Abstract
1. Functional GABA-gated chloride channels are formed when cRNA encoding the Drosophila melanogaster GABA receptor subunit RDL is injected into the cytoplasm of Xenopus oocytes. Two-electrode voltage-clamp was used to investigate allosteric modulation of GABA-induced currents recorded from the expressed, bicuculline-insensitive, RDL homo-oligomers. 2. Flunitrazepam (0.1 microM to 100 microM) had no effect on the amplitude of responses to 10 microM GABA (approximately EC10), whereas 4'chlorodiazepam (100 microM) enhanced the amplitude of submaximal responses to GABA. 3-Hydroxymethyl-beta-carboline (1 microM) and ethyl-beta-carboline-3-carboxylate (both 1 and 100 microM) had no effect on currents induced by 30 microM (approximately EC50) GABA. However 100 microM 3-hydroxymethyl-beta-carboline reduced potentiation by 4'chlorodiazepam. 3. The sodium salts of pentobarbitone (10 microM to 1 mM) and phenobarbitone (50 microM to 1 mM) dose-dependently enhanced submaximal GABA responses. Neither barbiturate activated currents in the absence of GABA. 4. At 10 microM, the steroids 5 alpha-pregnan-3 alpha-ol-20-one and alphaxalone (5 alpha-pregnan-3 alpha-ol-11,20-dione), potentiated submaximal GABA responses. The stereoselectivity of steroid action seen on vertebrate GABAA receptors was observed on RDL homo-oligomers as 5 alpha-pregnan-3 beta-ol-20-one (10 microM) was without effect. None of the three steroids tested activated currents in the absence of GABA. 5. The novel anticonvulsant, loreclezole (100 microM), potentiated the response to 10 microM GABA, but not that of saturating concentrations of GABA. delta-Hexachlorocyclohexane (0.1 microM to 30 microM) was a potent enhancer of submaximal responses to GABA of RDL. 6. The potencies of barbiturates and steroids on RDL homo-oligomers resemble those observed for several in situ insect GABA receptors, whereas those of benzodiazepine binding-site ligands are considerably reduced. The differences in the benzodiazepine pharmacology of RDL homo-oligomers and native GABA receptors, may reflect roles of other subunits in native insect receptors.
Full text
PDF

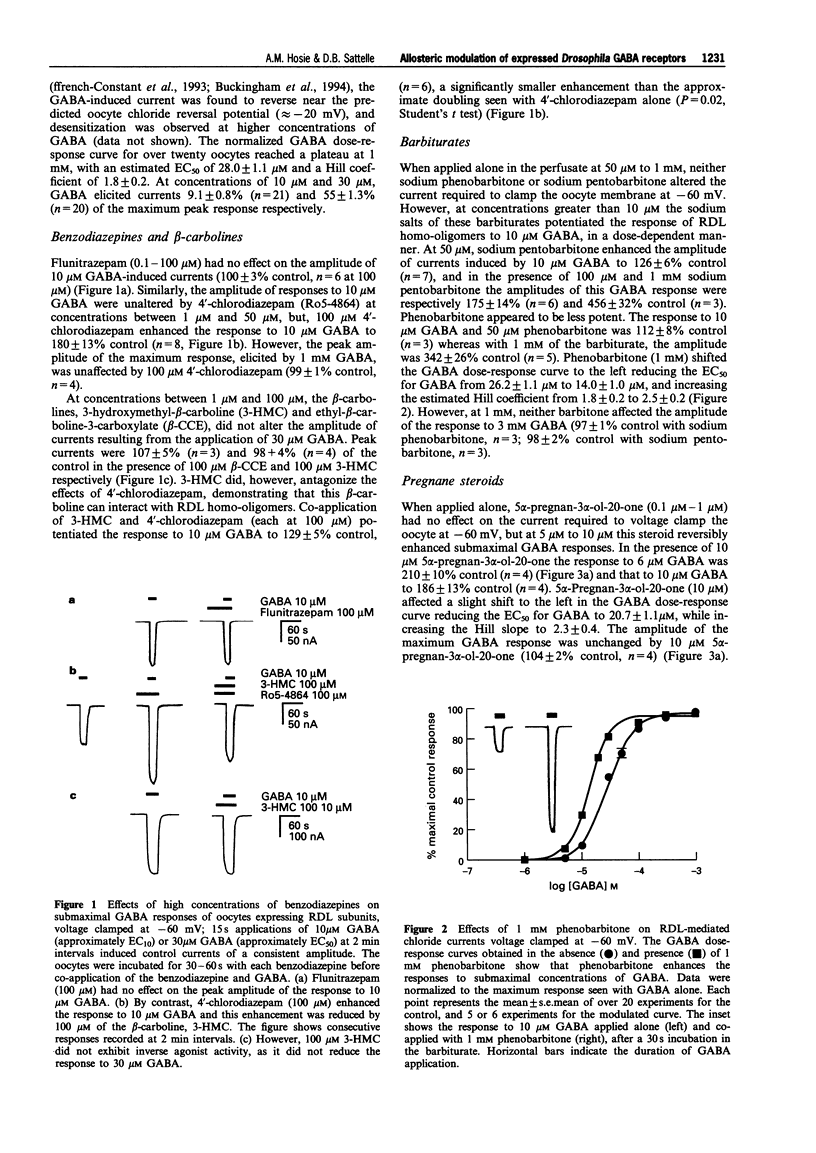
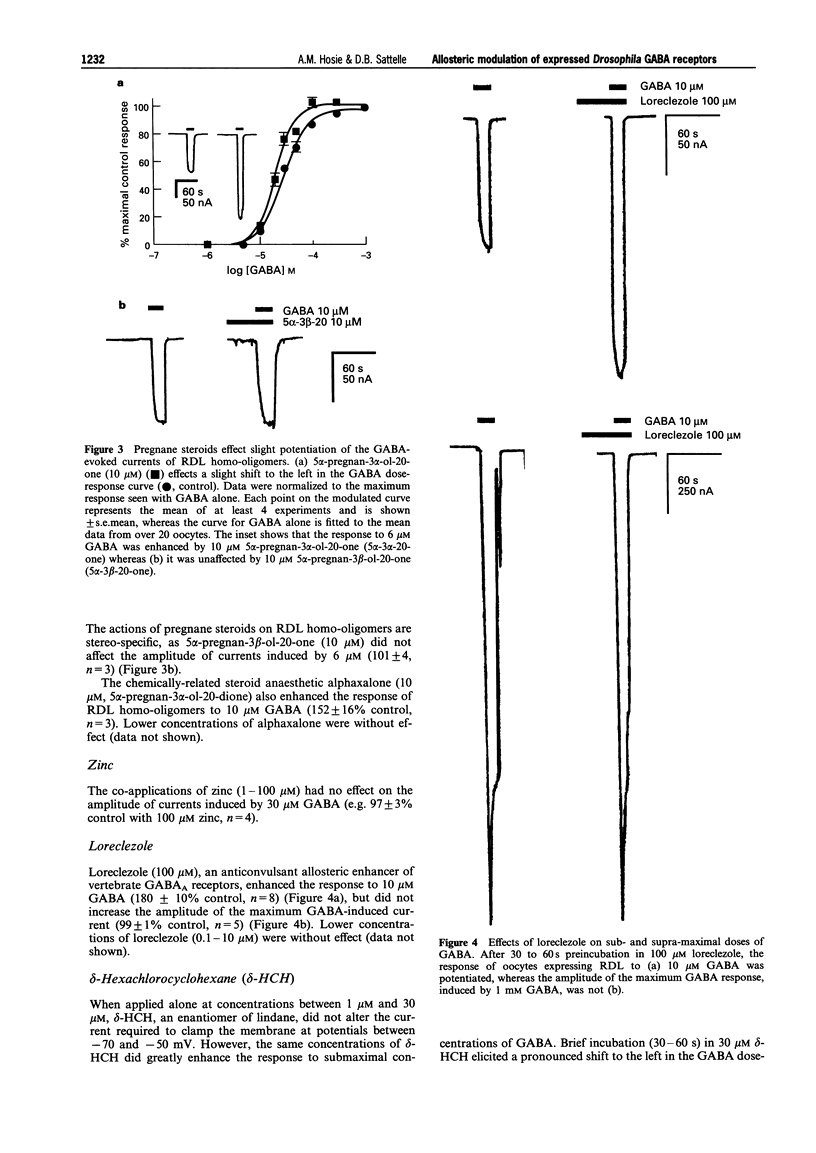
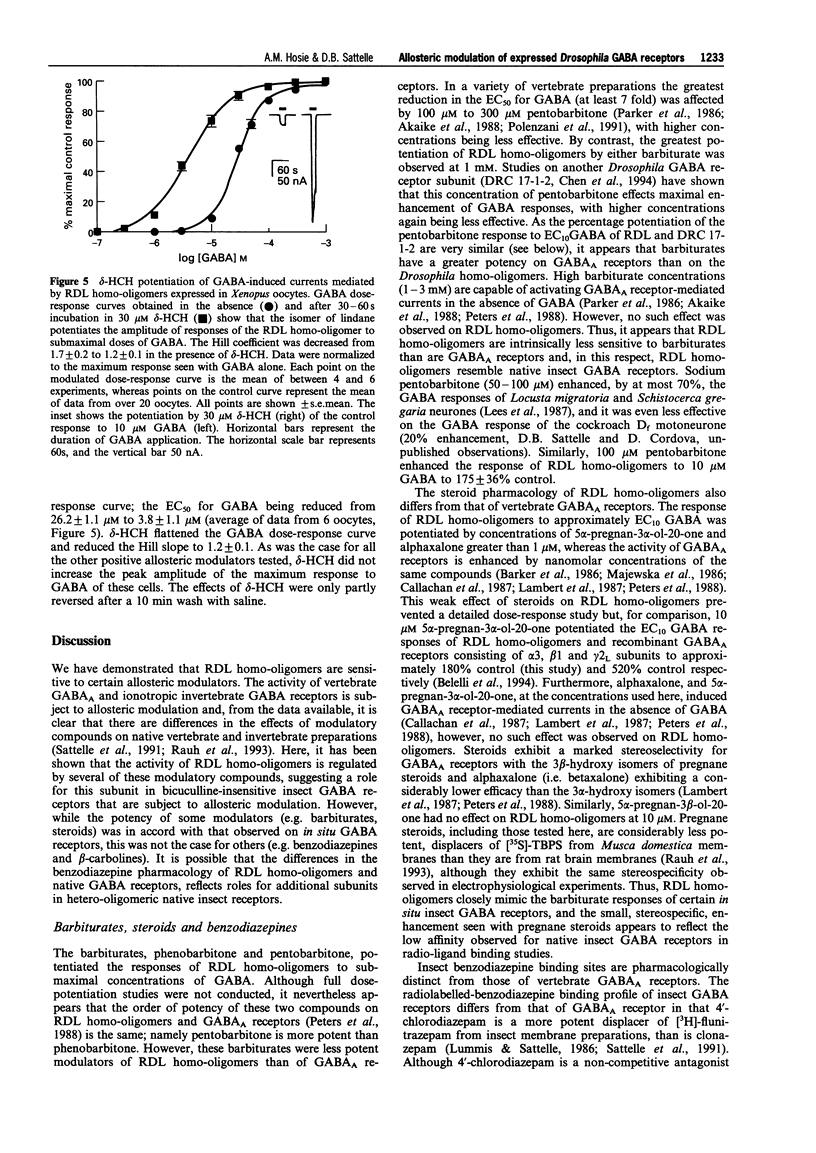




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike N., Hattori K., Inomata N., Oomura Y. gamma-Aminobutyric-acid- and pentobarbitone-gated chloride currents in internally perfused frog sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:367–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony N. M., Harrison J. B., Sattelle D. B. GABA receptor molecules of insects. EXS. 1993;63:172–209. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7265-2_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Schmiechen R., Neef G., Nielsen M., Petersen E. N. Interaction of convulsive ligands with benzodiazepine receptors. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1241–1243. doi: 10.1126/science.6281892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham S. D., Hosie A. M., Roush R. L., Sattelle D. B. Actions of agonists and convulsant antagonists on a Drosophila melanogaster GABA receptor (Rdl) homo-oligomer expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Nov 7;181(1-2):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90578-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callachan H., Cottrell G. A., Hather N. Y., Lambert J. J., Nooney J. M., Peters J. A. Modulation of the GABAA receptor by progesterone metabolites. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Aug 21;231(1264):359–369. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Belelli D., Lambert J. J., Peters J. A., Reyes A., Lan N. C. Cloning and functional expression of a Drosophila gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6069–6073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlison M. G. Invertebrate GABA and glutamate receptors: molecular biology reveals predictable structures but some unusual pharmacologies. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Dec;15(12):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90091-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draguhn A., Verdorn T. A., Ewert M., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional and molecular distinction between recombinant rat GABAA receptor subtypes by Zn2+. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):781–788. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90337-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenspan A., Wässle H., Bormann J. Pharmacology of GABA receptor Cl- channels in rat retinal bipolar cells. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):159–162. doi: 10.1038/361159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ffrench-Constant R. H., Mortlock D. P., Shaffer C. D., MacIntyre R. J., Roush R. T. Molecular cloning and transformation of cyclodiene resistance in Drosophila: an invertebrate gamma-aminobutyric acid subtype A receptor locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7209–7213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ffrench-Constant R. H., Rocheleau T. A., Steichen J. C., Chalmers A. E. A point mutation in a Drosophila GABA receptor confers insecticide resistance. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):449–451. doi: 10.1038/363449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. J., Schmitt B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H., Darlison M. G. Sequence of a Drosophila ligand-gated ion-channel polypeptide with an unusual amino-terminal extracellular domain. J Neurochem. 1994 Jun;62(6):2480–2483. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62062480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. E., Soderlund D. M., Knipple D. C. Characterization of a putative gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor beta subunit gene from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 15;193(2):474–482. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Chen J. S., Belelli D., Pritchett D. B., Seeburg P. H., Gee K. W. A steroid recognition site is functionally coupled to an expressed GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 12;188(6):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Gee K. W., Bolger M. B., Chen J. S. Differential responses of expressed recombinant human gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors to neurosteroids. J Neurochem. 1991 Nov;57(5):1818–1821. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb06388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. J., Rocheleau T., Zhang H. G., Jackson M. B., ffrench-Constant R. H. Expression of a Drosophila GABA receptor in a baculovirus insect cell system. Functional expression of insecticide susceptible and resistant GABA receptors from the cyclodiene resistance gene Rdl. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 13;335(3):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80409-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees G., Beadle D. J., Neumann R., Benson J. A. Responses to GABA by isolated insect neuronal somata: pharmacology and modulation by a benzodiazepine and a barbiturate. Brain Res. 1987 Jan 20;401(2):267–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91411-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Harrison N. L., Schwartz R. D., Barker J. L., Paul S. M. Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):1004–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.2422758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar N. S., Buckingham S. D., Sattelle D. B. Stable expression of a functional homo-oligomeric Drosophila GABA receptor in a Drosophila cell line. Proc Biol Sci. 1994 Dec 22;258(1353):307–314. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1994.0178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühl H., Kunz D., Pfeilschifter J. Expression of nitric oxide synthase in rat glomerular mesangial cells mediated by cyclic AMP. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13019.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Szamraj O., Miller T. t-[35S]butylbicyclophosphorothionate binding sites in invertebrate tissues. J Neurochem. 1989 Apr;52(4):1311–1318. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb01880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortells M. O., Lunt G. G. Evolutionary history of the ligand-gated ion-channel superfamily of receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Mar;18(3):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)93887-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Gundersen C. B., Miledi R. Actions of pentobarbital on rat brain receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2290–2297. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02290.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polenzani L., Woodward R. M., Miledi R. Expression of mammalian gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors with distinct pharmacology in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4318–4322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribilla I., Takagi T., Langosch D., Bormann J., Betz H. The atypical M2 segment of the beta subunit confers picrotoxinin resistance to inhibitory glycine receptor channels. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4305–4311. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Sontheimer H., Gorman C. M., Kettenmann H., Seeburg P. H., Schofield P. R. Transient expression shows ligand gating and allosteric potentiation of GABAA receptor subunits. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1306–1308. doi: 10.1126/science.2848320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Sontheimer H., Shivers B. D., Ymer S., Kettenmann H., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H. Importance of a novel GABAA receptor subunit for benzodiazepine pharmacology. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):582–585. doi: 10.1038/338582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puia G., Ducić I., Vicini S., Costa E. Does neurosteroid modulatory efficacy depend on GABAA receptor subunit composition? Receptors Channels. 1993;1(2):135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puia G., Santi M. R., Vicini S., Pritchett D. B., Purdy R. H., Paul S. M., Seeburg P. H., Costa E. Neurosteroids act on recombinant human GABAA receptors. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):759–765. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90202-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian H., Dowling J. E. Novel GABA responses from rod-driven retinal horizontal cells. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):162–164. doi: 10.1038/361162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian H., Dowling J. E. Pharmacology of novel GABA receptors found on rod horizontal cells of the white perch retina. J Neurosci. 1994 Jul;14(7):4299–4307. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-07-04299.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattelle D. B., Lummis S. C., Wong J. F., Rauh J. J. Pharmacology of insect GABA receptors. Neurochem Res. 1991 Mar;16(3):363–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00966100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattelle D. B., Pinnock R. D., Wafford K. A., David J. A. GABA receptors on the cell-body membrane of an identified insect motor neuron. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jan 22;232(1269):443–456. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena N. C., Macdonald R. L. Assembly of GABAA receptor subunits: role of the delta subunit. J Neurosci. 1994 Nov;14(11 Pt 2):7077–7086. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-07077.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W. GABAA receptors: ligand-gated Cl- ion channels modulated by multiple drug-binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Dec;13(12):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90142-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R., Trube G., Möhler H., Malherbe P. The effect of subunit composition of rat brain GABAA receptors on channel function. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A. Antagonism of flurazepam and other effects of Ro15-1788, PK8165 and Ro5-4864 on the GABA-A receptor complex in rat cuneate nucleus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 29;117(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart T. G., Constanti A. A novel effect of zinc on the lobster muscle GABA receptor. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jun 22;215(1200):327–341. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Rastogi S. K., Thyagarajan R. Separate site(s) of action of optical isomers of 1-methyl-5-phenyl-5-propylbarbituric acid with opposite pharmacological activities at the GABA receptor complex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 May 28;112(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford K. A., Bain C. J., Quirk K., McKernan R. M., Wingrove P. B., Whiting P. J., Kemp J. A. A novel allosteric modulatory site on the GABAA receptor beta subunit. Neuron. 1994 Apr;12(4):775–782. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford K. A., Lummis S. C., Sattelle D. B. Block of an insect central nervous system GABA receptor by cyclodiene and cyclohexane insecticides. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1989 Jun 22;237(1286):53–61. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1989.0036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingrove P. B., Wafford K. A., Bain C., Whiting P. J. The modulatory action of loreclezole at the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor is determined by a single amino acid in the beta 2 and beta 3 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4569–4573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. GABAA receptor channels: from subunits to functional entities. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Jun;2(3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90113-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward R. M., Polenzani L., Miledi R. Effects of hexachlorocyclohexanes on gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes by RNA from mammalian brain and retina. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;41(6):1107–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie X. M., Smart T. G. A physiological role for endogenous zinc in rat hippocampal synaptic neurotransmission. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):521–524. doi: 10.1038/349521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H. G., ffrench-Constant R. H., Jackson M. B. A unique amino acid of the Drosophila GABA receptor with influence on drug sensitivity by two mechanisms. J Physiol. 1994 Aug 15;479(Pt 1):65–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ffrench-Constant R. H., Rocheleau T. A. Drosophila gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor gene Rdl shows extensive alternative splicing. J Neurochem. 1993 Jun;60(6):2323–2326. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


