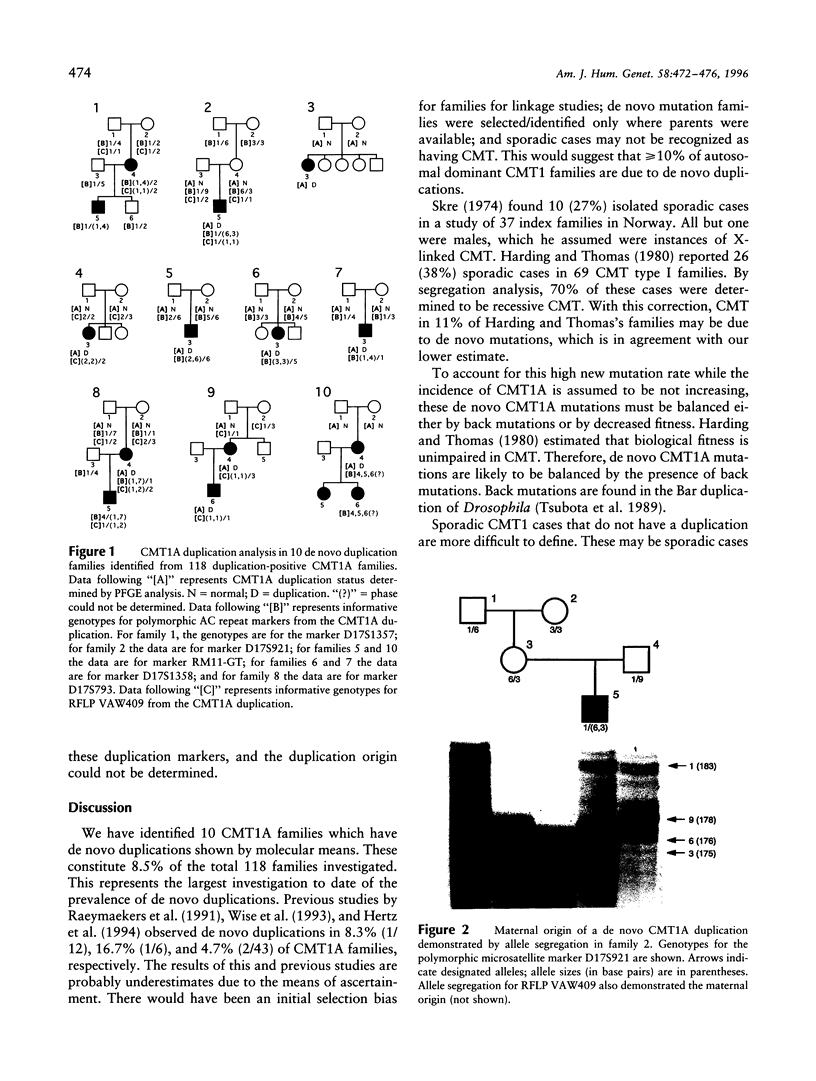
Abstract
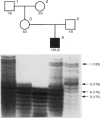
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) is the most common inherited peripheral neuropathy. Sporadic cases of CMT have been described since the earliest reports of the disease. The most frequent form of the disorder, CMT1A, is associated with a 1.5-Mb DNA duplication on chromosome 17p11.2, which segregates with the disease. In order to investigate the prevalence of de novo CMT1A duplications, this study examined 118 duplication-positive CMT1A families. In 10 of these families it was demonstrated that the disease had arisen as the result of a de novo mutation. By taking into account the ascertainment of families, it can be estimated that > or = 10% of autosomal dominant CMT1 families are due to de novo duplications. The CMT1A duplication is thought to be the product of unequal crossing over between parental chromosome 17 homologues during meiosis. Polymorphic markers from within the duplicated region were used to determine the parental origin of these de novo duplications in eight informative families. Seven were of paternal and one of maternal origin. This study represents the first report of a de novo duplication with a maternal origin and indicates that it is not a phenomenon associated solely with male meioses. Recombination fractions for the region duplicated in CMT1A are larger in females than in males. That suggests that oogenesis may be afforded greater protection from misalignment during synapsis, and/or that there may be lower activity of those factors or mechanisms that lead to unequal crossing over at the CMT1A locus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergoffen J., Trofatter J., Pericak-Vance M. A., Haines J. L., Chance P. F., Fischbeck K. H. Linkage localization of X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Feb;52(2):312–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair I. P., Kennerson M. L., Nicholson G. A. Detection of Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A duplication by the polymerase chain reaction. Clin Chem. 1995 Aug;41(8 Pt 1):1105–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths L. R., Zwi M. B., McLeod J. G., Nicholson G. A. Chromosome I linkage studies in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type I. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 May;42(5):756–771. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z., Sharma V., Patterson D., Litt M. TG repeat polymorphism at the D21S167 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4967–4967. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4967-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Thomas P. K. Genetic aspects of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy (types I and II). J Med Genet. 1980 Oct;17(5):329–336. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.5.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz J. M., Børglum A. D., Brandt C. A., Flint T., Bisgaard C. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A: the parental origin of a de novo 17p11.2-p12 duplication. Clin Genet. 1994 Oct;46(4):291–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1994.tb04162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogendijk J. E., Hensels G. W., Gabreëls-Festen A. A., Gabreëls F. J., Janssen E. A., de Jonghe P., Martin J. J., van Broeckhoven C., Valentijn L. J., Baas F. De-novo mutation in hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type I. Lancet. 1992 May 2;339(8801):1081–1082. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90668-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS H. Familial chronic hypertrophic polyneuropathy with paralysis of the extremities in cold weather. S Afr Med J. 1960 Sep 3;34:758–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennerson M. L., Gordon M. J., Blair I. P., Nicholson G. A. Single test for two hereditary neuropathies, CMT1A and HNPP. Clin Chem. 1995 Oct;41(10):1534–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebo R. V., Chance P. F., Dyck P. J., Redila-Flores M. T., Lynch E. D., Golbus M. S., Bird T. D., King M. C., Anderson L. A., Hall J. Chromosome 1 Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT1B) locus in the Fc gamma receptor gene region. Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;88(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00204921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupski J. R., de Oca-Luna R. M., Slaugenhaupt S., Pentao L., Guzzetta V., Trask B. J., Saucedo-Cardenas O., Barker D. F., Killian J. M., Garcia C. A. DNA duplication associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):219–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90613-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson G. A., Kennerson M. L., Keats B. J., Mesterovic N., Churcher W., Barker D., Ross D. A. Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1A mutation: apparent crossovers with D17S122 are due to a duplication. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Nov 1;44(4):455–460. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320440414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson G. A. Penetrance of the hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy Ia mutation: assessment by nerve conduction studies. Neurology. 1991 Apr;41(4):547–552. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palau F., Löfgren A., De Jonghe P., Bort S., Nelis E., Sevilla T., Martin J. J., Vilchez J., Prieto F., Van Broeckhoven C. Origin of the de novo duplication in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A: unequal nonsister chromatid exchange during spermatogenesis. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2031–2035. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. I., Franco B., Garcia C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Nakamura Y., Ledbetter D. H., Chakravarti A., Lupski J. R. Genetic mapping of autosomal dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in a large French-Acadian kindred: identification of new linked markers on chromosome 17. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):801–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. I., Roa B. B., Welcher A. A., Schoener-Scott R., Trask B. J., Pentao L., Snipes G. J., Garcia C. A., Francke U., Shooter E. M. The gene for the peripheral myelin protein PMP-22 is a candidate for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Nat Genet. 1992 Jun;1(3):159–165. doi: 10.1038/ng0692-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentao L., Wise C. A., Chinault A. C., Patel P. I., Lupski J. R. Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A duplication appears to arise from recombination at repeat sequences flanking the 1.5 Mb monomer unit. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):292–300. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeymaekers P., Timmerman V., Nelis E., De Jonghe P., Hoogendijk J. E., Baas F., Barker D. F., Martin J. J., De Visser M., Bolhuis P. A. Duplication in chromosome 17p11.2 in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1a (CMT 1a). The HMSN Collaborative Research Group. Neuromuscul Disord. 1991;1(2):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(91)90055-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisecker F., Leblhuber F., Lexner R., Radner G., Rosenkranz W., Wagner K. A sporadic form of hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies: clinical, electrodiagnostic, and molecular genetic findings. Neurology. 1994 Apr;44(4):753–755. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.4.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roa B. B., Garcia C. A., Pentao L., Killian J. M., Trask B. J., Suter U., Snipes G. J., Ortiz-Lopez R., Shooter E. M., Patel P. I. Evidence for a recessive PMP22 point mutation in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Nat Genet. 1993 Oct;5(2):189–194. doi: 10.1038/ng1093-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roa B. B., Garcia C. A., Suter U., Kulpa D. A., Wise C. A., Mueller J., Welcher A. A., Snipes G. J., Shooter E. M., Patel P. I. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Association with a spontaneous point mutation in the PMP22 gene. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 8;329(2):96–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307083290205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skre H. Genetic and clinical aspects of Charcot-Marie-Tooth's disease. Clin Genet. 1974;6(2):98–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb00638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubota S. I., Rosenberg D., Szostak H., Rubin D., Schedl P. The cloning of the Bar region and the B breakpoint in Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for a transposon-induced rearrangement. Genetics. 1989 Aug;122(4):881–890. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.4.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentijn L. J., Baas F., Wolterman R. A., Hoogendijk J. E., van den Bosch N. H., Zorn I., Gabreëls-Festen A. W., de Visser M., Bolhuis P. A. Identical point mutations of PMP-22 in Trembler-J mouse and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):288–291. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance J. M., Barker D., Yamaoka L. H., Stajich J. M., Loprest L., Hung W. Y., Fischbeck K., Roses A. D., Pericak-Vance M. A. Localization of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1a (CMT1A) to chromosome 17p11.2. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):623–628. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90355-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis J., Williamson R., Chamberlain S. Identification of a hypervariable microsatellite polymorphism within D9S15 tightly linked to Friedrich's ataxia. Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;85(1):98–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00276331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise C. A., Garcia C. A., Davis S. N., Heju Z., Pentao L., Patel P. I., Lupski J. R. Molecular analyses of unrelated Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease patients suggest a high frequency of the CMTIA duplication. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Oct;53(4):853–863. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]