Abstract
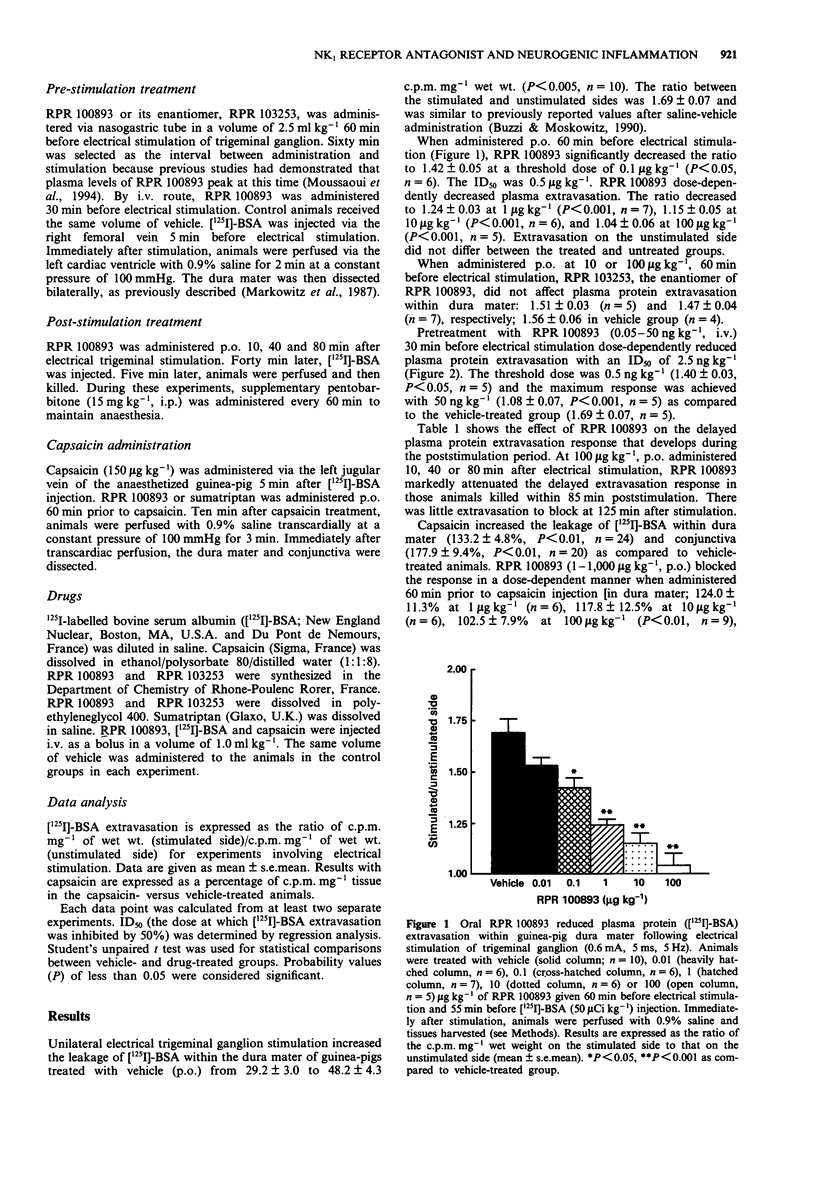
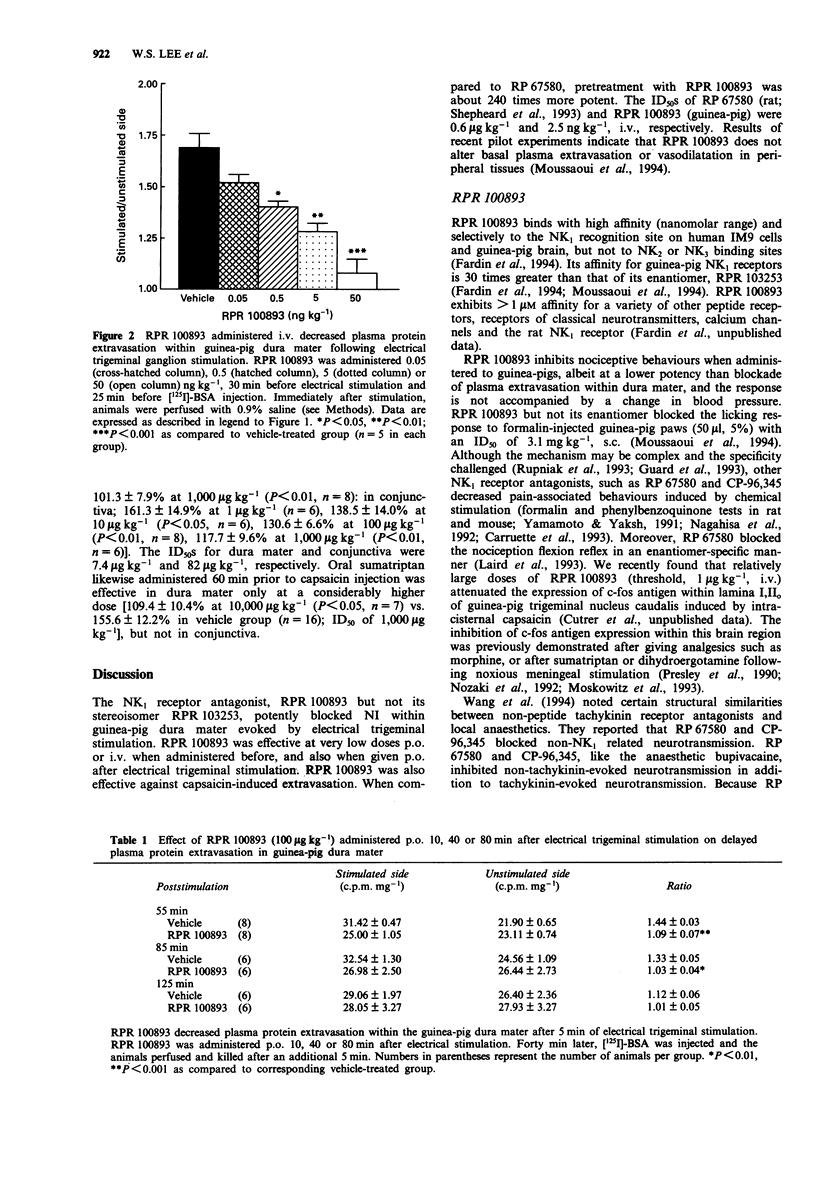
1. The ability of an NK1 receptor antagonist, RPR 100893, and its enantiomer, RPR 103253 to block neurogenic plasma protein extravasation in guinea-pig dura mater and conjunctiva was assessed following 125I-labelled bovine serum albumin ([125I]-BSA, 50 muCi kg-1, i.v.) and unilateral electrical stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion (0.6 mA, 5 ms, 5 Hz, 5 min) or capsaicin administration (150 micrograms kg-1, i.v.). 2. When administered p.o. 60 min prior to electrical stimulation, RPR 100893 (> or = 0.1 microgram kg-1) decreased plasma protein extravasation in dura mater in a dose-dependent manner, whereas the enantiomer (10 or 100 micrograms kg-1, p.o.) was inactive. 3. When given i.v. 30 min prior to electrical stimulation, RPR 100893 (> or = 0.5 ng kg-1) significantly inhibited plasma protein extravasation in the dura mater evoked by electrical stimulation in a dose-dependent manner. 4. RPR 100893 (100 micrograms kg-1, p.o.) also reduced the leakage when given 45 min before the guinea-pigs were killed and 10, 40 and 80 min after electrical trigeminal stimulation. 5. RPR 100893 given p.o. dose-dependently inhibited capsaicin-induced plasma protein extravasation with ID50S of 7.4 micrograms kg-1 and 82 micrograms kg-1 for dura mater and conjunctiva, respectively. 6. These results are consistent with the contention that NK1 receptors mediate neurogenic plasma protein leakage following trigeminal stimulation, and suggest that NK1 receptor antagonists of the perhydroisoindolone series may be useful for treating migraine and cluster headaches.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie D. T., Stubbs C. M., Connor H. E., Feniuk W. Neurokinin-induced changes in pial artery diameter in the anaesthetized guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):146–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzzi M. G., Moskowitz M. A., Peroutka S. J., Byun B. Further characterization of the putative 5-HT receptor which mediates blockade of neurogenic plasma extravasation in rat dura mater. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1421–1428. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzzi M. G., Moskowitz M. A. The antimigraine drug, sumatriptan (GR43175), selectively blocks neurogenic plasma extravasation from blood vessels in dura mater. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):202–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriadou V., Buzzi M. G., Moskowitz M. A., Theoharides T. C. Trigeminal sensory fiber stimulation induces morphological changes reflecting secretion in rat dura mater mast cells. Neuroscience. 1991;44(1):97–112. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90253-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriadou V., Buzzi M. G., Theoharides T. C., Moskowitz M. A. Ultrastructural evidence for neurogenically mediated changes in blood vessels of the rat dura mater and tongue following antidromic trigeminal stimulation. Neuroscience. 1992;48(1):187–203. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Rosendal-Helgesen S., Uddman R. Substance P: localization, concentration and release in cerebral arteries, choroid plexus and dura mater. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;234(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00217397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Boyle S. J., Tang K. W., Watling K. J., McKnight A. T., Woodruff G. N. The interaction of the NK1 receptor antagonist CP-96,345 with L-type calcium channels and its functional consequences. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan R. M., Ireland S. J., Jordan C. C., Beresford I. J., Deal M. J., Ward P. Receptor-selective, peptidase-resistant agonists at neurokinin NK-1 and NK-2 receptors: new tools for investigating neurokinin function. Neuropeptides. 1991 Jun;19(2):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Z., Byun B., Matsubara T., Moskowitz M. A. Time-dependent blockade of neurogenic plasma extravasation in dura mater by 5-HT1B/D agonists and endopeptidase 24.11. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):331–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara H., Nakanishi S. Selective inhibition of expression of the substance P receptor mRNA in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22441–22445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird J. M., Hargreaves R. J., Hill R. G. Effect of RP 67580, a non-peptide neurokinin1 receptor antagonist, on facilitation of a nociceptive spinal flexion reflex in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):713–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13632.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Chen L. Y., Mayberg M. R., Moskowitz M. A. Immunohistochemical evidence for a substance P-containing trigeminovascular pathway to pial arteries in cats. Brain Res. 1983 May 23;268(1):162–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Saito K., Moskowitz M. A. Neurogenically mediated leakage of plasma protein occurs from blood vessels in dura mater but not brain. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4129–4136. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04129.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara T., Moskowitz M. A., Byun B. CP-93,129, a potent and selective 5-HT1B receptor agonist blocks neurogenic plasma extravasation within rat but not guinea-pig dura mater. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):3–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A., Brody M., Liu-Chen L. Y. In vitro release of immunoreactive substance P from putative afferent nerve endings in bovine pia arachnoid. Neuroscience. 1983 Aug;9(4):809–814. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A., Buzzi M. G., Sakas D. E., Linnik M. D. Pain mechanisms underlying vascular headaches. Progress Report 1989. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1989;145(3):181–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A. Neurogenic versus vascular mechanisms of sumatriptan and ergot alkaloids in migraine. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Aug;13(8):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90097-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A., Nozaki K., Kraig R. P. Neocortical spreading depression provokes the expression of c-fos protein-like immunoreactivity within trigeminal nucleus caudalis via trigeminovascular mechanisms. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):1167–1177. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-01167.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A. The neurobiology of vascular head pain. Ann Neurol. 1984 Aug;16(2):157–168. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A. The visceral organ brain: implications for the pathophysiology of vascular head pain. Neurology. 1991 Feb;41(2 ):182–186. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.2_part_1.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moussaoui S. M., Montier F., Carruette A., Blanchard J. C., Laduron P. M., Garret C. A non-peptide NK1-receptor antagonist, RP 67580, inhibits neurogenic inflammation postsynaptically. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):259–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13562.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moussaoui S. M., Philippe L., Le Prado N., Garret C. Inhibition of neurogenic inflammation in the meninges by a non-peptide NK1 receptor antagonist, RP 67580. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul 20;238(2-3):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90879-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moussaoui S., Carruette A., Garret C. Further evidence that substance P is a mediator of both neurogenic inflammation and pain: two phenomena inhibited either by postsynaptic blockade of NK1 receptors or by presynaptic action of opioid receptor agonists. Regul Pept. 1993 Jul 2;46(1-2):424–425. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90108-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahisa A., Kanai Y., Suga O., Taniguchi K., Tsuchiya M., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Hess H. J. Antiinflammatory and analgesic activity of a non-peptide substance P receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;217(2-3):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90847-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shaughnessy C. T., Connor H. E. Neurokinin NK1 receptors mediate plasma protein extravasation in guinea-pig dura. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 May 19;236(2):319–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90605-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presley R. W., Menétrey D., Levine J. D., Basbaum A. I. Systemic morphine suppresses noxious stimulus-evoked Fos protein-like immunoreactivity in the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):323–335. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00323.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Dam T. V. Multiple tachykinin receptors in guinea pig brain. High densities of substance K (neurokinin A) binding sites in the substantia nigra. Neuropeptides. 1985 Jun;6(3):191–204. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P. Pharmacological receptors for substance P and neurokinins. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 12;40(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90349-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Beaumont A. Neutral endopeptidase-24.11 inhibitors: from analgesics to antihypertensives? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jun;11(6):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupniak N. M., Boyce S., Williams A. R., Cook G., Longmore J., Seabrook G. R., Caeser M., Iversen S. D., Hill R. G. Antinociceptive activity of NK1 receptor antagonists: non-specific effects of racemic RP67580. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1607–1613. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb14008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepheard S. L., Williamson D. J., Hill R. G., Hargreaves R. J. The non-peptide neurokinin1 receptor antagonist, RP 67580, blocks neurogenic plasma extravasation in the dura mater of rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):11–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Y., Tung S. R., Strichartz G. R., Håkanson R. Non-specific actions of the non-peptide tachykinin receptor antagonists, CP-96,345, RP 67580 and SR 48968, on neurotransmission. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):179–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yaksh T. L. Stereospecific effects of a nonpeptidic NK1 selective antagonist, CP-96,345: antinociception in the absence of motor dysfunction. Life Sci. 1991;49(26):1955–1963. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90637-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


