Abstract
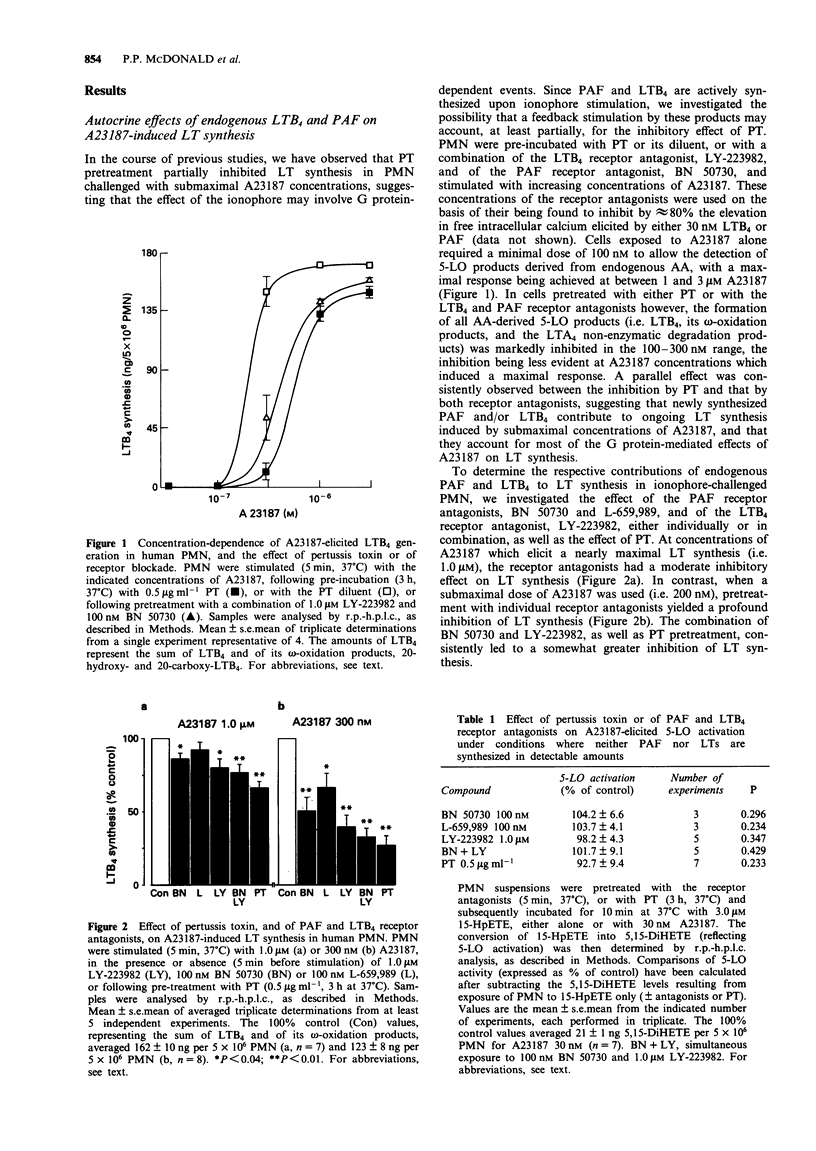
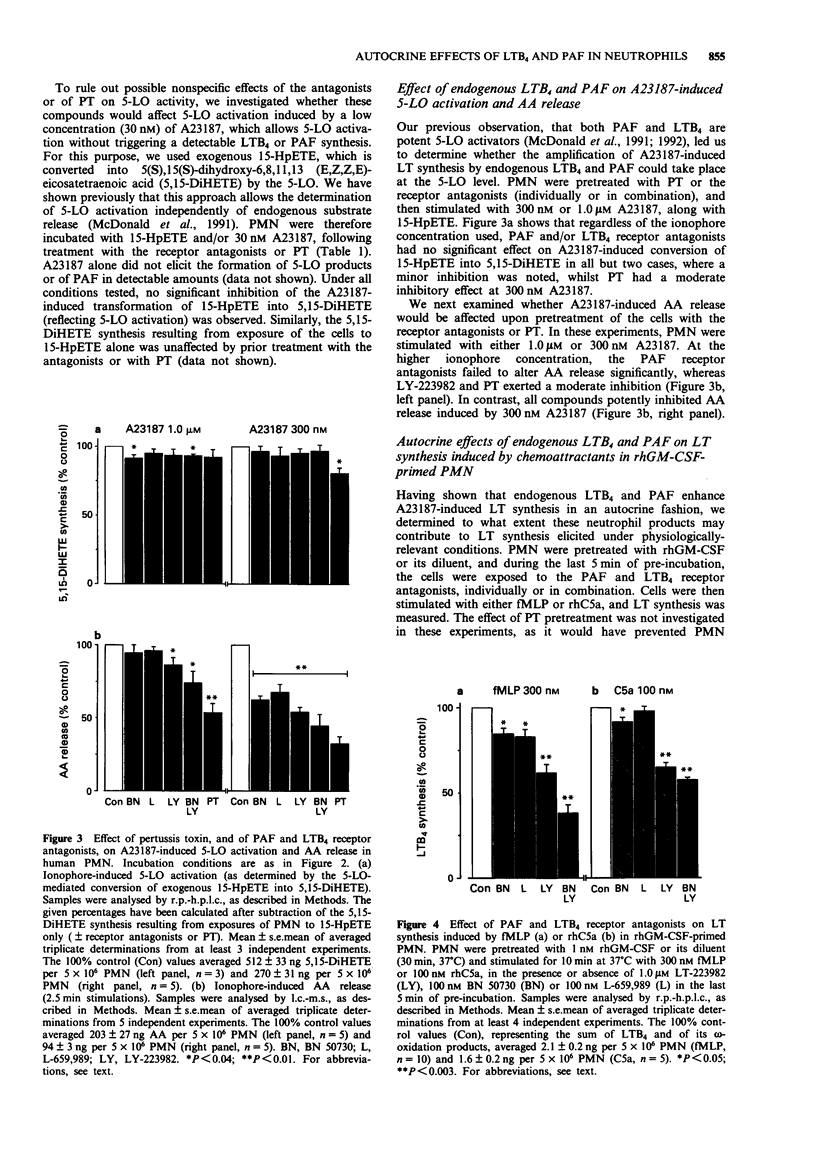
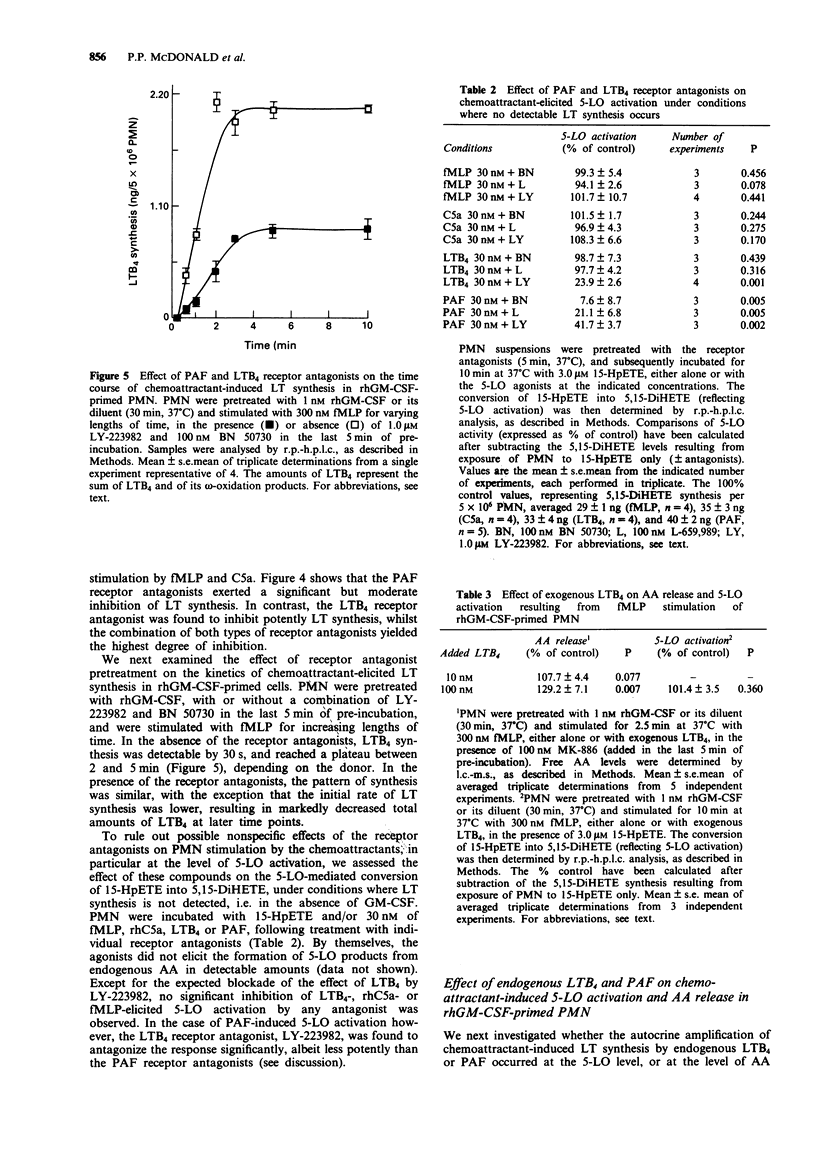
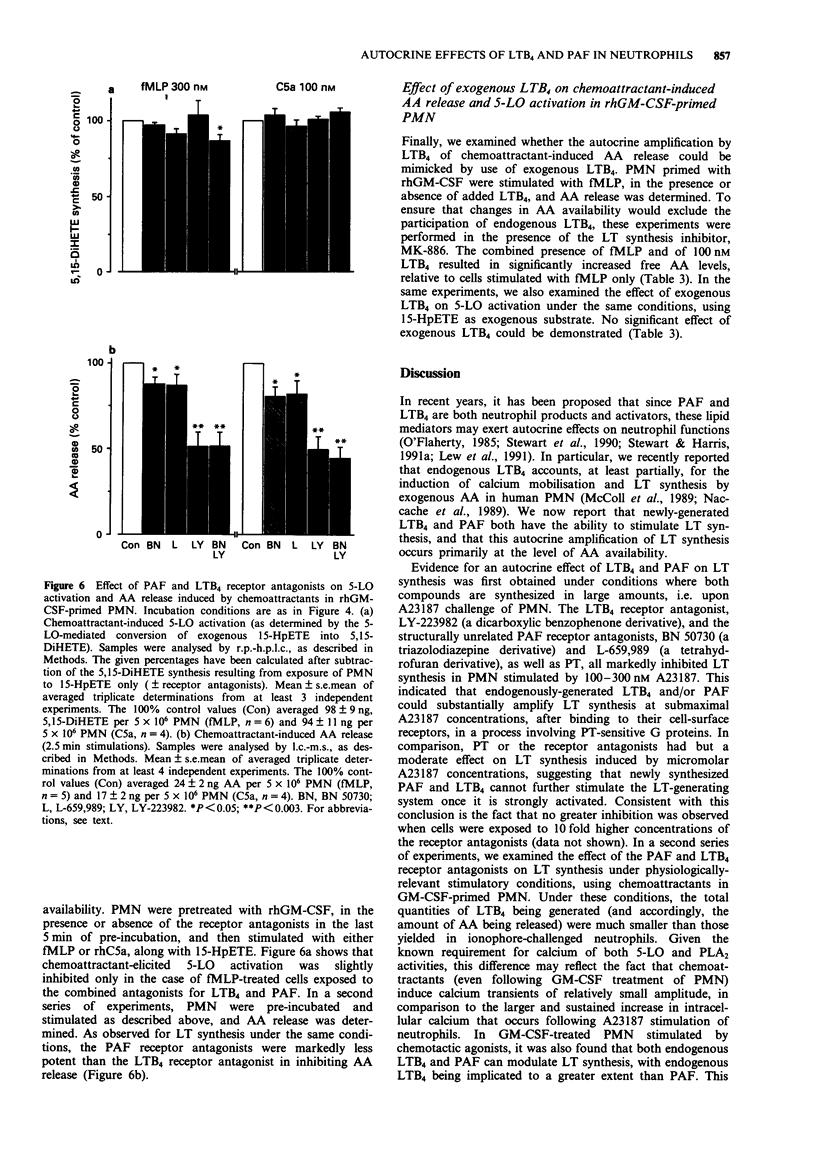
1. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) and leukotriene B4 (LTB4), two potent lipid mediators synthesized by activated neutrophils, are known to stimulate several neutrophil functional responses. In this study, we have determined that endogenous LTB4 and PAF exert autocrine effects on LT synthesis, as well as the underlying mechanism involved. 2. Pretreatment of neutrophils with either pertussis toxin (PT), or with receptor antagonists for LTB4 and PAF, resulted in an inhibition of LT synthesis induced by calcium ionophore, A23187. This inhibition was most marked at submaximal (100-300 nM) A23187 concentrations, whilst it was least at ionophore concentrations which induce maximal LT synthesis (1-3 microM). Thus newly-synthesized PAF and LTB4 can enhance LT synthesis induced by A23187 under conditions where the LT-generating system is not fully activated. 3. In recombinant human (rh) granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)-primed neutrophils, LT synthesis in response to chemoattractants (fMet-Leu-Phe or rhC5a) was also significantly inhibited by the LTB4 receptor antagonist, and to a lesser extent by PAF receptor antagonists. 4. Further investigation revealed that LTB4 and/or PAF exert their effects on LT synthesis via an effect on arachidonic acid (AA) availability, as opposed to 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) activation. Indeed, the receptor antagonists, as well as PT, inhibited LT synthesis and AA release to a similar extent, whereas 5-LO activation (assessed with an exogenous 5-LO substrate) was virtually unaffected under the same conditions. Accordingly, we showed that addition of exogenous LTB4 could enhance AA availability in response to chemoattractant challenge in rhGM-CSF-primed cells, without significantly affecting the 5-LO activation status.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borgeat P., Picard S., Vallerand P., Bourgoin S., Odeimat A., Sirois P., Poubelle P. E. Automated on-line extraction and profiling of lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1990;187:98–116. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)87014-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Arachidonic acid metabolism in polymorphonuclear leukocytes: effects of ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2148–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Sironi M., Bocchietto E., Mantovani A. Synthesis of platelet-activating factor by polymorphonuclear neutrophils stimulated with interleukin-8. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14598–14603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., Ellis J. M., Olson S. C., Wykle R. L. 1-O-alkyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. A common source of platelet-activating factor and arachidonate in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12014–12019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C. A., Zingg J., Maly F. E., de Weck A. L. Leukotriene production in human neutrophils primed by recombinant human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and stimulated with the complement component C5A and FMLP as second signals. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1281–1295. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeNichilo M. O., Stewart A. G., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a stimulant of platelet-activating factor and superoxide anion generation by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4896–4902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diez E., Mong S. Purification of a phospholipase A2 from human monocytic leukemic U937 cells. Calcium-dependent activation and membrane association. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14654–14661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey G. P., Chan C. K., Trudel S., Grinstein S. Actin assembly in electropermeabilized neutrophils: role of intracellular calcium. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1975–1982. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryden P., Duronio V., Martin L., Hudson A. T., Salari H. Inhibition of human neutrophil responses by alpha-cyano-3,4-dihydroxythiocinnamamide; a protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;106(3):656–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filep J. G., Földes-Filep E. Inhibition by calcium channel blockers of the binding of platelet-activating factor to human neutrophil granulocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94113-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R., Ferber E., Zort U. Reactive oxygen species are involved in the activation of cellular phospholipase A2. FEBS Lett. 1992 Sep 7;309(2):190–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81092-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Huang C. K., Gomez-Cambronero T. M., Waterman W. H., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein kinase in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirafuji M., Shinoda H. Platelet-leukocyte interaction in adhesion to endothelial cells induced by platelet-activating factor in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1333–1338. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Lam M. H. L-659,989: a useful probe in the detection of multiple conformational states of PAF receptors. Lipids. 1991 Dec;26(12):1148–1153. doi: 10.1007/BF02536520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Olson C. V., Grewal I. S. Platelet-activating factor mediated effects on human neutrophil function are inhibited by pertussis toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):632–638. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91938-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. B., Leslie C. C., Henson P. M., Riches D. W. Role of endogenously derived leukotrienes in the regulation of lysosomal enzyme expression in macrophages exposed to beta 1,3-glucan. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Mar;49(3):266–276. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.3.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. H., Morton D. R., Gorman R. R. Acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine stimulates leukotriene B4 synthesis in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1058–1065. doi: 10.1172/JCI110693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl S. R., Krump E., Naccache P. H., Caon A. C., Borgeat P. Activation of the human neutrophil 5-lipoxygenase by exogenous arachidonic acid: involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1265–1273. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl S. R., Krump E., Naccache P. H., Poubelle P. E., Braquet P., Braquet M., Borgeat P. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor increases the synthesis of leukotriene B4 by human neutrophils in response to platelet-activating factor. Enhancement of both arachidonic acid availability and 5-lipoxygenase activation. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1204–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. P., McColl S. R., Naccache P. H., Borgeat P. Activation of the human neutrophil 5-lipoxygenase by leukotriene B4. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):226–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. P., McColl S. R., Naccache P. H., Borgeat P. Studies on the activation of human neutrophil 5-lipoxygenase induced by natural agonists and Ca2+ ionophore A23187. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 1;280(Pt 2):379–385. doi: 10.1042/bj2800379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller S., Nigam S. Enhancement by staurosporine of platelet-activating factor formation in N-formyl peptide-challenged human neutrophils is mediated by intracellular platelet-activating factor binding sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):771–776. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., McColl S. R., Caon A. C., Borgeat P. Arachidonic acid-induced mobilization of calcium in human neutrophils: evidence for a multicomponent mechanism of action. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):461–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Winitz S., Qian N. X., Van Putten V., Johnson G. L., Heasley L. E. Phosphorylation and activation of a high molecular weight form of phospholipase A2 by p42 microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1960–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T. Neutrophil degranulation: evidence pertaining to its mediation by the combined effects of leukotriene B4, platelet-activating factor, and 5-HETE. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Feb;122(2):229–239. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Wykle R. L., Lees C. J., Shewmake T., McCall C. E., Thomas M. J. Neutrophil-degranulating action of 5,12-dihydroxy-6,8,10,14-eicosatetraenoic acid and 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. Comparison with other degranulating agents. Am J Pathol. 1981 Dec;105(3):264–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poubelle P. E., Bourgoin S., Naccache P. H., Borgeat P. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and opsonization synergistically enhance leukotriene B4 (LTB4) synthesis induced by phagocytosis in human neutrophils. Agents Actions. 1989 Jun;27(3-4):388–390. doi: 10.1007/BF01972830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poubelle P. E., De Medicis R., Naccache P. H. Monosodium urate and calcium pyrophosphate crystals differentially activate the excitation-response coupling sequence of human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90417-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riches D. W., Young S. K., Seccombe J. F., Henson J. E., Clay K. L., Henson P. M. The subcellular distribution of platelet-activating factor in stimulated human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3062–3070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. E., Duronio V., Wong S. I., McNeil M., Salari H. Solubilization of a functionally active platelet-activating factor receptor from rabbit platelets. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 1;278(Pt 2):405–410. doi: 10.1042/bj2780405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz-Munding M., Hatzelmann A., Ullrich V. The involvement of extracellular calcium in the formation of 5-lipoxygenase metabolites by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefcyk J., Yassin R., Volpi M., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Munoz J. J., Becker E. L., Feinstein M. B., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis but not cholera toxin inhibits the stimulated increase in actin association with the cytoskeleton in rabbit neutrophils: role of the "G proteins" in stimulus-response coupling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 15;126(3):1174–1181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., Waite M. Phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis by phospholipase A2 and C activities in human peripheral blood neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Dec;52(6):670–678. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.6.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. G., Dubbin P. N., Harris T., Dusting G. J. Platelet-activating factor may act as a second messenger in the release of icosanoids and superoxide anions from leukocytes and endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3215–3219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. G., Harris T., De Nichilo M., Lopez A. F. Involvement of leukotriene B4 and platelet-activating factor in cytokine priming of human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Immunology. 1991 Feb;72(2):206–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. G., Harris T. Involvement of platelet-activating factor in endotoxin-induced priming of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Lipid Mediat. 1991 Mar-Apr;3(2):125–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. G., Harris T. Platelet-activating factor may participate in signal transduction processes in rabbit leukocytes. Lipids. 1991 Dec;26(12):1044–1049. doi: 10.1007/BF02536499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessner T. G., O'Flaherty J. T., Wykle R. L. Stimulation of platelet-activating factor synthesis by a nonmetabolizable bioactive analog of platelet-activating factor and influence of arachidonic acid metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4794–4799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijkander J., Sundler R. Regulation of arachidonate-mobilizing phospholipase A2 by phosphorylation via protein kinase C in macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 26;311(3):299–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirthmueller U., De Weck A. L., Dahinden C. A. Platelet-activating factor production in human neutrophils by sequential stimulation with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and the chemotactic factors C5A or formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3213–3218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing M., Mattera R. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of phospholipase A2 by G-proteins and Ca2+ in HL60 granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25966–25975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


