Abstract
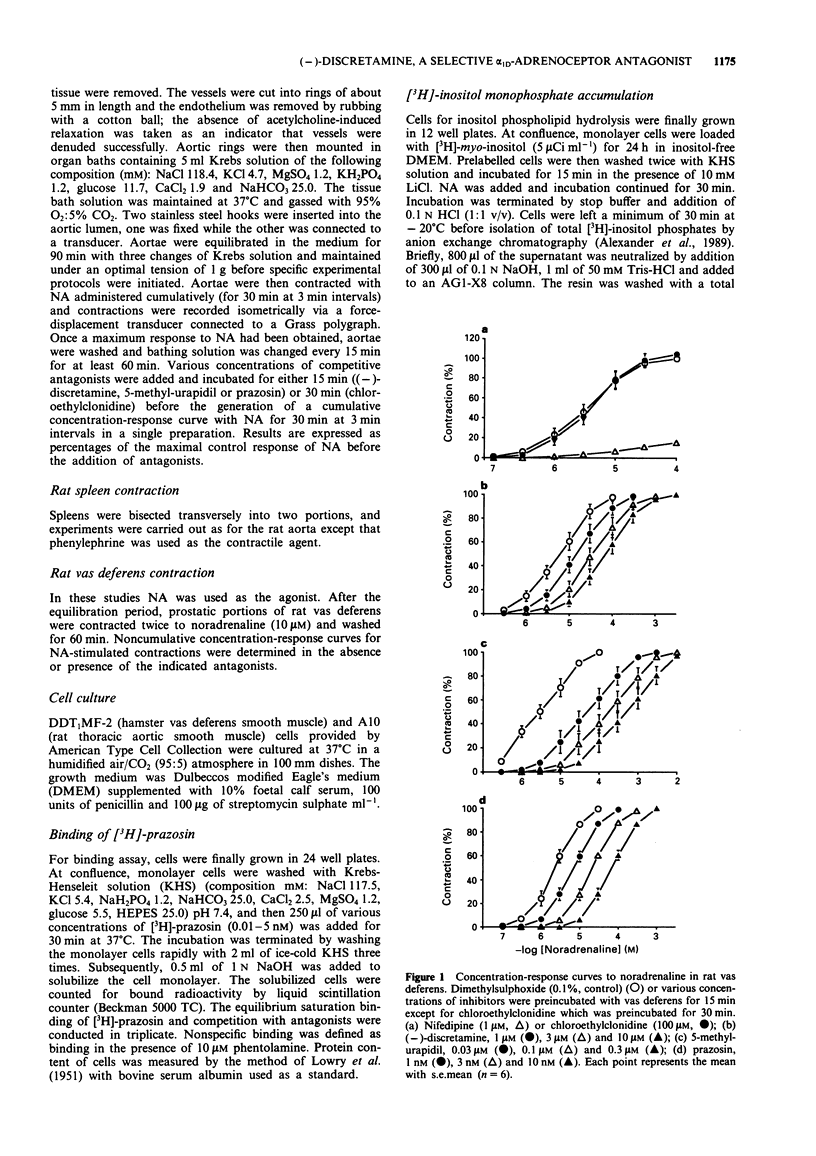
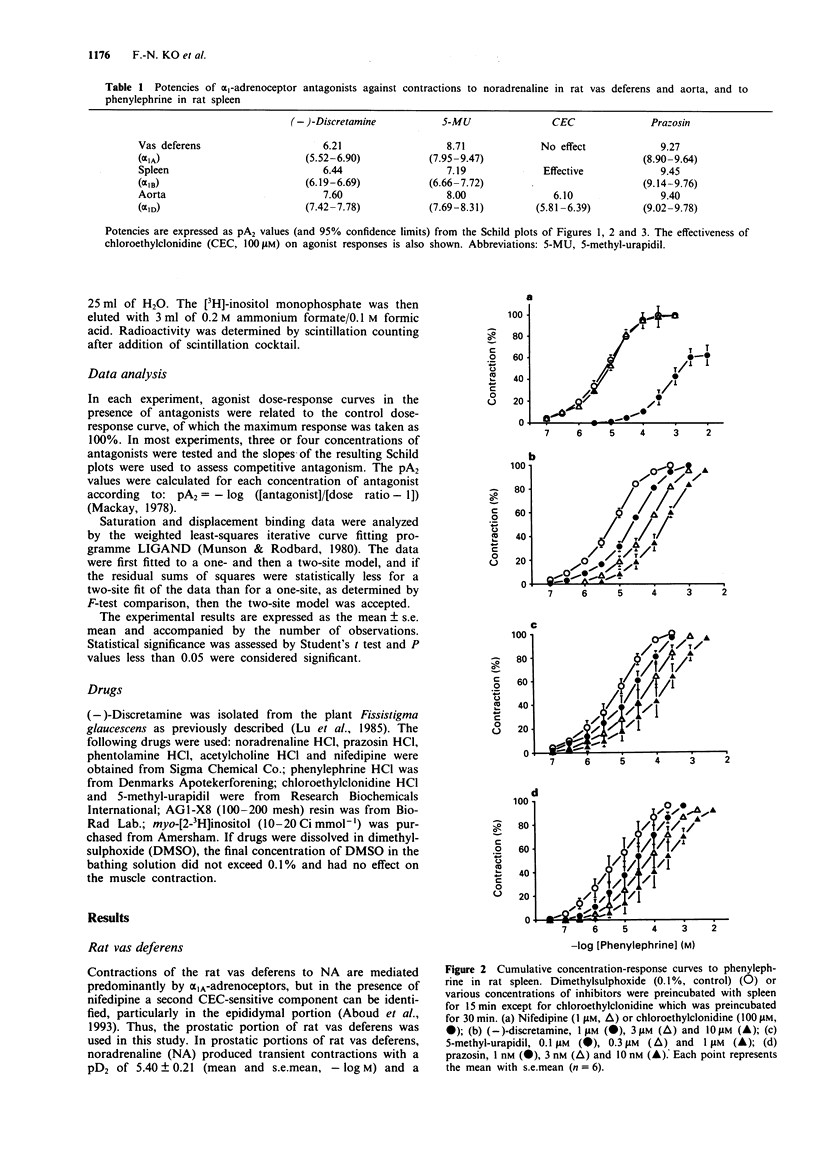
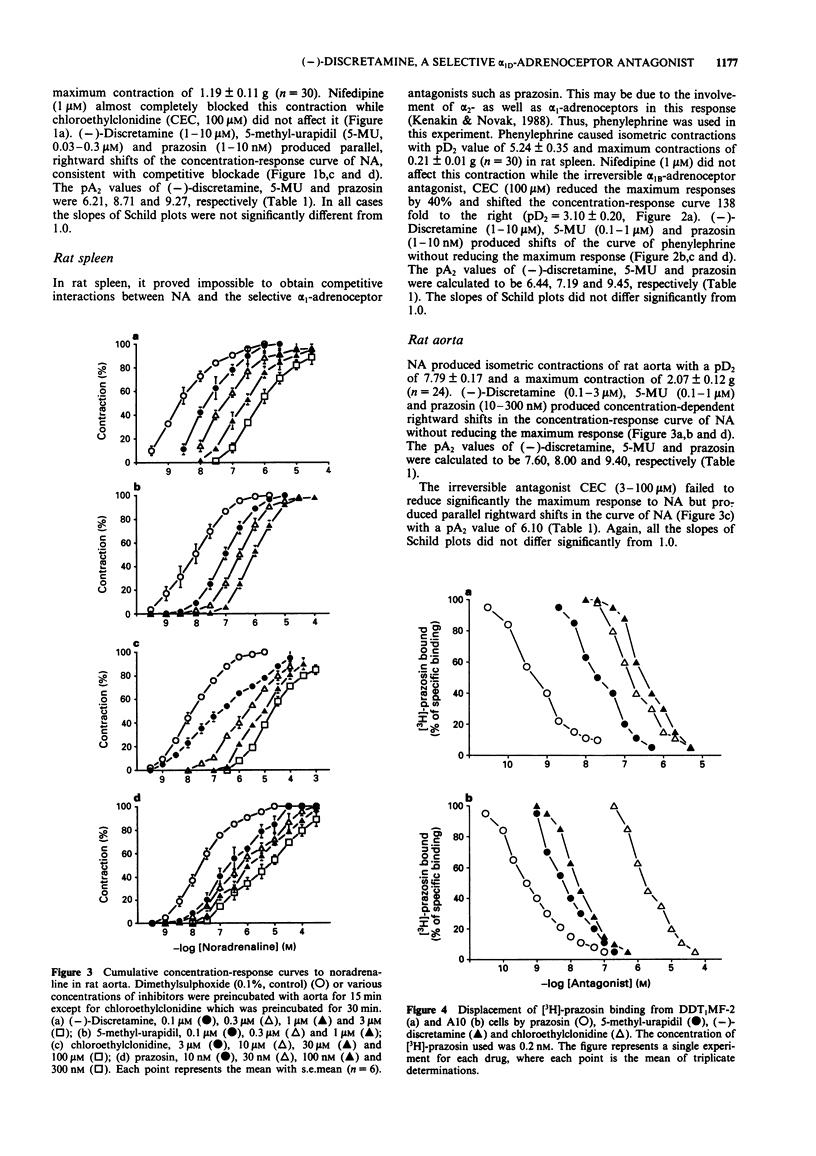
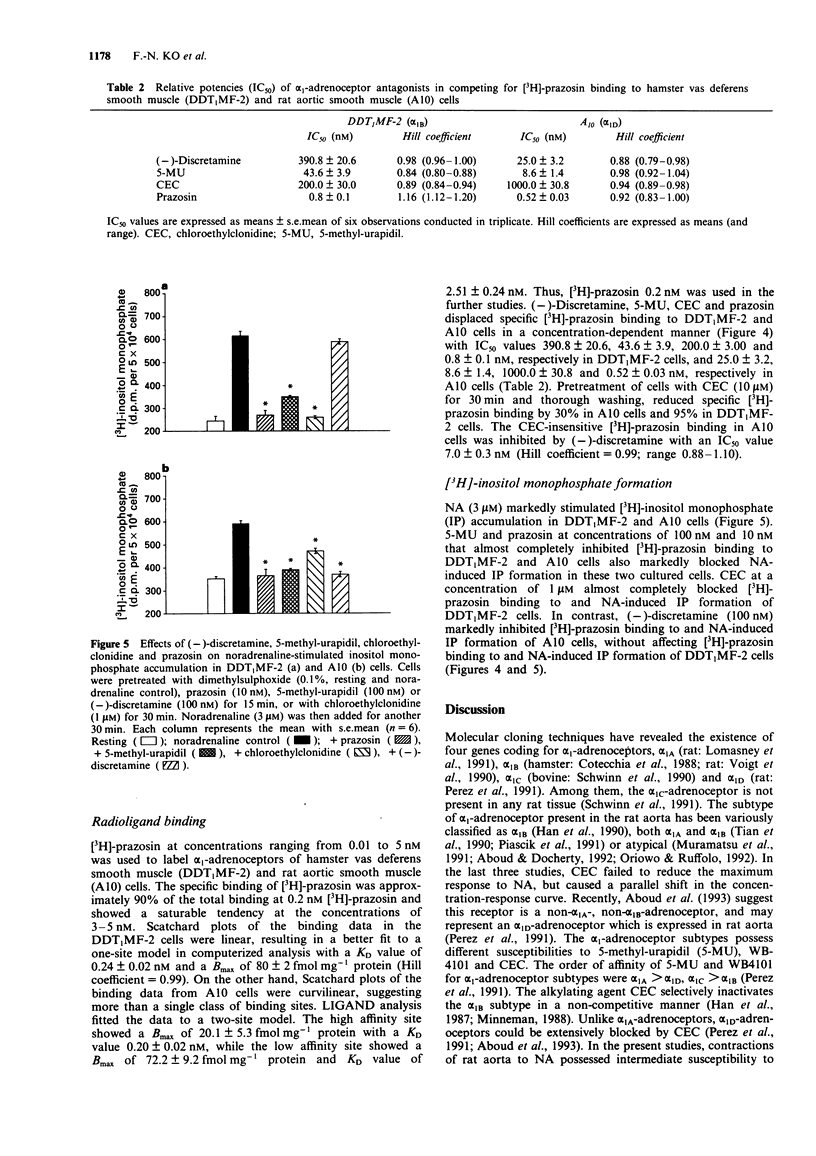
1. The selectivity of (-)-discretamine for alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes was investigated by use of functional and binding studies in rat vas deferens, spleen and aorta, and in cultured DDT1MF-2 and A10 cells. 2. In prostatic portions of rat vas deferens, the competitive antagonists (-)-discretamine, 5-methylurapidil (5-MU) and prazosin inhibited contractions to noradrenaline (NA) with pA2 values of 6.21, 8.71 and 9.27, respectively. The irreversible antagonist, chloroethylclonidine (CEC, 100 microM) failed to affect contractions to NA while nifedipine (1 microM) blocked them almost completely. 3. In rat spleen, the competitive antagonists (-)-discretamine, 5-MU and prazosin inhibited contractions to phenylephrine with pA2 values of 6.44, 7.19 and 9.45, respectively. CEC (100 microM) significantly reduced the maximum contraction to phenylephrine while nifedipine (1 microM) did not affect it. 4. In rat aorta, the competitive antagonists (-)-discretamine, 5-MU and prazosin inhibited contractions to NA with pA2 values of 7.60, 8.00 and 9.40, respectively. CEC also antagonized the contractions to NA in a competitive manner with a pA2 value of 6.10. 5. The specific binding of [3H]-prazosin to DDT1MF-2 and A10 cells was concentration-dependent and saturated at 3-5 nM with KD values of 0.24 +/- 0.02 and 0.20 +/- 0.02 nM, respectively.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboud R., Shafii M., Docherty J. R. Investigation of the subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediating contractions of rat aorta, vas deferens and spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):80–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander S. P., Kendall D. A., Hill S. J. Differences in the adenosine receptors modulating inositol phosphates and cyclic AMP accumulation in mammalian cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1241–1248. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes linked to different mechanisms for increasing intracellular Ca2+ in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):333–335. doi: 10.1038/329333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Esbenshade T. A., Minneman K. P. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in DDT1 MF-2 and BC3H-1 clonal cell lines. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 5;226(2):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90175-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Li J., Minneman K. P. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat blood vessels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94116-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanft G., Gross G. Subclassification of alpha 1-adrenoceptor recognition sites by urapidil derivatives and other selective antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):691–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12005.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. P., Novak P. J. Classification of phenoxybenzamine/prazosin-resistant contractions of rat spleen to norepinephrine by Schild analysis: similarities and differences to postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenoceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jan;244(1):206–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko F. N., Yu S. M., Su M. J., Wu Y. C., Teng C. M. Pharmacological activity of (-)-discretamine, a novel vascular alpha-adrenoceptor and 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor antagonist, isolated from Fissistigma glaucescens. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):882–888. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay D. How should values of pA2 and affinity constants for pharmacological competitive antagonists be estimated? J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 May;30(5):312–313. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes, inositol phosphates, and sources of cell Ca2+. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Jun;40(2):87–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Creese I. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: a reevaluation of [3H]WB4104 and [3H]prazosin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Kigoshi S., Ohmura T. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors involved in noradrenaline-induced contractions of rat thoracic aorta and dog carotid artery. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;57(4):535–544. doi: 10.1254/jjp.57.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriowo M. A., Ruffolo R. R., Jr Heterogeneity of postjunctional alpha 1-adrenoceptors in mammalian aortae: subclassification based on chlorethylclonidine, WB 4101 and nifedipine. J Vasc Res. 1992 Jan-Feb;29(1):33–40. doi: 10.1159/000158929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Graham R. M. Solution-phase library screening for the identification of rare clones: isolation of an alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piascik M. T., Sparks M. S., Pruitt T. A., Soltis E. E. Evidence for a complex interaction between the subtypes of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90491-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Szklut P. J., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Page S. O., Middleton J. P., Lorenz W., Liggett S. B., Yamamoto K., Lapetina E. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. The alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor: characterization of signal transduction pathways and mammalian tissue heterogeneity. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):619–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki E., Tsujimoto G., Tamura K., Hashimoto K. Two pharmacologically distinct alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in the contraction of rabbit aorta: each subtype couples with a different Ca2+ signalling mechanism and plays a different physiological role. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):725–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian W. N., Gupta S., Deth R. C. Species differences in chlorethylclonidine antagonism at vascular alpha-1 adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):877–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto G., Tsujimoto A., Suzuki E., Hashimoto K. Glycogen phosphorylase activation by two different alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes: methoxamine selectively stimulates a putative alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype (alpha 1a) that couples with Ca2+ influx. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):166–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt M. M., Kispert J., Chin H. M. Sequence of a rat brain cDNA encoding an alpha-1B adrenergic receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1053–1053. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


