Abstract
1. The 5-HT4 receptor has only recently been identified but has yet to be cloned. This paper describes the pharmacology of a potent and selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist, GR113808, which will be useful in the further characterization of this receptor. 2. On the guinea-pig ascending colon, GR113808 (1 nM-0.1 microM) behaved as an antagonist of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)-induced contraction, producing rightward displacements of the concentration-effect curve to 5-HT and a concentration-related depression of the maximum effect. However, the compound had no effect on cholecystokinin (CCK-8)-induced contraction in concentrations up to 1 microM. 3. In the guinea-pig colon preparation, onset and offset of the antagonism by GR113808 of 5-HT-induced contraction was examined. Incubation of the tissues for either 15 min, 30 min or 60 min produced similar rightward displacements of the concentration-effect curves to 5-HT, with no increase in the degree of depression of the maxima with increasing time of incubation. Experiments examining offset of antagonism (0.01 microM) demonstrated that washout for 30 min was required to reverse fully the effects of the antagonist. 4. Potency estimates in the colon for GR113808 were made by determining approximate pA2 values (30 min) using the Gaddum equation. The values obtained were 9.2, 9.7 and 9.2 when tested against the agonists 5-HT, 5-methoxytryptamine and R,S-zacopride respectively. 5. On the carbachol-contracted tunica muscularis mucosae preparation of the rat thoracic oesophagus, GR113808 behaved as an antagonist of 5-HT-induced relaxation, producing no reduction in maximum response.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


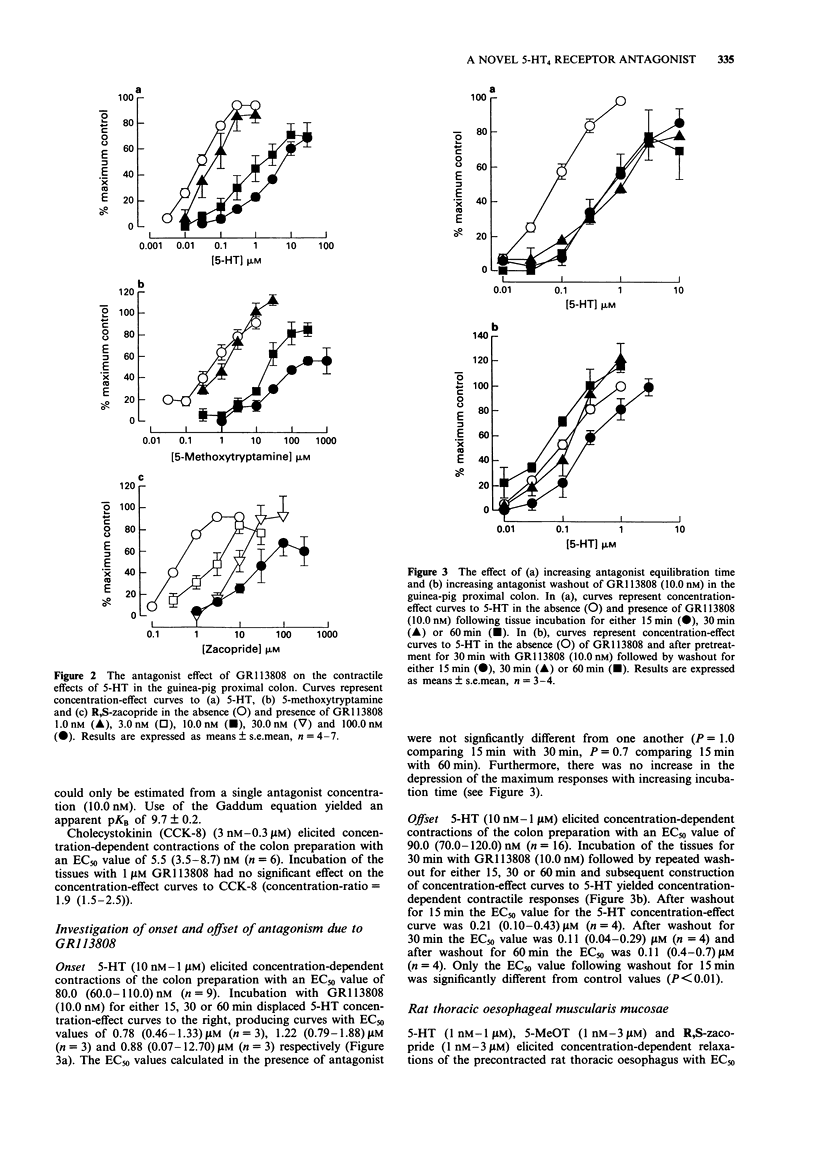
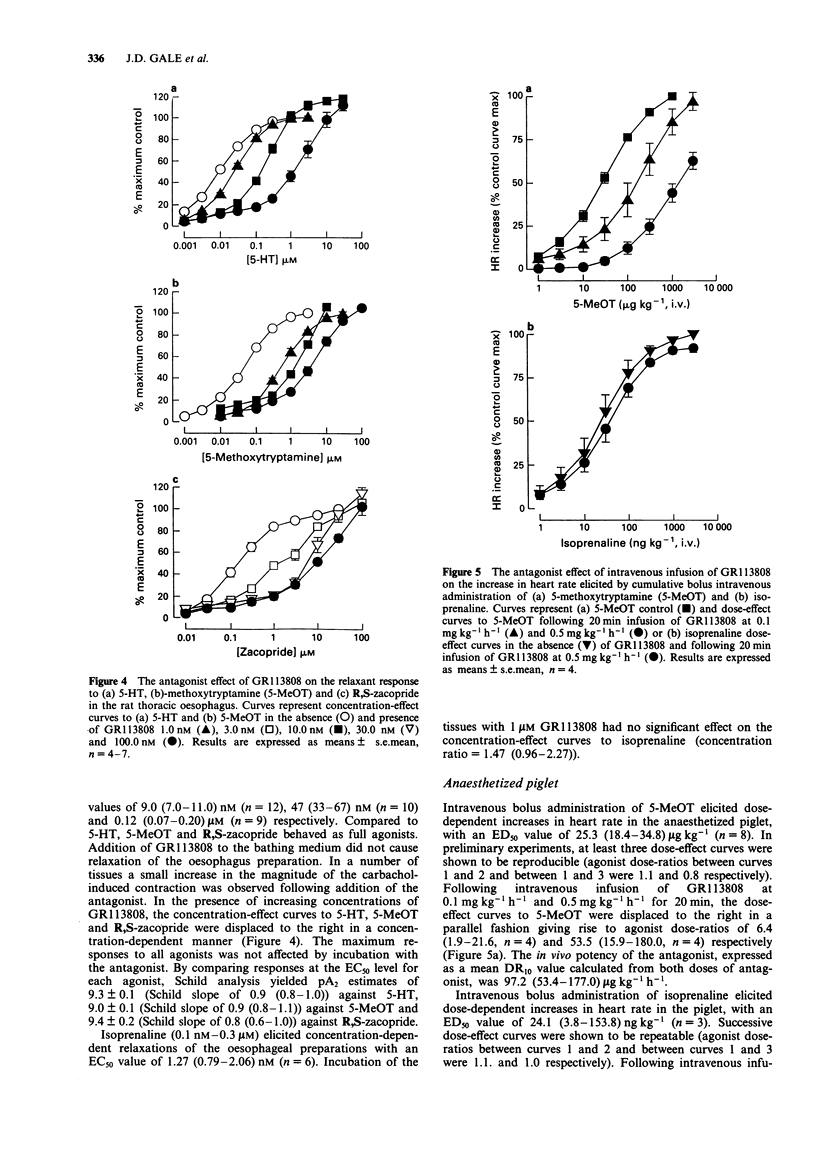


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apperley E., Humphrey P. P., Levy G. P. Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine and noradrenaline in rabbit isolated ear artery and aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;58(2):211–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb10398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter G. S., Craig D. A., Clarke D. E. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4 receptors mediate relaxation of the rat oesophageal tunica muscularis mucosae. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 May;343(5):439–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00169544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Sebben M., Dumuis A. Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine4(5-HT4) receptors positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in adult guinea pig hippocampal membranes: effect of substituted benzamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):408–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchheit K. H., Gamse R., Pfannkuche H. J. SDZ 205-557, a selective, surmountable antagonist for 5-HT4 receptors in the isolated guinea pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;345(4):387–393. doi: 10.1007/BF00176615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Sebben M., Bockaert J. The gastrointestinal prokinetic benzamide derivatives are agonists at the non-classical 5-HT receptor (5-HT4) positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in neurons. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;340(4):403–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00167041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Alvarez R., Johnson L. G., Leung E., Wong E. H. The action of SDZ 205,557 at 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT3 and 5-HT4) receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):376–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elswood C. J., Bunce K. T., Humphrey P. P. Identification of putative 5-HT4 receptors in guinea-pig ascending colon. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr 17;196(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90421-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H. Theories of drug antagonism. Pharmacol Rev. 1957 Jun;9(2):211–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman C. J., Kilpatrick G. J., Bunce K. T. Development of a radioligand binding assay for 5-HT4 receptors in guinea-pig and rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):618–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey P. P., Feniuk W., Perren M. J., Connor H. E., Oxford A. W., Coates L. H., Butina D. GR43175, a selective agonist for the 5-HT1-like receptor in dog isolated saphenous vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1123–1132. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumann A. J. Piglet sinoatrial 5-HT receptors resemble human atrial 5-HT4-like receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;342(5):619–622. doi: 10.1007/BF00169055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumann A. J., Sanders L., Brown A. M., Murray K. J., Brown M. J. A 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor in human atrium. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):879–885. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. The kinetics of action of acetylcholine antagonists in smooth muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Apr 19;164(996):488–510. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. J., Bunce K. T., Humphrey P. P. Investigation into the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor mediating smooth muscle relaxation in the rat oesophagus. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1067–1072. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. P., Engel G., Donatsch P., Stadler P. A. Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):126–131. doi: 10.1038/316126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavone A., Giraldo E., Giudici L., Turconi M., Sagrada A. DAU 6285: a novel antagonist at the putative 5-HT4 receptor. Life Sci. 1992;51(8):583–592. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90227-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtysik G., Imoto Y., Yatani A., Brown A. M. 5-Hydroxytryptamine antagonist ICS 205-930 blocks cardiac potassium, sodium and calcium currents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jun;245(3):773–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner M. J., Feniuk W., Humphrey P. P. Further characterization of the 5-HT receptor mediating vascular relaxation and elevation of cyclic AMP in porcine isolated vena cava. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):292–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meel J. C., Diederen W., Haigh R., Wienen W., Pairet M., Turconi M., Doods H. N. The novel 5-HT4 receptor antagonist DAU 6285 antagonizes 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced tachycardia in pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 23;233(2-3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90065-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalón C. M., den Boer M. O., Heiligers J. P., Saxena P. R. Mediation of 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced tachycardia in the pig by the putative 5-HT4 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):665–667. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waikar M. V., Hegde S. S., Ford A. P., Clarke D. E. Pharmacological analyses of endo-6-methoxy-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-1 H- benzimidazole-1-carboxylate hydrochloride (DAU 6285) at the 5-hydroxytryptamine4 receptor in the tunica muscularis mucosae of rat esophagus and ileum of guinea pig: role of endogenous 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):654–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


