Abstract
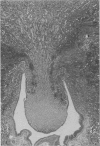
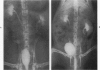
Retrograde pyelonephritis was produced in rats by introducing into the bladder a small refluxing inoculum of Escherichia coli that would enter the renal pelvis but not the blood stream. At the same time the left ureter was partially obstructed for 18 hours. This model differs from previous attempts to produce E coli pyelonephritis with large (0.6 ml) volumes infused into the bladder, because such large volumes cause bacteremia and hematogeneous pyelonephritis. Since retrograde E coli pyelonephritis in patients is not accompanied by positive blood cultures, the model described in this report is believed to accurately mimic human pyelonephritis and to allow a realistic approach to the study of immunity against retrograde infection in the urinary tract.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARANA J. A., KOZIJ V. M., JACKSON G. G. RETROGRADE E COLI URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN RATS. PATHOLOGIC AND BACTERIOLOGIC CHARACTERISTICS OF ASCENDING PYELONEPHRITIS. Arch Pathol. 1964 Nov;78:558–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andriole V. T. Water, acidosis, and experimental pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jan;49(1):21–30. doi: 10.1172/JCI106218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEER H., STAEHELIN T., DOUGLAS H., BRAUDE A. I. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PARTICLE SIZE AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF E. COLI BOIVIN ENDOTOXIN. J Clin Invest. 1965 Apr;44:592–602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks S. J., Lyons J. M., Braude A. I. Immunization against retrograde pyelonephritis. II. Prevention of retrograde Escherichia coli pyelonephritis with vaccines. Am J Pathol. 1974 Feb;74(2):359–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNEW I., BRAUDE A. I. Depression of phagocytosis by solutes in concentrations found in the kidney and urine. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1945–1953. doi: 10.1172/JCI104652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm G. D., Rivero O. R., Calnan J. S. The permeability of the renal pelvis during ureteric obstruction. Br J Surg. 1967 Dec;54(12):1023–1026. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800541212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corriere J. N., Jr, Murphy J. J. Vesicoureteral reflux and the intrarenal lymphatic system in the rat. Invest Urol. 1967 May;4(6):556–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enta T., Lockey S. D., Jr, Reed C. E. A rapid safe technique for repeated blood collection from small laboratory animals. The farmer's wife method. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):136–137. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierer J., Talner L., Braude A. I. Bacteremia in the pathogenesis of retrograde E. coli pyelonephritis in the rat. Am J Pathol. 1971 Aug;64(2):443–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried F. A., Wong R. J. Etiology of pyelonephritis: significance of hemolytic Escherichia coli. J Urol. 1970 Jun;103(6):718–721. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)62033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander A. M., Braude A. I. Experimental prostatitis: relationship to pyelonephritis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):645–651. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heney N. M., O'Morchoe P. J., O'Morchoe C. C. The renal lymphatic system during obstructed urine flow. J Urol. 1971 Oct;106(4):455–462. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D. Antibacterial activity of human urine. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2374–2390. doi: 10.1172/JCI105921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane W. F., Freedman L. R. Experimental pyelonephritis. XIV. Pyelonephritis in normal mice produced by inoculation of E. coli into the bladder lumen during water diuresis. Yale J Biol Med. 1967 Dec;40(3):231–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY J. J., MYINT M. K., RATTNER W. H., KLAUS R., SHALLOW J. The lymphatic system of the kidney. J Urol. 1958 Jul;80(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)66118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOLL H., BRAUDE A. I. Preparation and biological properties of a chemically modified Escherichia coli endotoxin of high immunogenic potency and low toxicity. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1935–1951. doi: 10.1172/JCI104419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'dell R. M., Brazil W. O., Schlegel J. U. Effectiveness of urea in prophylaxis of experimentally induced bacteriuria in rats. J Urol. 1967 Jan;97(1):145–146. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)63001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer E. W. Comparative anatomical observations of the mammalian renal pelvis and medulla. J Anat. 1968 Jan;102(Pt 2):321–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL J. U., CUELLAR J., O'DELL R. M. Bactericidal effect of urea. J Urol. 1961 Dec;86:819–822. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)65264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAPIRO A. P., BRAUDE A. I., SIEMIENSKI J. Hematogenous pyelonephritis in rats. IV. Relationship of bacterial species to the pathogenesis and sequelae of chronic pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1228–1240. doi: 10.1172/JCI103898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtin H. Sequestration of urea and nonurea solutes in renal tissues of rats with hereditary hypothalamic diabetes insipidus: effect of vasopressin and dehydration on the countercurrent mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):337–345. doi: 10.1172/JCI105348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]