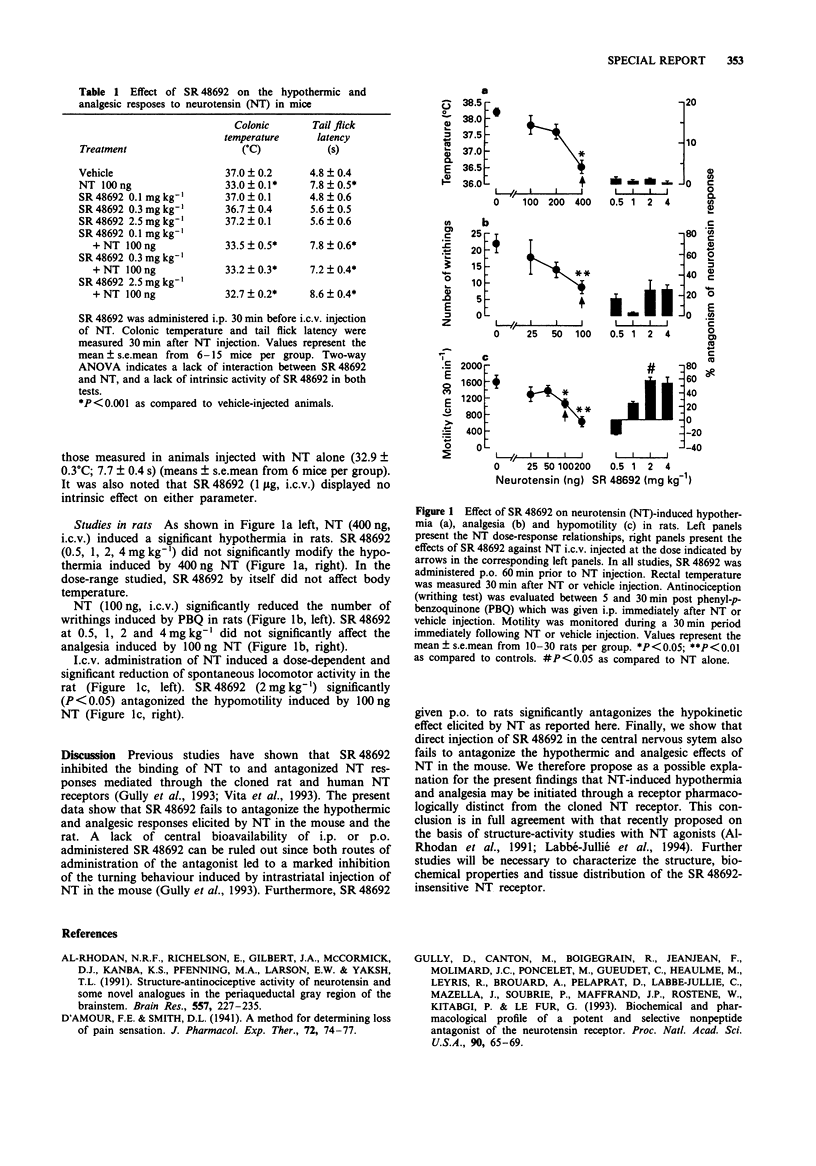
Abstract
The nonpeptide neurotensin (NT) antagonist, SR 48692, was recently shown to inhibit NT binding to the cloned rat and human NT receptor and to antagonize NT effects in a variety of in vitro and in vivo assays. Here, we show that, in contrast to its antagonistic action on NT-induced hypomotility in the rat, SR 48692 failed to antagonize NT-induced hypothermia and analgesia in the mouse and rat. We suggest that these effects might be mediated through a subtype of SR 48692-insensitive NT receptor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gully D., Canton M., Boigegrain R., Jeanjean F., Molimard J. C., Poncelet M., Gueudet C., Heaulme M., Leyris R., Brouard A. Biochemical and pharmacological profile of a potent and selective nonpeptide antagonist of the neurotensin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):65–69. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALEY T. J., MCCORMICK W. G. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):12–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé-Jullié C., Dubuc I., Brouard A., Doulut S., Bourdel E., Pelaprat D., Mazella J., Martinez J., Rostène W., Costentin J. In vivo and in vitro structure-activity studies with peptide and pseudopeptide neurotensin analogs suggest the existence of distinct central neurotensin receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Jan;268(1):328–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structure and functional expression of the cloned rat neurotensin receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vita N., Laurent P., Lefort S., Chalon P., Dumont X., Kaghad M., Gully D., Le Fur G., Ferrara P., Caput D. Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a high affinity human neurotensin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 8;317(1-2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Rodhan N. R., Richelson E., Gilbert J. A., McCormick D. J., Kanba K. S., Pfenning M. A., Nelson A., Larson E. W., Yaksh T. L. Structure-antinociceptive activity of neurotensin and some novel analogues in the periaqueductal gray region of the brainstem. Brain Res. 1991 Aug 23;557(1-2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90139-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


