Abstract
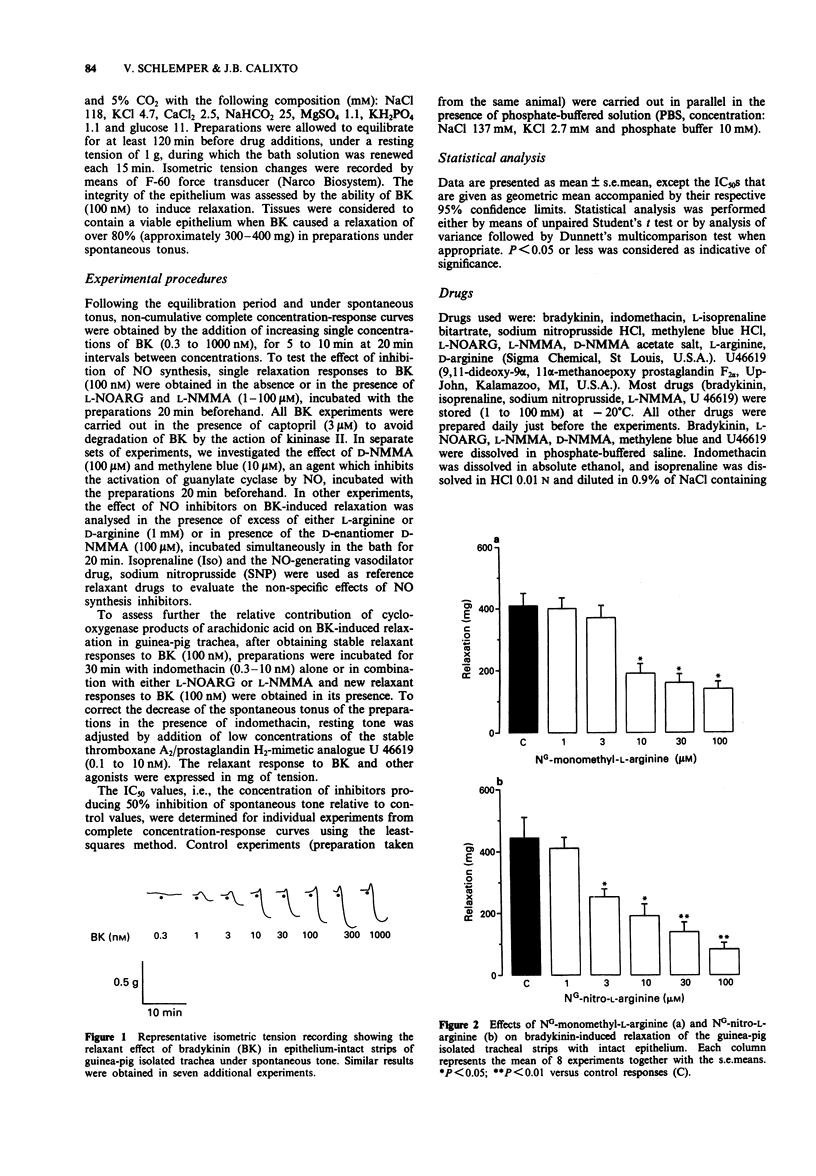
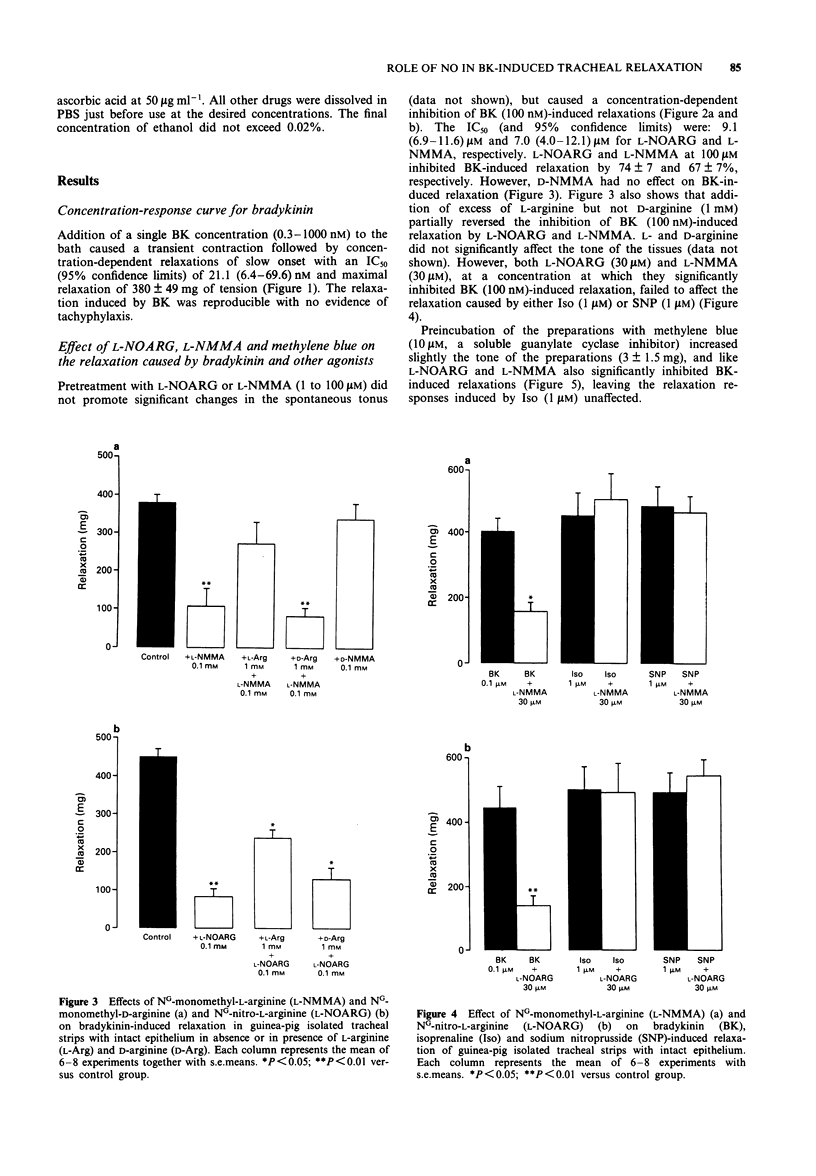
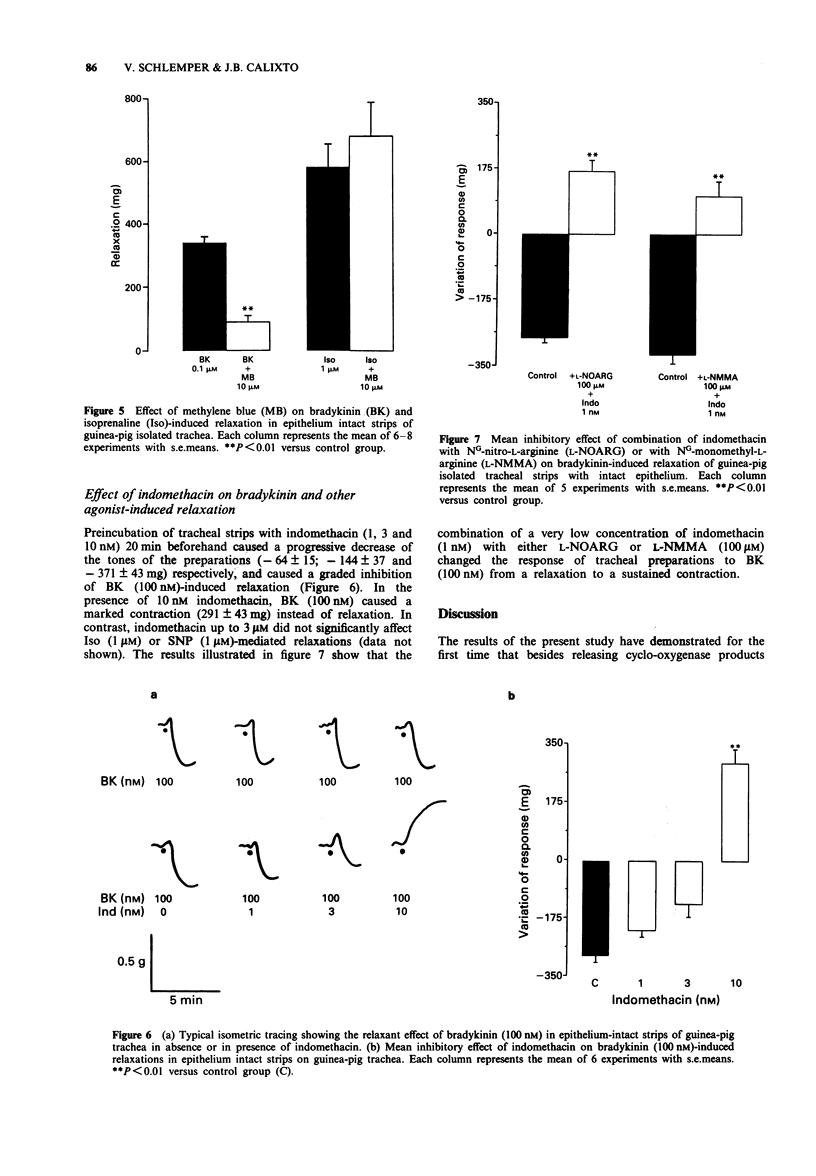
1. The effects of two nitric oxide (NO) biosynthesis-inhibitors NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOARG) and NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA) on the relaxation induced by bradykinin (BK, 100 nM), isoprenaline (Iso, 1 microM) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP, 1 microM) were investigated in epithelium-intact strips of guinea-pig isolated trachea. 2. Relaxations induced by BK (100 nM) in guinea-pig tracheal strips under spontaneous tone were inhibited in a concentration-related manner by L-NOARG and L-NMMA (1 to 100 microM), with IC50s (and 95% confidence limits) of 9.1 (6.9-11.6) microM and 7.0 (4.2-12.3) microM, respectively. However, at the maximal concentration (100 microM) used, neither of these drugs inhibited completely BK-induced relaxation (maximal inhibition of 74 +/- 7 and 67 +/- 7%, respectively). On the other hand, D-NMMA, the D-enantiomer of L-NMMA, up to 100 microM failed to inhibit BK-induced relaxation. The relaxation induced by Iso (1 microM) and SNP (1 microM) were not affected by either L-NOARG or L-NMMA (30 microM). 3. The inhibition of BK-induced relaxation caused by L-NOARG and L-NMMA was partially reversed by addition of excess of L-arginine but not D-arginine (1 mM). 4. Like L-NOARG and L-NMMA, methylene blue (10 microM), an agent that inhibits the activation of soluble guanylate cyclase by NO, also significantly inhibited BK-induced relaxation, leaving responses to Iso unaffected. 5. Indomethacin (0.3 nM to 10 nM), a cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, concentration-dependently inhibited BK-mediated relaxation, with an IC50 of 2.6 (1.7-3.8) nM, without affecting Iso and SNP-mediated relaxant responses. 6. A combination of a very low concentration of indomethacin (1 nM) and either L-NOARG or L-NMMA (100 microM) changed the response of tracheal preparations to BK (100 nM) from a relaxation to a sustained contraction. 7. These findings indicate that BK-induced relaxation in guinea-pig trachea is mediated jointly by the release of NO or a NO-related substance and a prostanoid, probably prostaglandin E2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J. Bradykinin and asthma. Thorax. 1992 Nov;47(11):979–983. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.11.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Chung K. F., Page C. P. Inflammatory mediators and asthma. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Mar;40(1):49–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Stretton D., Barnes P. J. Nitric oxide as an endogenous modulator of cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig airways. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 6;198(2-3):219–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90626-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berguer R., Hottenstein O. D., Palen T. E., Stewart J. M., Jacobson E. D. Bradykinin-induced mesenteric vasodilation is mediated by B2-subtype receptors and nitric oxide. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):G492–G496. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.3.G492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger C., Schini V. B., Moncada S., Vanhoutte P. M. Stimulation of cyclic GMP production in cultured endothelial cells of the pig by bradykinin, adenosine diphosphate, calcium ionophore A23187 and nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):152–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramley A. M., Samhoun M. N., Piper P. J. Effect of a bradykinin B2 antagonist on responses of intact and rubbed guinea-pig trachea in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98 (Suppl):786P–786P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramley A. M., Samhoun M. N., Piper P. J. The role of the epithelium in modulating the responses of guinea-pig trachea induced by bradykinin in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):762–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb13003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calixto J. B., Yunes R. A., Cruz A. B., Medeiros Y. S. Effect of compounds from Mandevilla velutina on bradykinin-mediated contractile and relaxant responses of the isolated guinea pig trachea. Agents Actions. 1992 Jul;36(3-4):222–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan C. L., Cohen R. A. Two mechanisms mediate relaxation by bradykinin of pig coronary artery: NO-dependent and -independent responses. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):H830–H835. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.3.H830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Ensor J. E., Burch R. M. Evidence that cultured airway smooth muscle cells contain bradykinin B2 and B3 receptors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Mar;4(3):273–277. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G. Role of kinins in airway diseases. Immunopharmacology. 1991 Jul-Aug;22(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(91)90051-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A., Mundel P., Mayer B., Preissler U., Philippin B., Kummer W. Nitric oxide synthase in guinea pig lower airway innervation. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Jan 12;149(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90760-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton D., McGiff J. C., Quilley J. Contribution of NO and cytochrome P450 to the vasodilator effect of bradykinin in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):722–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Murthy K. S., Jin J. G., Makhlouf G. M. Stimulation of nitric oxide from muscle cells by VIP: prejunctional enhancement of VIP release. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):G774–G778. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.4.G774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter C. A., Gruetter D. Y., Lyon J. E., Kadowitz P. J., Ignarro L. J. Relationship between cyclic guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate formation and relaxation of coronary arterial smooth muscle by glyceryl trinitrate, nitroprusside, nitrite and nitric oxide: effects of methylene blue and methemoglobin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Oct;219(1):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M. Bradykinin receptors: pharmacological properties and biological roles. Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Nov;56(2):131–190. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90016-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Buga G. M., Wood K. S., Byrns R. E., Chaudhuri G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9265–9269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Chang B., Kerwin J. F., Jr, Huang Z. J., Murad F. N omega-nitro-L-arginine: a potent inhibitor of endothelium-derived relaxing factor formation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 6;176(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90531-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan M. S., Johnson D. E. Nitric oxide mediates the neural nonadrenergic, noncholinergic relaxation of pig tracheal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):L511–L514. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.4.L511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelm M., Schrader J. Nitric oxide release from the isolated guinea pig heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 18;155(3):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil Z., Helme R. D. The quantitative contribution of nitric oxide and sensory nerves to bradykinin-induced inflammation in rat skin microvasculature. Brain Res. 1992 Aug 28;589(1):102–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91167-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontos H. A., Wei E. P., Povlishock J. T., Christman C. W. Oxygen radicals mediate the cerebral arteriolar dilation from arachidonate and bradykinin in cats. Circ Res. 1984 Sep;55(3):295–303. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.3.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamontagne D., König A., Bassenge E., Busse R. Prostacyclin and nitric oxide contribute to the vasodilator action of acetylcholine and bradykinin in the intact rabbit coronary bed. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;20(4):652–657. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199210000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. G., Rand M. J. Evidence that part of the NANC relaxant response of guinea-pig trachea to electrical field stimulation is mediated by nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):91–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi J., Couture R., Caranikas S., Regoli D. Pharmacological effects of peptides on tracheal smooth muscle. Pharmacology. 1982;25(1):39–50. doi: 10.1159/000137722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., al-Swayeh O. A., Chong N. W., Evans R. A., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro arginine (L-NOARG), a novel, L-arginine-reversible inhibitor of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):408–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Rees D. D., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1251–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand M. J. Nitrergic transmission: nitric oxide as a mediator of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neuro-effector transmission. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1992 Mar;19(3):147–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1992.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. P., Arleth A. J., Shikano K., Berkowitz B. A. Characterization and function of bradykinin receptors in vascular endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Oct;247(1):8–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J. F., Brave S. R., Charalambous L., Hobbs A. J., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro arginine inhibits non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic relaxations of guinea-pig isolated tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):663–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vials A., Burnstock G. Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors, L-NG-nitroarginine and L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester, on responses to vasodilators of the guinea-pig coronary vasculature. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):604–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemer G., Wirth K. Production of cyclic GMP via activation of B1 and B2 kinin receptors in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Aug;262(2):729–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


