Abstract
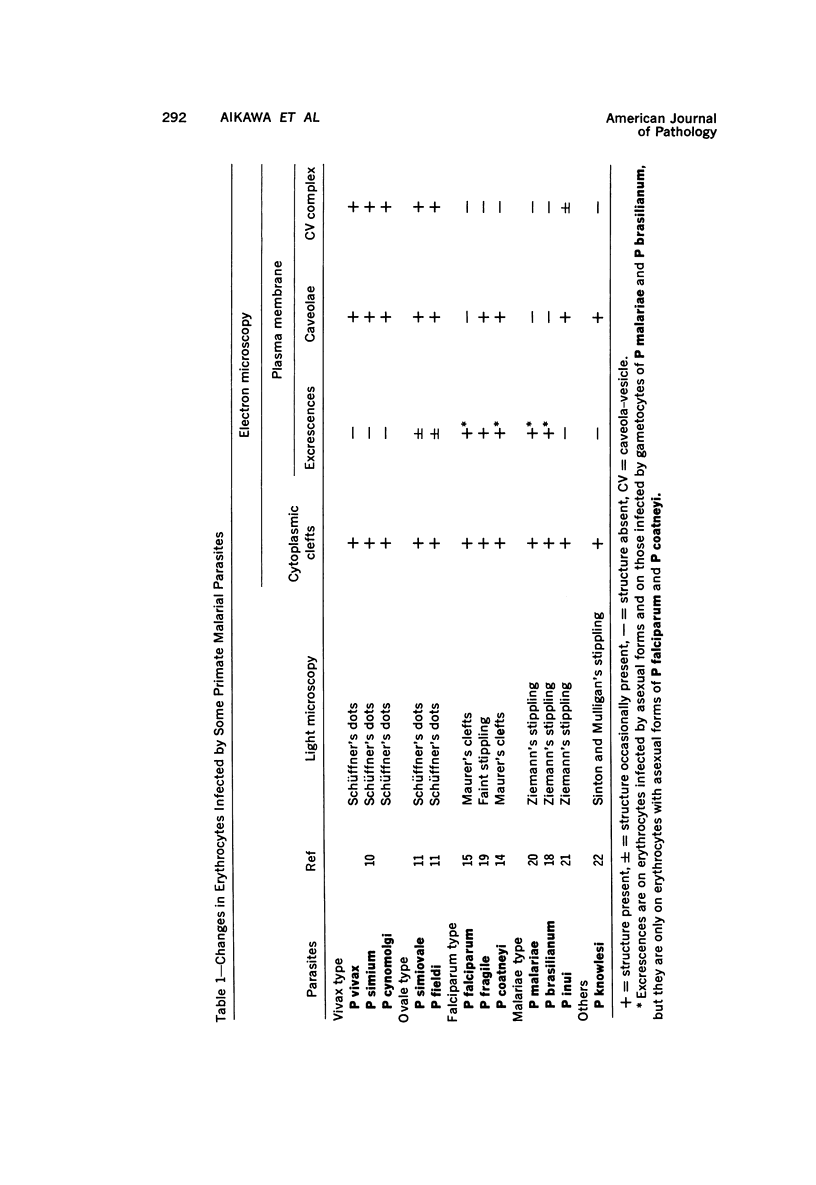
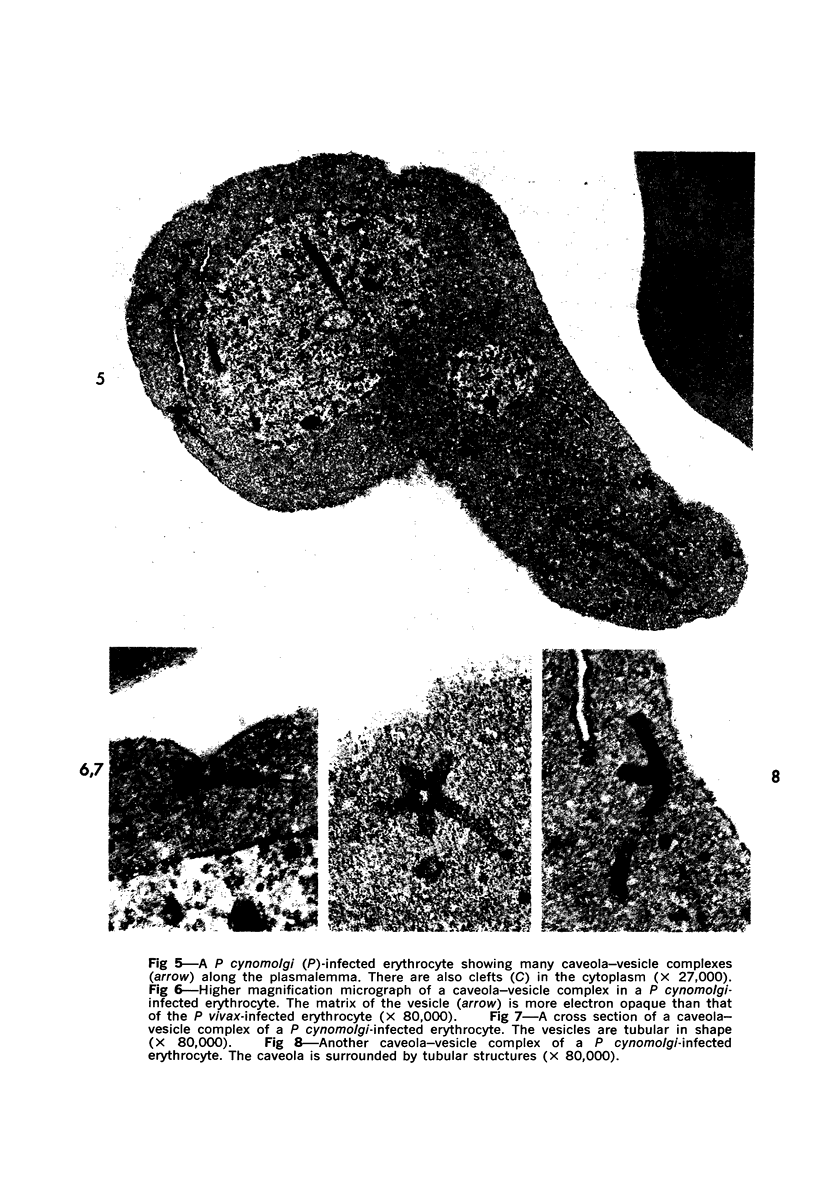
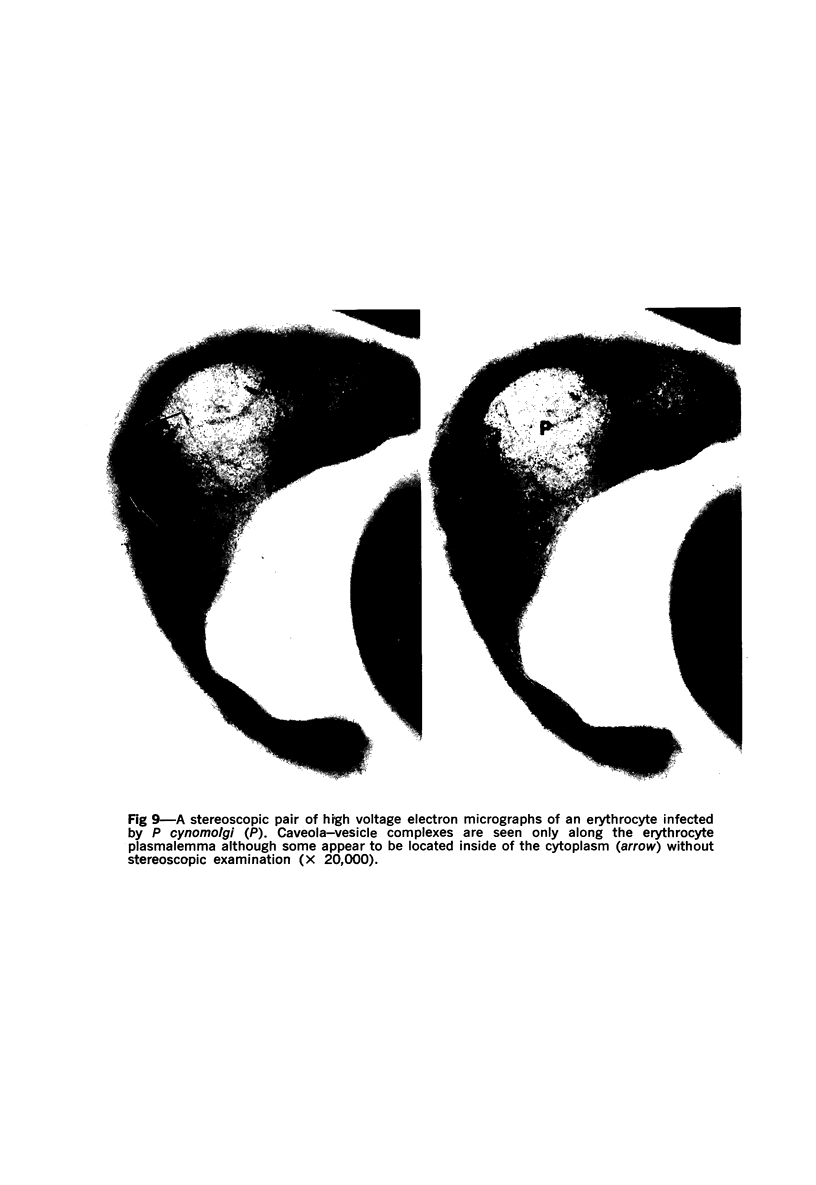
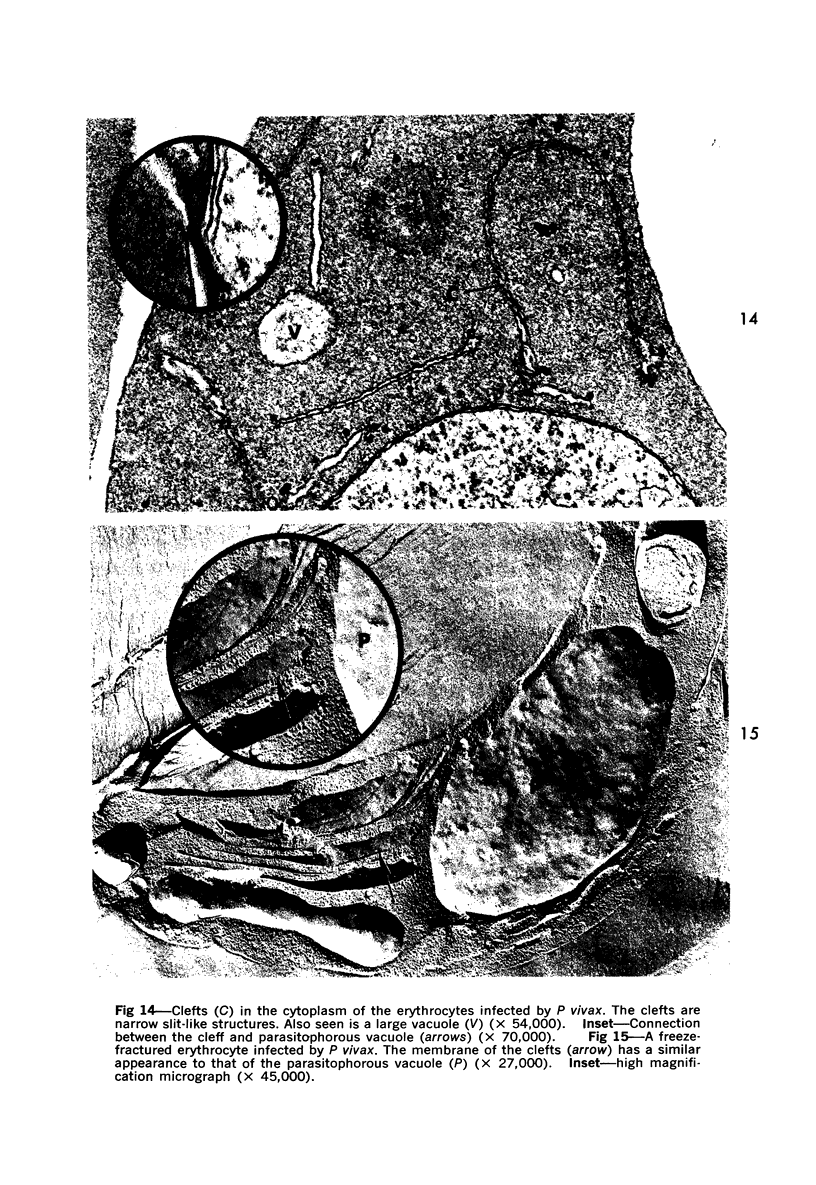
Erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium vivax and P cynomolgi, characterized by Schüffner's dots on Giemsa-stained thin films, were studied by electron microscopy and immunocytochemistry. A caveola-vesicle complex, which consisted of a caveola surrounded by vesicles, in an alveolar fashion, formed along the erythrocyte plasmalemma. Horseradish-peroxidase-labeled immunoglobulin from a monkey infected with P vivax bound to the vesicle membrane. Cationized ferritin appeared within the vesicles after incubation with viable parasitized erythrocytes, suggesting that these vesicles were pinocytotic in origin. This caveola-vesicle complex probably corresponds to Schüffner's dots because the alteration is unique to vivax- and ovale-type malarias, and its size and distribution are consistent with Schüffner's dots. Clefts observed within the cytoplasm of infected erythrocytes are present in all malarias and are unlikely candidates for Schüffner's data.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Rabbege J. R., Wellde B. T. Junctional apparatus in erythrocytes infected with malarial parasites. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;124(1):72–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Peroxidase labelled antibody and Fab conjugates with enhanced intracellular penetration. Immunochemistry. 1971 Dec;8(12):1175–1179. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremount H. N., Miller L. H. Deep vascular schizogony in Plasmodium fragile: organ distribution and ultrastructure of erythrocytes adherent to vascular endothelium. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Jan;24(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic G. J., Berwick L., Sorrentino M. Positive and negative colloidal iron as cell surface electron stains. Lab Invest. 1968 Jan;18(1):63–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse S. A., Miller L. H. Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Ultrastructure of parasitized erythrocytes in cardiac vessels. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Sep;20(5):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Fremount H. N., Luse S. A. Deep vascular schizogony of Plasmodium knowlesi in Macaca mulatta. Distribution in organs and ultrastructure of parasitized red cells. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Nov;20(6):816–824. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Powers K. G., Finerty J., Vanderberg J. P. Difference in surface charge between host cells and malarial parasites. J Parasitol. 1973 Oct;59(5):925–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H. The ultrastructure of red cells infected by Plasmodium falciparum in man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1972;66(3):459–462. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(72)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudzinska M. A., Trager W. The fine structure of trophozoites and gametocytes in Plasmodium coatneyi. J Protozool. 1968 Feb;15(1):73–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed T. M., Aikawa M., Sterling C., Rabbege J. Surface properties of extracellular malaria parasites: morphological and cytochemical study. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):750–761. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.750-761.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Theakston R. D. Comments on the ultrastructure of human erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium malariae. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1970 Sep;64(3):329–329. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1970.11686700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIE J. E., COATNEY G. R. Fluorescent antibody staining of human malaria parasites. Exp Parasitol. 1961 Sep;11:128–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(61)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]

















