. Y., Goldfine I. D., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Effect of metformin on carbohydrate and lipoprotein metabolism in NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]