Abstract
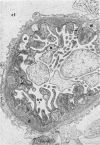
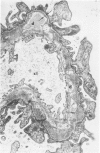
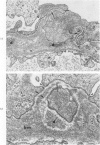
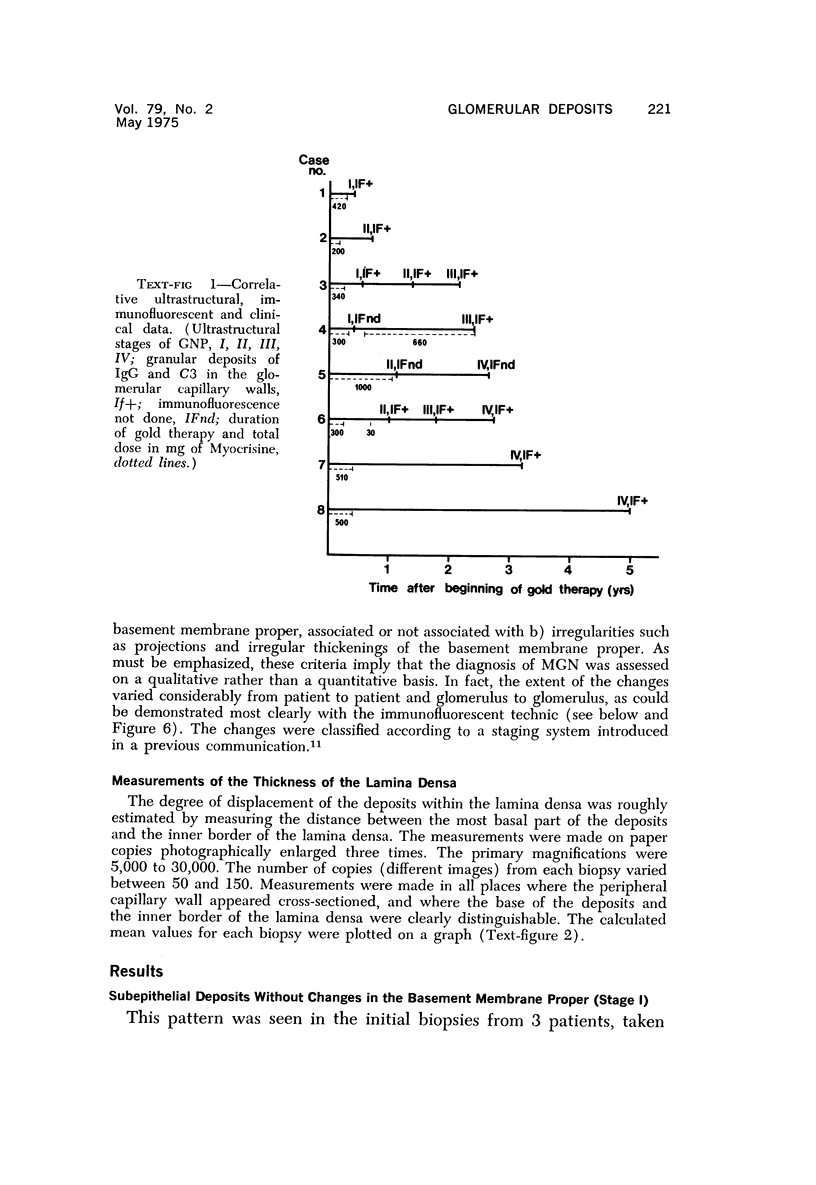
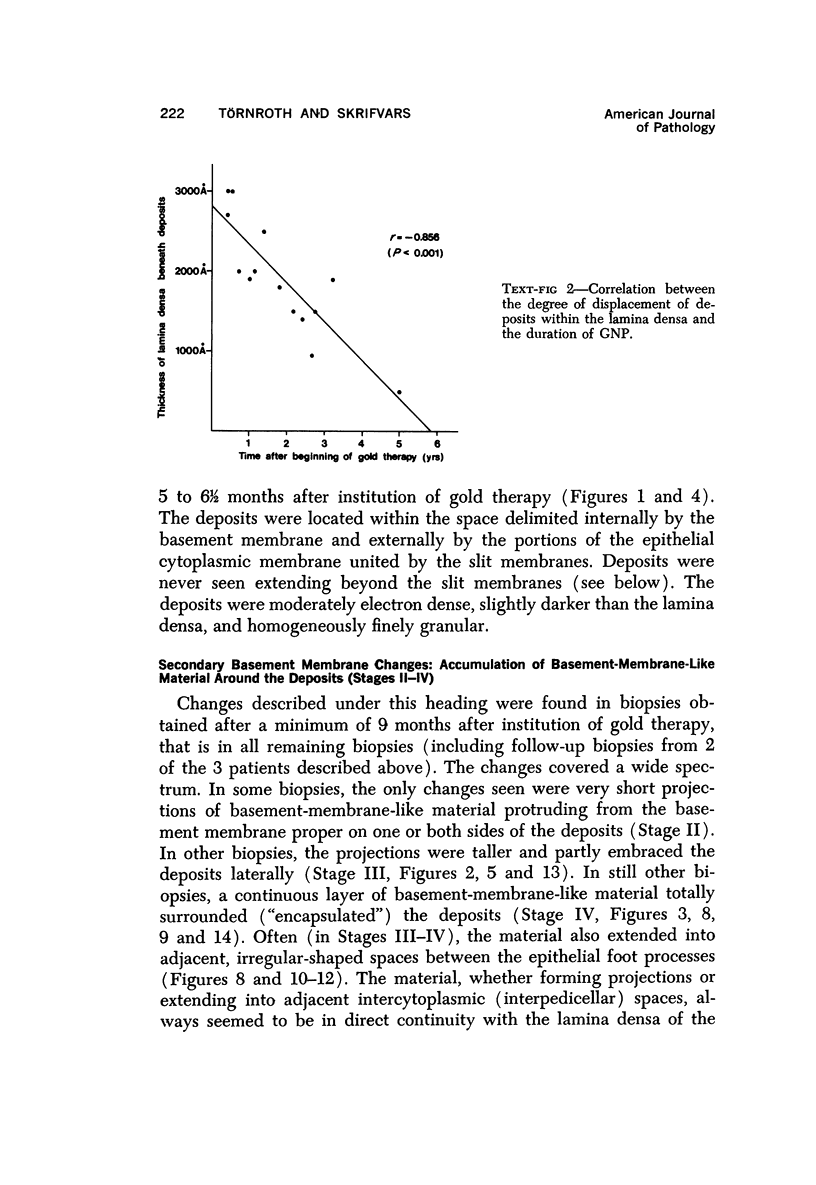
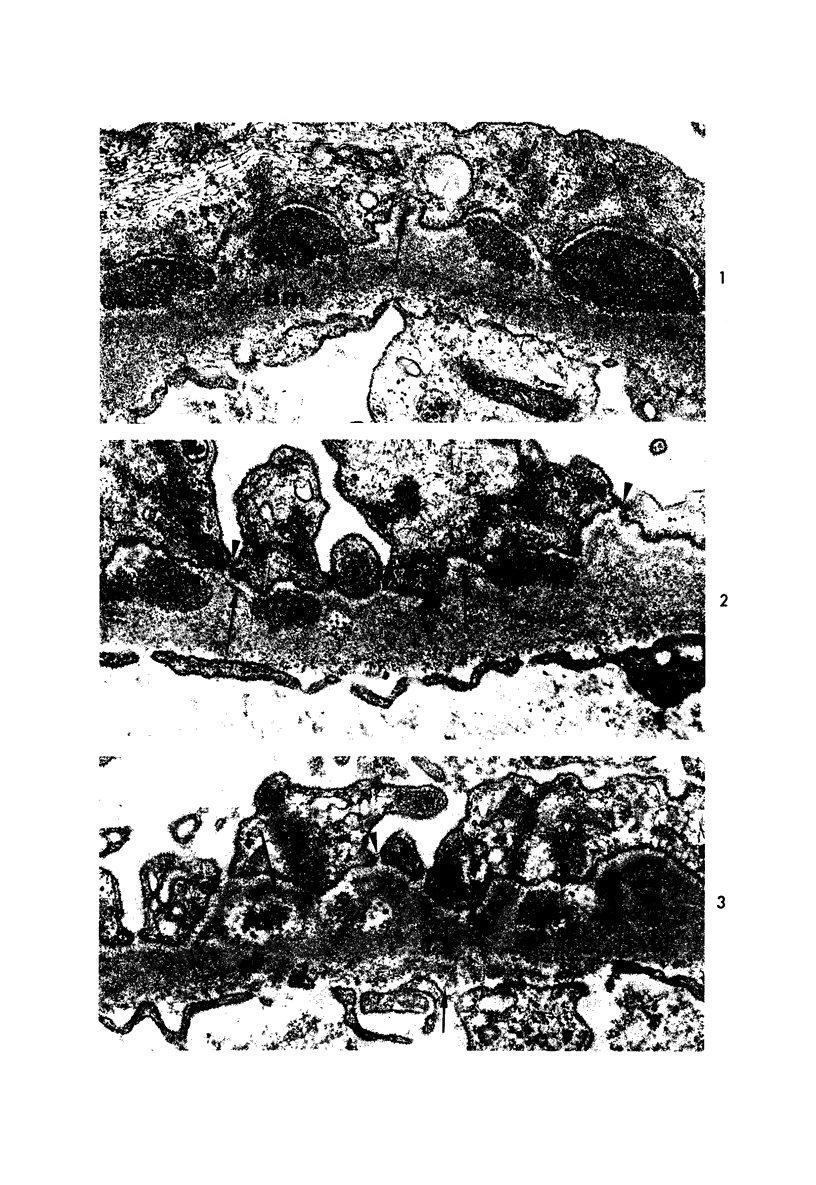
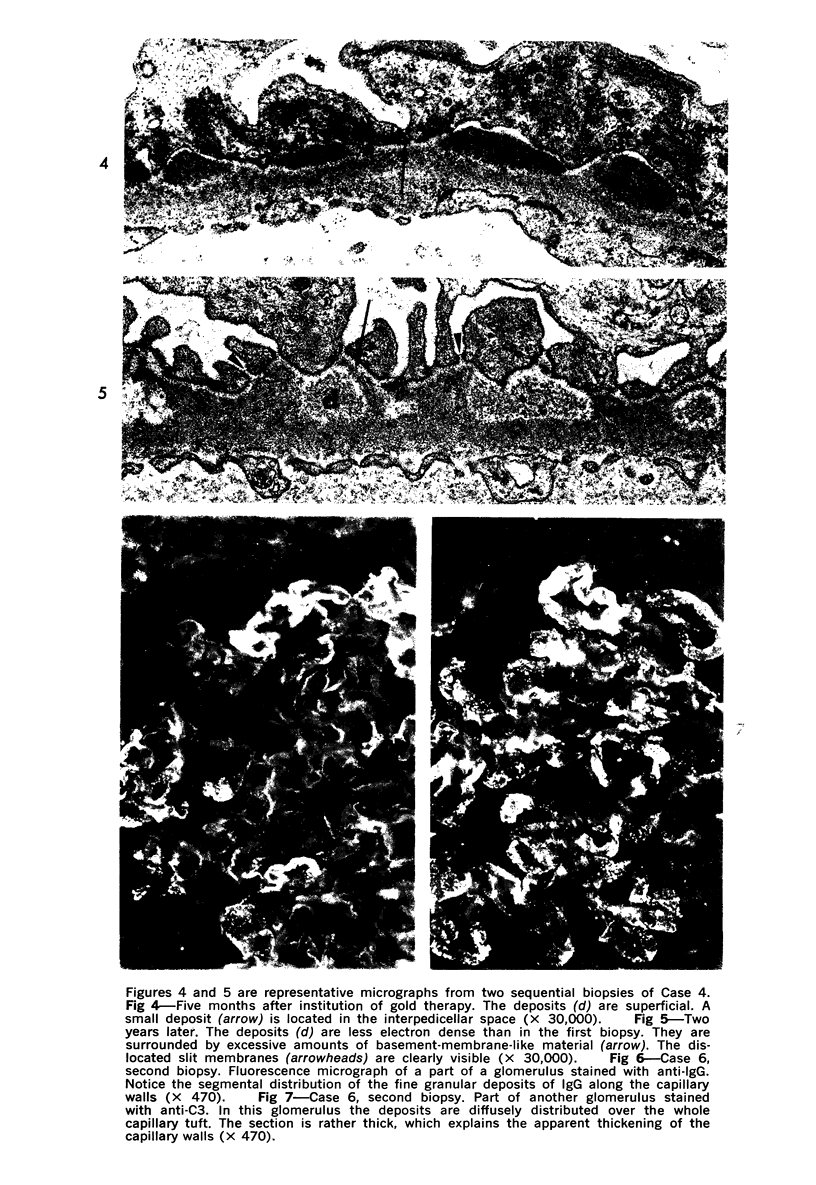
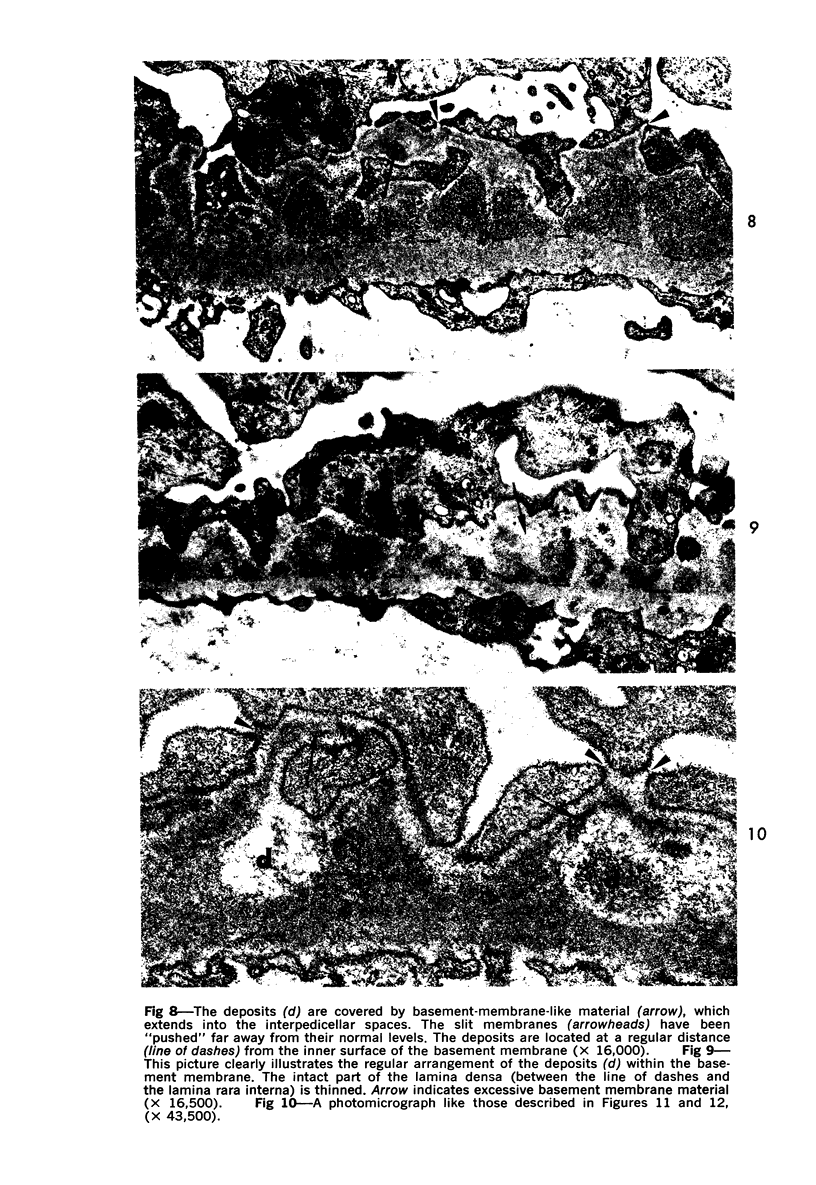
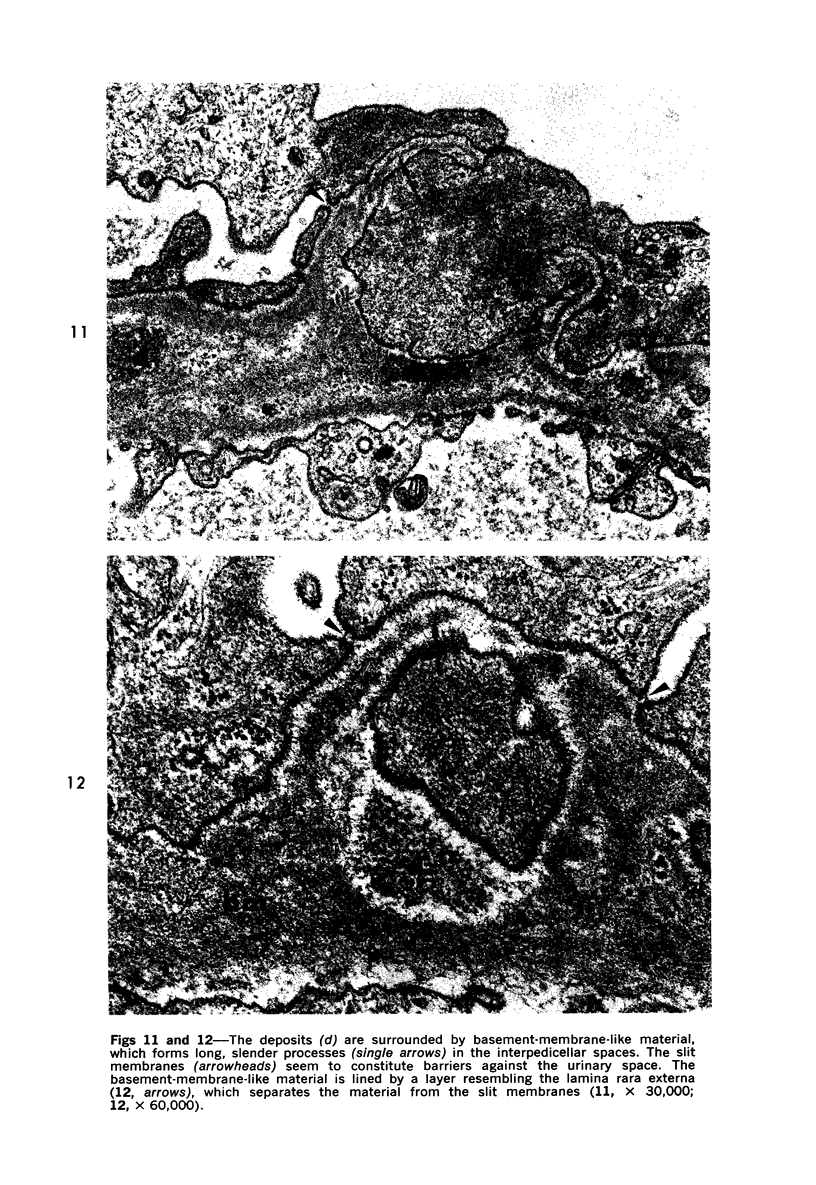
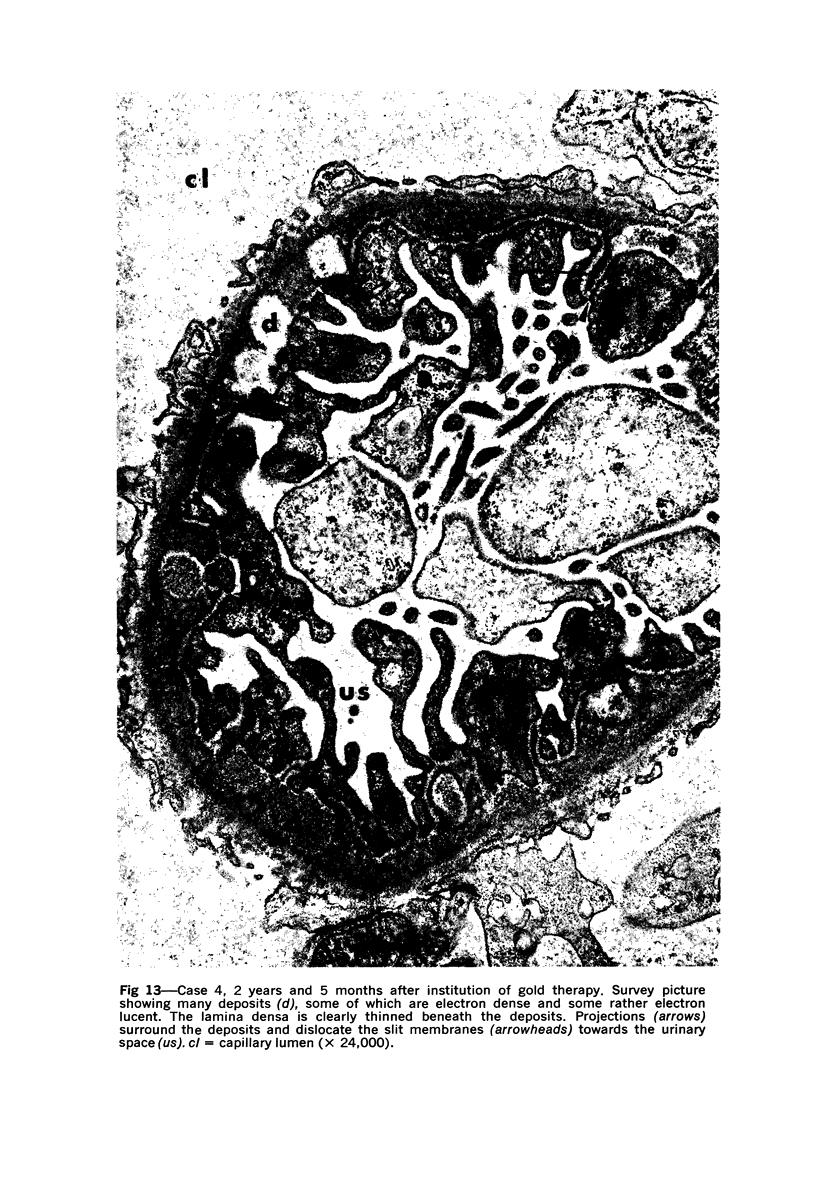
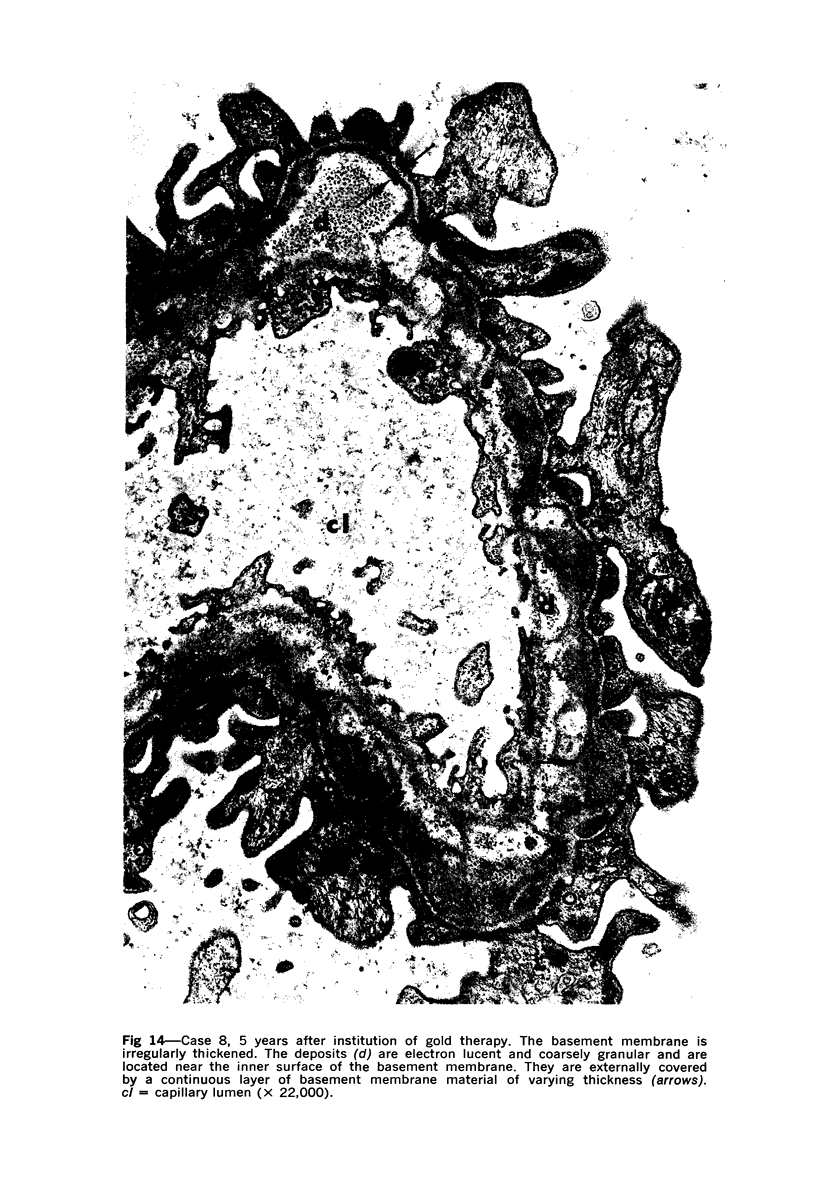
The morphogenesis of glomerular basement membrane changes associated with subepithelial immune deposits was studied in kidney biopsies from patients with gold-induced membranous glomerulonephoritis. Serial biopsies showed focal accumulations of additional basement membrane material around the deposits, suggesting that the deposited material stimulated the epithelium to increased synthesis. Moreover, the deposits were gradually displaced towards the inner (endothelia) side of the basement membrane during the course of the disease, suggesting that this layer undergoes a slow continuous turnover, with removal at its endothelial aspect. The two processes--increased epithelial synthesis and turnover--are suggested to constitute the basis of a natural healing process resulting in elimination of the deposits and structural restoration of the basement membrane. The epithelial slit membranes were dislocated externally by the deposits or the excessive basement membrane material, indicating that their barrier function is preserved even in this pathologic condition.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alousi M. A., Post R. S., Heymann W. Experimental autoimmune nephrosis in rats. Morphogenesis of the glomerular lesion: immunohistochemical and electron microscopic studies. Am J Pathol. 1969 Jan;54(1):47–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres G. A., Accinni L., Hsu K. C., Zabriskie J. B., Seegal B. C. Electron microscopic studies of human glomerulonephritis with ferritin-conjugated antibody. Localization of antigen-antibody complexes in glomerular structures of patients with acute glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1966 Feb 1;123(2):399–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bariéty J., Druet P., Lagrue G., Samarcq P., Milliez P. Les glomérulopathies "extra-membraneuses" (G.E.M.). Etude morphologique en microscopie optique, électronique et en immunofluorescence. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1970 Jan;18(1):5–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHURG J., GRISHMAN E., GOLSTEIN M. H., YUNIS S. L., PORUSH J. G. IDIOPATHIC NEPHROTIC SYNDROME IN ADULTS. A STUDY AND CLASSIFICATION BASED ON RENAL BIOPSIES. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jan 28;272:165–174. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196501282720401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHURG J., GRISHMAN E. Subacute glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jan-Feb;35(1):25–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Dixon F. J. Cell and tissue damage through antigen-antibody complexes. Calif Med. 1969 Aug;111(2):99–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., WISSIG S. L., PALADE G. E. Glomerular permeability. I. Ferritin transfer across the normal glomerular capillary wall. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:47–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. Glomerular permeability. Ultrastructural cytochemical studies using peroxidases as protein tracers. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta I. Electron microscopic analysis of glomerular basement membrane in membranous nephropathy. Jpn Circ J. 1972 Feb;36(2):137–152. doi: 10.1253/jcj.36.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES D. B. Nephrotic glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1957 Mar-Apr;33(2):313–329. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURTZ S. M., FELDMAN J. D. Experimental studies on the formation of the glomerular basement membrane. J Ultrastruct Res. 1962 Feb;6:19–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(62)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latta H. The glomerular cappillary wall. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Sep;32(5):526–544. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)80026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOVAT H. Z., McGREGOR D. D. The fine structure of the glomerulus in membranous glomerulonephritis (lipoid nephrosis) in adults. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Aug;32(2):109–127. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/32.2.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Blau E., Vernier R. L. Glomerular polyanion. Alteration in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1970 Dec;23(6):649–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. B., Nakane P. K. Basement membranes. Synthesis and deposition in response to cellular injury. Lab Invest. 1969 Jul;21(1):27–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollak V. E., Rosen S., Pirani C. L., Muehrcke R. C., Kark R. M. Natural history of lipoid nephrosis and of membranous glomerulonephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Dec;69(6):1171–1196. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-6-1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet G., Fillastre J. P., Morel-Maroger L., Bariety J. Change from diffuse proliferative to membranous glomerulonephritis: serial biopsies in four cases. Kidney Int. 1974 Jan;5(1):57–71. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald R., Karnovsky M. J. Porous substructure of the glomerular slit diaphragm in the rat and mouse. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):423–433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRUNK S. W., HAMMOND W. S., BENDITT E. P. THE RESOLUTION OF ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF FOUR SEQUENTIAL BIOPSIES. Lab Invest. 1964 May;13:401–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagel I., Treser G., Ty A., Yoshizawa N., Kleinberger H., Yuceoglu A. M., Wasserman E., Lange K. Occurrence and nature of glomerular lesions after group A streptococci infections in children. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Oct;79(4):492–499. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-4-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tönroth T., Skrifvars B. Gold nephropathy prototype of membranous glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1974 Jun;75(3):573–590. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERNIER R. L., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A. Studies of the human fetal kidney. I. Development of the glomerulus. J Pediatr. 1962 May;60:754–768. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(62)80103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes A. J., Senterfit L. B., Pollack A. D., Germuth F. G., Jr The effect of antigen excess on chronic immune complex glomerulonephritis. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1969 Jan;124(1):9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Karnovsky M. J., Fahimi H. D., Cotran R. S. An ultrastructural study of glomerular permeability using catalase and peroxidase as tracer proteins. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1153–1167. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. The origin, turnover and removal of glomerular basement-membrane. J Pathol. 1973 Jul;110(3):233–244. doi: 10.1002/path.1711100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Diagnosis of immunopathologic renal disease. Kidney Int. 1974 Jun;5(6):389–401. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]