Abstract
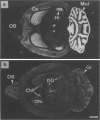
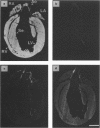
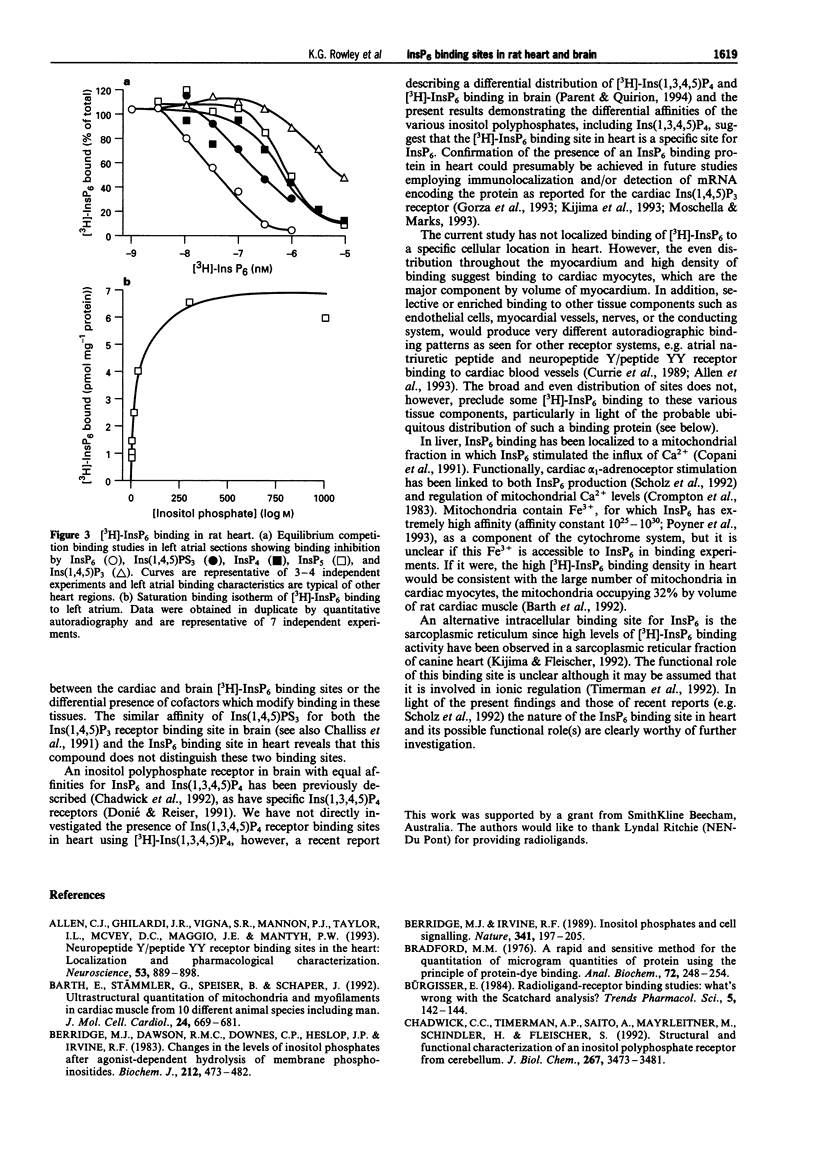
1. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) and inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP6) are produced in response to stimulation of cardiac alpha 1-adrenoceptors. While the role of Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptors is well-defined in many tissues including brain, the functional role of the putative InsP6-InsP6 receptor system in cardiac function is less clear. Using quantitative autoradiography, this study examined the characteristics and regional localization of [3H]-InsP6 binding sites in rat heart and compared the affinity of a range of inositol polyphosphates for [3H]-InsP6 and [3H]-Ins(1,4,5)P3 binding sites in heart and brain. 2. [3H]-InsP6 bound to a single, high affinity site in sections of rat heart (KD ranging from 22 +/- 1.9 nM in right atria to 35 +/- 2.6 nM in the interventricular septum, n = 7). The maximal number of binding sites (Bmax) ranged from 5.1 +/- 0.48 to 12 +/- 1.8 pmol mg-1 protein in left atrium and left ventricle, respectively. Inositol phosphates inhibited binding of [3H]-InsP6 with the order of potency: InsP6 > Ins(1,4,5)PS3 > inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate > or = inositol pentakisphosphate > Ins(1,4,5)P3 > > inositol mono- and bisphosphates, consistent with the labelling of an InsP6 binding site. 3. The Ins(1,4,5)P3 analogue, Ins(1,4,5)PS3, originally investigated as a putative selective radioligand for the Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptor, was a potent inhibitor of [3H]-InsP6 binding in all heart regions (K1 = 170-260 nM). The K1 of Ins(1,4,5)PS3 for the inhibition of [3H]-Ins(1,4,5)P3 binding in rat brain (60-220 nM) was similar to that observed for the inhibition of [3H]-InsP6 binding in heart, suggesting that Ins(1,4,5)PS3 is not a specific ligand for either Ins(1,4,5)P3 or InsP6 receptor binding sites. 4. Previous studies have detected [3H]-InsP6 binding in mitochondrial and sarcoplasmic reticulum fractions of heart and links between InsP6 and cardiac mitochondrial Ca2+ regulation have been proposed, suggesting further studies are warranted to determine the functional role(s) of InsP6 and InsP6 receptor binding sites in cardiac tissue.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen C. J., Ghilardi J. R., Vigna S. R., Mannon P. J., Taylor I. L., McVey D. C., Maggio J. E., Mantyh P. W. Neuropeptide Y/peptide YY receptor binding sites in the heart: localization and pharmacological characterization. Neuroscience. 1993 Apr;53(3):889–898. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90633-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth E., Stämmler G., Speiser B., Schaper J. Ultrastructural quantitation of mitochondria and myofilaments in cardiac muscle from 10 different animal species including man. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1992 Jul;24(7):669–681. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(92)93381-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick C. C., Timerman A. P., Saito A., Mayrleitner M., Schindler H., Fleischer S. Structural and functional characterization of an inositol polyphosphate receptor from cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3473–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Smith S. M., Potter B. V., Nahorski S. R. D-[35S(U)]inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphorothioate, a novel radioligand for the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. Complex binding to rat cerebellar membranes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80368-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copani A., Raciti G., Bruno V., Sortino M. A., Nicoletti F., Canonico P. L., Cambria A. Inositol hexakisphosphate stimulates 45Ca2+ influx in purified mitochondria from rat liver. Ital J Biochem. 1991 Sep-Oct;40(5):289–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M., Kessar P., Al-Nasser I. The alpha-adrenergic-mediated activation of the cardiac mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter and its role in the control of intramitochondrial Ca2+ in vivo. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):333–342. doi: 10.1042/bj2160333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie M. G., Schomer H., Lanier-Smith K. L., Baron D. A. Atrial natriuretic peptide binding sites in the mammalian heart: localization to endomural vessels. Cell Tissue Res. 1989;256(2):233–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00218880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donié F., Reiser G. Purification of a high-affinity inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate receptor from brain. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):453–457. doi: 10.1042/bj2750453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorza L., Schiaffino S., Volpe P. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in heart: evidence for its concentration in Purkinje myocytes of the conduction system. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(2):345–353. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Reynolds D. J., Poyner D. R., Hanley M. R. Identification of a novel inositol phosphate recognition site: specific [3H]inositol hexakisphosphate binding to brain regions and cerebellar membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 16;167(2):819–827. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92099-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijima Y., Fleischer S. Two types of inositol trisphosphate binding in cardiac microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):728–735. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92262-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijima Y., Saito A., Jetton T. L., Magnuson M. A., Fleischer S. Different intracellular localization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and ryanodine receptors in cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3499–3506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moschella M. C., Marks A. R. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor expression in cardiac myocytes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1137–1146. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Bruno V., Cavallaro S., Copani A., Sortino M. A., Canonico P. L. Specific binding sites for inositolhexakisphosphate in brain and anterior pituitary. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 May;37(5):689–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Bruno V., Fiore L., Cavallaro S., Canonico P. L. Inositol hexakisphosphate (phytic acid) enhances Ca2+ influx and D-[3H]aspartate release in cultured cerebellar neurons. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1026–1030. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A., Quirion R. Differential localization and pH dependency of phosphoinositide 1,4,5-IP3, 1,3,4,5-IP4 and IP6 receptors in rat and human brains. Eur J Neurosci. 1994 Jan 1;6(1):67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1994.tb00248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poyner D. R., Cooke F., Hanley M. R., Reynolds D. J., Hawkins P. T. Characterization of metal ion-induced [3H]inositol hexakisphosphate binding to rat cerebellar membranes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1032–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regunathan S., Reis D. J., Wahlestedt C. Specific binding of inositol hexakisphosphate (phytic acid) to adrenal chromaffin cell membranes and effects on calcium-dependent catecholamine release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 17;43(6):1331–1336. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90510-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz J., Troll U., Sandig P., Schmitz W., Scholz H., Schulte Am Esch J. Existence and alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of inositol polyphosphates in mammalian heart. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;42(1):134–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szwergold B. S., Graham R. A., Brown T. R. Observation of inositol pentakis- and hexakis-phosphates in mammalian tissues by 31P NMR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):874–881. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theibert A. B., Estevez V. A., Mourey R. J., Marecek J. F., Barrow R. K., Prestwich G. D., Snyder S. H. Photoaffinity labeling and characterization of isolated inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate- and inositol hexakisphosphate-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9071–9079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timerman A. P., Mayrleitner M. M., Lukas T. J., Chadwick C. C., Saito A., Watterson D. M., Schindler H., Fleischer S. Inositol polyphosphate receptor and clathrin assembly protein AP-2 are related proteins that form potassium-selective ion channels in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8976–8980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Colvin J. S., Snyder S. H. Inositol trisphosphate receptor localization in brain: variable stoichiometry with protein kinase C. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):159–161. doi: 10.1038/325159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor binding: autoradiographic localization in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1989 Jan;9(1):339–346. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-01-00339.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]