Abstract
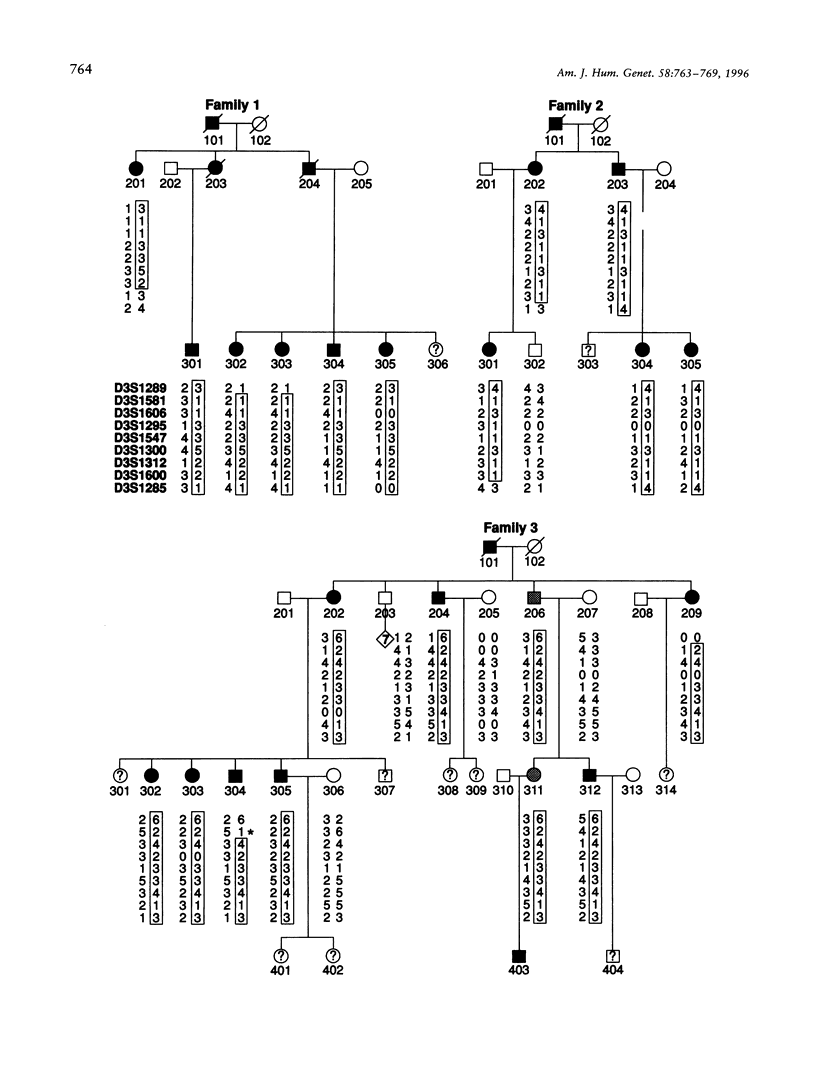
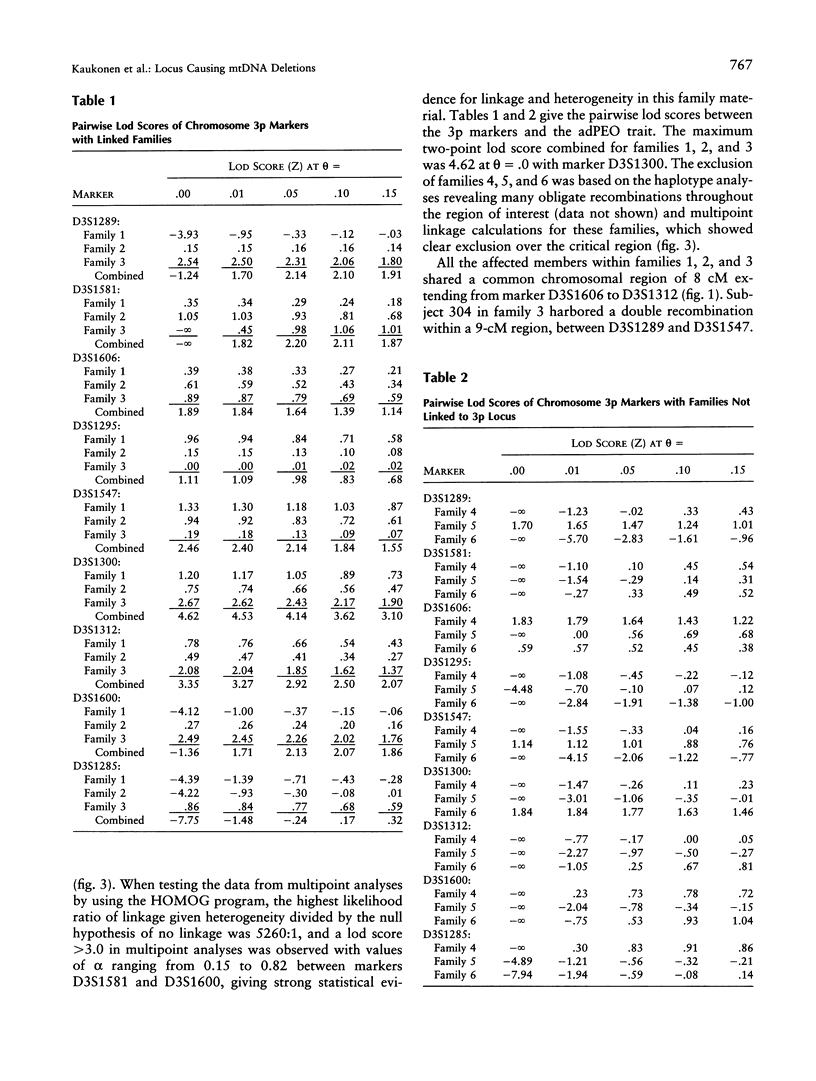
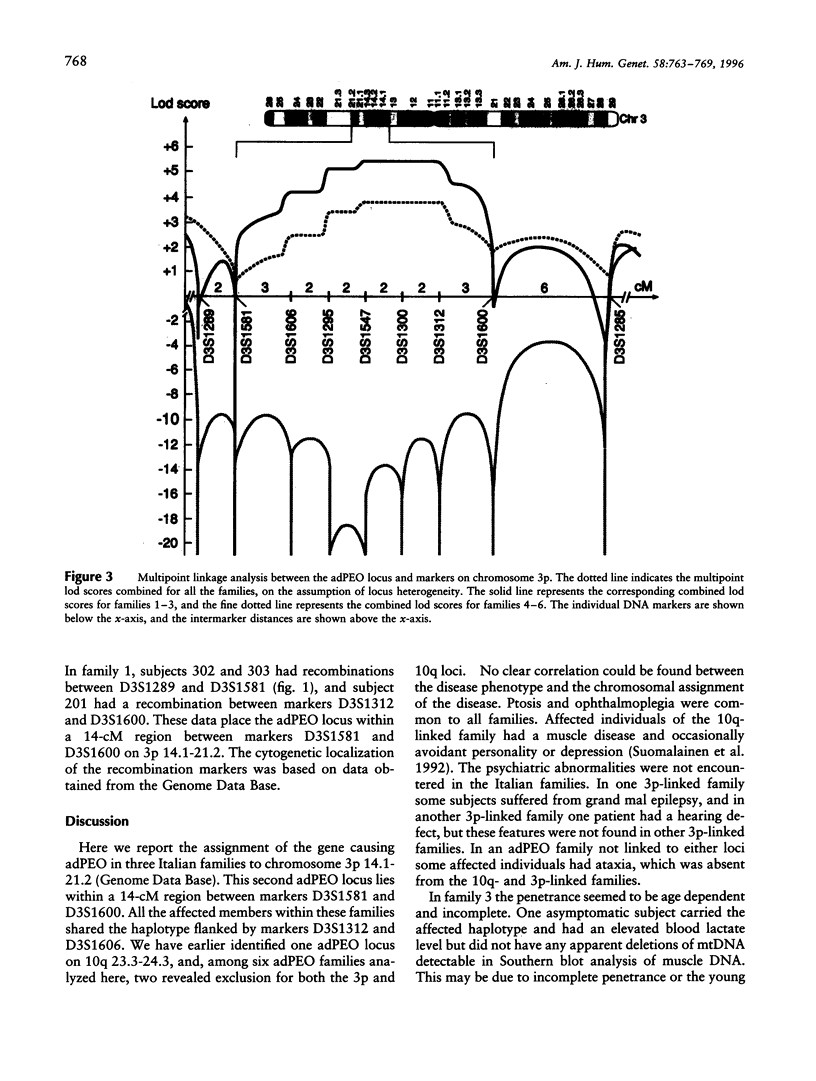
Autosomal dominant progressive external ophthalmoplegia (adPEO) is a disorder characterized by ptosis, progressive weakness of the external eye muscles, and general muscle weakness. The patients have multiple deletions of mtDNA on Southern blots or in PCR analysis of muscle DNA and a mild deficiency of one or more respiratory-chain enzymes carrying mtDNA-encoded subunits. The pattern of inheritance indicates a nuclear gene defect predisposing to secondary mtDNA deletions. Recently, in one Finnish family, we assigned an adPEO locus to chromosome 10q 23.3-24.3 but also excluded linkage to this same locus in two Italian adPEO families with a phenotype closely resembling the Finnish one. We applied a random mapping approach to informative non-10q-linked Italian families to assign the second locus for adPEO and found strong evidence for linkage on chromosome 3p 14.1-21.2 in three Italian families, with a maximum two-point lod score of 4.62 at a recombination fraction of .0. However, in three additional families, linkage to the same chromosomal region was clearly absent, indicating further genetic complexity of the adPEO trait.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corral-Debrinski M., Horton T., Lott M. T., Shoffner J. M., Beal M. F., Wallace D. C. Mitochondrial DNA deletions in human brain: regional variability and increase with advanced age. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):324–329. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortopassi G. A., Arnheim N. Detection of a specific mitochondrial DNA deletion in tissues of older humans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6927–6933. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moraes C. T., Shanske S., Tritschler H. J., Aprille J. R., Andreetta F., Bonilla E., Schon E. A., DiMauro S. mtDNA depletion with variable tissue expression: a novel genetic abnormality in mitochondrial diseases. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):492–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Computer-simulation methods in human linkage analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4175–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E. A., Rizzuto R., Moraes C. T., Nakase H., Zeviani M., DiMauro S. A direct repeat is a hotspot for large-scale deletion of human mitochondrial DNA. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):346–349. doi: 10.1126/science.2711184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer A. A., Gupta S. K., Shriram K., Cottingham R. W., Jr Avoiding recomputation in linkage analysis. Hum Hered. 1994 Jul-Aug;44(4):225–237. doi: 10.1159/000154222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servidei S., Zeviani M., Manfredi G., Ricci E., Silvestri G., Bertini E., Gellera C., Di Mauro S., Di Donato S., Tonali P. Dominantly inherited mitochondrial myopathy with multiple deletions of mitochondrial DNA: clinical, morphologic, and biochemical studies. Neurology. 1991 Jul;41(7):1053–1059. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.7.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoffner J. M., Lott M. T., Voljavec A. S., Soueidan S. A., Costigan D. A., Wallace D. C. Spontaneous Kearns-Sayre/chronic external ophthalmoplegia plus syndrome associated with a mitochondrial DNA deletion: a slip-replication model and metabolic therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7952–7956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen A., Kaukonen J., Amati P., Timonen R., Haltia M., Weissenbach J., Zeviani M., Somer H., Peltonen L. An autosomal locus predisposing to deletions of mitochondrial DNA. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):146–151. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen A., Majander A., Haltia M., Somer H., Lönnqvist J., Savontaus M. L., Peltonen L. Multiple deletions of mitochondrial DNA in several tissues of a patient with severe retarded depression and familial progressive external ophthalmoplegia. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):61–66. doi: 10.1172/JCI115856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeviani M., Bresolin N., Gellera C., Bordoni A., Pannacci M., Amati P., Moggio M., Servidei S., Scarlato G., DiDonato S. Nucleus-driven multiple large-scale deletions of the human mitochondrial genome: a new autosomal dominant disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Dec;47(6):904–914. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeviani M., Moraes C. T., DiMauro S., Nakase H., Bonilla E., Schon E. A., Rowland L. P. Deletions of mitochondrial DNA in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Neurology. 1988 Sep;38(9):1339–1346. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.9.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeviani M., Servidei S., Gellera C., Bertini E., DiMauro S., DiDonato S. An autosomal dominant disorder with multiple deletions of mitochondrial DNA starting at the D-loop region. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):309–311. doi: 10.1038/339309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


