Abstract
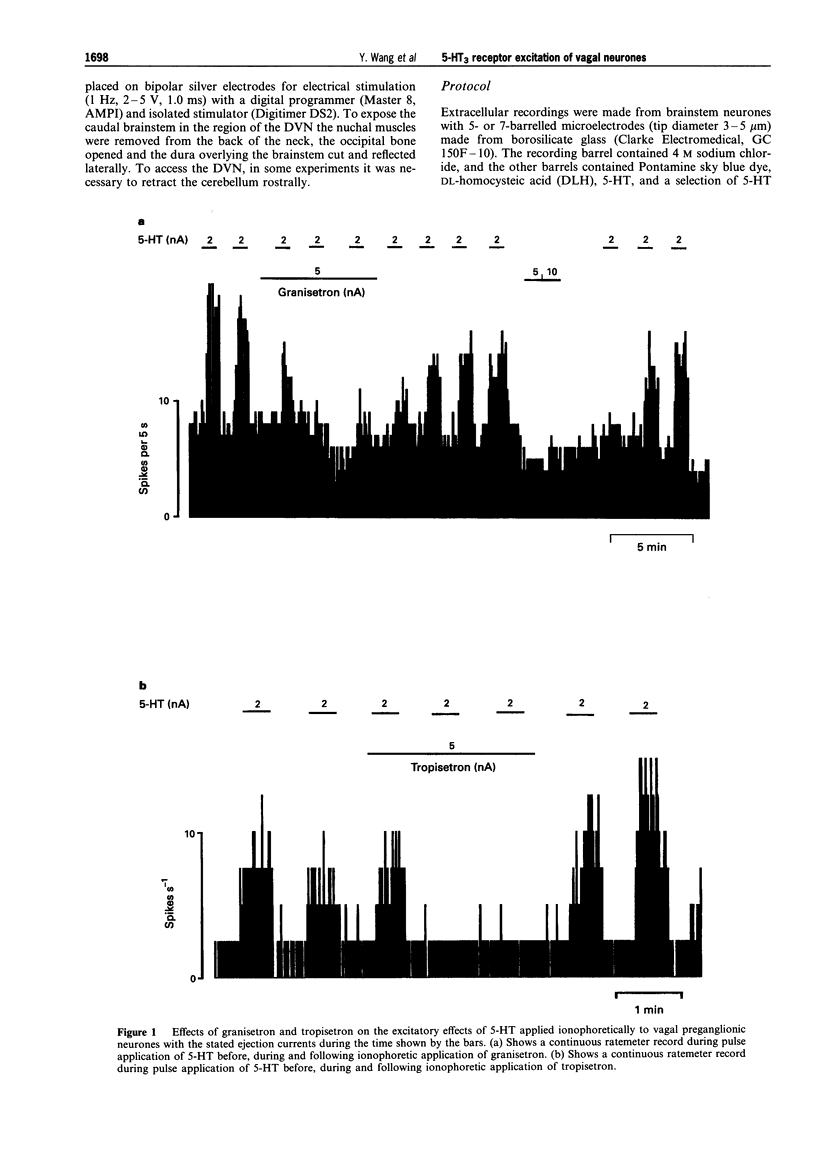
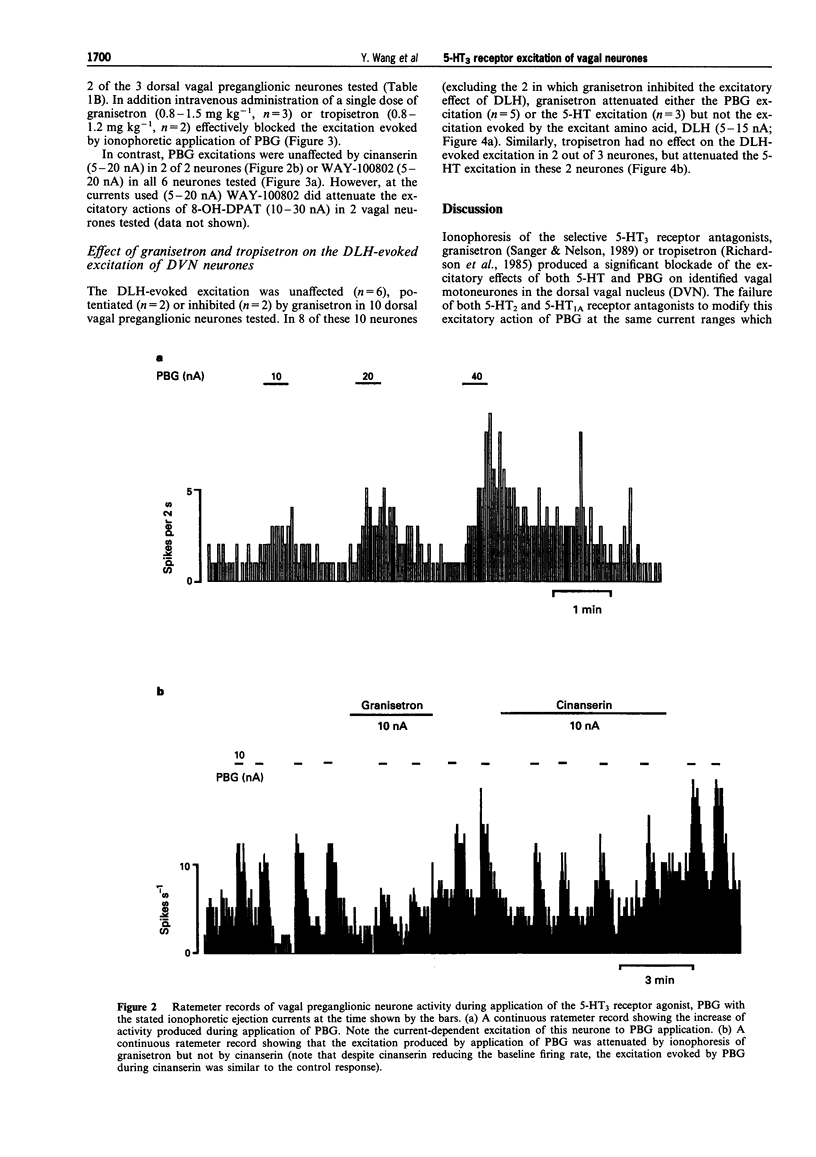
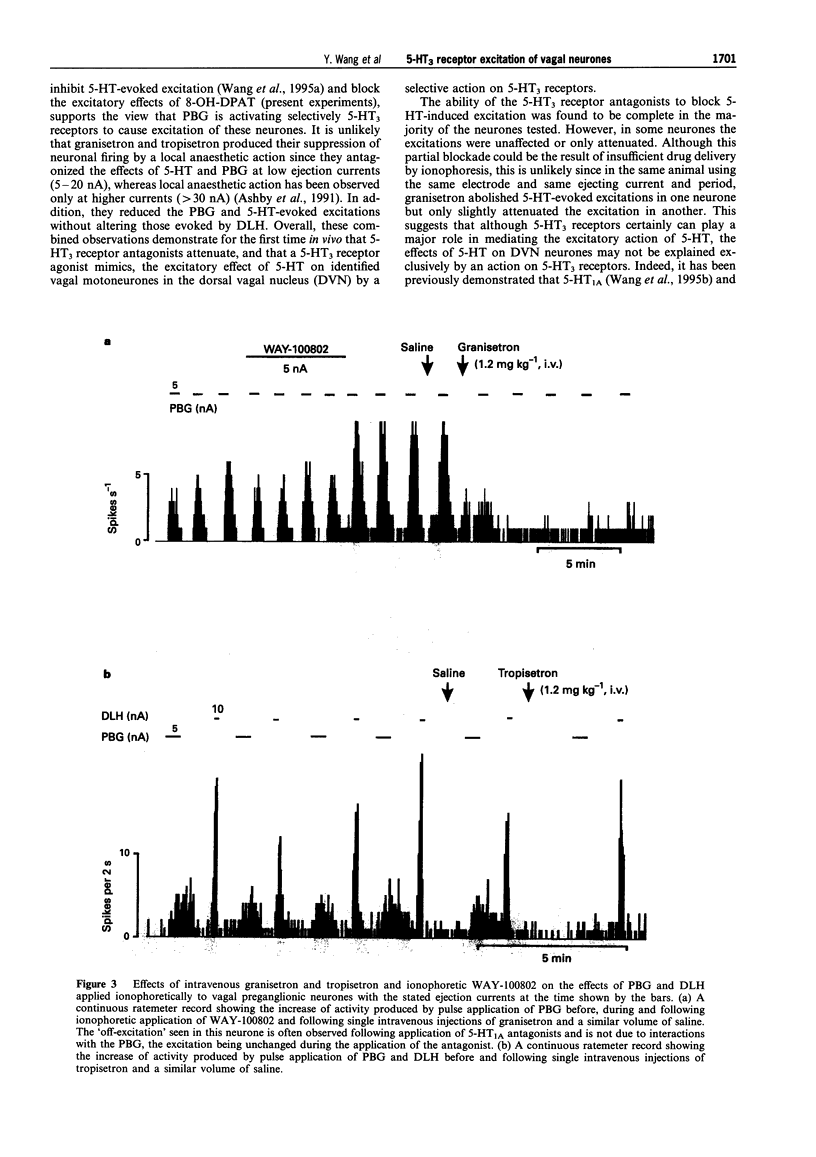
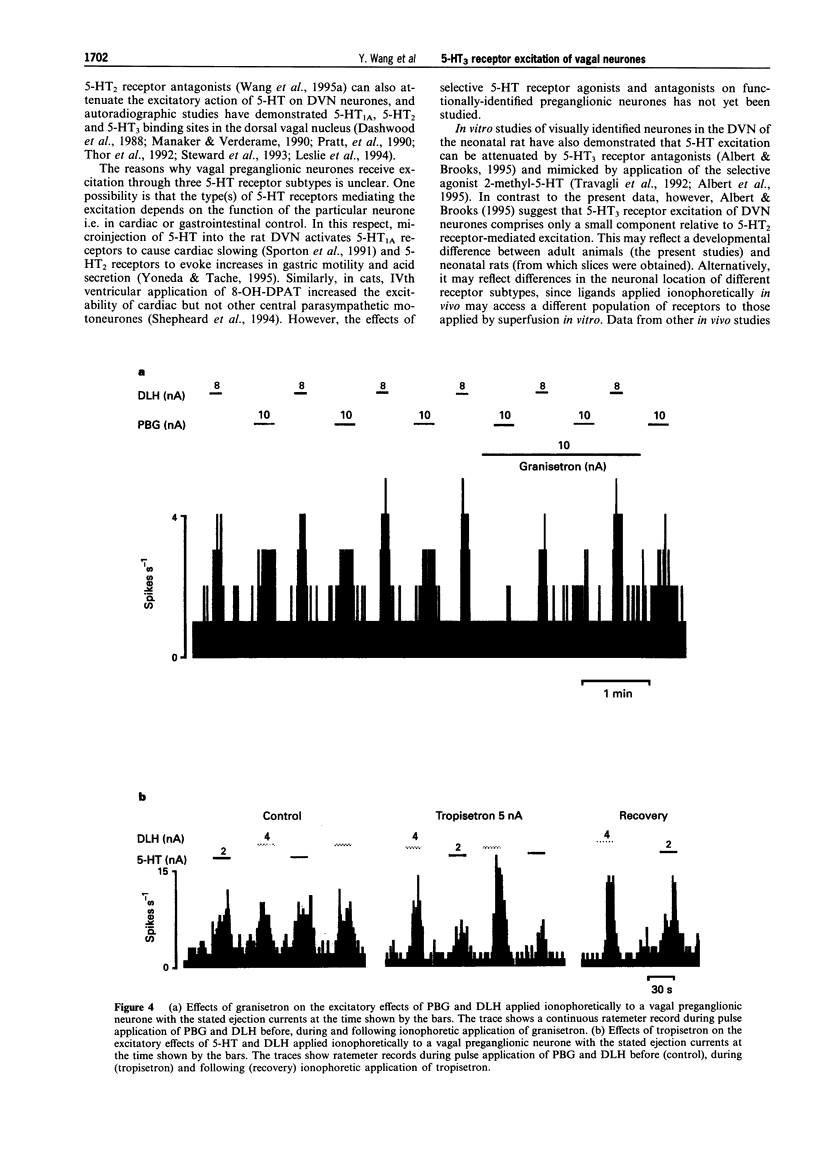
1. Extracellular recording were made from 141 vagal preganglionic neurones in the dorsal vagal nucleus (DVN). The effects of ionophoretic administration of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), the 5-HT3 receptor agonist, phenylbiguanide (PBG) and the antagonists, granisetron and tropisetron (ICS 205-930) on these vagal preganglionic neurones were studied in pentobarbitone sodium anaesthetized rats. 2. Ionophoretic application of 5-HT at low currents (< 10 nA) increased the activity in 46 (73%) of 63 neurones tested. Application of granisetron (5-20 nA) or tropisetron (5-20 nA) abolished or attenuated the 5-HT excitatory responses in 8 out of 11 and 5 out of 5 neurones respectively. At the currents used, neither antagonist had any effect on baseline firing rate. 3. Ionophoresis of the selective 5-HT3 receptor agonist, phenylbiguanide (0-40 nA) excited 54 (82%) of the 66 vagal neurones tested, whilst the remaining 12 neurones were unaffected. 4. Granisetron applied either ionophoretically (8/11) or intravenously (3/3),abolished or attenuated the excitations evoked by PBG. Similarly, tropisetron administered either ionophoretically (2/3) or intravenously (2/2), attenuated the PBG excitation. In contrast, the PBG excitations were unaffected by the 5-HT2 receptor antagonist, cinanserin (2/2), and the selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, WAY- 100802 (6/6). 5. In conclusion, excitation of vagal preganglionic neurones evoked by ionophoretic application of 5- HT is mediated in part by 5-HT3 receptors and activation of 5-HT3 receptors on and/or in the vicinity of vagal motoneurones causes excitation of these neurones.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby C. R., Jr, Minabe Y., Edwards E., Wang R. Y. 5-HT3-like receptors in the rat medial prefrontal cortex: an electrophysiological study. Brain Res. 1991 Jun 7;550(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91316-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby C. R., Jr, Zhang J. Y., Edwards E., Wang R. Y. The induction of serotonin3-like receptor supersensitivity and dopamine receptor subsensitivity in the rat medial prefrontal cortex after the intraventricular administration of the neurotoxin 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine: a microiontophoretic study. Neuroscience. 1994 May;60(2):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogle R. G., Pires J. G., Ramage A. G. Evidence that central 5-HT1A-receptors play a role in the von Bezold-Jarisch reflex in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):757–760. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootle D. J., Adcock J. J., Ramage A. G. Involvement of central 5-HT1A receptors in the reflex activation of pulmonary vagal motoneurones by inhaled capsaicin in anaesthetized cats. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Feb;117(4):724–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitravanshi V. C., Calaresu F. R. Additive effects of dopamine and 8-OH-DPAT microinjected into the nucleus ambiguus in eliciting vagal bradycardia in rats. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1992 Nov;41(1-2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(92)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futuro-Neto H. A., Pires J. G., Gilbey M. P., Ramage A. G. Evidence for the ability of central 5-HT1A receptors to modulate the vagal bradycardia induced by stimulating the upper airways of anesthetized rabbits with smoke. Brain Res. 1993 Dec 3;629(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91345-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaum S. R., Brooks P. A., Spyer K. M., Miller R. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine-3 receptors modulate synaptic activity in the rat nucleus tractus solitarius in vitro. Brain Res. 1992 Aug 28;589(1):62–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haxhiu M. A., Jansen A. S., Cherniack N. S., Loewy A. D. CNS innervation of airway-related parasympathetic preganglionic neurons: a transneuronal labeling study using pseudorabies virus. Brain Res. 1993 Jul 30;618(1):115–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90435-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo P. N., Deuchars J., Spyer K. M. Localization of cardiac vagal preganglionic motoneurones in the rat: immunocytochemical evidence of synaptic inputs containing 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Jan 22;327(4):572–583. doi: 10.1002/cne.903270408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Yakel J. L. The 5-HT3 receptor channel. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:447–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M. Brain stem localization of vagal preganglionic neurons. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1981 Apr;3(2-4):451–481. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(81)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manaker S., Verderame H. M. Organization of serotonin 1A and 1B receptors in the nucleus of the solitary tract. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Nov 22;301(4):535–553. doi: 10.1002/cne.903010405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall R. B., Escandon N. A., Harris L. T., Clement M. E. Tolerance development to the vagal-mediated bradycardia produced by 5-HT1A receptor agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Nov;271(2):776–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosaka S., Yamamoto T., Yasunaga K. Localization of vagal cardioinhibitory preganglionic neurons with rat brain stem. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jul 1;186(1):79–92. doi: 10.1002/cne.901860106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosaka S., Yasunaga K., Tamai S. Vagal cardiac preganglionic neurons: distribution, cell types, and reflex discharges. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):R92–R98. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1982.243.1.R92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. A., Malone H. M., Lambert J. J. Recent advances in the electrophysiological characterization of 5-HT3 receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Oct;13(10):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90119-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt G. D., Bowery N. G., Kilpatrick G. J., Leslie R. A., Barnes N. M., Naylor R. J., Jones B. J., Nelson D. R., Palacids J. M., Slater P. Consensus meeting agrees distribution of 5-HT3 receptors in mammalian hindbrain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):135–137. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90058-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN B., PIALA J. J., BURKE J. C., CRAVER B. N. A NEW, POTENT AND SPECIFIC SEROTONIN INHIBITOR, (SQ 10,643) 2'-(3-DIMETHYLAMINOPROPYLTHIO) CINNAMANILIDE HYDROCHLORIDE: ANTISEROTONIN ACTIVITY ON UTERUS AND ON GASTROINTESTINAL, VASCULAR, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS OF ANIMALS. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1964 Nov 1;152:132–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramage A. G., Fozard J. R. Evidence that the putative 5-HT1A receptor agonists, 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone, have a central hypotensive action that differs from that of clonidine in anaesthetised cats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 19;138(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. P., Engel G., Donatsch P., Stadler P. A. Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):126–131. doi: 10.1038/316126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger G. J., Nelson D. R. Selective and functional 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor antagonism by BRL 43694 (granisetron). Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 10;159(2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90695-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepheard S. L., Jordan D., Ramage A. G. Comparison of the effects of IVth ventricular administration of some tryptamine analogues with those of 8-OH-DPAT on autonomic outflow in the anaesthetized cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;111(2):616–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporton S. C., Shepheard S. L., Jordan D., Ramage A. G. Microinjections of 5-HT1A agonists into the dorsal motor vagal nucleus produce a bradycardia in the atenolol-pretreated anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):466–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbusch H. W. Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat-cell bodies and terminals. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):557–618. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward L. J., West K. E., Kilpatrick G. J., Barnes N. M. Labelling of 5-HT3 receptor recognition sites in the rat brain using the agonist radioligand [3H]meta-chlorophenylbiguanide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct 12;243(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90161-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. M., Spyer K. M., Izzo P. N. Central distribution of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and 5-hydroxytryptamine in vagal sensory afferents in the rat dorsal medulla. Neuroscience. 1994 Mar;59(1):195–210. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor K. B., Blitz-Siebert A., Helke C. J. Autoradiographic localization of 5HT1 binding sites in autonomic areas of the rat dorsomedial medulla oblongata. Synapse. 1992 Mar;10(3):217–227. doi: 10.1002/syn.890100305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Jones J. F., Ramage A. G., Jordan D. Effects of 5-HT and 5-HT1A receptor agonists and antagonists on dorsal vagal preganglionic neurones in anaesthetized rats: an ionophoretic study. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Oct;116(4):2291–2297. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



