Abstract
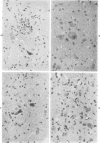
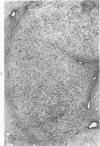
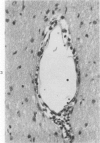
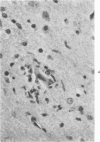
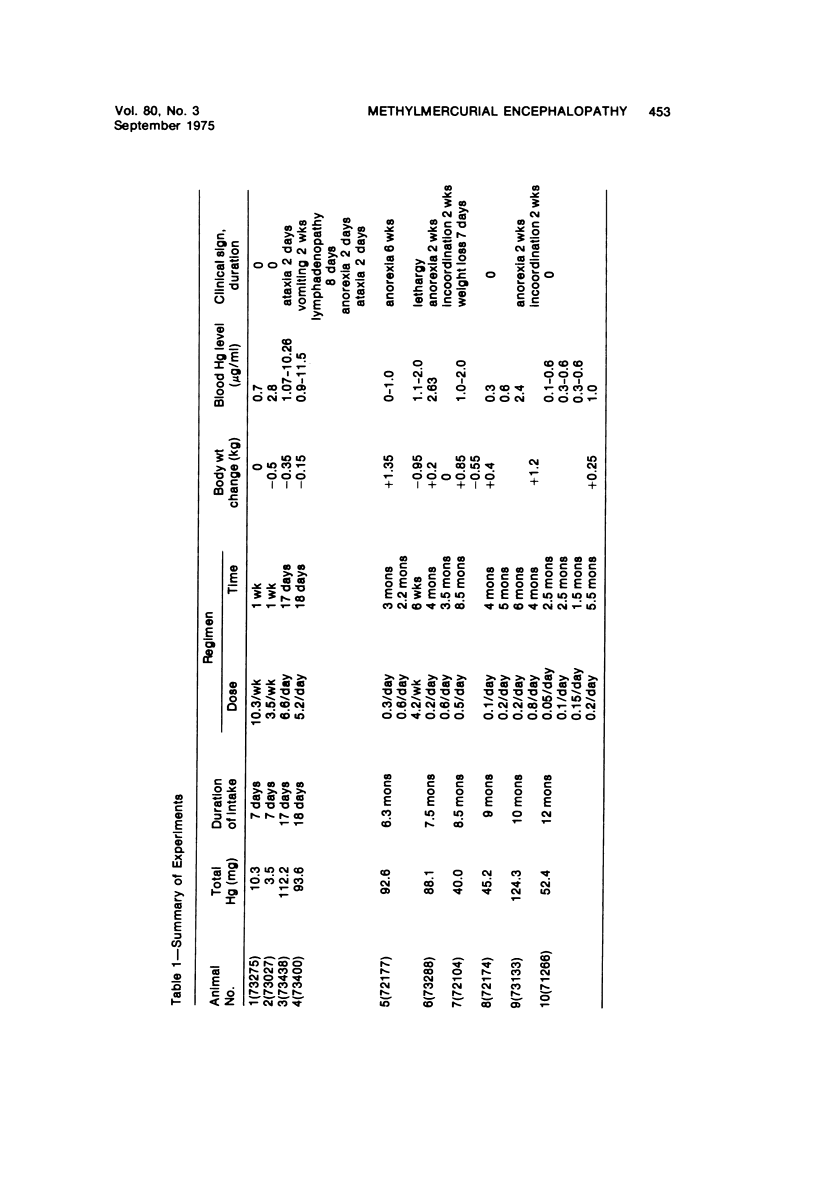
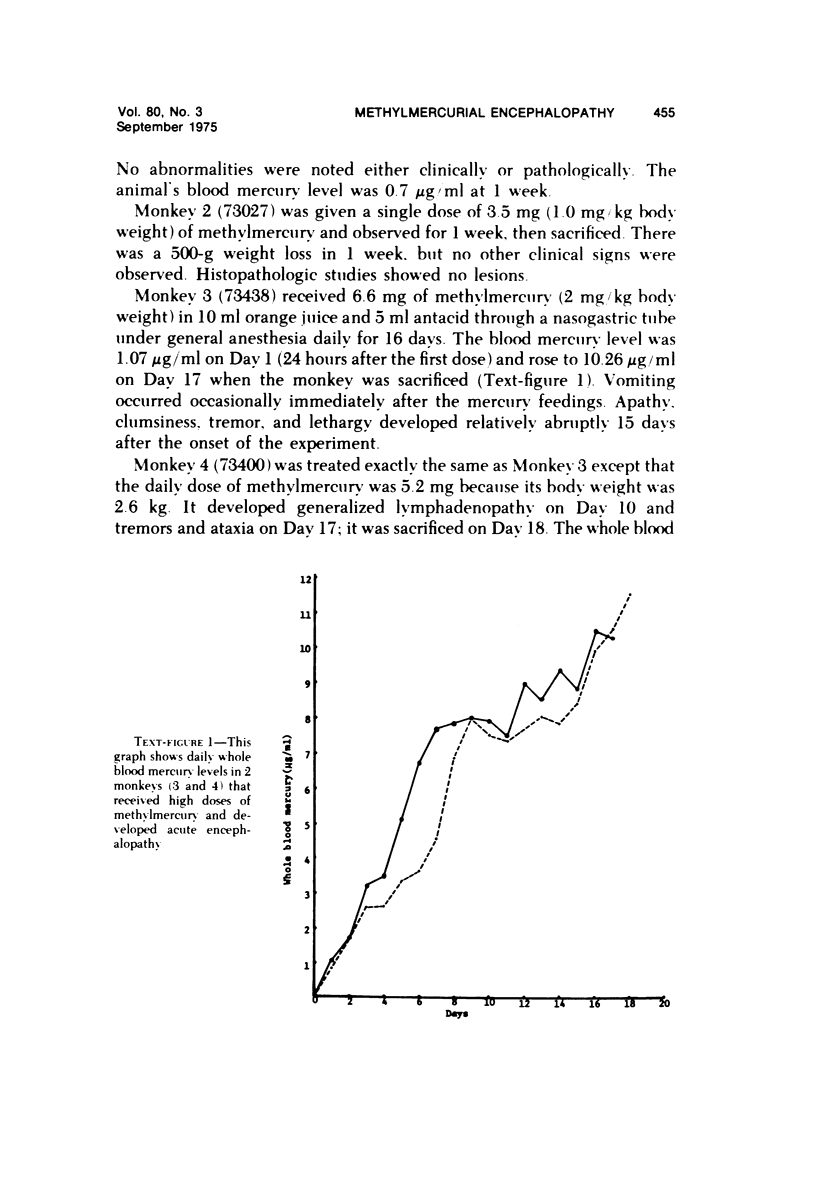
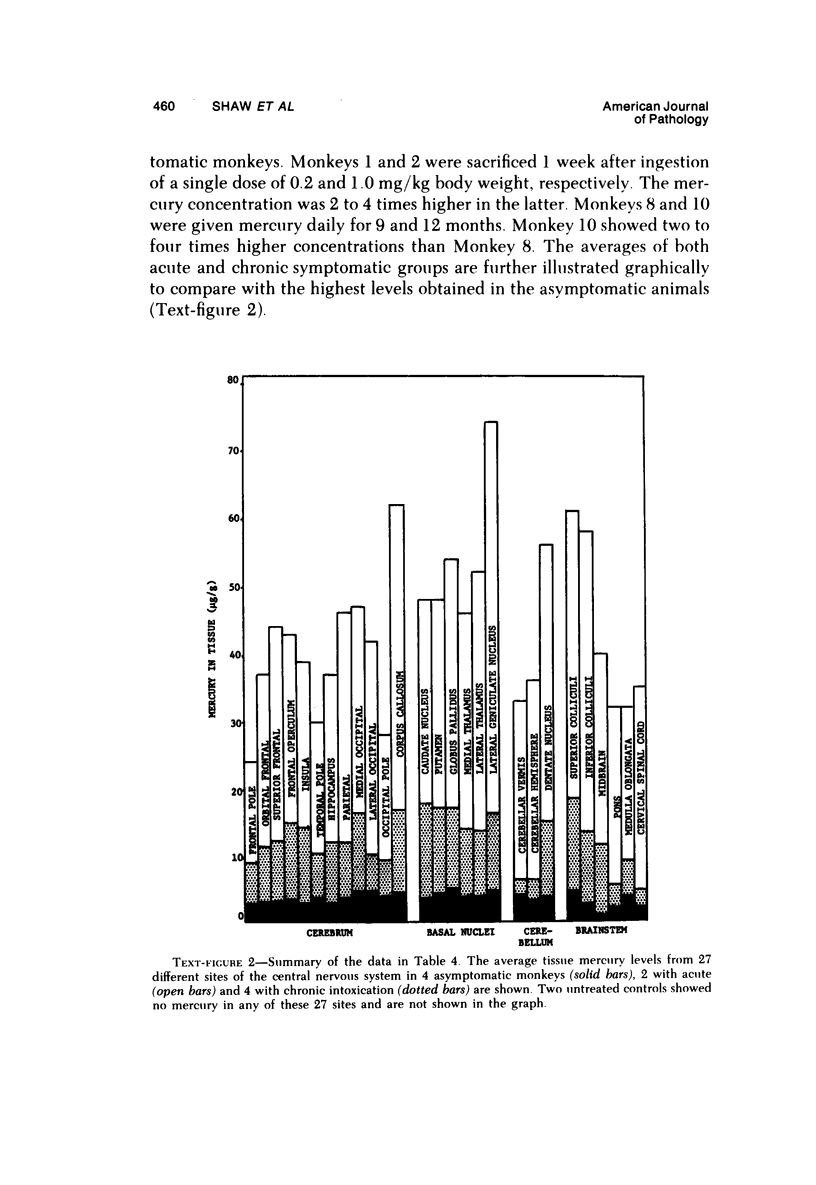
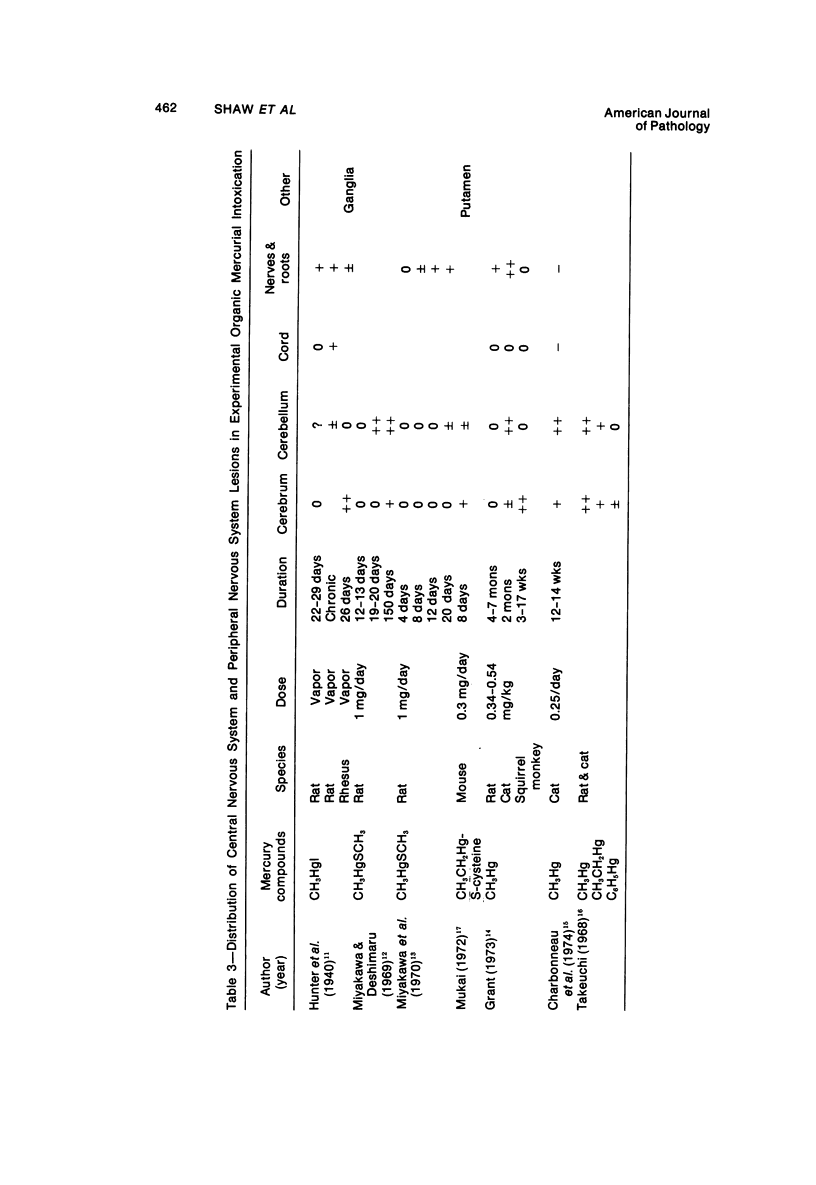
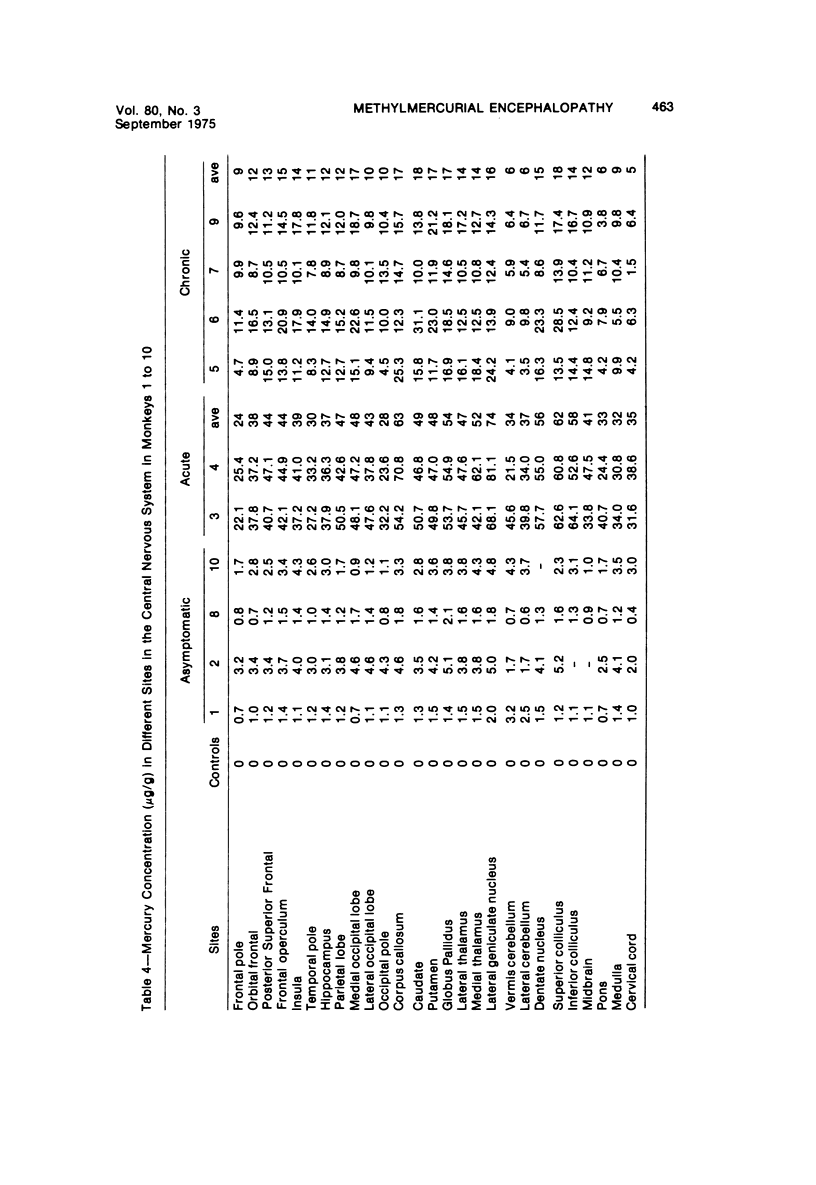
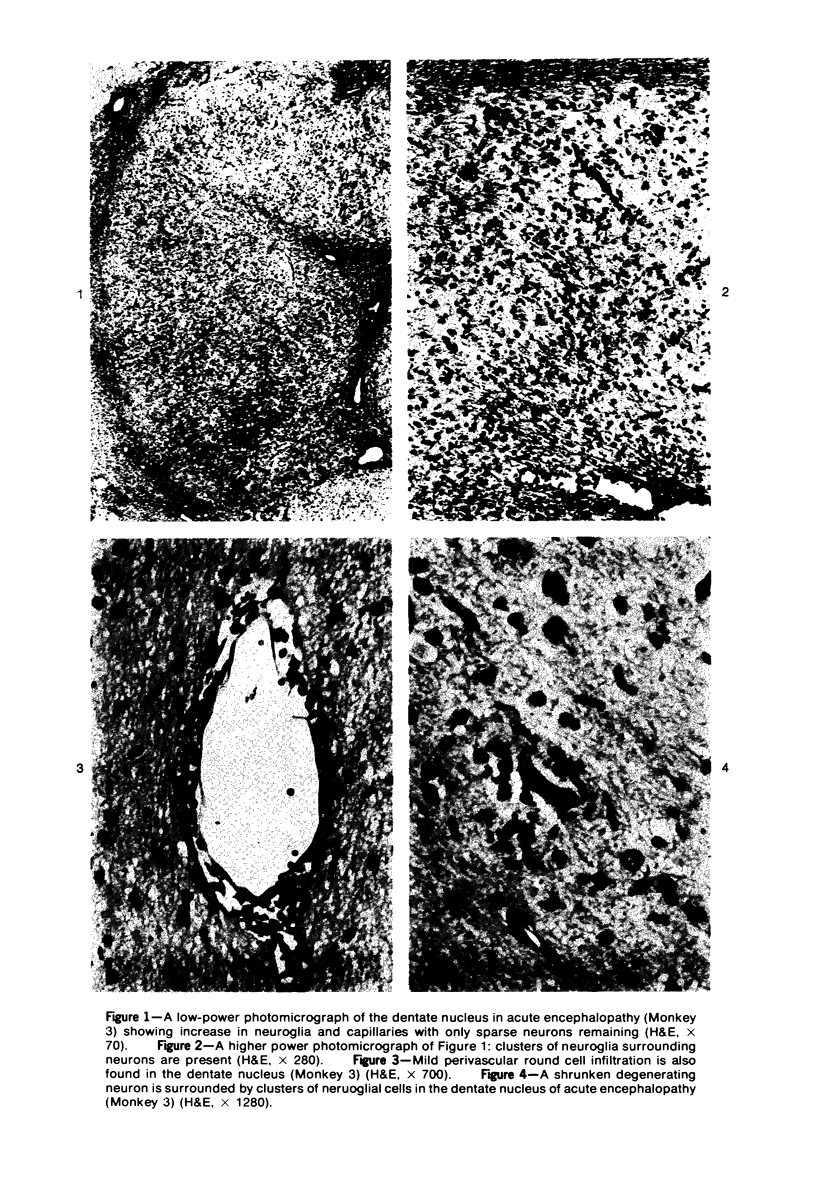
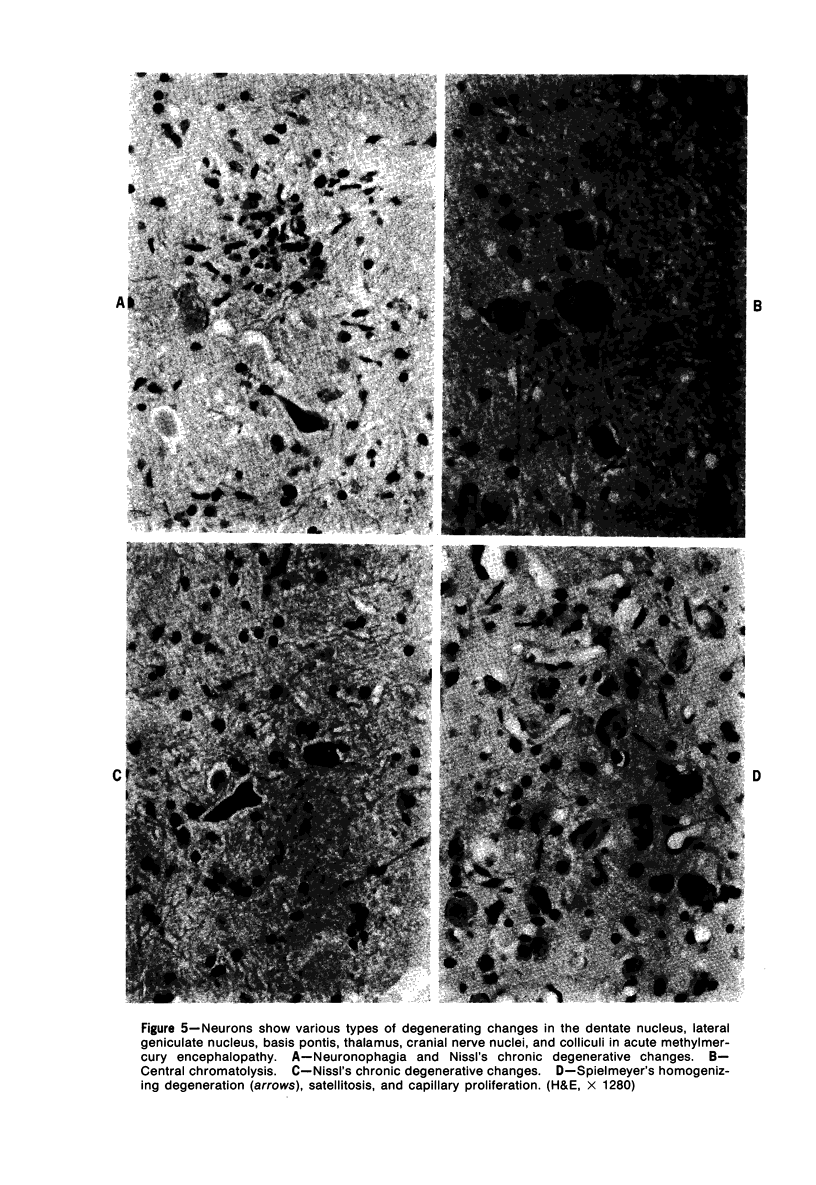
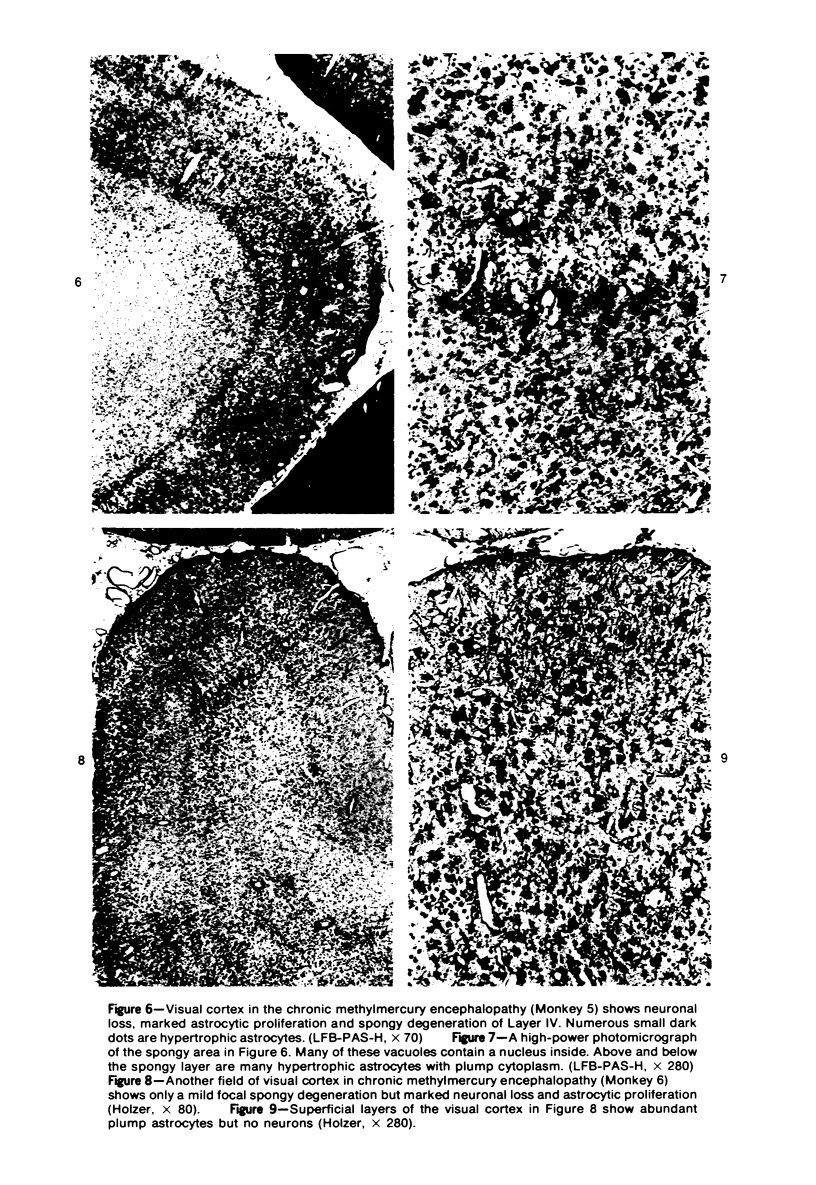
Acute and chronic intoxications of rhesus monkeys with methylmercury produced lesions in the central nervous system (CNS) with different distributions. Neuronal degeneration and astroglial proliferation predominated in the dentate nucleus, lateral geniculate nucleus, thalamus and pontine nuclei in 2 monkeys that received 2 mg/kg/day for 17 and 18 days, whereas pseudolaminar necrosis and astroglial proliferation were observed in the cerebral crotex, maximally in the calcarine and insular regions, in 4 monkeys that received 0.5 to 0.8 mg/kg/day for 3 to 8.5 months. Mercury concentrations in the CNS were much higher in the acutely intoxicated animals than in the chronically intoxicated animals, but the correlation between concentrations of mercury and the histologic destruction was not precise.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
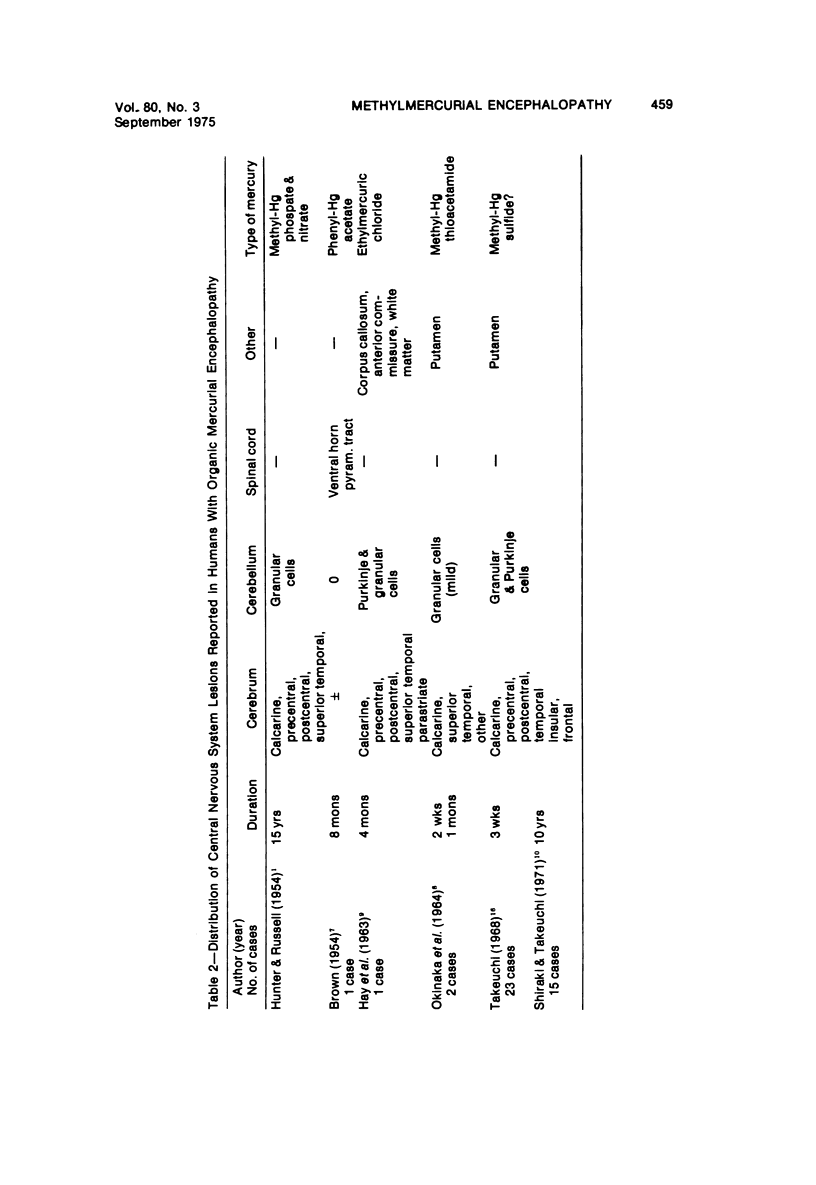
- BROWN I. A. Chronic mercurialism; a cause of the clinical syndrome of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1954 Dec;72(6):674–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. W., Hartmann H. A. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in experimental mercury intoxication. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;21(3):179–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00688496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. W., Hartmann H. A. Ultrastructural studies of the nervous system after mercury intoxication. I. Pathological changes in the nerve cell bodies. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;20(2):122–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00691129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. W., Hartmann H. A. Ultrastructural studies of the nervous system after mercury intoxication. II. Pathological changes in the nerve fibers. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;20(4):316–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00691749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau S. M., Munro I. C., Nera E. A., Willes R. F., Kuiper-Goodman T., Iverson F., Moodie C. A., Stoltz D. R., Armstrong F. A., Uthe J. F. Subacute toxicity of methylmercury in the adult cat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1974 Mar;27(3):569–581. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(74)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAY W. J., RICKARDS A. G., McMENEMEY W. H., CUMINGS J. N. Organic mercurial encephalopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963 Jun;26:199–202. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.26.3.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER D., RUSSELL D. S. Focal cerebellar and cerebellar atrophy in a human subject due to organic mercury compounds. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1954 Nov;17(4):235–241. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.17.4.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa T., Deshimaru M. Electron microscopical study of experimentally induced poisoning due to organic mercury compound. Mechanisof development of the morbid change. Acta Neuropathol. 1969;14(2):126–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00686349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa T., Deshimaru M., Sumiyoshi S., Teraoka A., Udo N., Hattori E., Tatetsu S. Experimental organic mercury poisoning--pathological changes in peripheral nerves. Acta Neuropathol. 1970;15(1):45–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00690688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottet N. K., Body R. L. Mercury burden of human autopsy organs and tissues. Arch Environ Health. 1974 Jul;29(1):18–24. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1974.10666520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottet N. K., Jensen H. M. The differentiation of chick embryonic skin. An electron microscopic study with a description of a peculiar epidermal cytoplasmic ultrastructure. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Sep;52(1):261–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90564-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai N. An experimental study of alkylmercurial encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;22(2):102–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00688778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKINAKA S., YOSHIKAWA M., MOZAI T., MIZUNO Y., TERAO T., WATANABE H., OGIHARA K., HIRAI S., YOSHINO Y., INOSE T. ENCEPHALOMYELOPATHY DUE TO AN ORGANIC MERCURY COMPOUND. Neurology. 1964 Jan;14:69–76. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki H. [Need for long-term study of organic mercury poisoning from the neuropathological viewpoint]. Shinkei Kenkyu No Shimpo. 1969 Apr;13(1):113–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]