Abstract
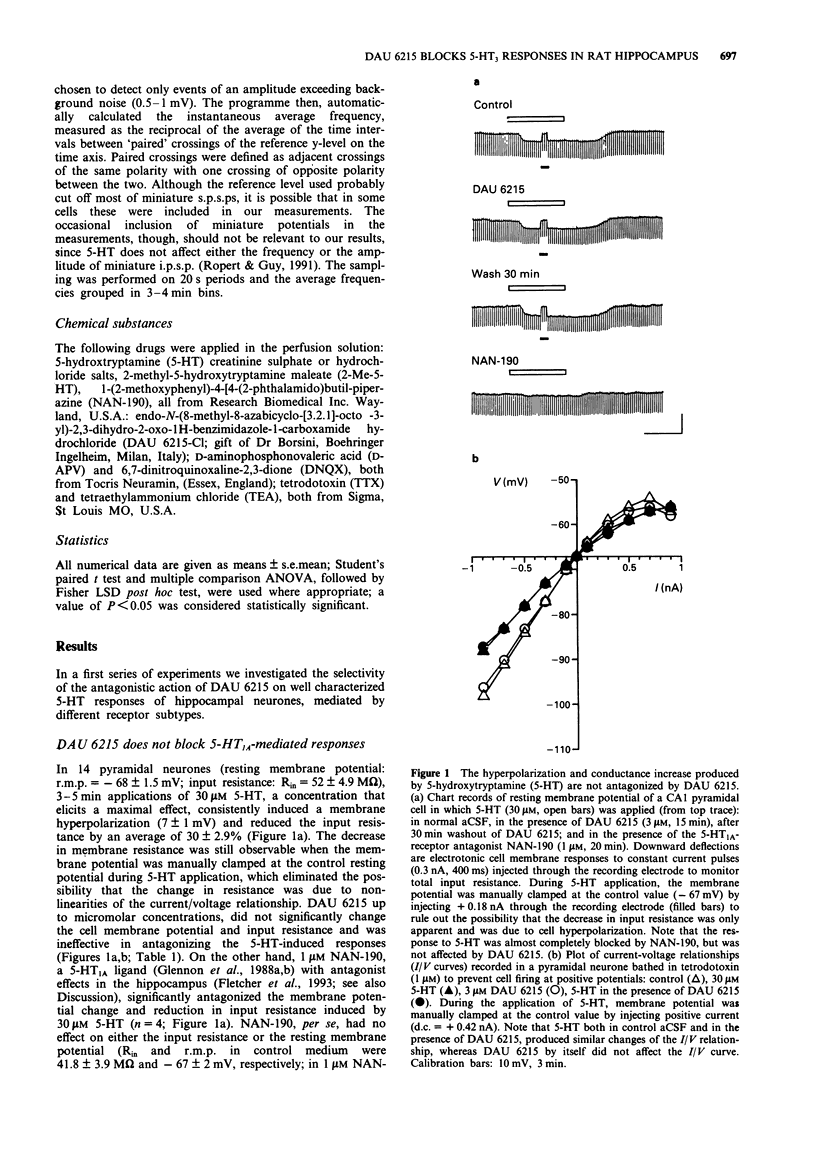
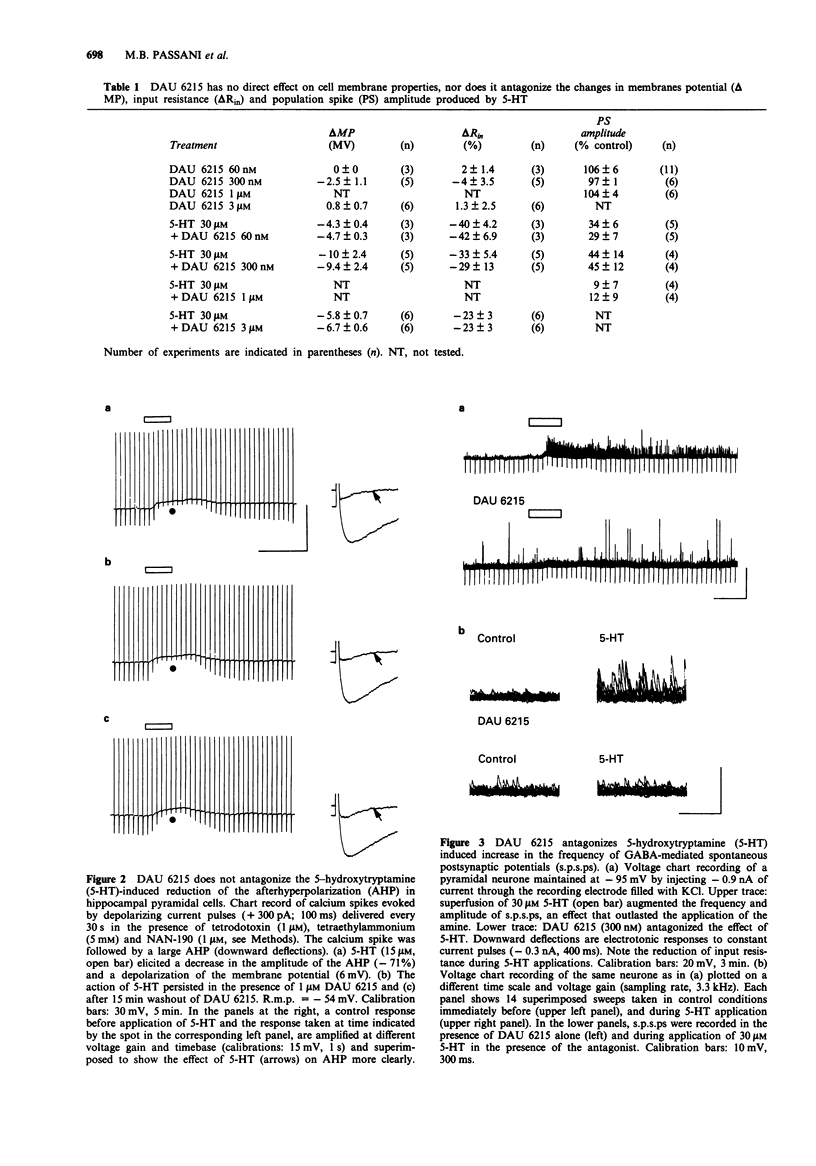
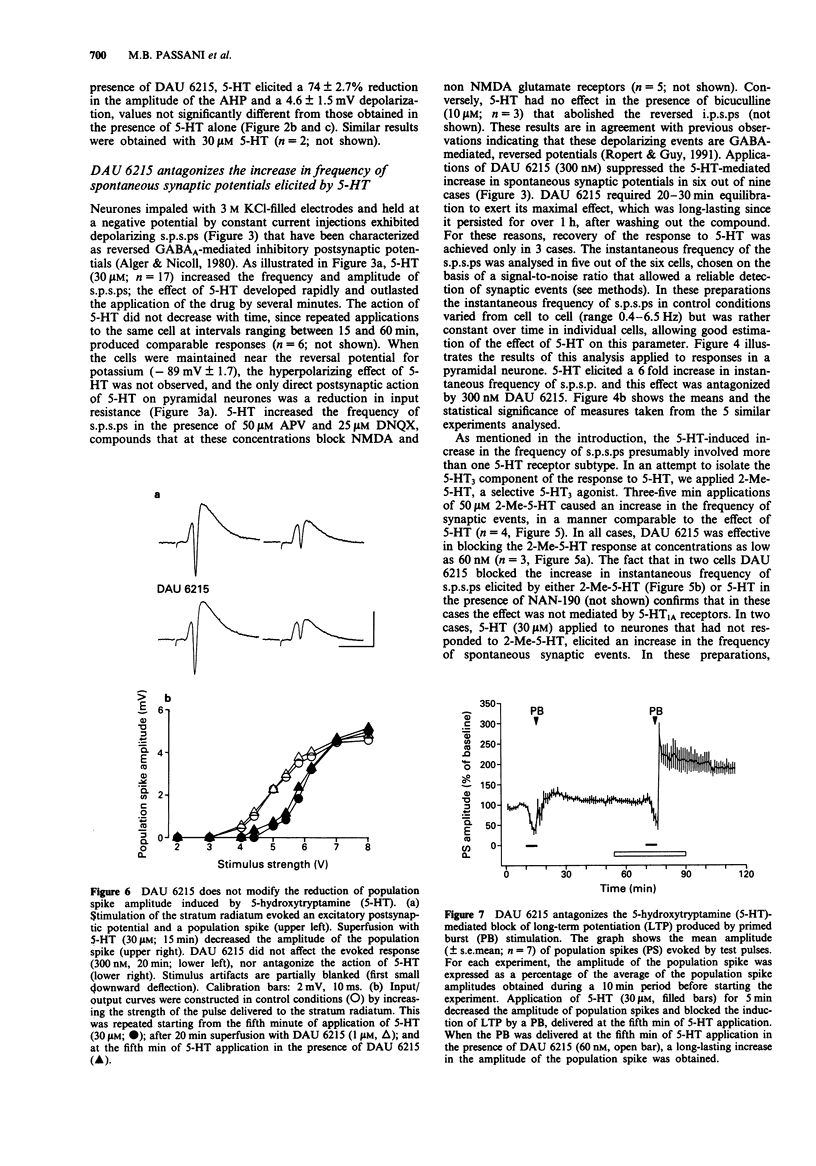
1. The aim of the present study was to test the effects of DAU 6215 (endo-N-(8-methyl-8-azabicyclo-[3.2.1]-octo-3-yl)-2,3-dihydro-2-ox o-1H- benzimidazole-1-carboxamide carboxamide hydrochloride), a newly synthesized, selective 5-hydroxytryptamine3 (5-HT3) antagonist, on the cell membrane properties and on characterized 5-HT-mediated responses of pyramidal neurones in the hippocampal CA1 region. 2. Administration of DAU 6215, even at concentrations several hundred fold its Ki, did not affect the cell membrane properties of pyramidal neurones, nor modify extracellularly recorded synaptic potentials, evoked by stimulating the Schaffer's collaterals. 3. Micromolar concentrations (15-30 microM) of 5-HT elicited several responses in pyramidal neurones that are mediated by distinct 5-HT receptor subtypes. DAU 6215 did not antagonize the 5-HT1A-induced membrane hyperpolarization and conductance increase, a response that was blocked by the selective 5-HT1A antagonist NAN-190 (1-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-[4-(2-phtalamido)butyl- piperazine). Similarly, DAU 6215 did not affect the membrane depolarization and decrease in amplitude of the afterhyperpolarization, elicited by the activation of putative 5-HT4 receptors. 4. 5-HT increased the frequency of spontaneous postsynaptic potentials (s.p.s.ps) recorded in pyramidal neurones loaded with chloride. In agreement with previous observations, most of the s.p.s.ps were reversed GABAergic events, produced by the activation of 5-HT3 receptors on interneurones, because they persisted in the presence of the glutamate NMDA and non NMDA antagonists, D-aminophosphonovaleric acid (APV; 50 microM) and 6,7-dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (DNQX; 25 microM), and were elicited by the selective 5-HT3 agonist, 2-methyl-5-HT (2-Me-5-HT, 50 microM).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

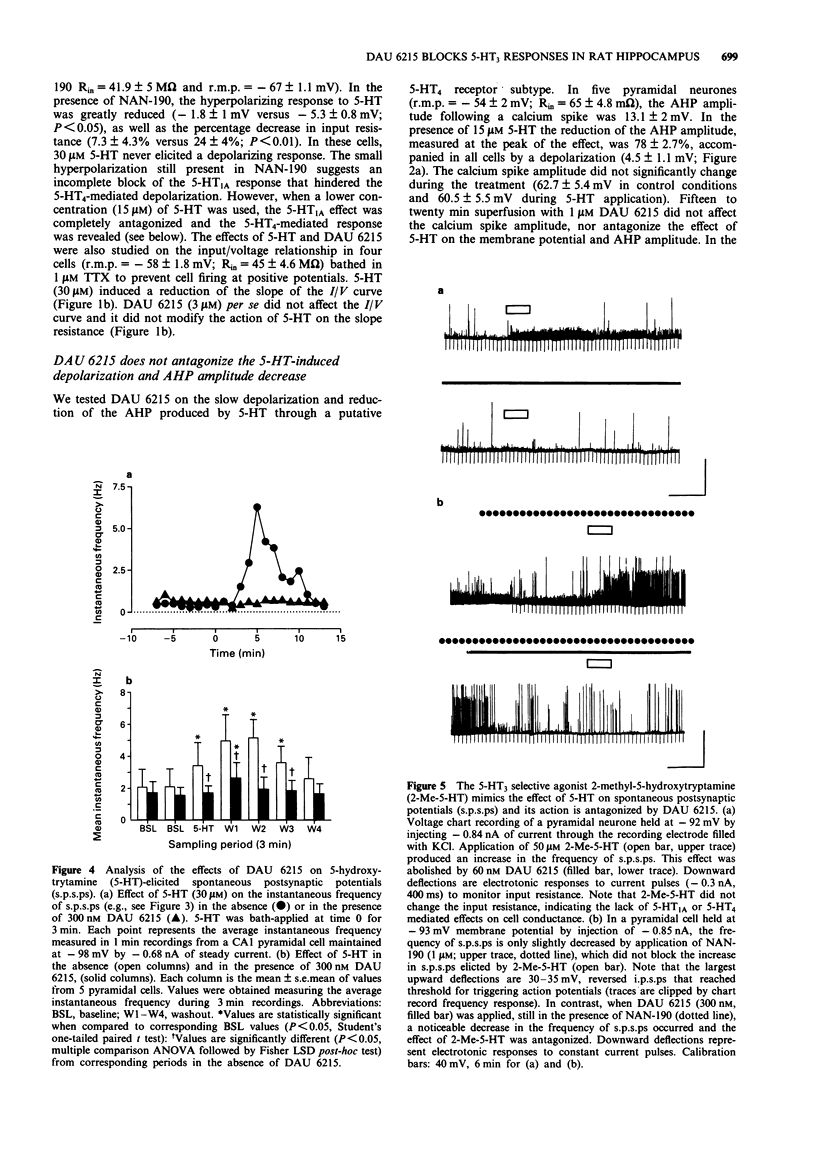



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. Spontaneous inhibitory post-synaptic potentials in hippocampus: mechanism for tonic inhibition. Brain Res. 1980 Oct 27;200(1):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Chaput Y. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4-like receptors mediate the slow excitatory response to serotonin in the rat hippocampus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jun;257(3):930–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1261–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.2430334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Nicoll R. A. Pharmacologically distinct actions of serotonin on single pyramidal neurones of the rat hippocampus recorded in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:99–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwyl R. Neurophysiological actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the vertebrate nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;35(6):451–468. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90031-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. M., Costall B., Coughlan J., Domeney A. M., Gerrard P. A., Kelly M. E., Naylor R. J., Onaivi E. S., Tomkins D. M., Tyers M. B. The effects of ondansetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, on cognition in rodents and primates. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1990 Apr;35(4):955–962. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(90)90385-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter G. S., Clarke D. E. Benzimidazolone derivatives act as 5-HT4 receptor ligands in rat oesophagus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 3;212(2-3):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90333-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck S. G., Choi K. C., List T. J. Comparison of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A-mediated hyperpolarization in CA1 and CA3 hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Oct;263(1):350–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck S. G., Clarke W. P., Goldfarb J. Spiperone differentiates multiple 5-hydroxytryptamine responses in rat hippocampal slices in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 8;116(1-2):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsini F., Brambilla A., Cesana R., Donetti A. The effect of DAU 6215, a novel 5HT-3 antagonist, in animal models of anxiety. Pharmacol Res. 1993 Feb-Mar;27(2):151–164. doi: 10.1006/phrs.1993.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla A., Ghiorzi A., Pitsikas N., Borsini F. DAU 6215, a novel 5-HT3-receptor antagonist, selectively antagonizes scopolamine-induced deficit in a passive-avoidance task, but not scopolamine-induced hypermotility in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;45(9):841–843. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1993.tb05698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey G. J., Costall B., Domeney A. M., Gerrard P. A., Jones D. N., Naylor R. J., Tyers M. B. Ondansetron and arecoline prevent scopolamine-induced cognitive deficits in the marmoset. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1992 May;42(1):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(92)90449-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaput Y., Araneda R. C., Andrade R. Pharmacological and functional analysis of a novel serotonin receptor in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul 17;182(3):441–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chugh Y., Saha N., Sankaranarayanan A., Sharma P. L. Memory enhancing effects of granisetron (BRL 43694) in a passive avoidance task. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 2;203(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90799-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colino A., Halliwell J. V. Differential modulation of three separate K-conductances in hippocampal CA1 neurons by serotonin. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):73–77. doi: 10.1038/328073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradetti R., Ballerini L., Pugliese A. M., Pepeu G. Serotonin blocks the long-term potentiation induced by primed burst stimulation in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices. Neuroscience. 1992;46(3):511–518. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90140-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domeney A. M., Costall B., Gerrard P. A., Jones D. N., Naylor R. J., Tyers M. B. The effect of ondansetron on cognitive performance in the marmoset. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991 Jan;38(1):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(91)90606-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Sebben M., Monferini E., Nicola M., Turconi M., Ladinsky H., Bockaert J. Azabicycloalkyl benzimidazolone derivatives as a novel class of potent agonists at the 5-HT4 receptor positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00251122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennon R. A., Naiman N. A., Lyon R. A., Titeler M. Arylpiperazine derivatives as high-affinity 5-HT1A serotonin ligands. J Med Chem. 1988 Oct;31(10):1968–1971. doi: 10.1021/jm00118a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennon R. A., Naiman N. A., Pierson M. E., Titeler M., Lyon R. A., Weisberg E. NAN-190: an arylpiperazine analog that antagonizes the stimulus effects of the 5-HT1A agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT). Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 23;154(3):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90212-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornung J. P., Celio M. R. The selective innervation by serotoninergic axons of calbindin-containing interneurons in the neocortex and hippocampus of the marmoset. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Jun 22;320(4):457–467. doi: 10.1002/cne.903200404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H. The action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on neuronal membranes and synaptic transmission in area CA1 of the hippocampus in vitro. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 15;197(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick G. J., Jones B. J., Tyers M. B. Identification and distribution of 5-HT3 receptors in rat brain using radioligand binding. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):746–748. doi: 10.1038/330746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosofsky B. E., Molliver M. E. The serotoninergic innervation of cerebral cortex: different classes of axon terminals arise from dorsal and median raphe nuclei. Synapse. 1987;1(2):153–168. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C. The distribution of serotonin binding sites in the hippocampal region of the rat brain. An autoradiographic study. Neuroscience. 1984 Nov;13(3):667–680. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Actions of noradrenaline recorded intracellularly in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones, in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:221–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitsikas N., Brambilla A., Borsini F. DAU 6215, a novel 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, improves performance in the aged rat in the Morris water maze task. Neurobiol Aging. 1993 Nov-Dec;14(6):561–564. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(93)90039-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitsikas N., Brambilla A., Borsini F. Effect of DAU 6215, a novel 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, on scopolamine-induced amnesia in the rat in a spatial learning task. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1994 Jan;47(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(94)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prisco S., Pessia M., Ceci A., Borsini F., Esposito E. Chronic treatment with DAU 6215, a new 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, causes a selective decrease in the number of spontaneously active dopaminergic neurons in the rat ventral tegmental area. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 7;214(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90089-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropert N., Guy N. Serotonin facilitates GABAergic transmission in the CA1 region of rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:121–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropert N. Inhibitory action of serotonin in CA1 hippocampal neurons in vitro. Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagrada A., Turconi M., Bonali P., Schiantarelli P., Micheletti R., Montagna E., Nicola M., Algate D. R., Rimoldi E. M., Donetti A. Antiemetic activity of the new 5-HT3 antagonist DAU 6215 in animal models of cancer chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1991;28(6):470–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00685825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Slawsky M. Probable calcium spikes in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. 5-HT antagonists in rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1976 Feb 13;103(1):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90699-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Physiological and pharmacological evidence for a serotonergic projection to the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1975 Aug 22;94(1):115–131. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90881-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. The action of serotonin in the rat hippocampal slice preparation. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:423–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teyler T. J., DiScenna P. Long-term potentiation. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:131–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turconi M., Donetti A., Schiavone A., Sagrada A., Montagna E., Nicola M., Cesana R., Rizzi C., Micheletti R. Pharmacological properties of a novel class of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 15;203(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turconi M., Nicola M., Quintero M. G., Maiocchi L., Micheletti R., Giraldo E., Donetti A. Synthesis of a new class of 2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-1H-benzimidazole-1-carboxylic acid derivatives as highly potent 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1990 Aug;33(8):2101–2108. doi: 10.1021/jm00170a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Hooff P., Galvan M. Electrophysiology of the 5-HT1A ligand MDL 73005EF in the rat hippocampal slice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr 24;196(3):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90442-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakel J. L., Jackson M. B. 5-HT3 receptors mediate rapid responses in cultured hippocampus and a clonal cell line. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakel J. L., Trussell L. O., Jackson M. B. Three serotonin responses in cultured mouse hippocampal and striatal neurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1273–1285. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


