Abstract
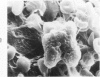
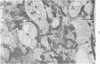
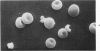
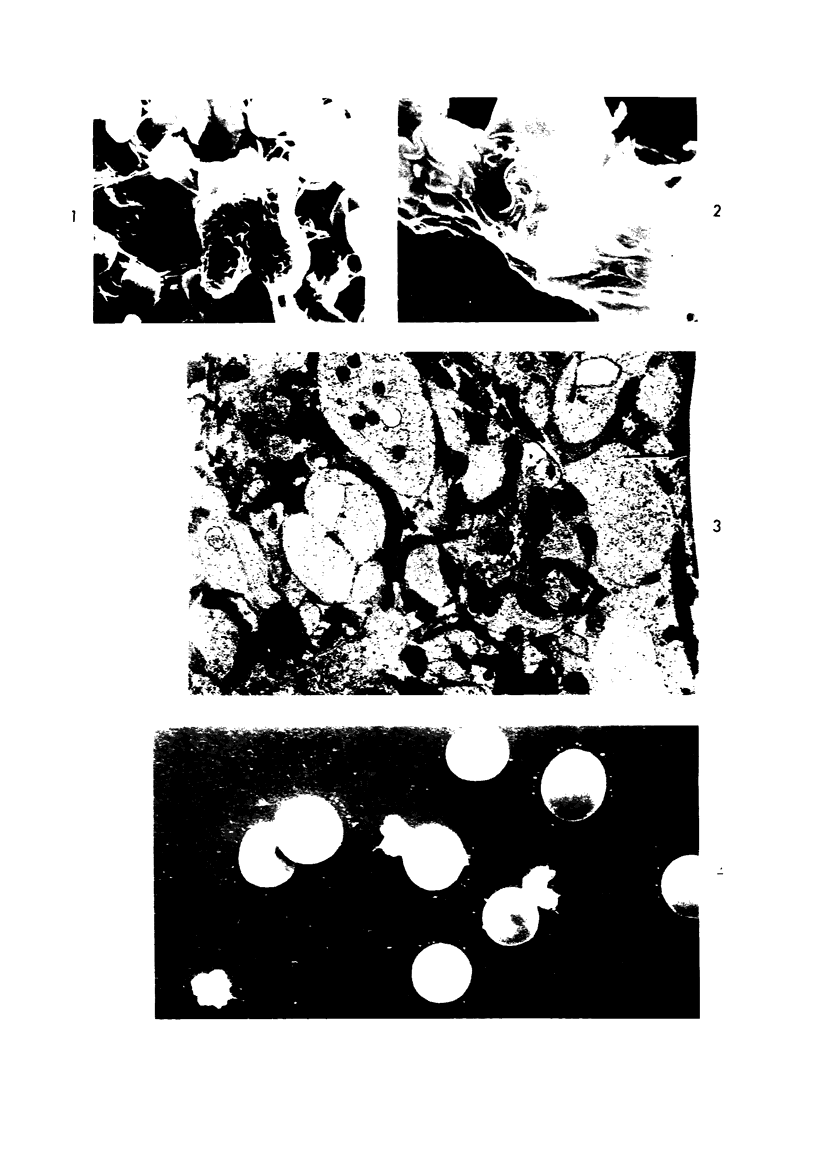
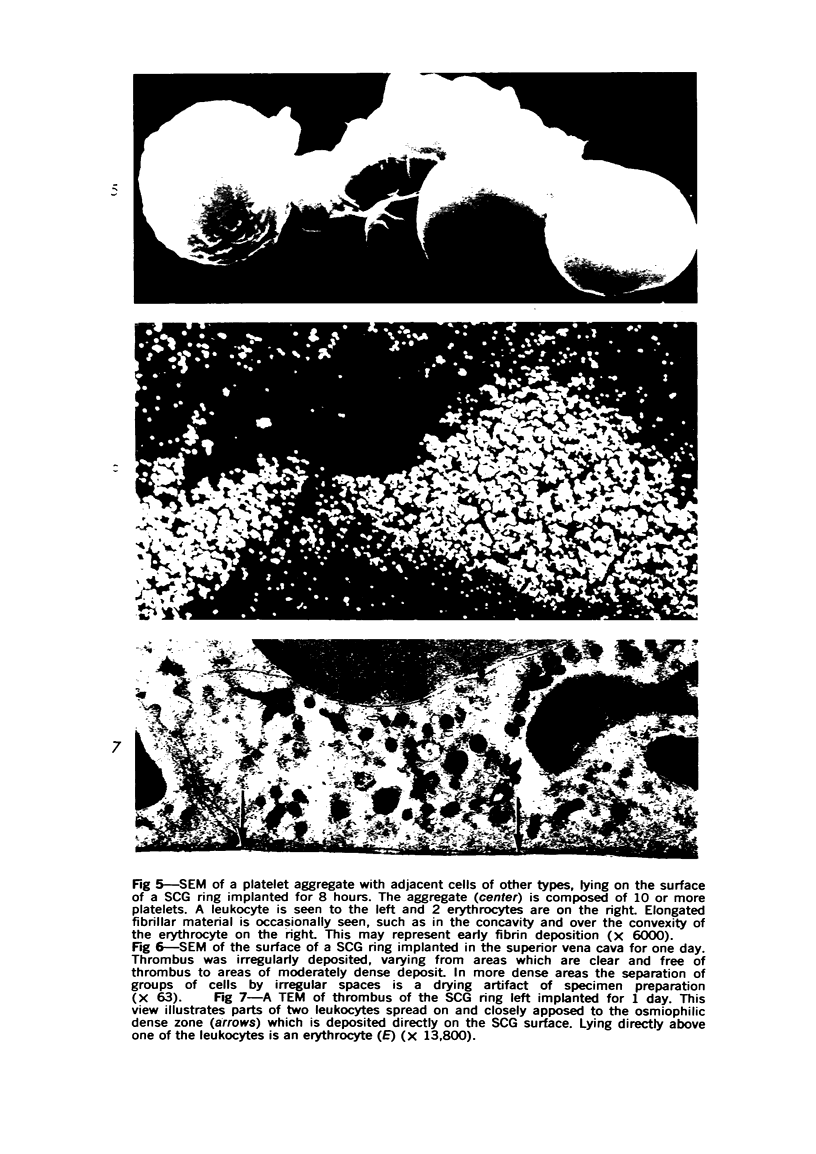
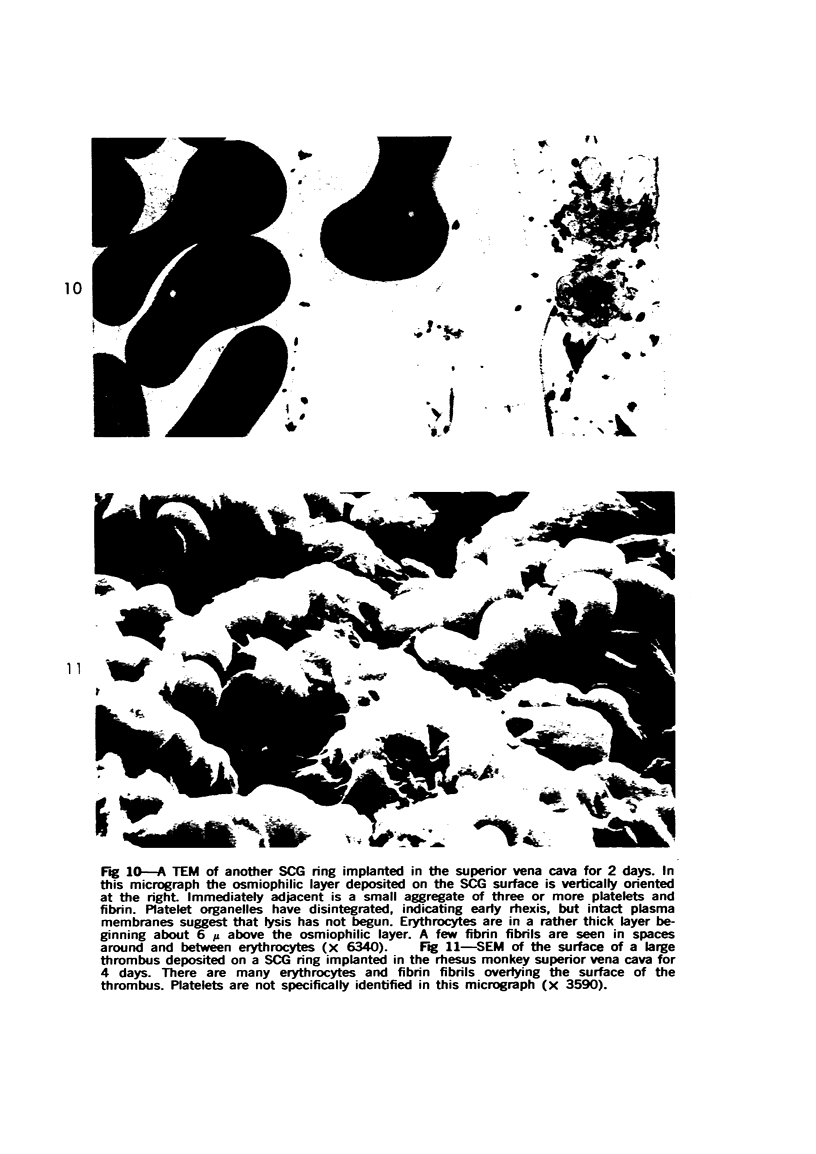
Thrombi deposited on prosthetic devices in the superior vena cava of the rhesus monkey were studied by morphologic and biochemical technics. Glass or silicone-coated glass (SCG) rings were implanted for 30 minutes to 14 days. Thrombus was deposited on the surface of each prosthetic device, and deposition was much greater and more rapid on glass surfaces than on SCG surfaces. On SCG surfaces, initial deposits consisting of single platelets, small platelet aggregates and erythrocytes were seen by scanning electron microscopy. These were followed by larger platelet aggregates, fibrin and, much later, leukocytes. Transmission electron micrographs revealed disintegration of the platelets forming aggregates and an osmiophilic deposit on the prosthetic surface. Shortened partial thromboplastin times were observed in all test animals but the sham-operated one, and therefore may be predictive of thrombus formation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruck S. D., Rabin S., Ferguson R. J. Evaluation of biocompatible materials. Biomater Med Devices Artif Organs. 1973;1(1):191–222. doi: 10.3109/10731197309118873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gott V. L., Furuse A. Antithrombogenic surfaces, classification and in vivo evaluation. Fed Proc. 1971 Sep-Oct;30(5):1679–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Niewiarowski S., Gurewich V., Thomas D. P. Measurement of fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products in serum by staphylococcal clumping test. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jan;75(1):93–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. J., Kline D. L., Alkjaersig N. Assay methods and standard preparations for plasmin, plasminogen and urokinase in purified systems, 1967-1968. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Apr 30;21(2):259–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. G., Read M. S. Some species differences in fibrinolysis and blood coagulation. J Biomed Mater Res. 1971 Jan;5(1):121–128. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820050109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. G. The interaction of blood hemostitic elements with aritificial surfaces. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1972;1:141–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODMAN N. F., Jr, MASON R. G., BRINKHOUS K. M. SOME PATHOGENETIC MECHANISMS OF WHITE THROMBUS FORMATION: AGGLUTINATION AND SELF-DESTRUCTION OF THE PLATELET. Fed Proc. 1963 Nov-Dec;22:1356–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W. Nonthrombogenic surfaces: critical review. Blood. 1971 Oct;38(4):509–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd M. E., McDevitt E., Goldsmith E. I. Blood-clotting mechanisms of nonhuman primates. Choice of the baboon model to simulate man. J Med Primatol. 1972;1(3):132–141. doi: 10.1159/000460376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN R. Postoperative thrombophilia. N Engl J Med. 1953 Jul 16;249(3):99–106. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195307162490304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]