Full text
PDF









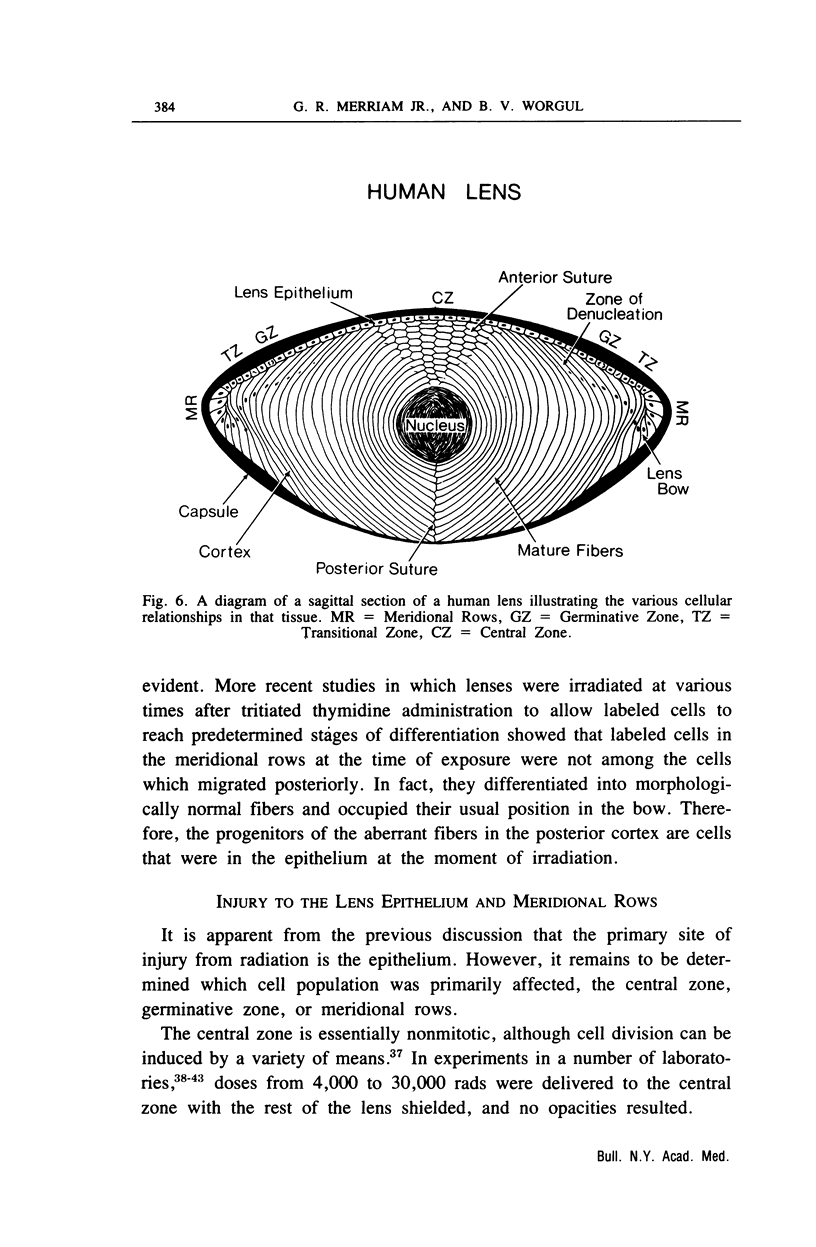








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broglio T. M., Worgul B. V. The lens epithelium and radiation cataract. IV. Ultrastructural studies of interphase death in the meridional rows. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982;39(1):49–57. doi: 10.1007/BF02892836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COGAN D. G., DONALDSON D. D., REESE A. B. Clinical and pathological characteristics of radiation cataract. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1952 Jan;47(1):55–70. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1952.01700030058006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COGAN D. G., DREISLER K. K. Minimal amount of x-ray exposure causing lens opacities in the human eye. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1953 Jul;50(1):30–34. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1953.00920030033005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constable I. J., Goitein M., Koehler A. M., Schmidt R. A. Small-field irradiation of monkey eyes with protons and photons. Radiat Res. 1976 Feb;65(2):304–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht E. F., Merriam G. R., Jr, Schwartz M. S., Parsons R. W. The relative biologic effectiveness of cobalt 60 gamma and 200 kv. X radiation for cataract induction. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1968 Jan;102(1):71–80. doi: 10.2214/ajr.102.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANNA C., O'BRIEN J. E. Lens epithelial cell proliferation and migration in radiation cataracts. Radiat Res. 1963 May;19:1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Reddan J. R., Unakar N. J., Bagchi M. The control of cell division in the ocular lens. Int Rev Cytol. 1971;31:215–300. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden J. H., Rothstein H., Worgul B. V., Merriam G. R., Jr Hypophysectomy exerts a radioprotective effect on frog lens. Experientia. 1980 Jan 15;36(1):116–118. doi: 10.1007/BF02004009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEINFELDER P. J., RILEY E. F. Further studies of effects of x-radiation on partially shielded lens of rabbit. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1956 Jan;55(1):84–86. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1956.00930030086012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRIAM G. R., Jr, BIAVATI B. J., BATEMAN J. L., ROSSI H. H., BOND V. P., GOODMAN L., FOCHT E. F. THE DEPENDENCE OF RBE ON THE ENERGY OF FAST NEUTRONS. IV. INDUCTION OF LENS OPACITIES IN MICE. Radiat Res. 1965 May;25:123–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
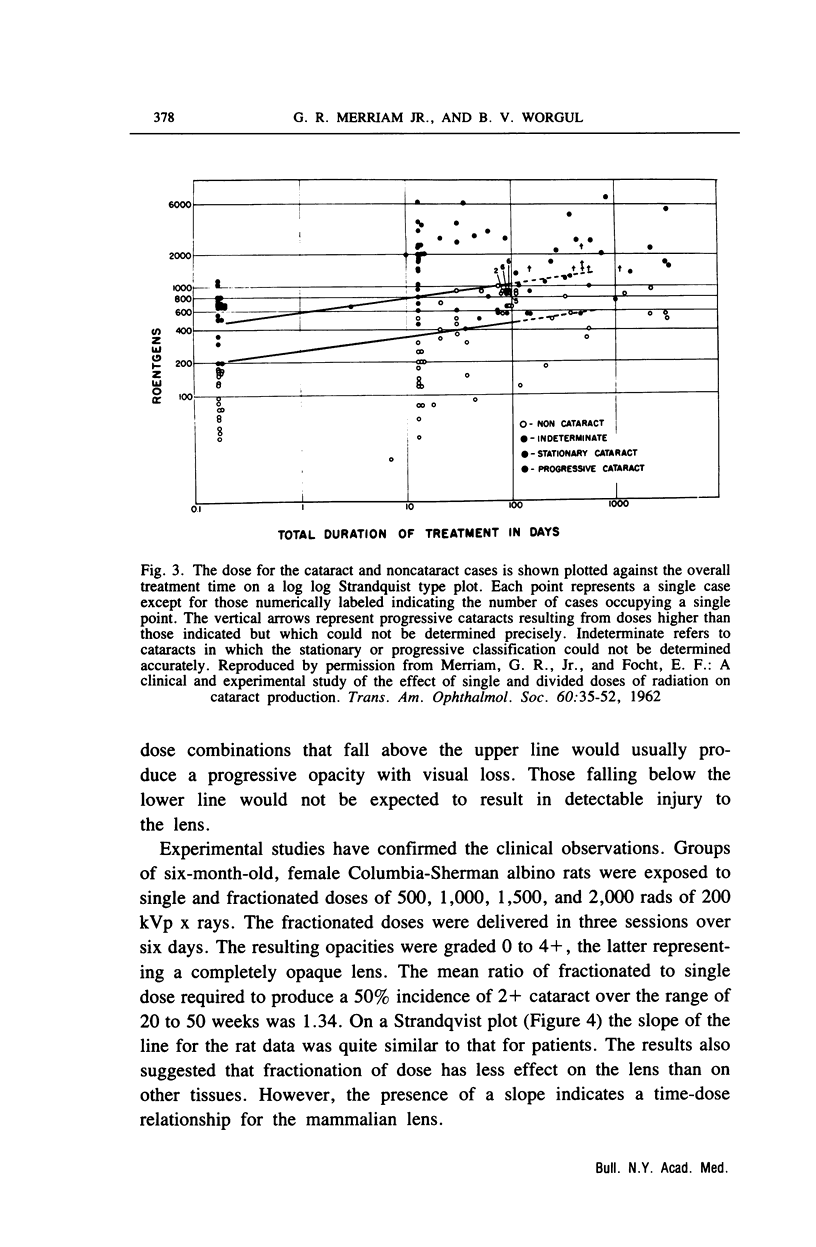
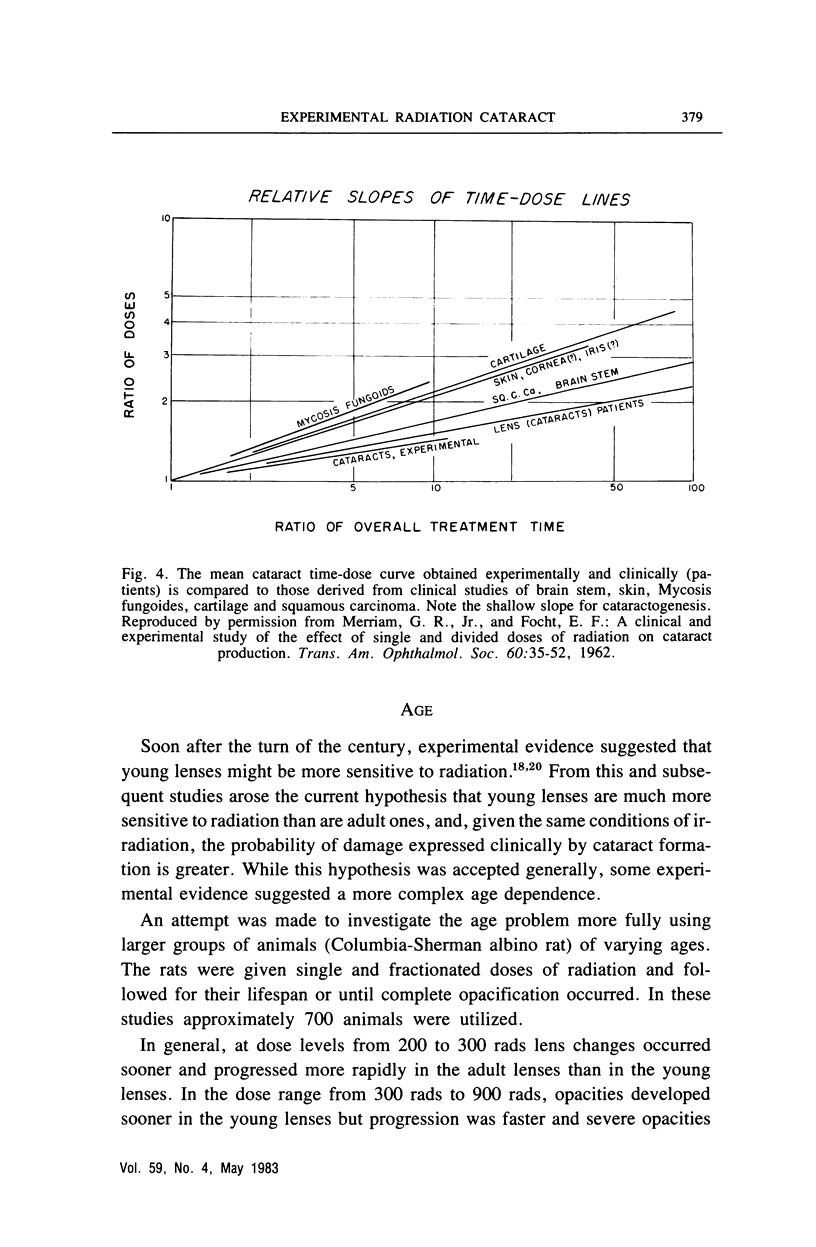
- MERRIAM G. R., Jr, FOCHT E. F. A clinical and experimental study of the effect of single and divided doses of radiation on cataract production. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1962;60:35–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRIAM G. R., Jr, FOCHT E. F. A clinical study of radiation cataracts and the relationship to dose. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1957 May;77(5):759–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merriam G. R., Jr, Szechter A. The effect of age on the radiosensitivity of rat lenses. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1973;71:88–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merriam G. R., Jr, Szechter A. The relative radiosensitivity of rat lenses as a function of age. Radiat Res. 1975 Jun;62(3):488–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. G. IRRADIATION CATARACT. Br J Ophthalmol. 1934 Sep;18(9):497–511. doi: 10.1136/bjo.18.9.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIRIE A., DRANCE S. M. Modification of x-ray damage to the lens by partial shielding. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1959 Jul;1:293–304. doi: 10.1080/09553005914550391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIRIE A., FLANDERS P. H. Effect of x-rays on partially shielded lens of the rabbit. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1957 Jun;57(6):849–854. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1957.00930050863009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUNTENNEY I., SCHOCH D. Studies on the mechanism of lens injury in radiation cataract. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1953;51:285–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUNTENNEY I., SHOCH D. The ciliary body in radiation cataract. Am J Ophthalmol. 1954 Nov;38(5):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(54)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J. L. Potential profiles in the crystalline lens of the frog. Exp Eye Res. 1974 Sep;19(3):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(74)90141-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J. L. The movement of procion dye in the crystalline lens. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Feb;13(2):147–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein H., Worgul B. V., Medvedovsky C., Merriam G. R., Jr G0/G1 arrest of cell proliferation in the ocular lens prevents development of radiation cataract. Ophthalmic Res. 1982;14(3):215–220. doi: 10.1159/000265195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCULLICA L., GRIMES P., MCELVAIN N. FURTHER AUTORADIOGRAPHIC STUDIES OF THE LENS EPITHELIUM. NORMAL AND X-IRRADIATED RAT EYES. Arch Ophthalmol. 1963 Nov;70:659–665. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1963.00960050661015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCULLICA L., GRIMES P., McELVAIN N. DNA synthesis in the rat lens epithelium after roentgen irradiation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1962 Dec;68:792–800. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1962.00960030796014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeten B. W., Eshaghian J. Human posterior subcapsular cataract. A gross and flat preparation study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978 Sep;96(9):1653–1658. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910060279020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias C. A., Budinger T. F., Lyman J. T. Radiation-induced light flashes observed by human subjects in fast neutron, x-ray and positive pion beams. Nature. 1971 Apr 30;230(5296):596–598. doi: 10.1038/230596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON SALLMANN L., CARAVAGGIO L., MUNOZ C. M., DRUNGIS A. Species differences in the radiosensitivity of the lens. Am J Ophthalmol. 1957 May;43(5):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(57)91508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON SALLMANN L. The lens epithelium in the pathogenesis of cataract; the XIII Edward Jackson Memorial lecture. Am J Ophthalmol. 1957 Aug;44(2):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(57)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worgul B. V., Bito L. Z., Merriam G. R., Jr Intraocular inflammation produced by X-irradiation of the rabbit eye. Exp Eye Res. 1977 Jul;25(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(77)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worgul B. V., Low S., Merriam G. R., Jr The lens epithelium and radiation cataract. III. The influence of age on the nuclear fragmentation of the meridional row cells following X irradiation. Radiat Res. 1982 Jul;91(1):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worgul B. V., Merriam G. R., Jr The lens epithelium and radiation cataracts. II. Interphase death in the meridional rows? Radiat Res. 1980 Oct;84(1):115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worgul B. V., Merriam G. R., Jr The role of inflammation in radiation cataractogenesis. Exp Eye Res. 1981 Aug;33(2):167–173. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(81)80065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worgul B. V., Merriam G. R., Szechter A., Srinivasan D. Lens epithelium and radiation cataract. I. Preliminary studies. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976 Jun;94(6):996–999. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1976.03910030506013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worgul B. V., Rothstein H. On the mechanism of thyroid mediated mitogenesis in adult anura. I. Preliminary analysis of growth kinetics and macromolecular syntheses, in lens epithelium, under the influence of exogenous triiodothyronine. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1974 Sep;7(5):415–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1974.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von SALLMANN L. Experimental studies on early lens changes after roentgen irradiation. I. Morphological and cytochemical changes. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1951 Feb;45(2):149–164. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1951.01700010154003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]