Abstract
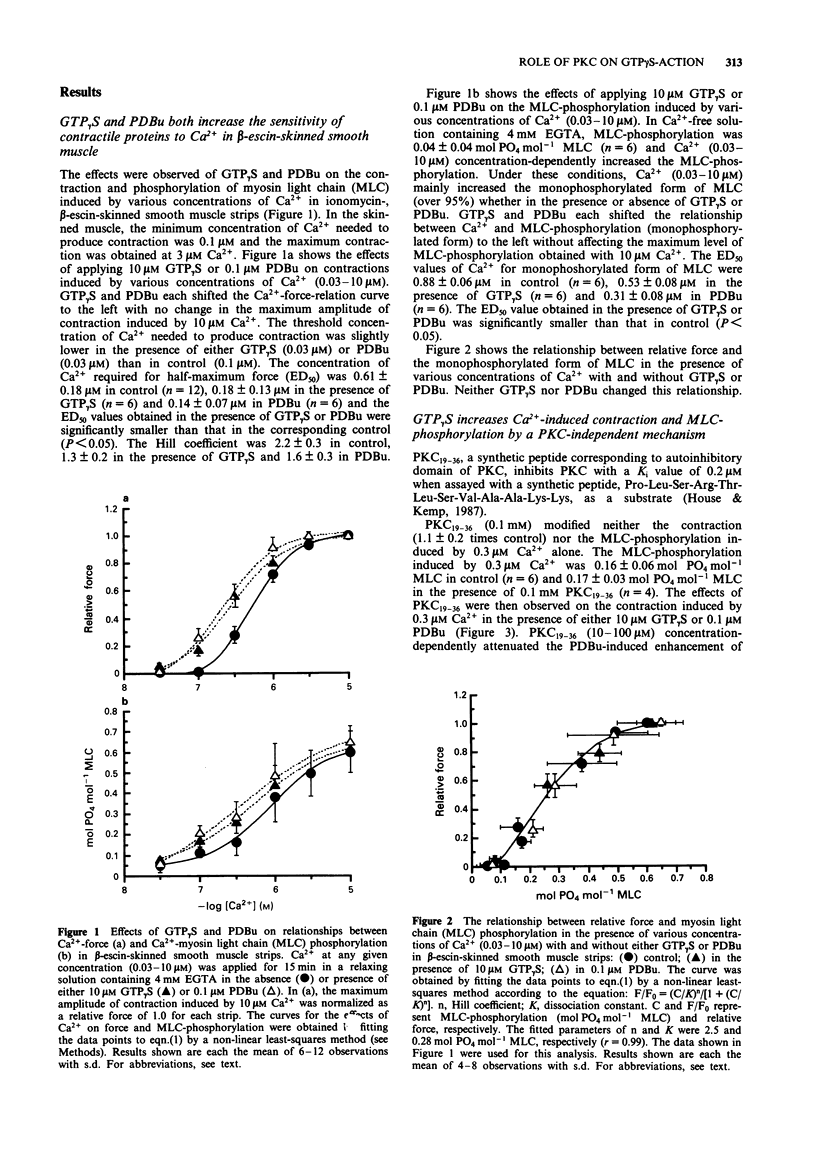
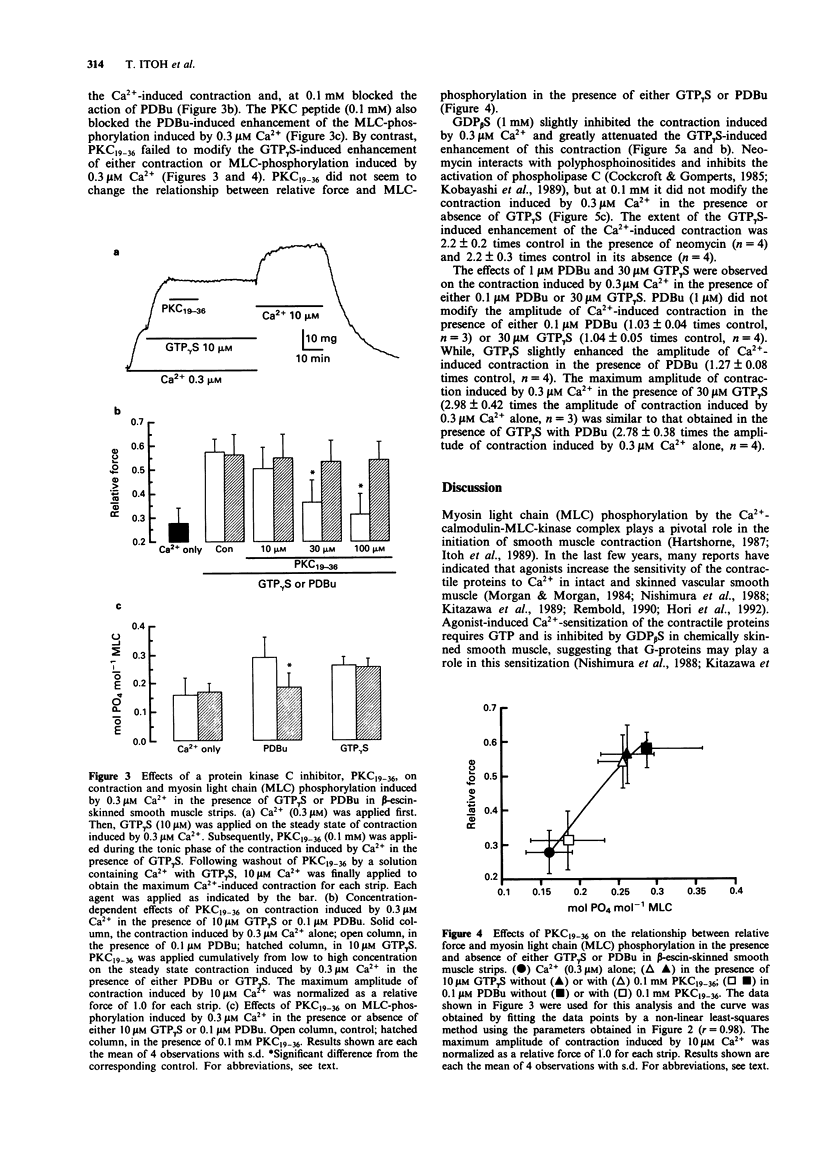
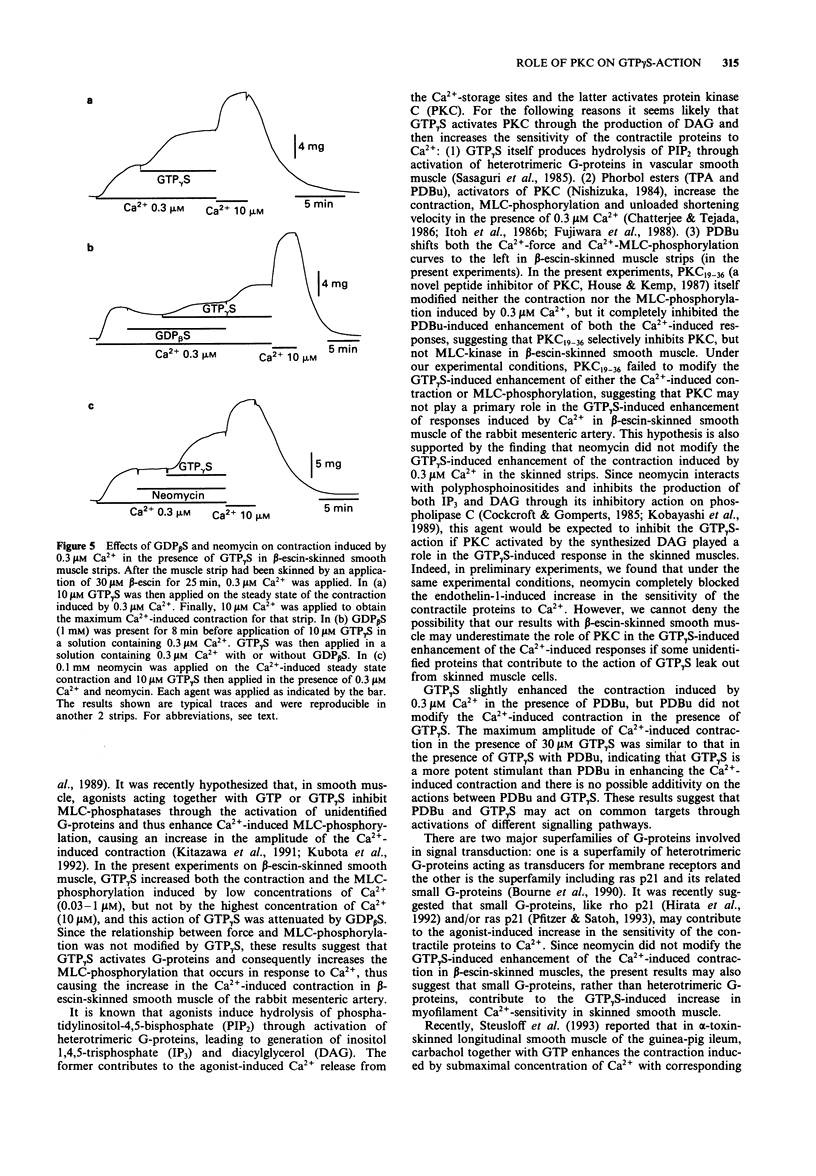
1. To investigate the role of protein kinase C in the increase mediated by guanosine 5'-triphosphate (GTP)-binding proteins (G-proteins) in the sensitivity of the contractile proteins to Ca2+ in vascular smooth muscle, the effect of a novel peptide inhibitor of protein kinase C (PKC19-36) on Ca(2+)-induced contraction and myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation was studied in the presence and absence of guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) (GTP gamma S) in beta-escin-skinned smooth muscle strips of rabbit mesenteric artery. For comparison, the effects were also observed of PKC19-36 on the action of phorbol 12,13-dibutylate (PDBu, an activator of PKC) on the two Ca(2+)-induced responses. 2. In beta-escin-skinned strips treated with ionomycin, Ca2+ (0.1-3 microM) concentration-dependently produced contraction in parallel with an increase in MLC-phosphorylation. GTP gamma S (10 microM) and PDBu (0.1 microM) each shifted both the Ca(2+)-force and Ca(2+)-MLC-phosphorylation relationships to the left without a significant change in either maximum response. The relationship between force and MLC-phosphorylation was not modified by either GTP gamma S or PDBu, indicating that the sensitivity of MLC-phosphorylation to Ca2+ is enhanced by both GTP gamma S and PDBu. 3. PKC19-36 itself modified neither the contraction nor MLC-phosphorylation induced by Ca2+ but it did block the PDBu-induced enhancement of these two Ca(2+)-induced responses. By contrast, PKC19-36 did not modify the GTP gamma S-induced enhancement of the two Ca(2+)-induced responses.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee M., Tejada M. Phorbol ester-induced contraction in chemically skinned vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):C356–C361. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.3.C356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Itoh T., Kubota Y., Kuriyama H. Actions of a phorbol ester on factors regulating contraction in rabbit mesenteric artery. Circ Res. 1988 Nov;63(5):893–902. doi: 10.1161/01.res.63.5.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Itoh T., Kubota Y., Kuriyama H. Effects of guanosine nucleotides on skinned smooth muscle tissue of the rabbit mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1989 Jan;408:535–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong M. C., Fuglsang A., Alessi D., Kobayashi S., Cohen P., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Arachidonic acid inhibits myosin light chain phosphatase and sensitizes smooth muscle to calcium. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21492–21498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Kikuchi A., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Kaibuchi K., Matsuura Y., Seki H., Saida K., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 in the GTP-enhanced calcium ion sensitivity of smooth muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8719–8722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori M., Sato K., Sakata K., Ozaki H., Takano-Ohmuro H., Tsuchiya T., Sugi H., Kato I., Karaki H. Receptor agonists induce myosin phosphorylation-dependent and phosphorylation-independent contractions in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):506–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Inagaki M., Kanamaru K., Hidaka H. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase by Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4547–4550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Ikebe M., Kargacin G. J., Hartshorne D. J., Kemp B. E., Fay F. S. Effects of modulators of myosin light-chain kinase activity in single smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):164–167. doi: 10.1038/338164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kajikuri J., Kuriyama H. Characteristic features of noradrenaline-induced Ca2+ mobilization and tension in arterial smooth muscle of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1992 Nov;457:297–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kanmura Y., Kuriyama H. Inorganic phosphate regulates the contraction-relaxation cycle in skinned muscles of the rabbit mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:231–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kanmura Y., Kuriyama H., Sumimoto K. A phorbol ester has dual actions on the mechanical response in the rabbit mesenteric and porcine coronary arteries. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:515–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Gaylinn B. D., Denney G. H., Somlyo A. P. G-protein-mediated Ca2+ sensitization of smooth muscle contraction through myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1708–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Kobayashi S., Horiuti K., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Receptor-coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle. Role of the phosphatidylinositol cascade, G-proteins, and modulation of the contractile response to Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5339–5342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Kitazawa T., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Cytosolic heparin inhibits muscarinic and alpha-adrenergic Ca2+ release in smooth muscle. Physiological role of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in pharmacomechanical coupling. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17997–18004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Nomura M., Kamm K. E., Mumby M. C., Stull J. T. GTP gamma S-dependent regulation of smooth muscle contractile elements. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 1):C405–C410. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.2.C405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Stimulus-specific patterns of intracellular calcium levels in smooth muscle of ferret portal vein. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:155–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura F., Mino T., Yamamoto J., Naka M., Tanaka T. Identification of the regulatory site in smooth muscle calponin that is phosphorylated by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6194–6201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., Sellers J. R., Adelstein R. S., Hidaka H. Protein kinase C modulates in vitro phosphorylation of the smooth muscle heavy meromyosin by myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8808–8814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Kolber M., van Breemen C. Norepinephrine and GTP-gamma-S increase myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in alpha-toxin permeabilized arterial smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persechini A., Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. Different phosphorylated forms of myosin in contracting tracheal smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6293–6299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rembold C. M. Modulation of the [Ca2+] sensitivity of myosin phosphorylation in intact swine arterial smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:77–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaguri T., Hirata M., Kuriyama H. Dependence on Ca2+ of the activities of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate phosphatase in smooth muscles of the porcine coronary artery. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):497–503. doi: 10.1042/bj2310497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton T. A., Haeberle J. R. Phosphorylation by protein kinase C of the 20,000-dalton light chain of myosin in intact and chemically skinned vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2749–2754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


