Abstract
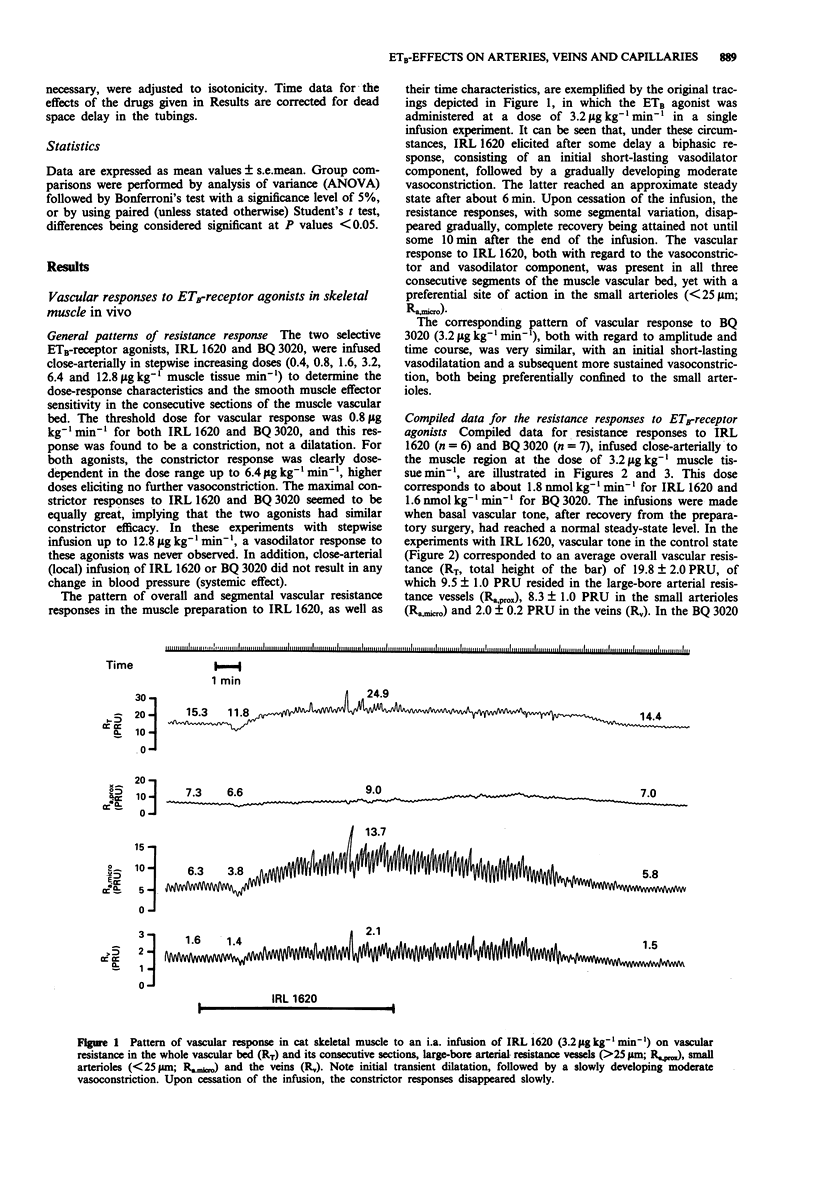
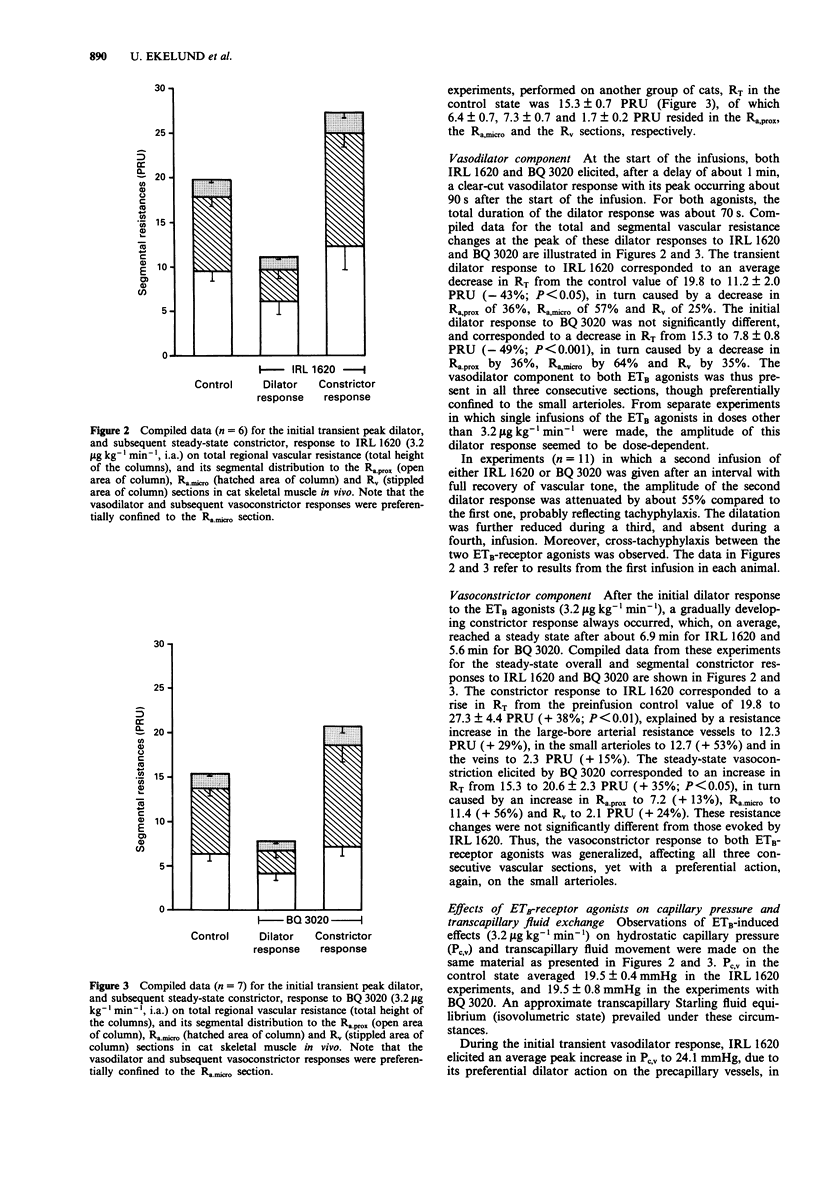
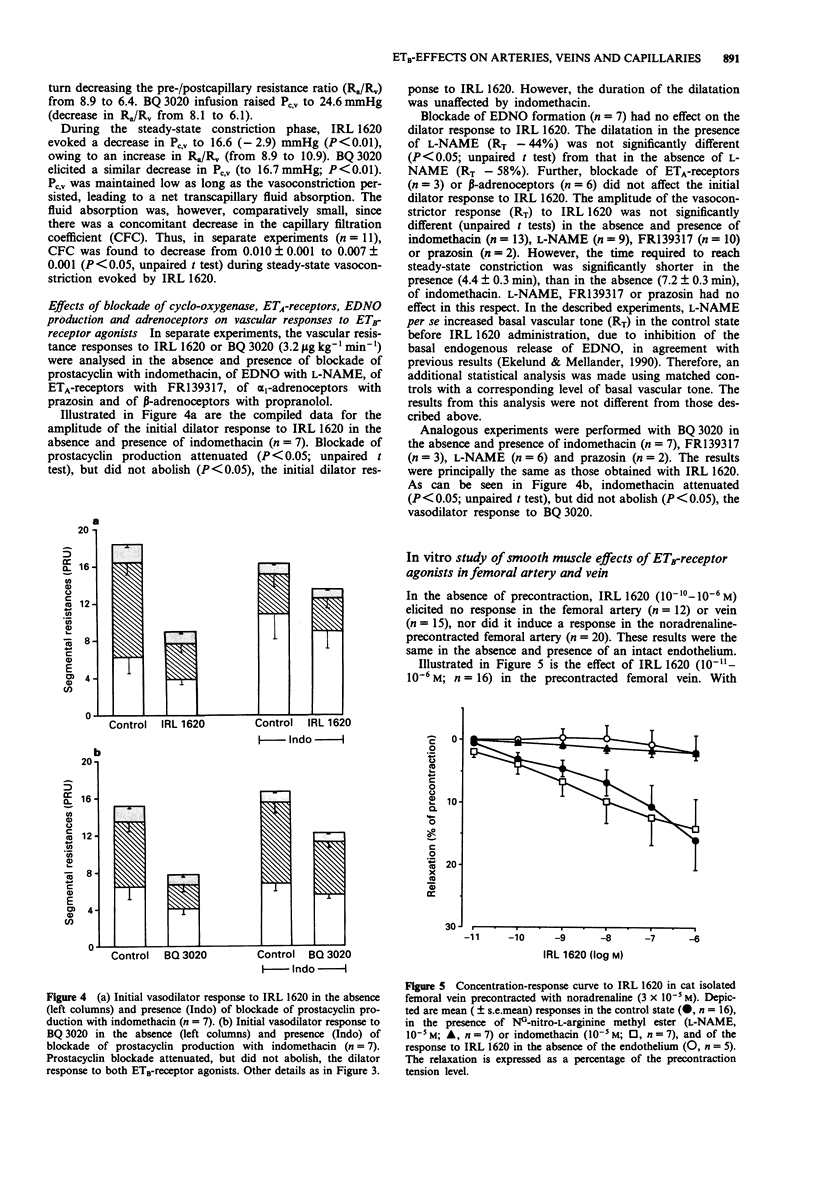
1. This paper describes, in quantitative terms, the in vivo effects of two selective ETB-receptor agonists (IRL 1620 and BQ 3020) on vascular resistance (tone) in the following consecutive sections of the vascular bed of sympathectomized cat skeletal muscle: large-bore arterial resistance vessels (> 25 microns), small arterioles (< 25 microns) and the veins. The effects on capillary pressure transcapillary fluid exchange were also recorded. 2. Both IRL 1620 and BQ 3020, infused i.a. to the muscle preparation, evoked an initial transient dilator response followed by a moderate dose-dependent constrictor response, both being preferentially confined to the small arterioles. The dilator response was associated with a transient increase, and the constrictor response with a sustained decrease, in capillary pressure, the latter causing net transcapillary fluid absorption. The capillary filtration coefficient decreased during the constrictor response, indicating constriction of terminal arterioles/precapillary sphincters. 3. The vascular responses to the ETB-receptor agonists were unaffected by blockade of endothelium-derived nitric oxide (NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester) and by selective ETA-receptor blockade (FR139317). However, blockade of prostacyclin production with indomethacin decreased the amplitude of the dilator response, and decreased the time required to reach a steady-state vasoconstrictor response to the ETB-receptor agonists. 4. The effect of ETB-receptor stimulation on vascular tone was also evaluated in vitro on the cat femoral artery and vein. IRL 1620 had no effect on the femoral artery but caused a weak dose-dependent relaxation in the femoral vein. This large vein relaxation response seemed to be mediated by endothelium-derived nitric oxide and not by prostacyclin.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aramori I., Nakanishi S. Coupling of two endothelin receptor subtypes to differing signal transduction in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12468–12474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigaud M., Pelton J. T. Discrimination between ETA- and ETB-receptor-mediated effects of endothelin-1 and [Ala1,3,11,15]endothelin-1 by BQ-123 in the anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):912–918. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björnberg J., Grände P. O., Maspers M., Mellander S. Site of autoregulatory reactions in the vascular bed of cat skeletal muscle as determined with a new technique for segmental vascular resistance recordings. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Jun;133(2):199–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Orléans-Juste P., Télémaque S., Claing A., Ihara M., Yano M. Human big-endothelin-1 and endothelin-1 release prostacyclin via the activation of ET1 receptors in the rat perfused lung. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):773–775. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund U., Albert U., Edvinsson L., Mellander S. In-vivo effects of endothelin-1 and ETA receptor blockade on arterial, venous and capillary functions in skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1993 Jul;148(3):273–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1993.tb09558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund U., Björnberg J., Grände P. O., Albert U., Mellander S. Myogenic vascular regulation in skeletal muscle in vivo is not dependent of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Feb;144(2):199–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund U. In vivo effects of endothelin-2, endothelin-3 and ETA receptor blockade on arterial, venous and capillary functions in cat skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1994 Jan;150(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1994.tb09658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujitani Y., Ueda H., Okada T., Urade Y., Karaki H. A selective agonist of endothelin type B receptor, IRL 1620, stimulates cyclic GMP increase via nitric oxide formation in rat aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Nov;267(2):683–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. NG-monomethyl-L-arginine does not inhibit the hindquarters vasodilator action of endothelin-1 in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 21;171(2-3):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högestätt E. D., Andersson K. E., Edvinsson L. Mechanical properties of rat cerebral arteries as studied by a sensitive device for recording of mechanical activity in isolated small blood vessels. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jan;117(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T. Endothelins: homeostatic and compensatory actions in the circulatory and endocrine systems. Endocr Rev. 1993 Jun;14(3):256–268. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-3-256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Kimura S., Yanagisawa M., Goto K. Molecular and cellular mechanism of endothelin regulation. Implications for vascular function. Circulation. 1991 Oct;84(4):1457–1468. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.4.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maspers M., Björnberg J., Grände P. O., Mellander S. Sympathetic alpha-adrenergic control of large-bore arterial vessels, arterioles and veins, and of capillary pressure and fluid exchange in whole-organ cat skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990 Apr;138(4):509–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb08879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maspers M., Björnberg J., Mellander S. Relation between capillary pressure and vascular tone over the range from maximum dilatation to maximum constriction in cat skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990 Sep;140(1):73–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb08977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellander S., Björnberg J., Maspers M., Myrhage R. Method for continuous recording of hydrostatic exchange vessel pressure in cat skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Mar;129(3):325–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland S., McMullen D. M., Delaney C. L., Lee V. G., Hunt J. T. Venous smooth muscle contains vasoconstrictor ETB-like receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91163-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubanyi G. M., Botelho L. H. Endothelins. FASEB J. 1991 Sep;5(12):2713–2720. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.12.1916094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki T., Ihara M., Fukuroda T., Yamagiwa M., Yano M. [Ala1,3,11,15]endothelin-1 analogs with ETB agonistic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91367-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Molecular characterization of endothelin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson M. S. Endothelins: multifunctional renal peptides. Physiol Rev. 1993 Apr;73(2):375–411. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.2.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogabe K., Nirei H., Shoubo M., Nomoto A., Ao S., Notsu Y., Ono T. Pharmacological profile of FR139317, a novel, potent endothelin ETA receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Mar;264(3):1040–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai M., Umemura I., Yamasaki K., Watakabe T., Fujitani Y., Oda K., Urade Y., Inui T., Yamamura T., Okada T. A potent and specific agonist, Suc-[Glu9,Ala11,15]-endothelin-1(8-21), IRL 1620, for the ETB receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 30;184(2):953–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90683-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Télémaque S., Lemaire D., Claing A., D'Orléans-Juste P. Phosphoramidon-sensitive effects of big endothelins in the perfused rabbit kidney. Hypertension. 1992 Oct;20(4):518–523. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.20.4.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Battistini B., Allcock G. H., Vane J. R. Endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediate vasoconstriction and prostanoid release in the isolated kidney of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec 21;250(3):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90032-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



