Abstract
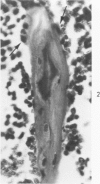
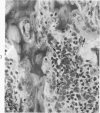
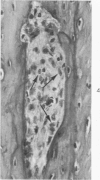
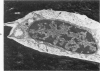
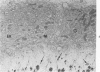
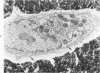
Osteoblasts and osteocytes in adult thyroparathyroidectomized (TxPTx) rats fed a low calcium vitamin D-free diet and given parathyroid (PTH) had ultrastructural evidence of increased activity compared to controls. Osteoblasts in PTH-treated rats had prominent rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatuses and large mitochondria. The plasma membranes were extensively convoluted and associated with initial loci of mineralization in osteoid. Osteocytes contained increased rough endoplasmic reticulum, well-developed Golgi apparatuses and large mitochondria. Lacunar walls were roughened, but osteocytic osteolysis was not observed. Osteoclasts were encountered more frequently in PTH-treated rats, but their ultrastructural features were similar to those of controls. Osteoblasts and osteocytes in controls appeared to be inactive cells lining quiescent mineral surfaces. Parathyroid hormone treatment increased serum calcium levels and urinary hydroxyproline excretion, indicating enhanced resorption of bone mineral and matrix. Bone alkaline phosphatase and calcium-adenosine triphosphatase activities were elevated after PTH treatment and may be related to increased calcium transport by bone cells. These findings were interpreted to suggest that PTH mobilizes bone mineral by osteoclasis and increases metabolic activity of the osteocyte-osteoblast pump.
Full text
PDF





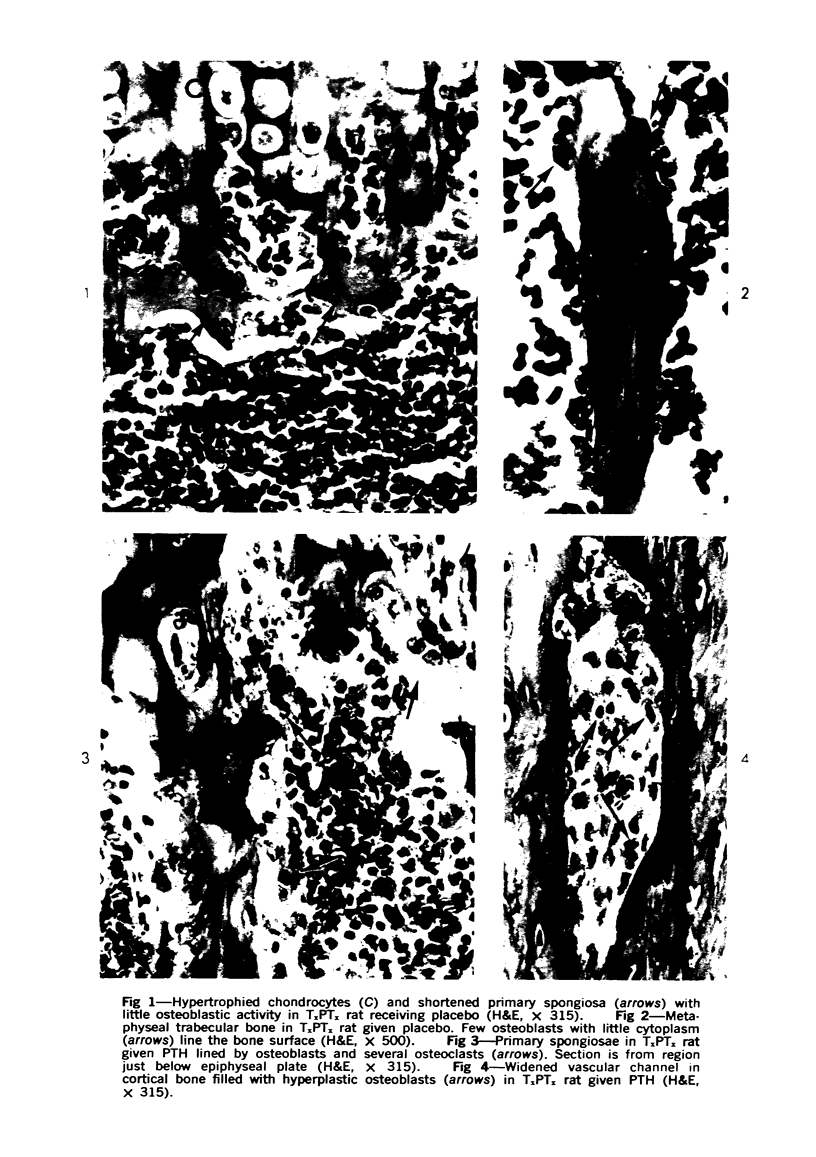
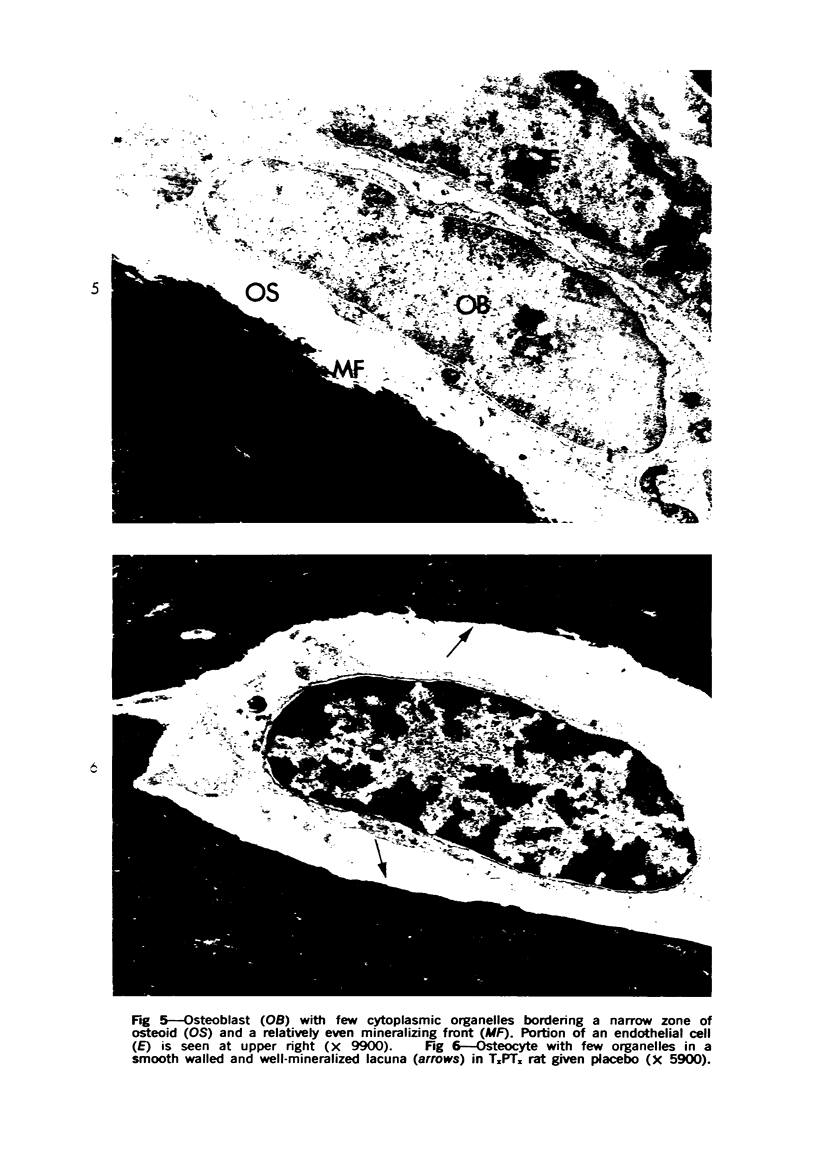
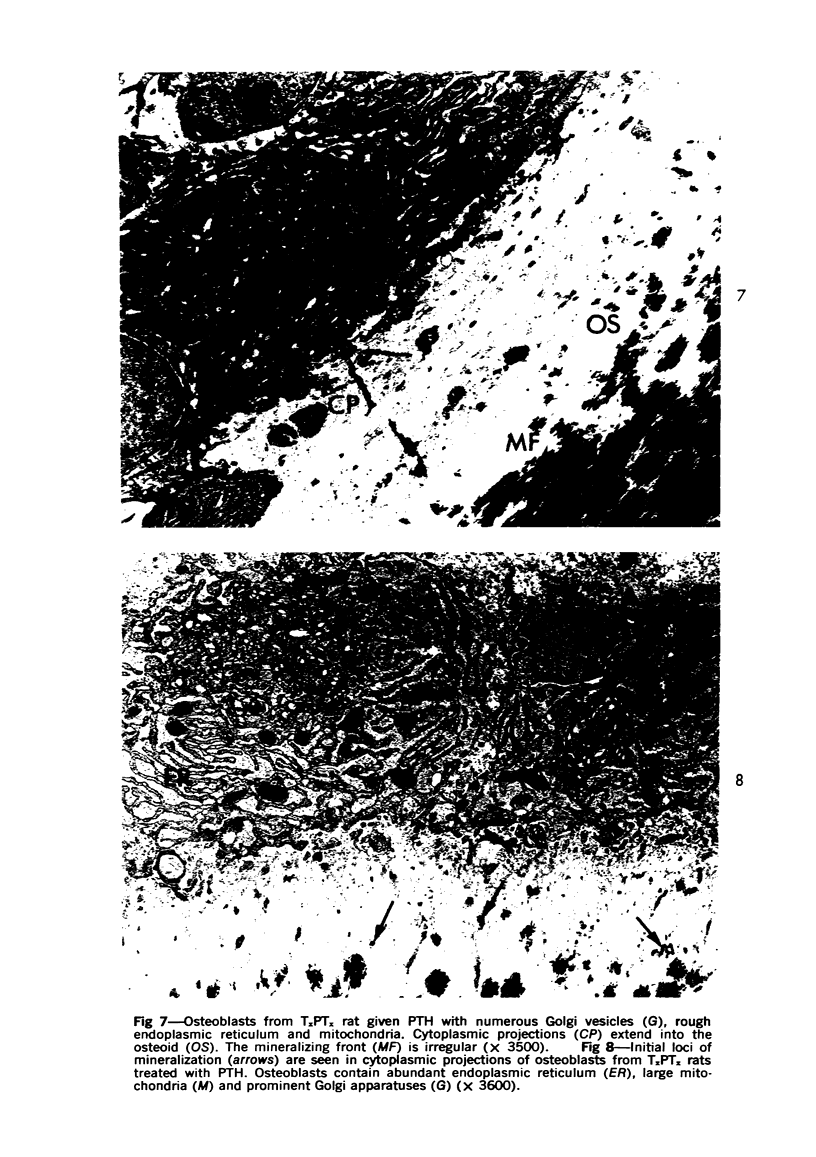
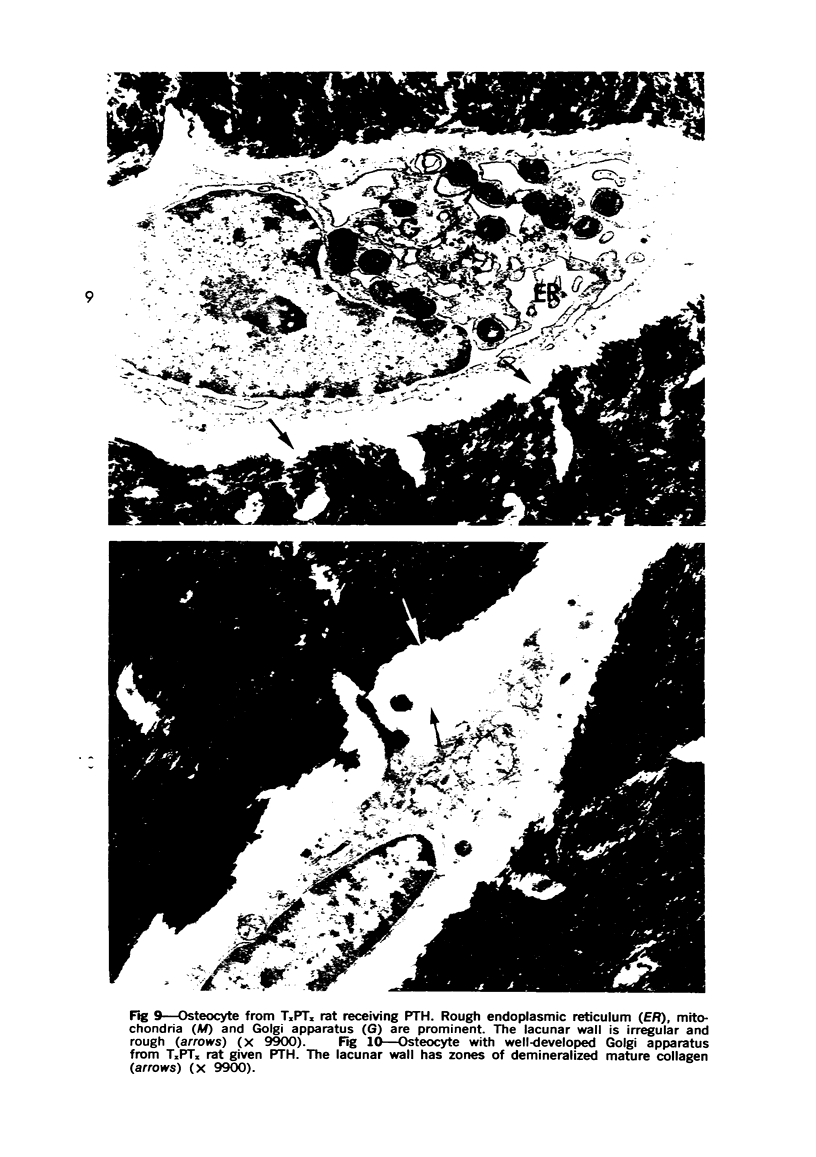


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold J. S., Frost H. M., Buss R. O. The osteocyte as a bone pump. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1971;78:47–55. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197107000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baud C. A. Submicroscopic structure and functional aspects of the osteocyte. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1968 Jan-Feb;56:227–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. A., Paschall H. A., Robinson R. A. Changes in the fine structure of bone cells after the administration of parathyroid extract. J Cell Biol. 1967 Apr;33(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F. The kidney as an endocrine organ for the production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 , a calcium-mobilizing hormone. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 16;289(7):359–365. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308162890710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthlin G., Ericsson J. L. Fine structural localization of alkaline phosphomonoesterase in the fracture callus of the rat. Isr J Med Sci. 1971 Mar;7(3):488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M., Nagode L. A., Rasmussen H. Induction of intestinal brush border alkaline phosphatase by vitamin D and identity with ca-ATPase. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1199–1201. doi: 10.1038/2281199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jande S. S. Effects of parathormone on osteocytes and their surrounding bone matrix. An electron microscopic study. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;130(4):463–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00307000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallio D. M., Garant P. R., Minkin C. Ultrastructural effects of calcitonin on osteoclasts in tissue culture. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 May;39(3):205–216. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalu D. N., Doyle F. H., Pennock J., Foster G. V. Parathyroid hormone and experimental osteosclerosis. Lancet. 1970 Jun 27;1(7661):1363–1366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivirikko K. I., Laitinen O., Prockop D. J. Modifications of a specific assay for hydroxyproline in urine. Anal Biochem. 1967 May;19(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivirikko K. I. Urinary excretion of hydroxyproline in health and disease. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1970;5:93–163. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363705-5.50008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. L., Melancon M. J., Jr, DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D stimulated, calcium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase from brush borders of rat small intestine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jun 27;35(6):819–823. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90697-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. L., Martin J. H. Intracellular transport of calcium and its relationship to homeostasis and mineralization. An electron microscope study. Am J Med. 1971 May;50(5):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menczel J., Eilon G., Klein T., Tishbee A. The effect of PTH and vitamin D on bone alkaline phosphatase. Calcif Tissue Res. 1970;(Suppl):51–51. doi: 10.1007/BF02152349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Mircheff A. K., Adams T. H., Spielvogel A. Studies on the mechanism of action of calciferol. 3. Vitamin D-mediated increase of intestinal brush order alkaline phosphatase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 14;215(2):348–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASMUSSEN H., DELUCA H., ARNAUD C., HAWKER C., VONSTEDINGK M. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VITAMIN D AND PARATHYROID HORMONE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Dec;42:1940–1946. doi: 10.1172/JCI104880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Fleisch H. Pyrophosphate, phosphonates and pyrophosphatases in the regulation of calcification and calcium homeostasis. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Sep;63(9):876–876. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Remagen W. Effects of parathyroid extract on calcium metabolism and on bone morphology in the intact rat. Z Gesamte Exp Med. 1971;155(2):87–97. doi: 10.1007/BF02046262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmage R. V., Cooper C. W., Park H. Z. Regulation of calcium transport in bone by parathyroid hormone. Vitam Horm. 1970;28:103–140. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60889-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrode S. E., Capen C. C., Nagode L. A. Fine structural and enzymatic evaluation of bone in thyroparathyroidectomized rats receiving various levels of vitamin D. Lab Invest. 1973 Jan;28(1):29–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wergedal J., Stauffer M., Baylink D., Rich C. Inhibition of bone matrix formation, mineralization, and resorption in thyroparathyroidectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1052–1058. doi: 10.1172/JCI107270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]