Abstract
1. Activation of CB1 receptors by plant cannabinoids or the endogenous ligand, anandamide, causes hypotension via a sympathoinhibitory action in anaesthetized rats. In mouse isolated vas deferens, activation of CB1 receptors inhibits the electrically evoked twitch response. To determine if these effects are related to presynaptic inhibition of noradrenaline (NA) release, we examined the effects of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta 9-THC), anandamide and the CB1 antagonist, SR141716A, on exocytotic NA release in rat isolated atria and vasa deferentia. 2. In isolated atria and vasa deferentia preloaded with [3H]-NA, electrical field stimulation caused [3H]-NA release, which was abolished by tetrodotoxin 0.5 microM and concentration-dependently inhibited by delta 9-THC or anandamide, 0.3-10 microM. The inhibitory effect of delta 9-THC and anandamide was competitively antagonized by SR 141716A, 1-10 microM. 3. Tyramine, 1 microM, also induced [3H]-NA release, which was unaffected by tetrodotoxin, delta 9-THC or anandamide in either atria or vasa deferentia. 4. CB1 receptor mRNA is present in the superior cervical ganglion, as well as in whole brain, cerebellum, hypothalamus, spleen, and vas deferens and absent in medulla oblongata and atria, as demonstrated by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. There was no evidence of the presence of CB1A receptor mRNA in ganglia, brain, or cerebellum. These results suggest that activation of presynaptic CB1 receptors located on peripheral sympathetic nerve terminals mediate sympathoinhibitory effects in vitro and in vivo.
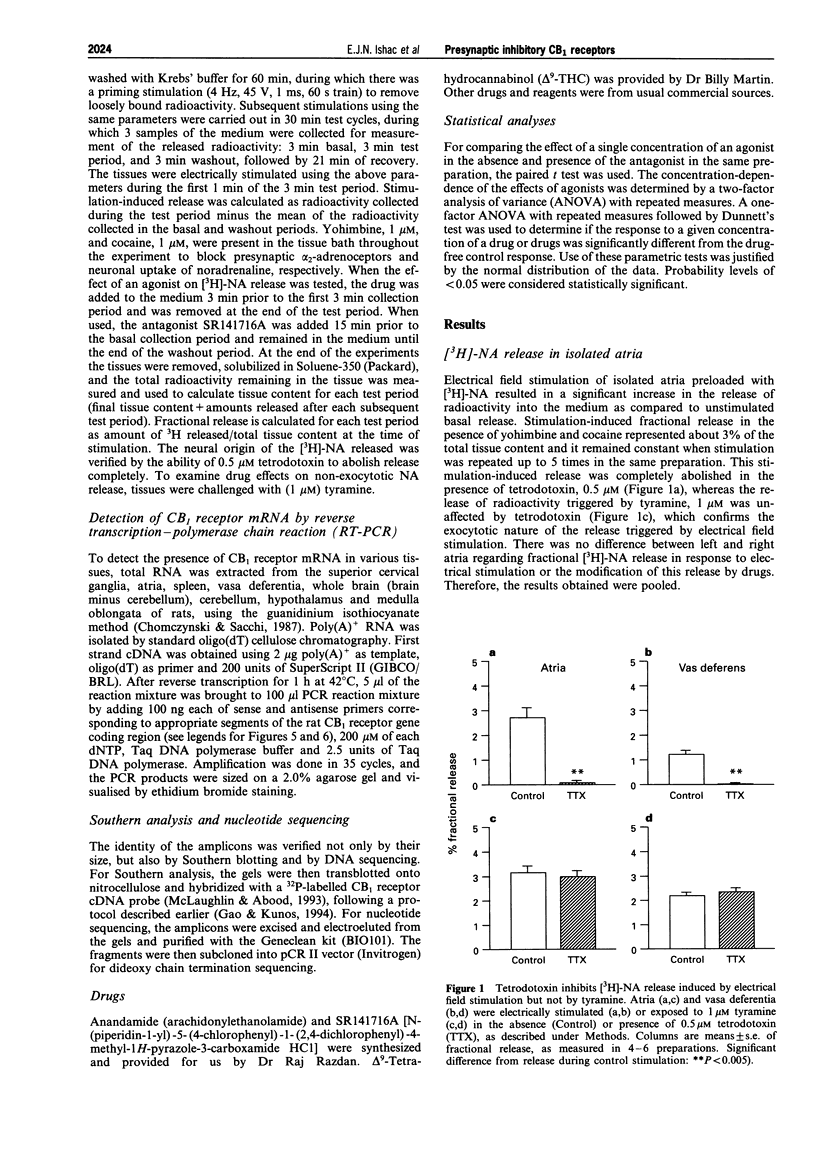
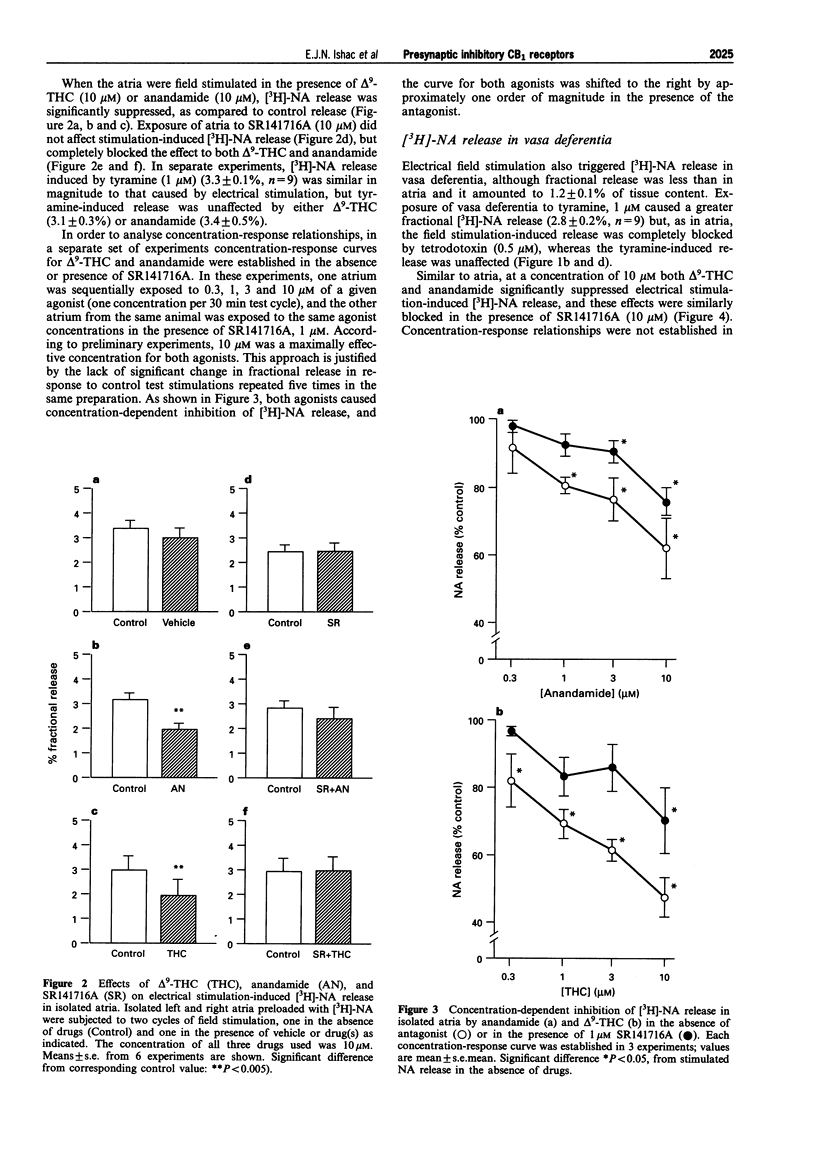
Full text
PDF
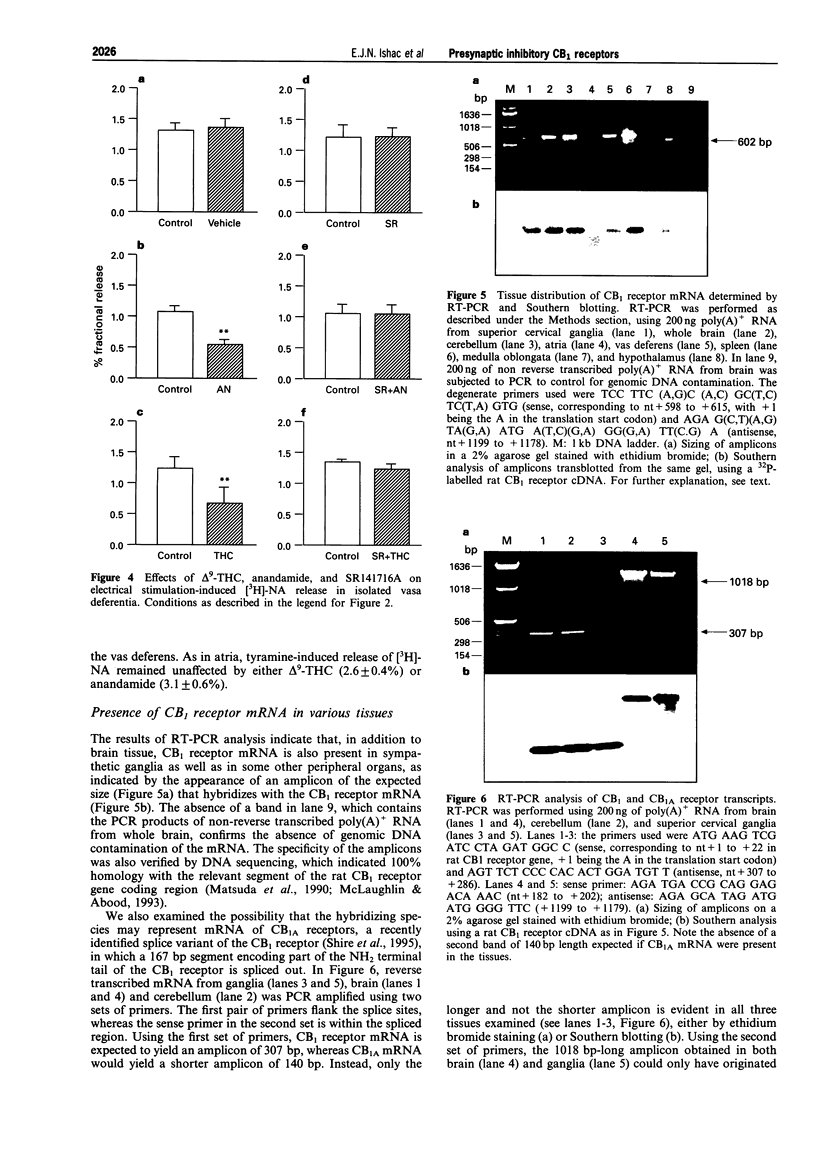


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devane W. A., Hanus L., Breuer A., Pertwee R. G., Stevenson L. A., Griffin G., Gibson D., Mandelbaum A., Etinger A., Mechoulam R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1946–1949. doi: 10.1126/science.1470919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao B., Kunos G. Transcription of the rat alpha 1B adrenergic receptor gene in liver is controlled by three promoters. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15762–15767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gérard C. M., Mollereau C., Vassart G., Parmentier M. Molecular cloning of a human cannabinoid receptor which is also expressed in testis. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):129–134. doi: 10.1042/bj2790129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Lynn A. B., Little M. D., Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., de Costa B. R., Rice K. C. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski N. E., Abood M. E., Kessler F. K., Martin B. R., Schatz A. R. Identification of a functionally relevant cannabinoid receptor on mouse spleen cells that is involved in cannabinoid-mediated immune modulation. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;42(5):736–742. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y. Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Jun;18(2):997–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda L. A., Lolait S. J., Brownstein M. J., Young A. C., Bonner T. I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):561–564. doi: 10.1038/346561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin C. R., Abood M. E. Developmental expression of cannabinoid receptor mRNA. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1993 Nov 19;76(1):75–78. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(93)90124-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechoulam R., Ben-Shabat S., Hanus L., Ligumsky M., Kaminski N. E., Schatz A. R., Gopher A., Almog S., Martin B. R., Compton D. R. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 Jun 29;50(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)00109-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Thomas K. L., Abu-Shaar M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):61–65. doi: 10.1038/365061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertwee R. G., Stevenson L. A., Elrick D. B., Mechoulam R., Corbett A. D. Inhibitory effects of certain enantiomeric cannabinoids in the mouse vas deferens and the myenteric plexus preparation of guinea-pig small intestine. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):980–984. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi-Carmona M., Barth F., Héaulme M., Shire D., Calandra B., Congy C., Martinez S., Maruani J., Néliat G., Caput D. SR141716A, a potent and selective antagonist of the brain cannabinoid receptor. FEBS Lett. 1994 Aug 22;350(2-3):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00773-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shire D., Carillon C., Kaghad M., Calandra B., Rinaldi-Carmona M., Le Fur G., Caput D., Ferrara P. An amino-terminal variant of the central cannabinoid receptor resulting from alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):3726–3731. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.3726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstrand N. O., Swedin G. Effect of reserpine on the noradrenaline content of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicle compared with the submaxillary gland and the heart of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Mar;72(3):370–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb03859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura T., Kondo S., Sukagawa A., Nakane S., Shinoda A., Itoh K., Yamashita A., Waku K. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol: a possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand in brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Oct 4;215(1):89–97. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga K., Lake K., Martin B. R., Kunos G. Novel antagonist implicates the CB1 cannabinoid receptor in the hypotensive action of anandamide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 May 24;278(3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00181-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer R. R., Cavero I., Ertel R. J., Solomon T. A., Buckley J. P. Role of the central autonomic nervous system in the hypotension and bradycardia induced by (-)-delta 9-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1974 Mar;26(3):186–192. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1974.tb09252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]