Abstract
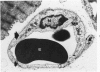
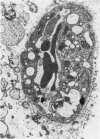
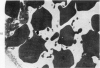
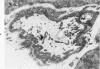
The pathogenesis of hemorrhage induced by rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) venom was investigated at the electron microscopic level. Swiss-Webster white mice were injected intramuscularly with one-fifth the LD50 dose of whole venom. Muscle samples were obtained by biopsy 2 minutes, 30 minutes and 3 hours after venom injection. Capillaries in the endomysium were in various stages of degeneration. Endothelial cells of damaged capillaries contained dilatated endoplasmic reticulum and perinuclear space, and, in many cases, swollen cytoplasm. Blebbing of endothelial cytoplasm of swollen and nonswollen cells was observed. These changes were followed by rupture of the plasma membrane which resulted in the subsequent extravasation of blood. Platelet aggregations plugged gaps in vessel walls and often completely occluded the lumina of capillaries. The experimental injection of rattlesnake venom induced hemorrhage by rhexis. The same or a similar pathogenesis is probably responsible for hemorrhage which occurs in actual snakebite cases.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ginn F. L., Shelburne J. D., Trump B. F. Disorders of cell volume regulation. I. Effects of inhibition of plasma membrane adenosine triphosphatase with ouabain. Am J Pathol. 1968 Dec;53(6):1041–1071. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff H. F., Gottlob R. A fine structure study of injury to the endothelial cells of the rabbit abdominal aorta by various stimuli. Angiology. 1967 Jul;18(7):440–451. doi: 10.1177/000331976701800704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Tu A. T. Antivenin for the treatment of local tissue damage due to envenomation by Southeast Asian snakes. Ineffectiveness in the prevention of local tissue damage in mice after envenomation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Sep;19(5):880–884. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Tu A. T. Morphology of local tissue damage in experimental snake envenomation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Oct;52(5):538–542. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Porras J. M. Biochemistry of snake venoms. Clin Toxicol. 1970 Sep;3(3):389–431. doi: 10.3109/15563657008990116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYNN J. A. RAPID TOLUIDINE BLUE STAINING OF EPON-EMBEDDED AND MOUNTED "ADJACENT" SECTIONS. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jul;44:57–58. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MINTON S. A., Jr Polyvalent antivenin in treatment of experimental snake venom poisoning. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1954 Nov;3(6):1077–1082. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1954.3.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Margaretten W., Csavossy I. An electron microscope study of the effects of bacterial endotoxin on the blood-vascular system. Lab Invest. 1966 Dec;15(12):1815–1829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Moroz C., De Vries A., Csavossy I., Cruse V. The action of hemorrhagin and phospholipase derived from Vipera palestinae venom on the microcirculation. Lab Invest. 1970 May;22(5):387–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G. Vessel wall and thrombogenesis--endotoxin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973 Feb 28;29(1):11–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRISH H. M., SILBERG S. L., GOLDNER J. C. SNAKEBITE A PEDIATRIC PROBLEM. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1965 Apr;4:237–241. doi: 10.1177/000992286500400413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEMPAK J. G., WARD R. T. AN IMPROVED STAINING METHOD FOR ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Sep;22:697–701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. M., Kainer R. A., Tu A. T. Myonecrosis induced by rattlesnake venom. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1972 Apr;67(1):127–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willms-Kretschmer K., Majno G. Ischemia of the skin. Electron microscopic study of vascular injury. Am J Pathol. 1969 Mar;54(3):327–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]