Abstract
Anticipation refers to worsening severity or earlier age at onset with each generation for an inherited disease and primarily has been described for neurodegenerative illnesses resulting from expansion of trinucleotide repeats. We have tested for evidence of anticipation in familial leukemia. Of 49 affected individuals in nine families transmitting autosomal dominant acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), the mean age at onset is 57 years in the grandparental generation, 32 years in the parental generation, and 13 years in the youngest generation (P < .001). Of 21 parent-child pairs with AML, 19 show younger ages at onset in the child and demonstrate a mean decline in age at onset of 28 years (P < .001). Of 18 affected individuals from seven pedigrees with autosomal dominant chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), the mean age at onset in the parental generation is 66 years versus 51 years in the youngest generation (P = .008). Of nine parent-child pairs with CLL, eight show younger ages at onset in the child and reveal a mean decline in age at onset of 21 years (P = .001). Inspection of rare pedigrees transmitting acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, multiple types of leukemia, and lymphoma is also compatible with anticipation. Sampling bias is unlikely to explain these findings. This suggests that dynamic mutation of unstable DNA sequence repeats could be a common mechanism of inherited hematopoietic malignancy with implications for the role of somatic mutation in the more frequent sporadic cases. We speculate on three possible candidate genes for familial leukemia with anticipation: a locus on 21q22.1-22.2, CBL2 on 11q23.3, and CBFB or a nearby gene on 16q22.
Full text
PDF
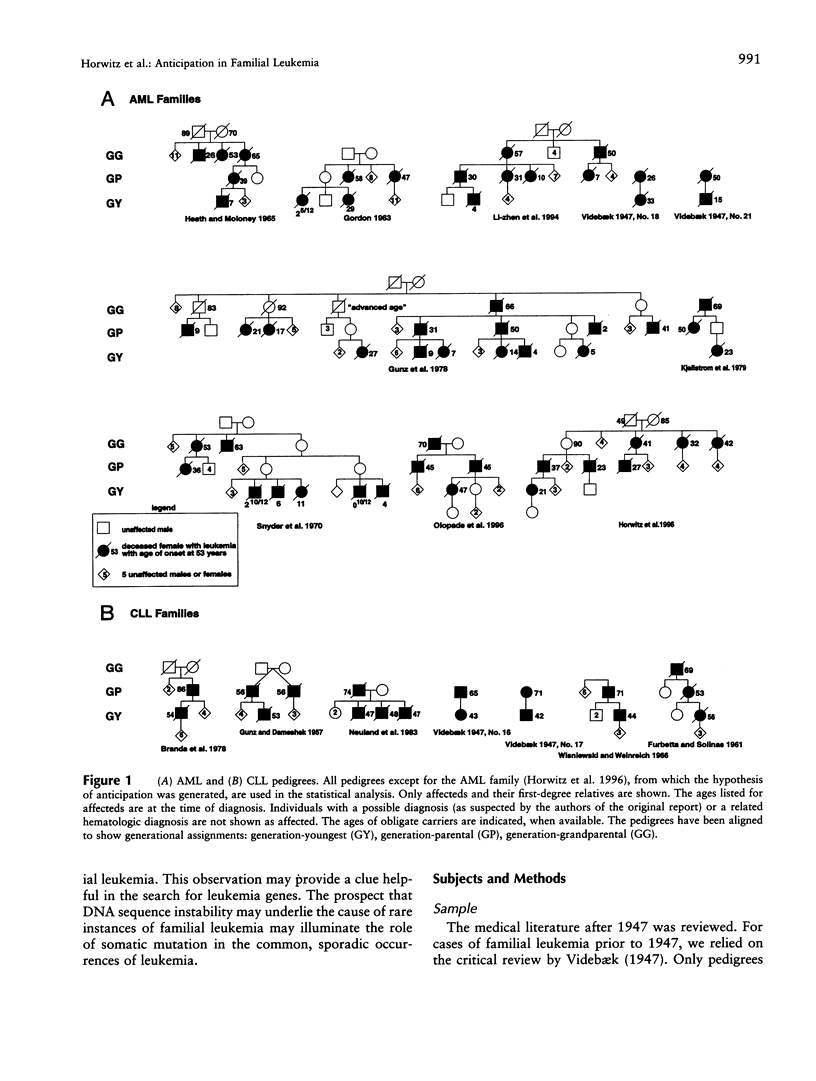

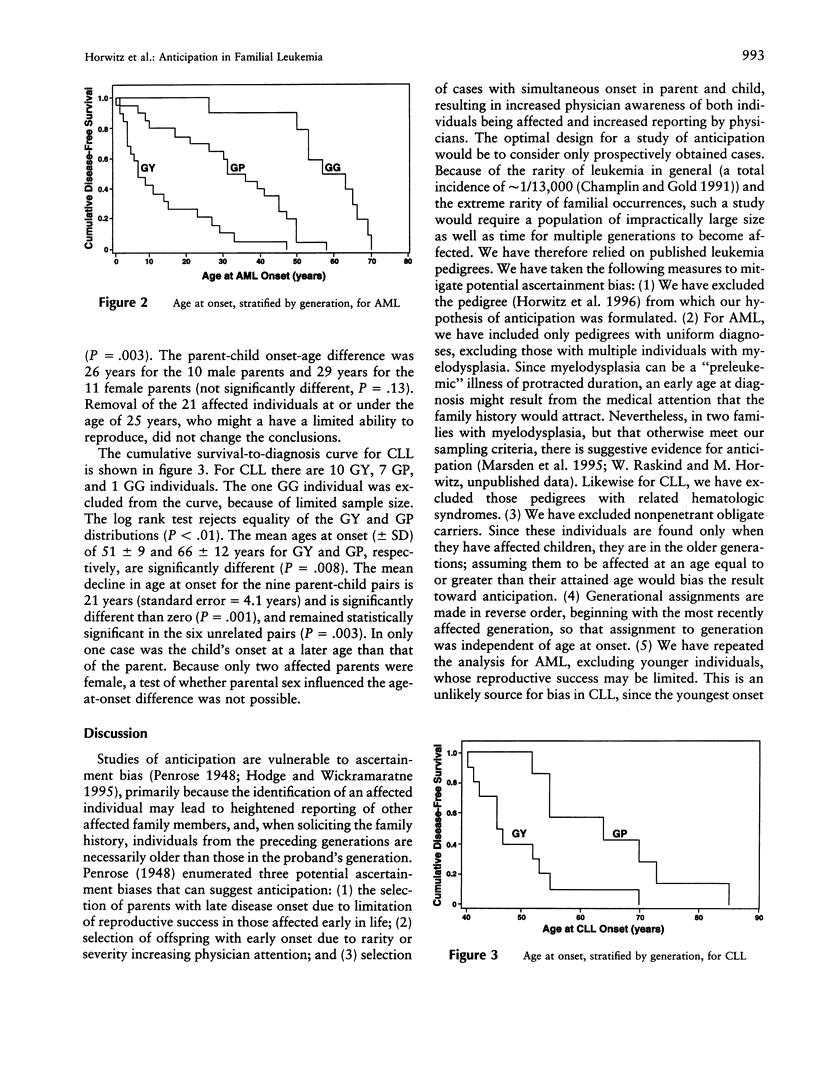

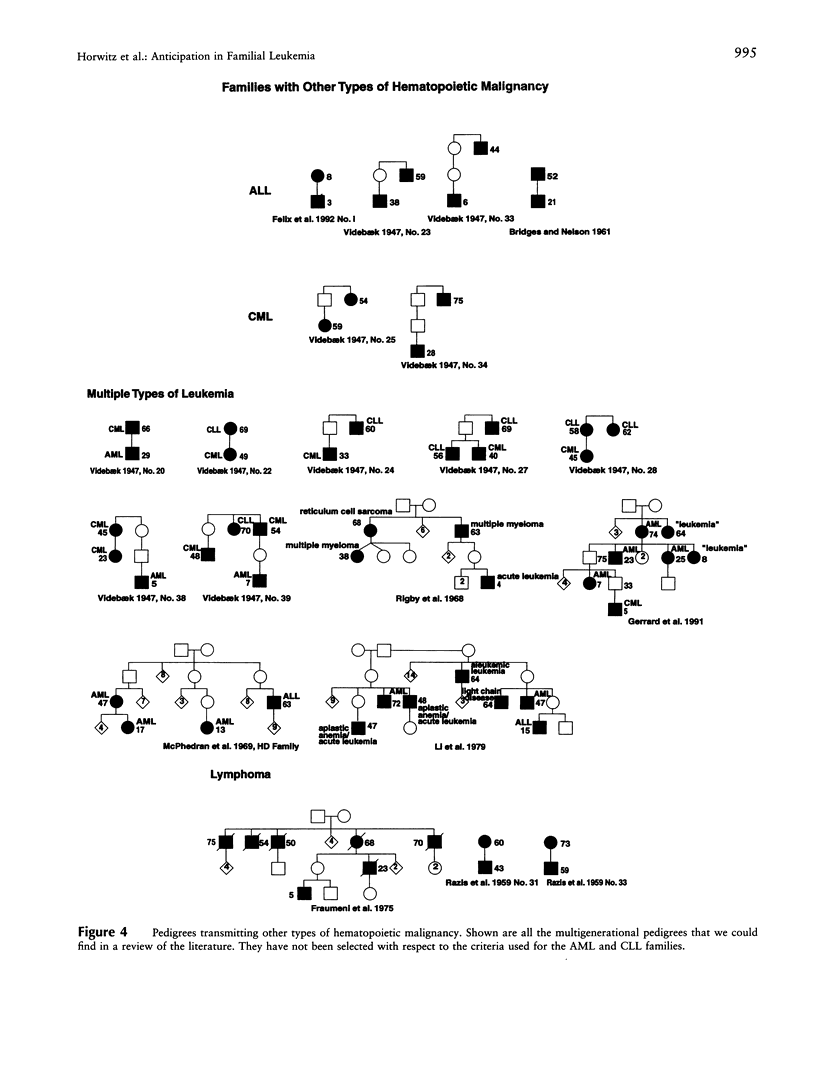



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRIDGES J. M., NELSON M. G. Familial leukaemia. Acta Haematol. 1961;26:246–251. doi: 10.1159/000206658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banfi S., Zoghbi H. Y. Molecular genetics of hereditary ataxias. Baillieres Clin Neurol. 1994 Aug;3(2):281–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleyl S., Nelson L., Odelberg S. J., Ruttenberg H. D., Otterud B., Leppert M., Ward K. A gene for familial total anomalous pulmonary venous return maps to chromosome 4p13-q12. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;56(2):408–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branda R. F., Ackerman S. K., Handwerger B. S., Howe R. B., Douglas S. D. Lymphocyte studies in familial chronic lymphatic leukemia. Am J Med. 1978 Mar;64(3):508–514. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carero-Valenzuela R., Lindblad K., Payami H., Johnson W., Schalling M., Stenroos E. S., Shattuc S., Nutt J., Brice A., Litt M. No evidence for association of familial Parkinson's disease with CAG repeat expansion. Neurology. 1995 Sep;45(9):1760–1763. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.9.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitambar C. R., Robinson W. A., Glode L. M. Familial leukemia and aplastic anemia associated with monosomy 7. Am J Med. 1983 Nov;75(5):756–762. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90404-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowton S. B., Beardsley D., Jamison D., Blattner S., Li F. P. Studies of a familial platelet disorder. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):557–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix C. A., D'Amico D., Mitsudomi T., Nau M. M., Li F. P., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Cole D. E., McCalla J., Reaman G. H., Whang-Peng J. Absence of hereditary p53 mutations in 10 familial leukemia pedigrees. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):653–658. doi: 10.1172/JCI115907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro M. T., García-Sagredo J. M., Resino M., del Potro E., Villegas A., Mediavilla J., Espinós D., San Román C. Chromosomal disorder and neoplastic diseases in a family with inherited fragile 16. Causality or casualty? Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1994 Dec;78(2):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(94)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraumeni J. F., Wertelecki W., Blattner W. A., Jensen R. D., Leventhal B. G. Varied manifestations of a familial lymphoproliferative disorder. Am J Med. 1975 Jul;59(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON R. D. HEREDITARY FACTORS IN HUMAN LEUKAEMIA: A REPORT OF FOUR CASES OF LEUKAEMIA IN A FAMILY. Australas Ann Med. 1963 Aug;12:202–207. doi: 10.1111/imj.1963.12.3.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNZ F., DAMESHEK W. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia in a family, including twin brothers and a son. J Am Med Assoc. 1957 Jul 20;164(12):1323–1325. doi: 10.1001/jama.1957.62980120001007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenhaus R., Johns M. M., 3rd, Wang P., Rai K., Sidransky D. Mutator phenotype in a subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1996 Jan 1;87(1):38–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Israels E. D., Bishop A. J., Schroeder M. L., Beattie L. L., McNicol A., Israels S. J., Walz D., Greenberg A. H., Ray M. Inherited platelet-storage pool deficiency associated with a high incidence of acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1991 Oct;79(2):246–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb04529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunz F. W., Gunz J. P., Vincent P. C., Bergin M., Johnson F. L., Bashir H., Kirk R. L. Thirteen cases of leukemia in a family. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Jun;60(6):1243–1250. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.6.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH C. W., Jr, MOLONEY W. C. FAMILIAL LEUKEMIA; FIVE CASES OF ACUTE LEUKEMIA IN THREE GENERATIONS. N Engl J Med. 1965 Apr 29;272:882–887. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196504292721703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajra A., Collins F. S. Structure of the leukemia-associated human CBFB gene. Genomics. 1995 Apr 10;26(3):571–579. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80177-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. S., Harley H. G., Reardon W., Shaw D. J. Anticipation in myotonic dystrophy: new light on an old problem. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;51(1):10–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He L. Z., Lu L. H., Chen Z. Z. Genetic mechanism of leukemia predisposition in a family with 7 cases of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1994 Aug;76(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(94)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C. Y., Otterud B., Legare R. D., Varvil T., Saxena R., DeHart D. B., Kohler S. E., Aster J. C., Dowton S. B., Li F. P. Linkage of a familial platelet disorder with a propensity to develop myeloid malignancies to human chromosome 21q22.1-22.2. Blood. 1996 Jun 15;87(12):5218–5224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E., Wickramaratne P. Statistical pitfalls in detecting age-of-onset anticipation: the role of correlation in studying anticipation and detecting ascertainment bias. Psychiatr Genet. 1995 Spring;5(1):43–47. doi: 10.1097/00041444-199521000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M., Sabath D. E., Smithson W. A., Radich J. A family inheriting different subtypes of acute myelogenous leukemia. Am J Hematol. 1996 Aug;52(4):295–304. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8652(199608)52:4<295::AID-AJH9>3.0.CO;2-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höweler C. J., Busch H. F., Geraedts J. P., Niermeijer M. F., Staal A. Anticipation in myotonic dystrophy: fact or fiction? Brain. 1989 Jun;112(Pt 3):779–797. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.3.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indraccolo S., Simon M., Hehlmann R., Erfle V., Chieco-Bianchi L., Leib-Moesch C. Genetic instability of a dinucleotide repeat-rich region in three hematologic malignancies. Leukemia. 1995 Sep;9(9):1517–1522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen P., Hauge M., Henningsen K., Hobolth N., Mikkelsen M., Philip J. An (11;21) translocation in four generations with chromosome 11 abnormalities in the offspring. A clinical, cytogenetical, and gene marker study. Hum Hered. 1973;23(6):568–585. doi: 10.1159/000152624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Penny L., Mattina T., Yu S., Baker E., Voullaire L., Langdon W. Y., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I., Tunnacliffe A. Association of a chromosome deletion syndrome with a fragile site within the proto-oncogene CBL2. Nature. 1995 Jul 13;376(6536):145–149. doi: 10.1038/376145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellström T., Barkenius G., Malmquist J., Rausing A. Familial monocytic leukaemia. A report of two families. Scand J Haematol. 1979 Oct;23(4):272–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb02861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Spada A. R., Paulson H. L., Fischbeck K. H. Trinucleotide repeat expansion in neurological disease. Ann Neurol. 1994 Dec;36(6):814–822. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li F. P., Hecht F., Kaiser-McCaw B., Baranko P. V., Potter N. U. Ataxia-pancytopenia: syndrome of cerebellar ataxia, hypoplastic anemia, monosomy 7, and acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1981 Nov;4(3):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(81)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li F. P., Marchetto D. J., Vawter G. F. Acute leukemia and preleukemia in eight males in a family: an X-linked disorder? Am J Hematol. 1979;6(1):61–69. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830060109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. P., Hajra A., Wijmenga C., Collins F. S. Molecular pathogenesis of the chromosome 16 inversion in the M4Eo subtype of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1995 May 1;85(9):2289–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden K., Challis D., Kimber R. Familial myelodysplastic syndrome with onset late in life. Am J Hematol. 1995 Jun;49(2):153–156. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830490210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhedran P., Heath C. W., Jr, Lee J. Patterns of familial leukemia. Ten cases of leukemia in two interrelated families. Cancer. 1969 Aug;24(2):403–407. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196908)24:2<403::aid-cncr2820240224>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchardt C., Yaniv M. A human homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae SNF2/SWI2 and Drosophila brm genes potentiates transcriptional activation by the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4279–4290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06112.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuland C. Y., Blattner W. A., Mann D. L., Fraser M. C., Tsai S., Strong D. M. Familial chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Dec;71(6):1143–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olopade O. I., Roulston D., Baker T., Narvid S., Le Beau M. M., Freireich E. J., Larson R. A., Golomb H. M. Familial myeloid leukemia associated with loss of the long arm of chromosome 5. Leukemia. 1996 Apr;10(4):669–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzer S., Kuhl D. P., Caskey C. T. Unstable triplet repeat sequences: a source of cancer mutations? Stem Cells. 1995 Mar;13(2):146–157. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530130206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIS D. V., DIAMOND H. D., CRAVER L. F. Familial Hodgkin's disease: its significance and implications. Ann Intern Med. 1959 Nov;51:933–971. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-51-5-933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranen N. G., Stine O. C., Abbott M. H., Sherr M., Codori A. M., Franz M. L., Chao N. I., Chung A. S., Pleasant N., Callahan C. Anticipation and instability of IT-15 (CAG)n repeats in parent-offspring pairs with Huntington disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Sep;57(3):593–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. G., Pratt P. T., Rosenlof R. C., Lemon H. M. Genetic relationships in familial leukemia and lymphoma. Arch Intern Med. 1968 Jan;121(1):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robledo M., Martinez B., Arranz E., Trujillo M. J., Gonzalez Ageitos A., Rivas C., Benitez J. Genetic instability of microsatellites in hematological neoplasms. Leukemia. 1995 Jun;9(6):960–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Billett E., Petronis A., Ying D., Parsons T., Macciardi F. M., Meltzer H. Y., Lieberman J., Joffe R. T., Ross C. A. Psychosis and genes with trinucleotide repeat polymorphism. Hum Genet. 1996 Feb;97(2):244–246. doi: 10.1007/BF02265274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Gerber H. P., Schaffner W. Basal components of the transcription apparatus (RNA polymerase II, TATA-binding protein) contain activation domains: is the repetitive C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II a "portable enhancer domain"? Mol Reprod Dev. 1994 Oct;39(2):215–225. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080390215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Q., Townes P. L., Padden C., Newburger P. E. An in-frame trinucleotide repeat in the coding region of the human cellular glutathione peroxidase (GPX1) gene: in vivo polymorphism and in vitro instability. Genomics. 1994 Sep 1;23(1):292–294. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder A. L., Henderson E. S., Li F. P., Todaro G. J. Possible inherited leukaemogenic factors in familial acute myelogenous leukaemia. Lancet. 1970 Mar 21;1(7647):586–589. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91626-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I. Simple tandem DNA repeats and human genetic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3636–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski D., Weinreich J. Lymphatische Leukämie bei Vater und Sohn. Blut. 1966 Jan;12(4):241–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01632449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. D. Cytogenetic and molecular analysis of chromosome 11q23 abnormalities in leukaemia. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1992 Oct;5(4):881–895. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3536(11)80050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


