Abstract
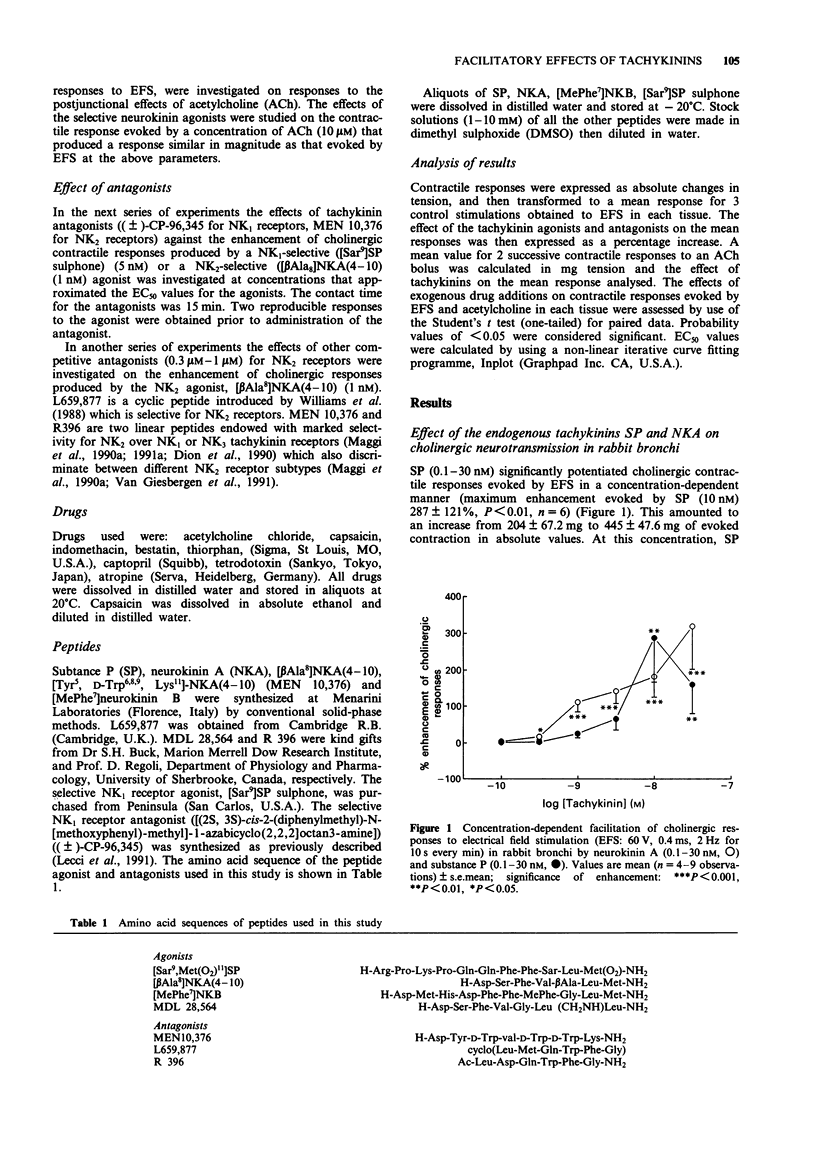
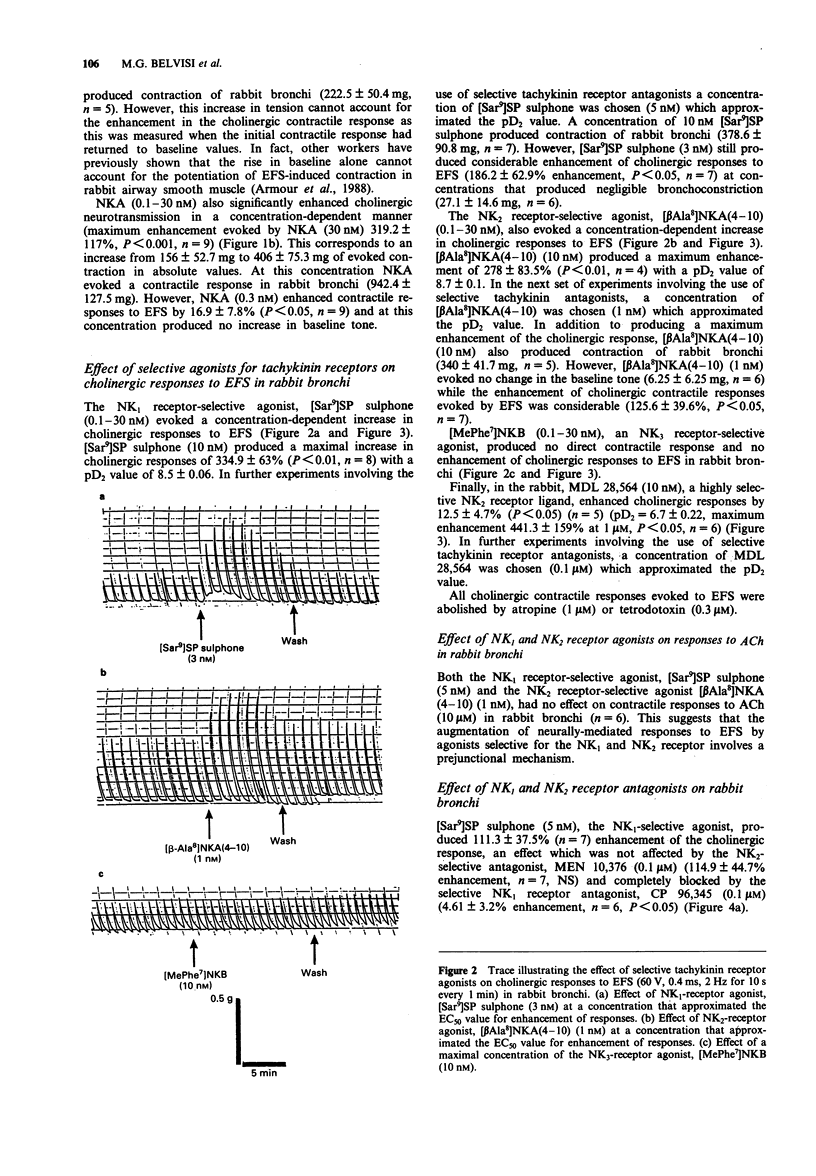
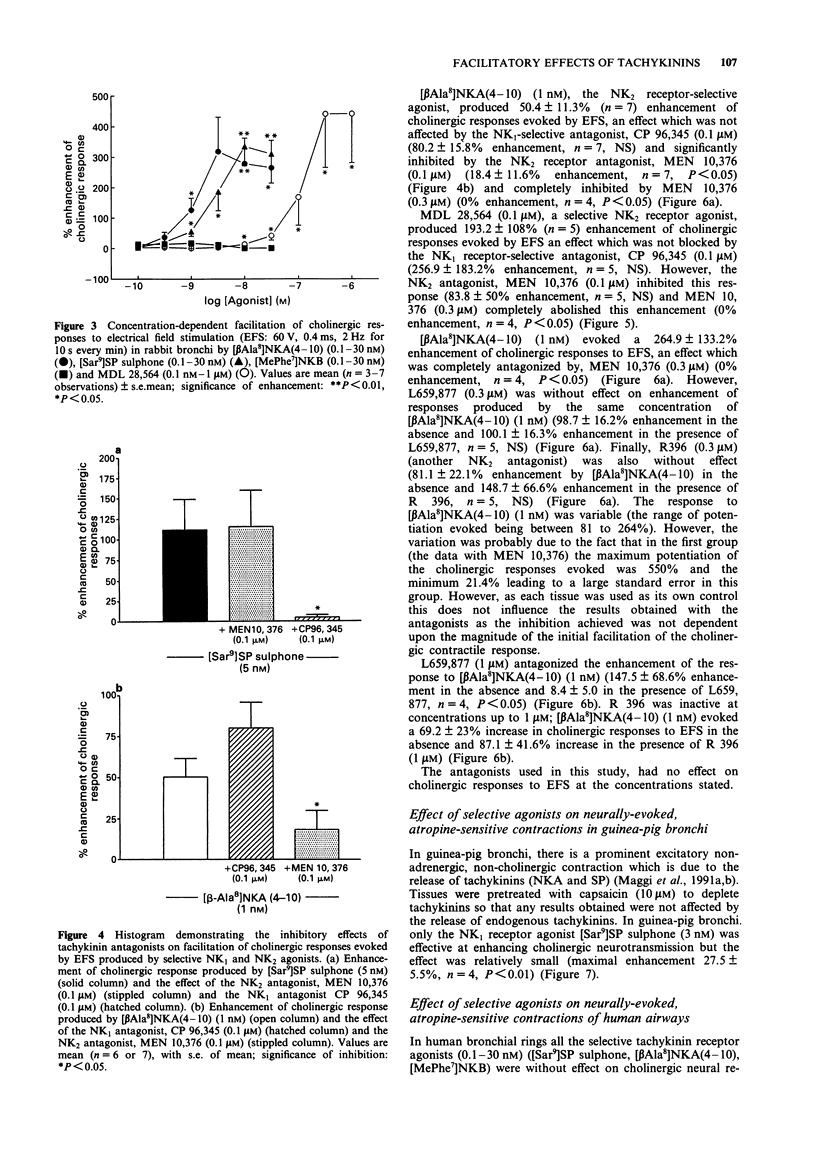
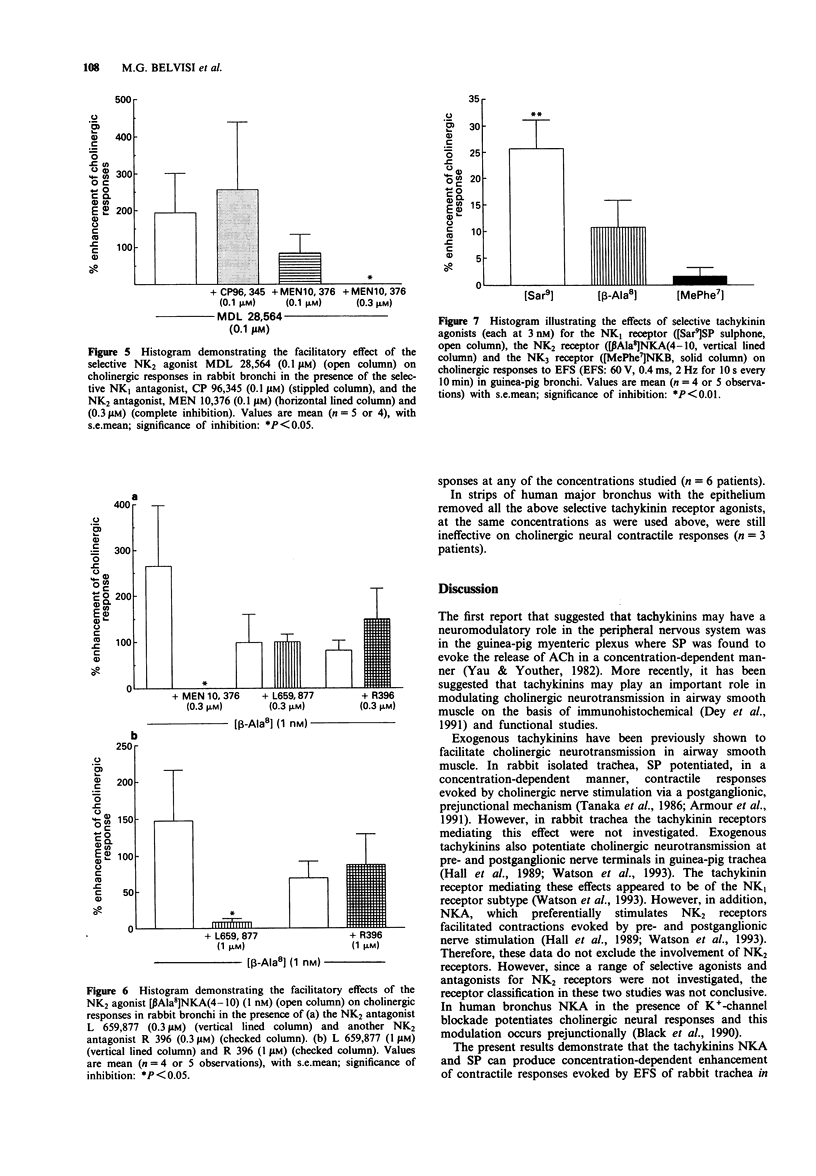
1. Exogenous tachykinins modulate cholinergic neurotransmission in rabbit and guinea-pig airways. We have investigated the effect of selective tachykinin receptor agonists and antagonists on cholinergic neurotransmission evoked by electrical field stimulation (EFS) of bronchial rings in rabbit, guinea-pig and human airways in vitro to assess which type of tachykinin receptor is mediating this facilitatory effect. 2. Bronchial rings were set up for isometric tension recording. Contractile responses to EFS (60 V, 0.4 ms, 2 Hz for 10 s every min) and exogenous acetylcholine (ACh) were obtained and the effects of selective tachykinin agonists and antagonists were investigated. 3. In rabbit bronchi the endogenous tachykinins, substance P (SP) and neurokinin A (NKA) (10 nM) potentiated cholinergic responses to EFS (by 287.6 +/- 121%, P < 0.01 and 181.4 +/- 56.5%, P < 0.001 respectively). 4. The NK1 receptor selective agonist, [Sar9]SP sulphone (10 nM) evoked a maximal facilitatory action on cholinergic responses of 334.9 +/- 63% (P < 0.01) (pD2 = 8.5 +/- 0.06) an effect which was blocked by the selective NK1-receptor antagonist, CP 96,345 (100 nM) (P < 0.05) but not by the NK2 receptor antagonist, MEN 10,376 (100 nM). The NK2 receptor selective agonist, [beta Ala8]NKA(4-10) (10 nM), produced a maximum enhancement of 278 +/- 83.5% (P < 0.01) (pD2 = 8.7 +/- 0.1) an effect which was blocked by MEN 10,376 (100 nM) (P < 0.05) and not by CP 96,345. [MePhe7]NKB, an NK3 receptor selective agonist was without effect.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Advenier C., Naline E., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Relative potencies of neurokinins in guinea pig trachea and human bronchus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 9;139(2):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa H., Miyazaki N., Inoue H., Ikeda T., Shigematsu N. Effect of endogenous tachykinins on neuro-effector transmission of vagal nerve in guinea-pig tracheal tissue. Respiration. 1990;57(5):338–342. doi: 10.1159/000195867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armour C. L., Johnson P. R., Black J. L. Nedocromil sodium inhibits substance P-induced potentiation of cholinergic neural responses in the isolated innervated rabbit trachea. J Auton Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;11(3):167–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1991.tb00316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armour C. L., Johnson P. R., Black J. L. Potentiation of contraction of rabbit airway smooth muscle by some cyclooxygenase products. Prostaglandins. 1988 Jun;35(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(88)90119-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Cuss F. M., Palmer J. B. The effect of airway epithelium on smooth muscle contractility in bovine trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):685–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. L., Johnson P. R., Alouan L., Armour C. L. Neurokinin A with K+ channel blockade potentiates contraction to electrical stimulation in human bronchus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 May 16;180(2-3):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90315-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck S. H., Harbeson S. L., Hassmann C. F., 3rd, Shatzer S. A., Rouissi N., Nantel F., van Giersbergen P. L. [Leu9 psi(CH2NH)Leu10]-neurokinin A (4-10) (MDL 28,564) distinguishes tissue tachykinin peptide NK2 receptors. Life Sci. 1990;47(10):PL37–PL41. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90605-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillier P., Advenier C., Drapeau G., Marsac J., Regoli D. Comparison of the effects of epithelium removal and of an enkephalinase inhibitor on the neurokinin-induced contractions of guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):675–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey R. D., Altemus J. B., Michalkiewicz M. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal peptide- and substance P-containing nerves originating from neurons of airway ganglia in cat bronchi. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Feb 8;304(2):330–340. doi: 10.1002/cne.903040213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion S., Rouissi N., Nantel F., Drapeau G., Regoli D., Naline E., Advenier C. Receptors for neurokinins in human bronchus and urinary bladder are of the NK-2 type. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar 20;178(2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90477-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., D'Orléans-Juste P., Dion S., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N. E., Regoli D. Selective agonists for substance P and neurokinin receptors. Neuropeptides. 1987 Jul;10(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Skidgel R. A. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) and related regulators of peptide hormones. FASEB J. 1989 Feb;3(2):145–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppetti P., Patacchini R., Cecconi R., Tramontana M., Meini S., Romani A., Nardi M., Maggi C. A. Effects of capsaicin, tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and bradykinin in the pig iris sphincter muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;341(4):301–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00180655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. K., Barnes P. J., Meldrum L. A., Maclagan J. Facilitation by tachykinins of neurotransmission in guinea-pig pulmonary parasympathetic nerves. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):274–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecci A., Giuliani S., Patacchini R., Viti G., Maggi C. A. Role of NK1 tachykinin receptors in thermonociception: effect of (+/-)-CP 96,345, a non-peptide substance P antagonist, on the hot plate test in mice. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Aug 19;129(2):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90485-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Saria A., Cuello C. Substance P-immunoreactive sensory nerves in the lower respiratory tract of various mammals including man. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;235(2):251–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00217848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Ballati L., Lecci A., Manzini S., Patacchini R., Renzetti A. R., Rovero P., Quartara L., Giachetti A. In vivo evidence for tachykininergic transmission using a new NK-2 receptor-selective antagonist, MEN 10,376. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jun;257(3):1172–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Giuliani S., Rovero P., Dion S., Regoli D., Giachetti A., Meli A. Competitive antagonists discriminate between NK2 tachykinin receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):589–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Perretti F., Meini S., Manzini S., Santicioli P., Del Bianco E., Meli A. The effect of thiorphan and epithelium removal on contractions and tachykinin release produced by activation of capsaicin-sensitive afferents in the guinea-pig isolated bronchus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jan-Feb;341(1-2):74–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00195061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Rovero P., Santicioli P. Tachykinin receptors and noncholinergic bronchoconstriction in the guinea-pig isolated bronchi. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Aug;144(2):363–367. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.2.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martling C. R., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Lundberg J. M. Occurrence and effects of multiple tachykinins; substance P, neurokinin A and neuropeptide K in human lower airways. Life Sci. 1987 Apr 20;40(16):1633–1643. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naline E., Devillier P., Drapeau G., Toty L., Bakdach H., Regoli D., Advenier C. Characterization of neurokinin effects and receptor selectivity in human isolated bronchi. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Sep;140(3):679–686. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.3.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patacchini R., Maggi C. A., Rovero P., Regoli D., Drapeau G., Meli A. Effect of thiorphan on tachykinin-induced potentiation of nerve-mediated contractions of the rat isolated vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Aug;250(2):678–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. F., Aursudkij B., Barnes P. J. Effects of tachykinins on mucus secretion in human bronchi in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 19;174(2-3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90322-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. F., Belvisi M. G., Aursudkij B., Evans T. W., Barnes P. J. Effects and interactions of sensory neuropeptides on airway microvascular leakage in guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1109–1116. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen R. O., Webber S. E., Widdicombe J. G. Effects of neuropeptides and capsaicin on the canine tracheal vasculature in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1262–1270. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa K., Tamaoki J., Nadel J. A., Borson D. B. Enkephalinase inhibitor potentiates substance P- and electrically induced contraction in ferret trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1401–1405. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton D., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. The effect of sensory nerve depletion on cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea pig airways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):1073–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda J., Smart B. M., Krause J. E. Regional distribution of neuropeptide gamma and other tachykinin peptides derived from the substance P gene in the rat. Regul Pept. 1990 May 21;28(3):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(90)90030-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka D. T., Grunstein M. M. Effect of substance P on neurally mediated contraction of rabbit airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):458–463. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson N., Maclagan J., Barnes P. J. Endogenous tachykinins facilitate transmission through parasympathetic ganglia in guinea-pig trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):751–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13638.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau W. M., Youther M. L. Direct evidence for a release of acetylcholine from the myenteric plexus of guinea pig small intestine by substance P. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 30;81(4):665–668. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Giersbergen P. L., Shatzer S. A., Henderson A. K., Lai J., Nakanishi S., Yamamura H. I., Buck S. H. Characterization of a tachykinin peptide NK2 receptor transfected into murine fibroblast B82 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1661–1665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


