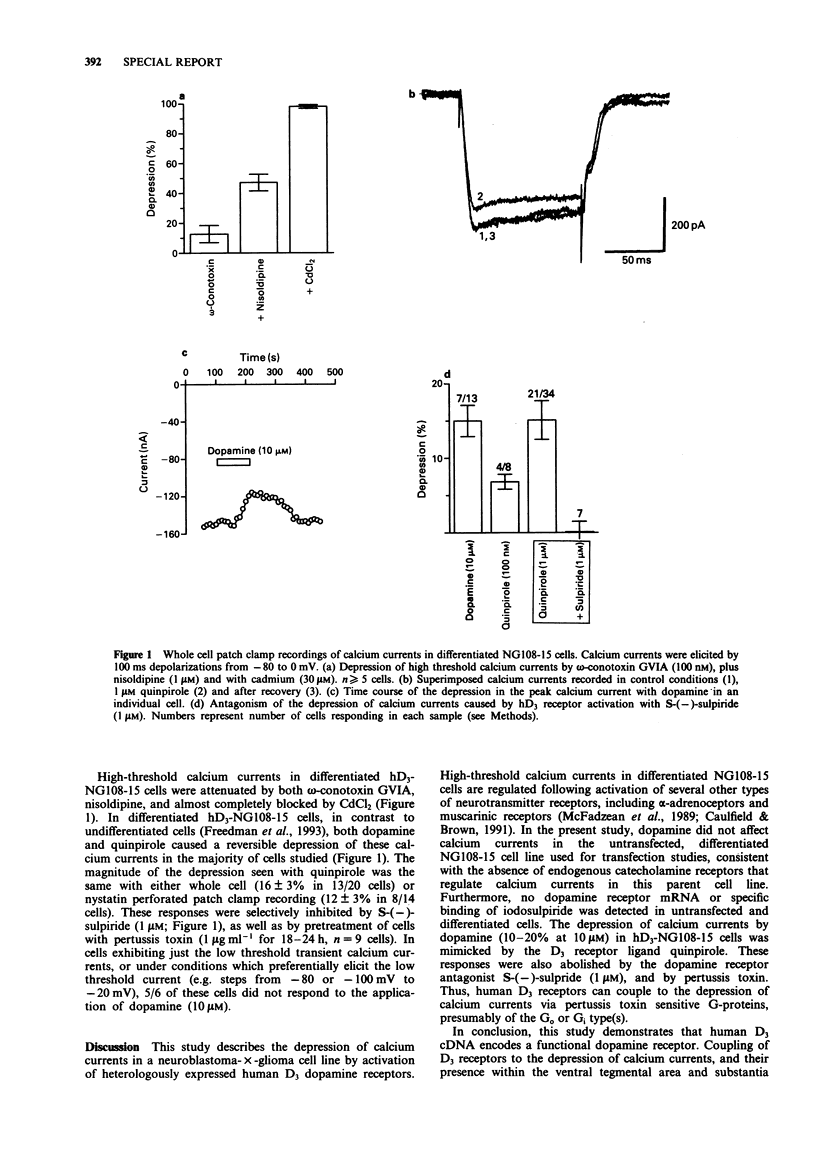
Abstract
This study describes the depression of calcium currents caused by activation of human D3 dopamine receptors which have been stably expressed in the neuroblastoma x glioma NG108-15 cell line. Transfected cells, which had been differentiated with prostaglandin E1 and isobutylmethylxanthine, exclusively expressed D3 receptor mRNA, which was demonstrated by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction techniques. Transfected cells had high affinity binding sites for iodosulpiride, with a Kd of 0.8 nM and receptor density of 240 fmol mg-1 protein. Calcium currents were recorded using nystatin-perforated patch clamp techniques. In contrast to untransfected cells that had been differentiated, high-threshold calcium currents in differentiated hD3-NG108-15 cells were depressed by application of dopamine and quinpirole. These responses were abolished by the dopamine receptor antagonist S-(-)-sulpiride (1 microM), demonstrating that they were caused by the activation of the transfected dopamine receptors. Coupling of human D3 receptors to calcium currents was sensitive to the action of pertussis toxin, suggesting the involvement of G-proteins of the Gi and/or G(o) subtype. These results demonstrate that human D3 receptors represent a functional class of dopamine receptor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry-Kravis E., Freedman S. B., Dawson G. Specific receptor-mediated inhibition of cyclic AMP synthesis by dopamine in a neuroblastoma X brain hybrid cell line NCB-20. J Neurochem. 1984 Aug;43(2):413–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb00917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthenet M. L., Souil E., Martres M. P., Sokoloff P., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. Localization of dopamine D3 receptor mRNA in the rat brain using in situ hybridization histochemistry: comparison with dopamine D2 receptor mRNA. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 15;564(2):203–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91456-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro S. W., Strange P. G. Coupling of D2 and D3 dopamine receptors to G-proteins. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 11;315(3):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81168-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield M. P., Brown D. A. Pharmacology of the putative M4 muscarinic receptor mediating Ca-current inhibition in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid (NG 108-15) cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lledo P. M., Homburger V., Bockaert J., Vincent J. D. Differential G protein-mediated coupling of D2 dopamine receptors to K+ and Ca2+ currents in rat anterior pituitary cells. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90273-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister G., Knowles M. R., Patel S., Marwood R., Emms F., Seabrook G. R., Graziano M., Borkowski D., Hey P. J., Freedman S. B. Characterisation of a chimeric hD3/D2 dopamine receptor expressed in CHO cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 7;324(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81537-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadzean I., Mullaney I., Brown D. A., Milligan G. Antibodies to the GTP binding protein, Go, antagonize noradrenaline-induced calcium current inhibition in NG108-15 hybrid cells. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabrook G. R., Patel S., Marwood R., Emms F., Knowles M. R., Freedman S. B., McAllister G. Stable expression of human D3 dopamine receptors in GH4C1 pituitary cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 9;312(2-3):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80918-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Giros B., Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):146–151. doi: 10.1038/347146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


