Abstract
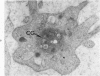
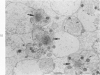
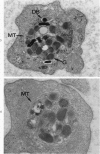
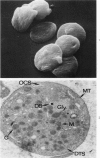
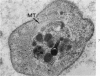
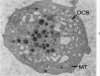
A23187, an ionophore which selectively transports calcium across cell membranes into cytoplasm or releases the divalent cation from intracellular storage sites, was shown in previous studies to stimulate platelet aggregation and the release reaction. The nature of its influence on platelet function suggested that an increase in cytoplasmic calcium ion concentration might be a critical factor linking stimulation to secretion through the platelet contractile mechanism. The present investigation has examined the effects of A23187 in platelet ultrastructure and aggregation after incubation with various concentrations of the drug. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy revealed changes in the form and internal organization of platelets following exposure to A23187 that were identical to those which develop in the cells after exposure to potent agents such as collagen and thrombin. High concentrations of ionophore caused destruction of the platelets on prolonged incubation, while the effects of low concentrations on structure and aggregation reversed completely. Recovered platelets were as sensitive to other aggregating agents as control cells. The findings support the concept that platelets are a form of muscle cell and the internal transformation stimulated by A23187 and other aggregating agents is a manifestation of contractile activity. Inactivation of A23187 by plasma followed by recovery of unaltered appearance indicates that platelets have an active mechanism for reducing the level of cytoplasmic calcium.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson R., Lundholm L., Mohme-Lundholm E., Nilsson K. Role of cyclic AMP and Ca++ in metabolic and mechanical events in smooth muscle. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;1:213–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUNSTEINER H., PAKESCH F. Thrombocytoasthenia and thrombocytopathia-old names and new diseases. Blood. 1956 Nov;11(11):965–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessis M., Breton-Gorius J. Les microtubules et les fibrilles dans les plaquettes étalées. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1965 Jul-Aug;5(4):657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettex-Galland M., Lüscher E. F. Thrombosthenin, the contractile protein from blood platelets and its relation to other contractile proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1965;20:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., White J. G. Platelet interaction with bacteria. I. Reaction phases and effects of inhibitors. Am J Pathol. 1971 Nov;65(2):367–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E. Electron microscope observations of the platelet-fibrin relationship in blood clotting. Blood. 1955 May;10(5):528–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietze G., Hepp K. D. Effect of 3'5'-AMP on calcium-activated ATPase in rat heart sarcolemma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90659-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYDON G. B., COREY D. L. Platelets in the thromboplastin generation test. Electron microscopic studies. Arch Pathol. 1961 Jun;71:615–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOVIG T. The ultrastructure of rabbit blood platelet aggregates. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1962 Dec 20;8:455–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER R. V. Electron microscopic observations on platelets from human blood. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Nov;28(5):447–460. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/28.5.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPPEL G. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur Funktionsmorphologie der Thrombozyten und zum Gerinnungsablauf im normalen Menschlichen Nativblut. I. Frühe Veranderungen der Thrombozyten. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1958;47(4):401–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUHNKE E. Elektronenoptische Untersuchungen über die Veränderung der Thrombocyten und des Fibringerinnsels im Verlaufe der Gerinnung unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Retraktion. Pflugers Arch. 1958;268(2):87–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00386082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher E. F., Probst E., Bettex-Galland M. Thrombosthenin: structure and function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Oct 27;201:122–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Properties of ionophores with broad range cation selectivity. Fed Proc. 1973 Jun;32(6):1698–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RINEHART J. F. Electron microscopic studies of sectioned white blood cells and platelets; with observations on the derivation of specific granules from mitochondria. Am J Clin Pathol. 1955 Jun;25(6):605–619. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/25.6.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODMAN N. F., Jr, MASON R. G., McDEVITT N. B., BRINKHOUS K. M. Morphologic alterations of human blood platelets during early phases of clotting. Electron microscopic observations of thin sections. Am J Pathol. 1962 Mar;40:271–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W., Kensler P. C., Levine L. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate in human blood platelets. IV. Regulatory role of cyclic amp in platelet function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Oct 27;201:61–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Baldassare J., Inesi G. The effect of calcium ionophores on fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Dec;60(6):735–749. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.6.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statland B. E., Heagan B. M., White J. G. Uptake of calcium by platelet relaxing factor. Nature. 1969 Aug 2;223(5205):521–522. doi: 10.1038/223521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Effects of heat on platelet structure and function. Blood. 1968 Aug;32(2):324–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Electron microscopic studies of platelet secretion. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1974;2(0):49–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Interaction of membrane systems in blood platelets. Am J Pathol. 1972 Feb;66(2):295–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Krumwiede M. Influence of cytochalasin B on the shape change induced in platelets by cold. Blood. 1973 Jun;41(6):823–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Rao G. H., Gerrard J. M. Effects of the lonophore A23187 on blood platelets I. Influence on aggregation and secretion. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):135–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. The interplatelet zone. Am J Pathol. 1970 Jan;58(1):19–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Uptake of latex particles by blood platelets: phagocytosis or sequestration? Am J Pathol. 1972 Dec;69(3):439–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Wilkinson J. R., Hamill R. L., Horng J. S. Effects of antibiotic ionophore, A23187, on oxidative phosphorylation and calcium transport of liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jun;156(2):578–585. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90308-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]