Abstract
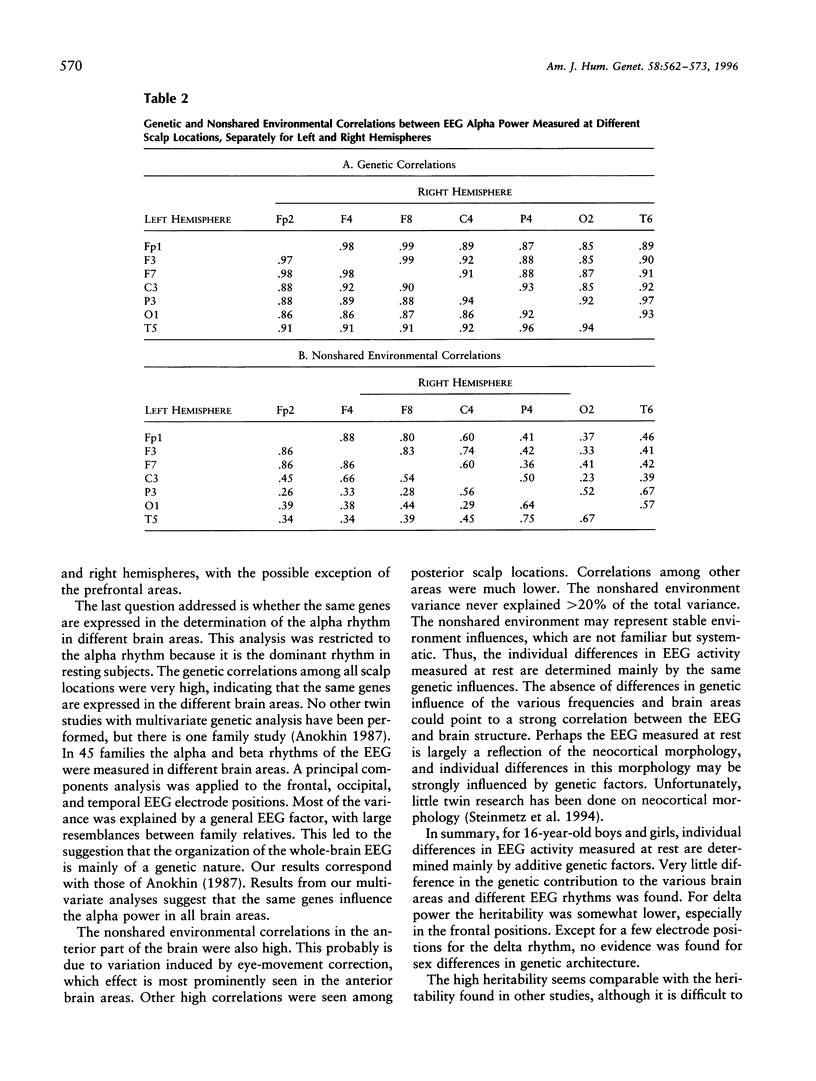
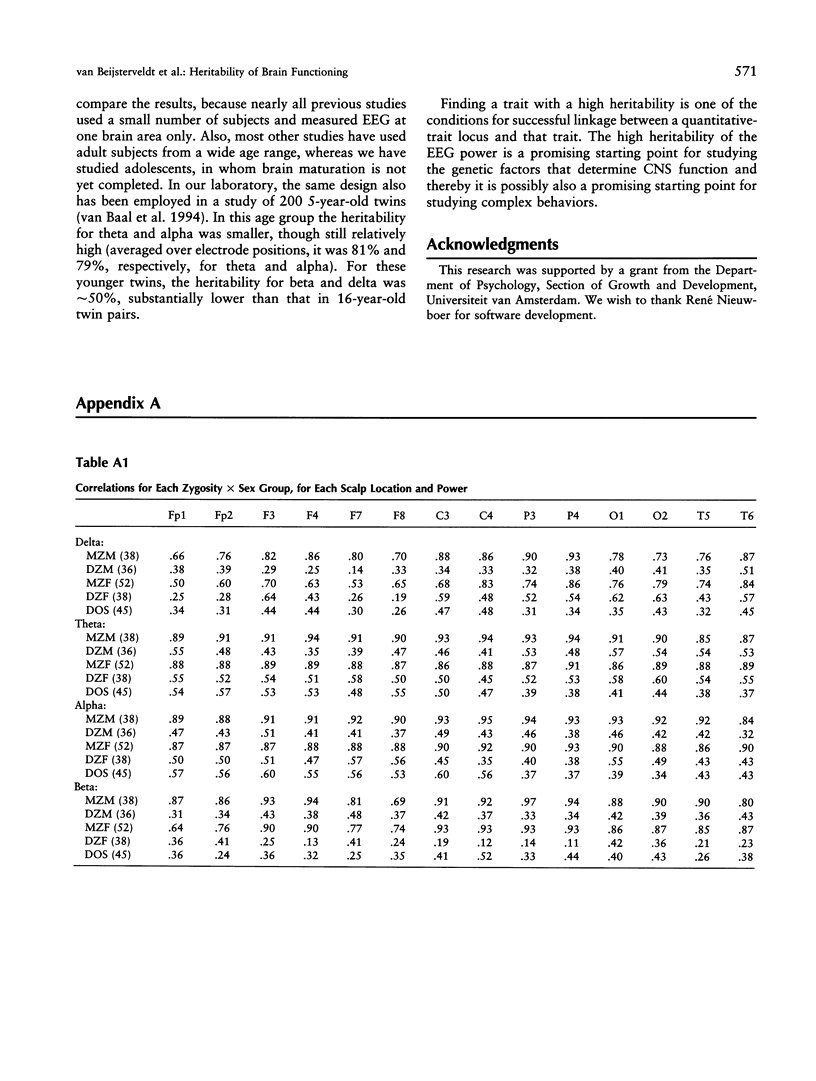
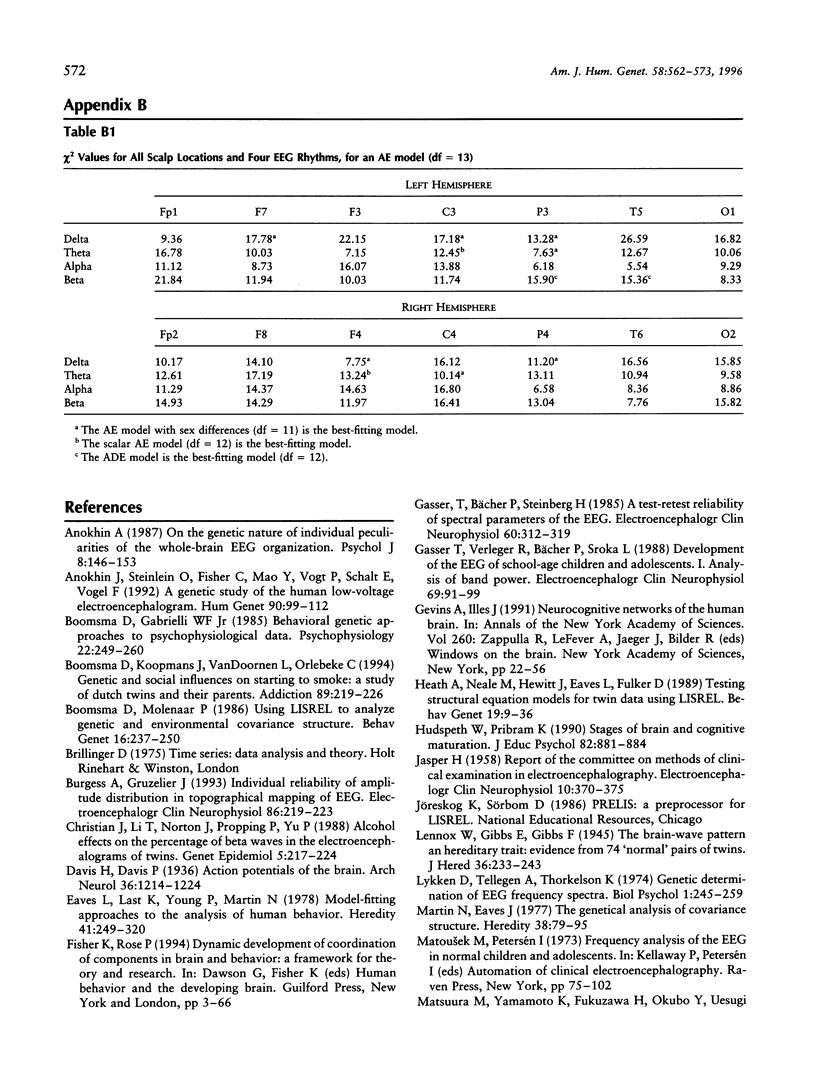
To study the genetic and environmental contributions to individual differences in CNS functioning, the electroencephalogram (EEG) was measured in 213 twin pairs age 16 years. EEG was measured in 91 MZ and 122 DZ twins. To quantify sex differences in the genetic architecture, EEG was measured in female and male same-sex twins and in opposite-sex twins. EEG was recorded on 14 scalp positions during quiet resting with eyes closed. Spectral powers were calculated for four frequency bands: delta, theta, alpha, and beta. Twin correlations pointed toward high genetic influences for all these powers and scalp locations. Model fitting confirmed these findings; the largest part of the variance of the EEG is explained by additive genetic factors. The averaged heritabilites for the delta, theta, alpha and beta frequencies was 76%, 89%, 89%, and 86%, respectively. Multivariate analyses suggested that the same genes for EEG alpha rhythm were expressed in different brain areas in the left and right hemisphere. This study shows that brain functioning, as indexed by rhythmic brain-electrical activity, is one of the most heritable characteristics in humans.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anokhin A., Steinlein O., Fischer C., Mao Y., Vogt P., Schalt E., Vogel F. A genetic study of the human low-voltage electroencephalogram. Hum Genet. 1992 Sep-Oct;90(1-2):99–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00210751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boomsma D. I., Gabrielli W. F., Jr Behavioral genetic approaches to psychophysiological data. Psychophysiology. 1985 May;22(3):249–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1985.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boomsma D. I., Koopmans J. R., Van Doornen L. J., Orlebeke J. F. Genetic and social influences on starting to smoke: a study of Dutch adolescent twins and their parents. Addiction. 1994 Feb;89(2):219–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1994.tb00881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boomsma D. I., Molenaar P. C. Using LISREL to analyze genetic and environmental covariance structure. Behav Genet. 1986 Mar;16(2):237–250. doi: 10.1007/BF01070799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian J. C., Li T. K., Norton J. A., Jr, Propping P., Yu P. L. Alcohol effects on the percentage of beta waves in the electroencephalograms of twins. Genet Epidemiol. 1988;5(4):217–224. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370050403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaves L. J., Last K. A., Young P. A., Martin N. G. Model-fitting approaches to the analysis of human behaviour. Heredity (Edinb) 1978 Dec;41(3):249–320. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1978.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser T., Bächer P., Steinberg H. Test-retest reliability of spectral parameters of the EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1985 Apr;60(4):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(85)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser T., Verleger R., Bächer P., Sroka L. Development of the EEG of school-age children and adolescents. I. Analysis of band power. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1988 Feb;69(2):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(88)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lykken D. T., Tellegen A., Thorkelson K. Genetic determination of EEG frequency spectra. Biol Psychol. 1974;1(4):245–259. doi: 10.1016/0301-0511(74)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. G., Eaves L. J. The genetical analysis of covariance structure. Heredity (Edinb) 1977 Feb;38(1):79–95. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1977.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura M., Yamamoto K., Fukuzawa H., Okubo Y., Uesugi H., Moriiwa M., Kojima T., Shimazono Y. Age development and sex differences of various EEG elements in healthy children and adults--quantification by a computerized wave form recognition method. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1985 May;60(5):394–406. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(85)91013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pivik R. T., Broughton R. J., Coppola R., Davidson R. J., Fox N., Nuwer M. R. Guidelines for the recording and quantitative analysis of electroencephalographic activity in research contexts. Psychophysiology. 1993 Nov;30(6):547–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1993.tb02081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock V. E., Schneider L. S., Lyness S. A. Reliability of topographic quantitative EEG amplitude in healthy late-middle-aged and elderly subjects. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991 Jul;79(1):20–26. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(91)90152-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsdijk F. V., Boomsma D. I., Vernon P. A. Genetic analysis of peripheral nerve conduction velocity in twins. Behav Genet. 1995 Jul;25(4):341–348. doi: 10.1007/BF02197283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinsky M. C., Oken B. S., Morehead L. Test-retest reliability in EEG frequency analysis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991 Nov;79(5):382–392. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(91)90203-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonová O., Roth B., Stein J. EEG studies of healthy population--normal rhythms of resting recording. Acta Univ Carol Med (Praha) 1967;13(7):543–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stassen H. H., Bomben G., Propping P. Genetic aspects of the EEG: an investigation into the within-pair similarity of monozygotic and dizygotic twins with a new method of analysis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1987 Jun;66(6):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(87)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinlein O., Anokhin A., Yping M., Schalt E., Vogel F. Localization of a gene for the human low-voltage EEG on 20q and genetic heterogeneity. Genomics. 1992 Jan;12(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90408-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz H., Herzog A., Huang Y., Hackländer T. Discordant brain-surface anatomy in monozygotic twins. N Engl J Med. 1994 Oct 6;331(14):951–952. doi: 10.1056/nejm199410063311419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steriade M., Gloor P., Llinás R. R., Lopes de Silva F. H., Mesulam M. M. Report of IFCN Committee on Basic Mechanisms. Basic mechanisms of cerebral rhythmic activities. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1990 Dec;76(6):481–508. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(90)90001-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher R. W. Cyclic cortical reorganization during early childhood. Brain Cogn. 1992 Sep;20(1):24–50. doi: 10.1016/0278-2626(92)90060-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher R. W., Walker R. A., Giudice S. Human cerebral hemispheres develop at different rates and ages. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1110–1113. doi: 10.1126/science.3576224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trubnikov V., Uvarova L., Alfimova M., Orlova V., Ozerova N., Abrosimov N. Neurophysiological and psychological predictors of genetic risk for schizophrenia. Behav Genet. 1993 Sep;23(5):455–459. doi: 10.1007/BF01067980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F. The genetic basis of the normal human electroencephalogram (EEG). Humangenetik. 1970 Sep 17;10(2):91–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00295509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beijsterveldt C. E., Boomsma D. I. Genetics of the human electroencephalogram (EEG) and event-related brain potentials (ERPs): a review. Hum Genet. 1994 Oct;94(4):319–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00201587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


