Abstract
1. Radioligand binding assays have been used to determine the affinities of a series of ATP derivatives with modifications of the polyphosphate chain, adenine and ribose moieties of the ATP molecule for [H]-alpha,beta-methylene ATP ([3H]-alpha,beta-MeATP) binding sites in rat urinary bladder. 2. The replacement of the bridging oxygen in the triphosphate chain of ATP (pIC50 = 5.58) with a methylene or imido group markedly increased the affinity (691 fold in IC50 values for beta,gamma-imidoATP, 15 fold for beta,gamma-methylene ATP), and the replacement of an ionized oxygen on the gamma-phosphate with a sulphur (ATP gamma S) also led to increased affinity (5623 fold in IC50 values). 3. Modifications at N6, N1, and C-8 positions on the purine base usually reduced the affinity of ATP (a decrease of 2.8 fold in IC50 values for N6-methylATP and 8.9 fold for 8-bromo ATP), while the attachment of an alkylthio group to the C-2 position greatly increased the affinity for P2x-purinoceptors (from 3.5 to 98 fold increase in IC50 values). 4. Replacement of the 3'-hydroxyl group on the ribose with substituted amino or acylamino groups produced more potent P2x-purinoceptor agonists (an increase of 447 fold in IC50 values for 3'-deoxy-3'-benzylamino ATP and 28 fold for 3'-deoxy-3'-(4-hydroxyphenylpropionyl)amino ATP. 5. Diadenosine polyphosphates (Ap[n]A) were also shown to displace the [3H]-alpha,beta-MeATP binding. The rank order of potency was Ap6A > Ap5A > Ap4A >> Ap3A >> Ap2A.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


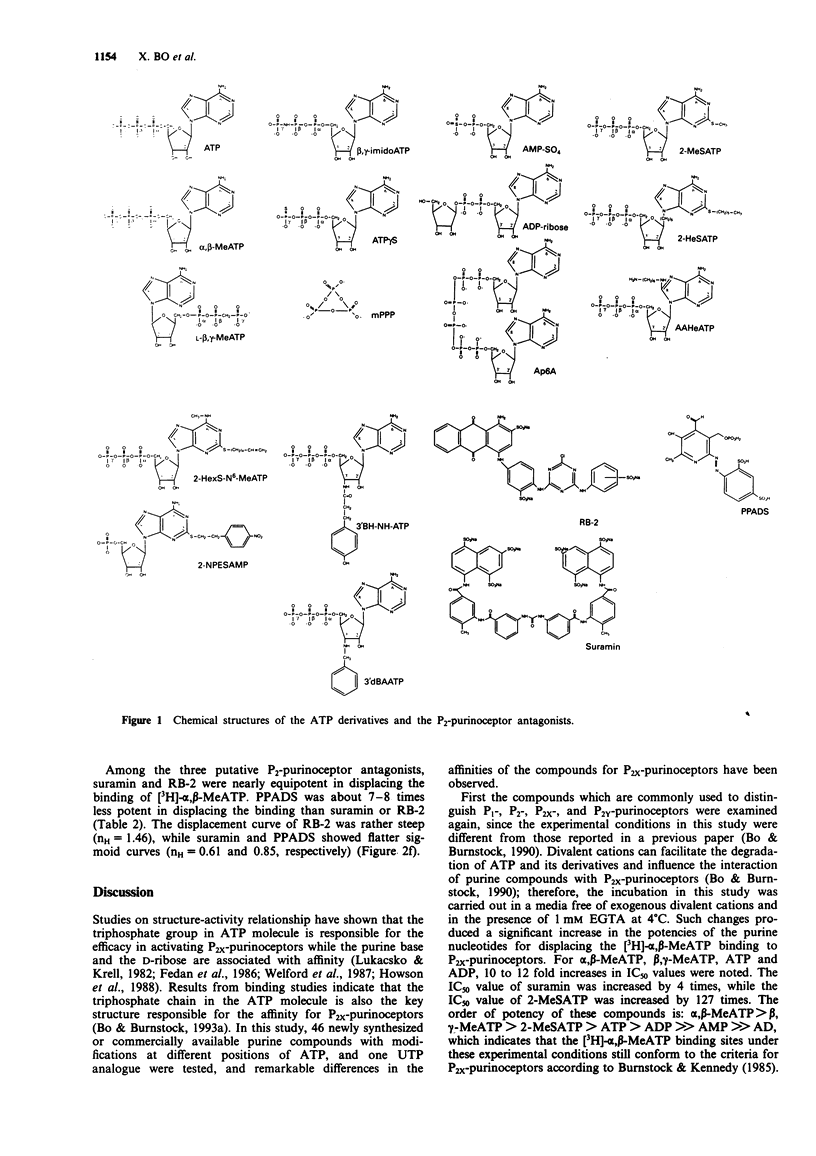
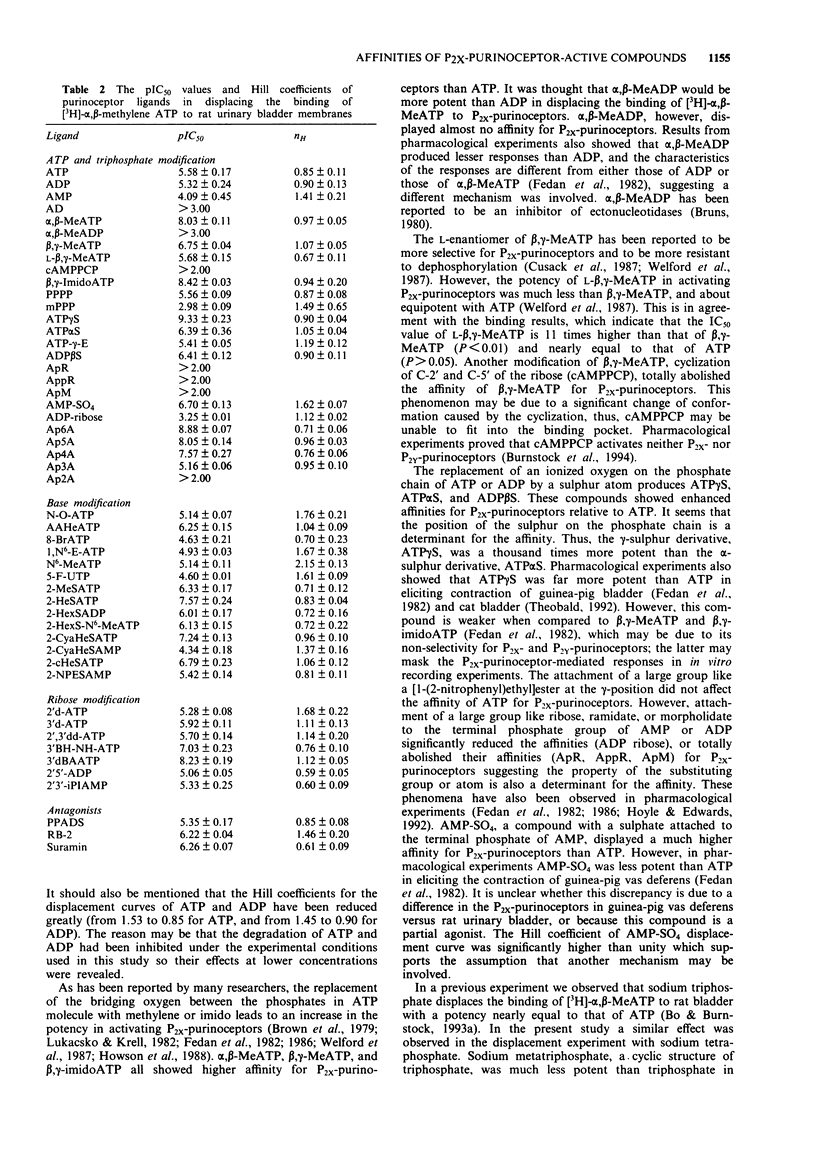
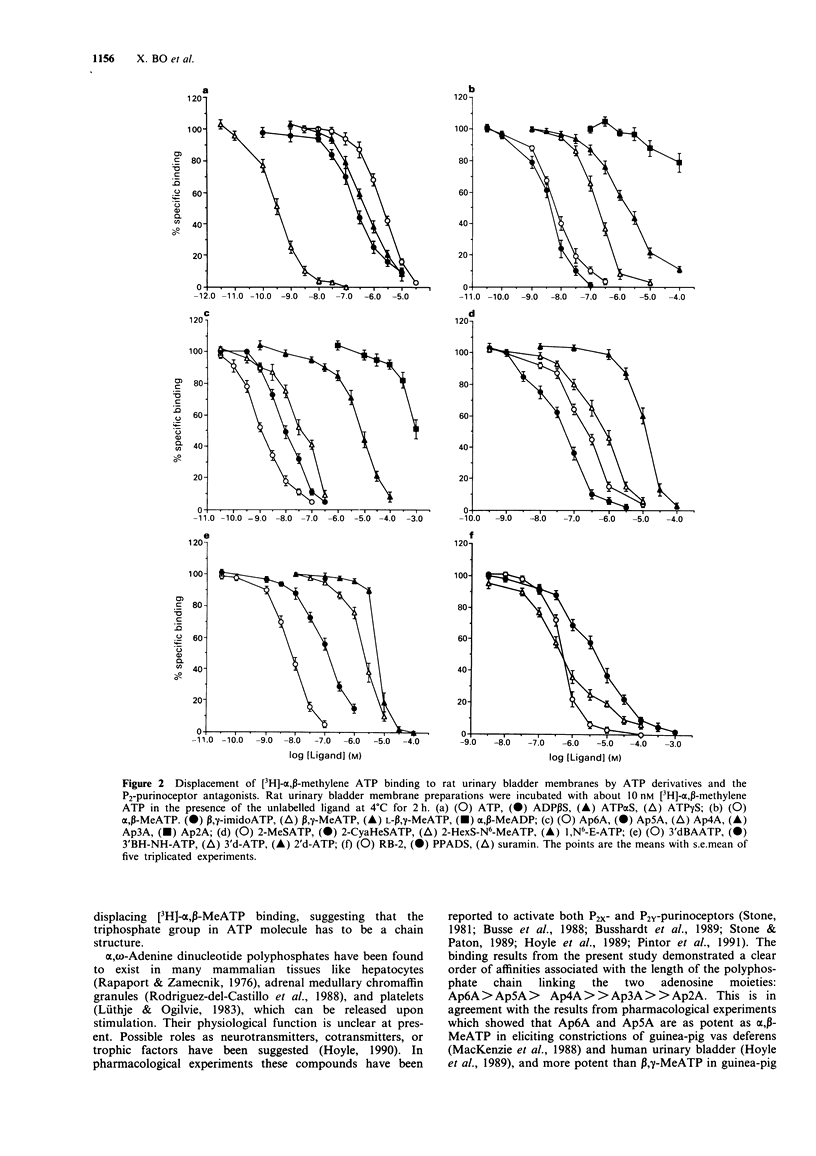



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bo X. N., Burnstock G. High- and low-affinity binding sites for [3H]-alpha, beta-methylene ATP in rat urinary bladder membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):291–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo X., Burnstock G. Heterogeneous distribution of [3H]alpha,beta-methylene ATP binding sites in blood vessels. J Vasc Res. 1993 Mar-Apr;30(2):87–101. doi: 10.1159/000158980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo X., Burnstock G. Triphosphate, the key structure of the ATP molecule responsible for interaction with P2X-purinoceptors. Gen Pharmacol. 1993 May;24(3):637–640. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(93)90223-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C., Burnstock G., Cocks T. Effects of adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) and beta-gamma-methylene ATP on the rat urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;65(1):97–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb17337.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F. Adenosine receptor activation by adenine nucleotides requires conversion of the nucleotides to adenosine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980;315(1):5–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00504224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Cusack N. J., Hills J. M., MacKenzie I., Meghji P. Studies on the stereoselectivity of the P2-purinoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;79(4):907–913. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Ogilvie A., Pohl U. Vasomotor activity of diadenosine triphosphate and diadenosine tetraphosphate in isolated arteries. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 2):H828–H832. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.5.H828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busshardt E., Gerok W., Häussinger D. Regulation of hepatic parenchymal and non-parenchymal cell function by the diadenine nucleotides Ap3A and Ap4A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 9;1010(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo L. K. The effect of reactive blue, an antagonist of ATP, on the isolated urinary bladders of guinea-pig and rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Apr;33(4):248–250. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack N. J., Hourani S. M., Loizou G. D., Welford L. A. Pharmacological effects of isopolar phosphonate analogues of ATP on P2-purinoceptors in guinea-pig taenia coli and urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;90(4):791–795. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Gibb A. J., Colquhoun D. ATP receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):144–147. doi: 10.1038/359144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Derkach V., Surprenant A. ATP mediates fast synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):503–505. doi: 10.1038/357503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Hogaboom G. K., O'Donnell J. P. Further comparison of contractions of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig isolated vas deferens induced by ATP and related analogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 7;129(3):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90438-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Hogaboom G. K., Westfall D. P., O'Donnell J. P. Comparison of contractions of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig vas deferens induced by ATP and related nucleotides. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 9;81(2):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Lamport S. J. P2-purinoceptor antagonists. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:182–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough G. R., Maguire M. H., Satchell D. G. Three new adenosine triphosphate analogs. Synthesis and effects on isolated gut. J Med Chem. 1973 Oct;16(10):1188–1190. doi: 10.1021/jm00268a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Chapple C., Burnstock G. Isolated human bladder: evidence for an adenine dinucleotide acting on P2X-purinoceptors and for purinergic transmission. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 12;174(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90881-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Edwards G. A. Activation of P1- and P2Y-purinoceptors by ADP-ribose in the guinea-pig taenia coli, but not of P2X-purinoceptors in the vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):367–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Knight G. E., Burnstock G. Suramin antagonizes responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists and purinergic nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig urinary bladder and taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):617–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H. Pharmacological activity of adenine dinucleotides in the periphery: possible receptor classes and transmitter function. Gen Pharmacol. 1990;21(6):827–831. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(90)90440-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht G., Friebe T., Grimm U., Windscheif U., Bungardt E., Hildebrandt C., Bäumert H. G., Spatz-Kümbel G., Mutschler E. PPADS, a novel functionally selective antagonist of P2 purinoceptor-mediated responses. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;217(2-3):217–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90877-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacsko P., Krell R. D. Response of the guinea-pig urinary bladder to purine and pyrimidine nucleotides. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jun 4;80(4):401–406. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthje J., Ogilvie A. The presence of diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P3-triphosphate (Ap3A) in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie I., Kirkpatrick K. A., Burnstock G. Comparative study of the actions of AP5A and alpha,beta-methylene ATP on nonadrenergic, noncholinergic neurogenic excitation in the guinea-pig vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):699–706. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11578.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Humphrey P. P. Distribution and characterisation of [3H]alpha,beta-methylene ATP binding sites in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;348(6):608–617. doi: 10.1007/BF00167237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molineaux C. J., Lasdun A., Michaud C., Orlowski M. Endopeptidase-24.15 is the primary enzyme that degrades luteinizing hormone releasing hormone both in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):624–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Torres M., Castro E., Miras-Portugal M. T. Characterization of diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) binding sites in cultured chromaffin cells: evidence for a P2y site. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1980–1984. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport E., Zamecnik P. C. Presence of diadenosine 5',5''' -P1, P4-tetraphosphate (Ap4A) in mamalian cells in levels varying widely with proliferative activity of the tissue: a possible positive "pleiotypic activator". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3984–3988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchell D. G., Maguire M. H. Inhibitory effects of adenine nucleotide analogs on the isolated guinea-pig taenia coli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Dec;195(3):540–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Schultz G. Involvement of pyrimidinoceptors in the regulation of cell functions by uridine and by uracil nucleotides. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silinsky E. M., Gerzanich V., Vanner S. M. ATP mediates excitatory synaptic transmission in mammalian neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):762–763. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Actions of adenine dinucleotides on the vas deferens, guinea-pig taenia caeci and bladder. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct 22;75(2-3):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Paton D. M. Possible subtypes of ATP receptor producing contraction of rat vas deferens, revealed by cross-desensitisation. Gen Pharmacol. 1989;20(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(89)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theobald R. J., Jr Subclasses of purinoceptors in feline bladder. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 15;229(2-3):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90545-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welford L. A., Cusack N. J., Hourani S. M. The structure-activity relationships of ectonucleotidases and of excitatory P2-purinoceptors: evidence that dephosphorylation of ATP analogues reduces pharmacological potency. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 2;141(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90418-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziganshin A. U., Hoyle C. H., Bo X., Lambrecht G., Mutschler E., Bäumert H. G., Burnstock G. PPADS selectively antagonizes P2X-purinoceptor-mediated responses in the rabbit urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1491–1495. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


