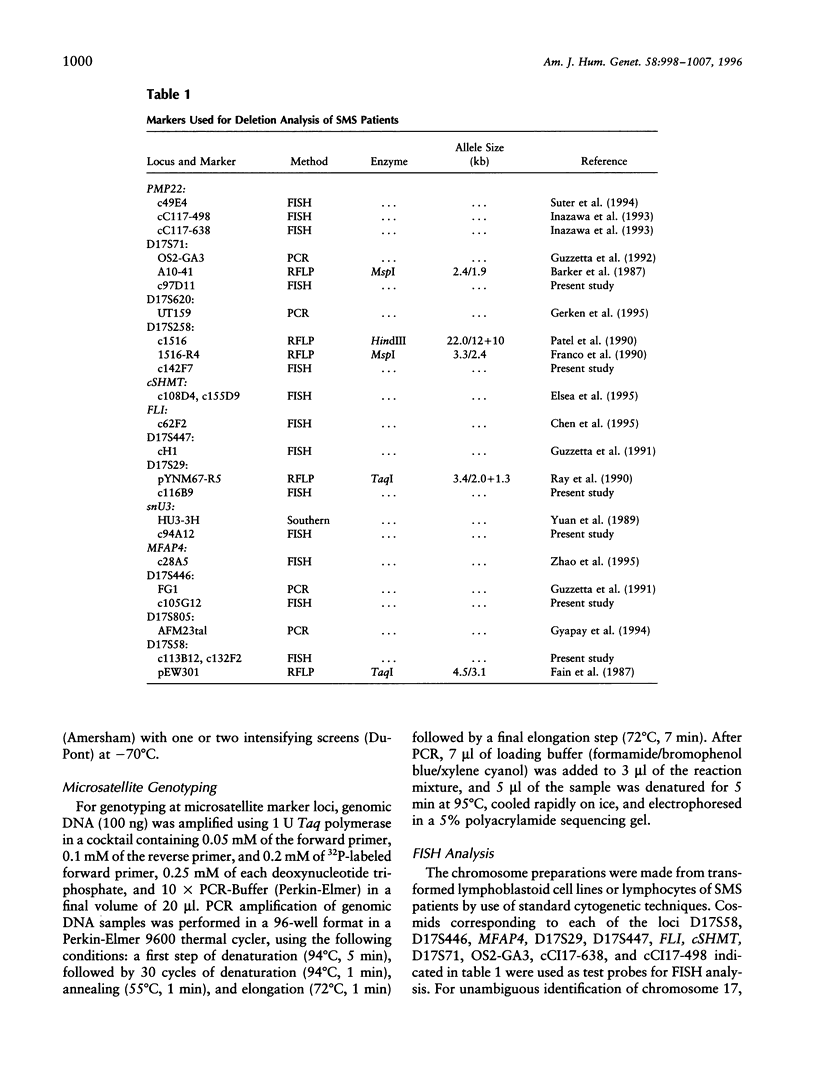
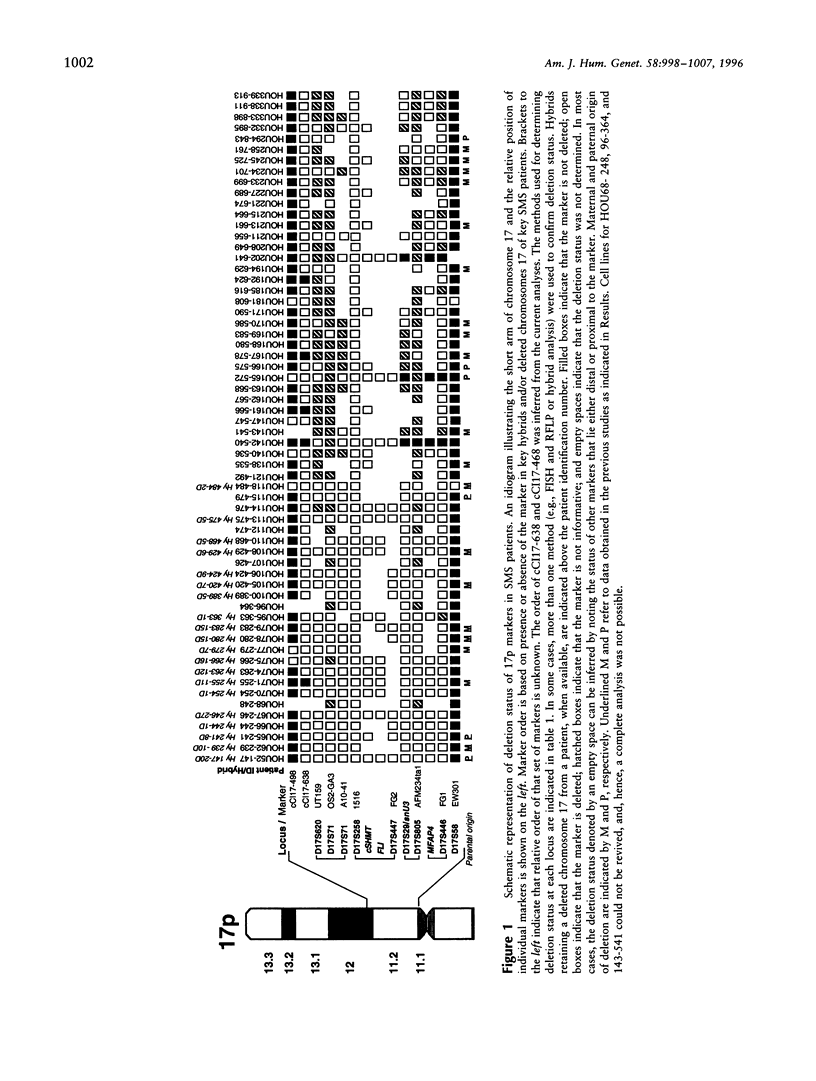
Abstract
Smith-Magenis syndrome (SMS) is a clinically recognizable, multiple congenital anomalies/mental retardation syndrome caused by an interstitial deletion involving band p11.2 of chromosome 17. Toward the molecular definition of the interval defining this microdeletion syndrome, 62 unrelated SMS patients in conjunction with 70 available unaffected parents were molecularly analyzed with respect to the presence or absence of 14 loci in the proximal region of the short arm of chromosome 17. A multifaceted approach was used to determine deletion status at the various loci that combined (i) FISH analysis, (ii)PCR and Southern analysis of somatic cell hybrids retaining the deleted chromosome 17 from selected patients, and (iii) genotype determination of patients for whom a parent(s) was available at four microsatellite marker loci and at four loci with associated RFLPs. The relative order of two novel anonymous markers and a new microsatellite marker was determined in 17p11.2. The results confirmed that the proximal deletion breakpoint in the majority of SMS patients is located between markers D17S58 (EW301) and D17S446 (FG1) within the 17p11.1-17p11.2 region. The common distal breakpoint was mapped between markers cCI17-638, which lies distal to D17S71, and cCI17-498, which lies proximal to the Charcot Marie-Tooth disease type 1A locus. The locus D17S258 was found to be deleted in all 62 patients, and probes from this region can be used for diagnosis of the SMS deletion by FISH. Ten patients demonstrated molecularly distinct deletions; of these, two patients had smaller deletions and will enable the definition of the critical interval for SMS.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. A., Gusella J. F. Use of cyclosporin A in establishing Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human lymphoblastoid cell lines. In Vitro. 1984 Nov;20(11):856–858. doi: 10.1007/BF02619631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Bardoni B., Guioli S., Basler E., Camerino G. Two families of low-copy-number repeats are interspersed on Xp22.3: implications for the high frequency of deletions in this region. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Wright E., Nguyen K., Cannon L., Fain P., Goldgar D., Bishop D. T., Carey J., Baty B., Kivlin J. Gene for von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis is in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1100–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.3107130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance P. F., Abbas N., Lensch M. W., Pentao L., Roa B. B., Patel P. I., Lupski J. R. Two autosomal dominant neuropathies result from reciprocal DNA duplication/deletion of a region on chromosome 17. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Feb;3(2):223–228. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandley A. C. On the parental origin of de novo mutation in man. J Med Genet. 1991 Apr;28(4):217–223. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.4.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. S., Gunaratne P. H., Hoheisel J. D., Young I. G., Miklos G. L., Greenberg F., Shaffer L. G., Campbell H. D., Lupski J. R. The human homologue of the Drosophila melanogaster flightless-I gene (flil) maps within the Smith-Magenis microdeletion critical region in 17p11.2. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):175–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevillard C., Le Paslier D., Passage E., Ougen P., Billault A., Boyer S., Mazan S., Bachellerie J. P., Vignal A., Cohen D. Relationship between Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1A and Smith-Magenis regions. snU3 may be a candidate gene for the Smith-Magenis syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1235–1243. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley A. F., Leversha M. A., Voullaire L. E., Rogers J. G. Five cases demonstrating the distinctive behavioural features of chromosome deletion 17(p11.2 p11.2) (Smith-Magenis syndrome). J Paediatr Child Health. 1990 Feb;26(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1990.tb02372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsea S. H., Juyal R. C., Jiralerspong S., Finucane B. M., Pandolfo M., Greenberg F., Baldini A., Stover P., Patel P. I. Haploinsufficiency of cytosolic serine hydroxymethyltransferase in the Smith-Magenis syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;57(6):1342–1350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain P. R., Barker D. F., Goldgar D. E., Wright E., Nguyen K., Carey J., Johnson J., Kivlin J., Willard H., Mathew C. Genetic analysis of NF1: identification of close flanking markers on chromosome 17. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan Y. S., Farrell S. A. Prenatal diagnosis of interstitial deletion of 17(p11.2p11.2) (Smith-Magenis syndrome) Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jan 15;49(2):253–254. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320490220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finucane B. M., Jaeger E. R., Kurtz M. B., Weinstein M., Scott C. I., Jr Eye abnormalities in the Smith-Magenis contiguous gene deletion syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Feb 15;45(4):443–446. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finucane B. M., Konar D., Haas-Givler B., Kurtz M. B., Scott C. I., Jr The spasmodic upper-body squeeze: a characteristic behavior in Smith-Magenis syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1994 Jan;36(1):78–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1994.tb11770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finucane B. M., Kurtz M. B., Babu V. R., Scott C. I., Jr Mosaicism for deletion 17p11.2 in a boy with the Smith-Magenis syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Feb 15;45(4):447–449. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco B., Rincon-Limas D., Nakamura Y., Patel P. I., Lupski J. R. Two MspI RFLPs at the D17S258 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7196–7196. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7196-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerken S. C., Albertsen H., Elsner T., Ballard L., Holik P., Lawrence E., Moore M., Zhao X., White R. A strategy for constructing high-resolution genetic maps of the human genome: a genetic map of chromosome 17p, ordered with meiotic breakpoint-mapping panels. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;56(2):484–499. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Guzzetta V., Montes de Oca-Luna R., Magenis R. E., Smith A. C., Richter S. F., Kondo I., Dobyns W. B., Patel P. I., Lupski J. R. Molecular analysis of the Smith-Magenis syndrome: a possible contiguous-gene syndrome associated with del(17)(p11.2). Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1207–1218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzzetta V., Franco B., Trask B. J., Zhang H., Saucedo-Cardenas O., Montes de Oca-Luna R., Greenberg F., Chinault A. C., Lupski J. R., Patel P. I. Somatic cell hybrids, sequence-tagged sites, simple repeat polymorphisms, and yeast artificial chromosomes for physical and genetic mapping of proximal 17p. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90124-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill M. A., Roberts S. H., Maguire M. J., Laurence K. M. Interstitial deletion of 17p11.2: case report and review. Ann Genet. 1988;31(1):36–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ijdo J. W., Lindsay E. A., Wells R. A., Baldini A. Multiple variants in subtelomeric regions of normal karyotypes. Genomics. 1992 Dec;14(4):1019–1025. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inazawa J., Saito H., Ariyama T., Abe T., Nakamura Y. High-resolution cytogenetic mapping of 342 new cosmid markers including 43 RFLP markers on human chromosome 17 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics. 1993 Jul;17(1):153–162. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juyal R. C., Finucane B., Shaffer L. G., Lupski J. R., Greenberg F., Scott C. I., Baldini A., Patel P. I. Apparent mosaicism for del(17)(p11.2) ruled out by fluorescence in situ hybridization in a Smith-Magenis syndrome patient. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Nov 20;59(3):406–407. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320590332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juyal R. C., Greenberg F., Mengden G. A., Lupski J. R., Trask B. J., van den Engh G., Lindsay E. A., Christy H., Chen K. S., Baldini A. Smith-Magenis syndrome deletion: a case with equivocal cytogenetic findings resolved by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Sep 11;58(3):286–291. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320580317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Kallioniemi A., Mascio L., Sudar D., Pinkel D., Deaven L., Gray J. Physical mapping of chromosome 17 cosmids by fluorescence in situ hybridization and digital image analysis. Genomics. 1994 Mar 1;20(1):125–128. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Matsuura S., Kuwajima K., Tokashiki M., Izumikawa Y., Naritomi K., Niikawa N., Kajii T. Diagnostic hand anomalies in Smith-Magenis syndrome: four new patients with del (17)(p11.2p11.2) Am J Med Genet. 1991 Nov 1;41(2):225–229. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320410219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. M., Yen P. H., Shapiro L. J. Characterization of a low copy repetitive element S232 involved in the generation of frequent deletions of the distal short arm of the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1117–1122. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood D., Hecht F., Dowman C., Hecht B. K., Rizkallah T. H., Goodwin T. M., Allanson J. Chromosome subband 17p11.2 deletion: a minute deletion syndrome. J Med Genet. 1988 Nov;25(11):732–737. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.11.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncla A., Livet M. O., Auger M., Mattei J. F., Mattei M. G., Giraud F. Smith-Magenis syndrome: a new contiguous gene syndrome. Report of three new cases. J Med Genet. 1991 Sep;28(9):627–632. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.9.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncla A., Piras L., Arbex O. F., Muscatelli F., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Fontes M. Physical mapping of microdeletions of the chromosome 17 short arm associated with Smith-Magenis syndrome. Hum Genet. 1993 Feb;90(6):657–660. doi: 10.1007/BF00202487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. I., Franco B., Garcia C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Nakamura Y., Ledbetter D. H., Chakravarti A., Lupski J. R. Genetic mapping of autosomal dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in a large French-Acadian kindred: identification of new linked markers on chromosome 17. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):801–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. I., Garcia C., Montes de Oca-Luna R., Malamut R. I., Franco B., Slaugenhaupt S., Chakravarti A., Lupski J. R. Isolation of a marker linked to the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type IA gene by differential Alu-PCR of human chromosome 17-retaining hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Dec;47(6):926–934. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. I., Roa B. B., Welcher A. A., Schoener-Scott R., Trask B. J., Pentao L., Snipes G. J., Garcia C. A., Francke U., Shooter E. M. The gene for the peripheral myelin protein PMP-22 is a candidate for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Nat Genet. 1992 Jun;1(3):159–165. doi: 10.1038/ng0692-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil S. R., Bartley J. A. Interstitial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 17. Hum Genet. 1984;67(2):237–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00273011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrij F., Giles R. H., Dauwerse H. G., Saris J. J., Hennekam R. C., Masuno M., Tommerup N., van Ommen G. J., Goodman R. H., Peters D. J. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome caused by mutations in the transcriptional co-activator CBP. Nature. 1995 Jul 27;376(6538):348–351. doi: 10.1038/376348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray R., Rincon-Limas D., Wright R. A., Davis S. N., Lupski J. R., Patel P. I. Three polymorphisms at the D17S29 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4958–4958. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roa B. B., Garcia C. A., Pentao L., Killian J. M., Trask B. J., Suter U., Snipes G. J., Ortiz-Lopez R., Shooter E. M., Patel P. I. Evidence for a recessive PMP22 point mutation in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Nat Genet. 1993 Oct;5(2):189–194. doi: 10.1038/ng1093-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. C., McGavran L., Robinson J., Waldstein G., Macfarlane J., Zonona J., Reiss J., Lahr M., Allen L., Magenis E. Interstitial deletion of (17)(p11.2p11.2) in nine patients. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jul;24(3):393–414. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320240303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton R. F., Dobyns W. B., Greenberg F., DeSana J. B., Moore C., Fidone G., Runge G. H., Feldman P., Sekhon G. S., Pauli R. M. Interstitial deletion of (17)(p11.2p11.2): report of six additional patients with a new chromosome deletion syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jul;24(3):421–432. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320240305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter U., Snipes G. J., Schoener-Scott R., Welcher A. A., Pareek S., Lupski J. R., Murphy R. A., Shooter E. M., Patel P. I. Regulation of tissue-specific expression of alternative peripheral myelin protein-22 (PMP22) gene transcripts by two promoters. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25795–25808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Li X. M., Tsai S. P., Johnson C., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. Frequent deletions of the human X chromosome distal short arm result from recombination between low copy repetitive elements. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90472-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Reddy R. Genes for human U3 small nucleolar RNA contain highly conserved flanking sequences. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 1;1008(1):14–22. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Z., Lee C. C., Jiralerspong S., Juyal R. C., Lu F., Baldini A., Greenberg F., Caskey C. T., Patel P. I. The gene for a human microfibril-associated glycoprotein is commonly deleted in Smith-Magenis syndrome patients. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Apr;4(4):589–597. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zori R. T., Lupski J. R., Heju Z., Greenberg F., Killian J. M., Gray B. A., Driscoll D. J., Patel P. I., Zackowski J. L. Clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular evidence for an infant with Smith-Magenis syndrome born from a mother having a mosaic 17p11.2p12 deletion. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Sep 15;47(4):504–511. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rijk-van Andel J. F., Catsman-Berrevoets C. E., van Hemel J. O., Hamers A. J. Clinical and chromosome studies of three patients with Smith-Magenis syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1991 Apr;33(4):343–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1991.tb14885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



